We looked at 700 plant-based foods to see how healthy they really are. Here’s what we found
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re thinking about buying plant-based foods, a trip to the supermarket can leave you bewildered.
There are plant-based burgers, sausages and mince. The fridges are loaded with non-dairy milk, cheese and yoghurt. Then there are the tins of beans and packets of tofu.
But how much is actually healthy?
Our nutritional audit of more than 700 plant-based foods for sale in Australian supermarkets has just been published. We found some products are so high in salt or saturated fat, we’d struggle to call them “healthy”.
We took (several) trips to the supermarket
In 2022, we visited two of each of four major supermarket retailers across Melbourne to collect information on the available range of plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products.
We took pictures of the products and their nutrition labels.
We then analysed the nutrition information on the packaging of more than 700 of these products. This included 236 meat substitutes, 169 legumes and pulses, 50 baked beans, 157 dairy milk substitutes, 52 cheese substitutes and 40 non-dairy yoghurts.
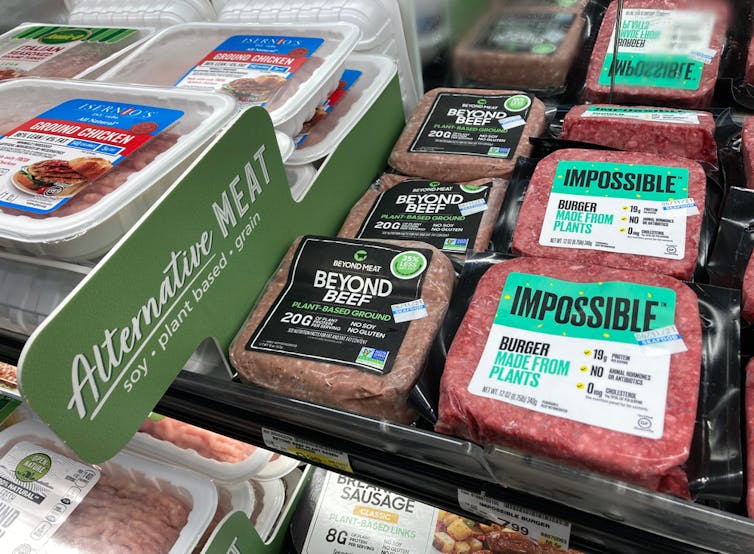
Plant-based meats were surprisingly salty
We found a wide range of plant-based meats for sale. So, it’s not surprising we found large variations in their nutrition content.
Sodium, found in added salt and which contributes to high blood pressure, was our greatest concern.
The sodium content varied from 1 milligram per 100 grams in products such as tofu, to 2,000mg per 100g in items such as plant-based mince products.
This means we could eat our entire daily recommended sodium intake in just one bowl of plant-based mince.
An audit of 66 plant-based meat products in Australian supermarkets conducted in 2014 found sodium ranged from 316mg in legume-based products to 640mg in tofu products, per 100g. In a 2019 audit of 137 products, the range was up to 1,200mg per 100g.
In other words, the results of our audit seems to show a consistent trend of plant-based meats getting saltier.

Michael Vi/Shutterstock
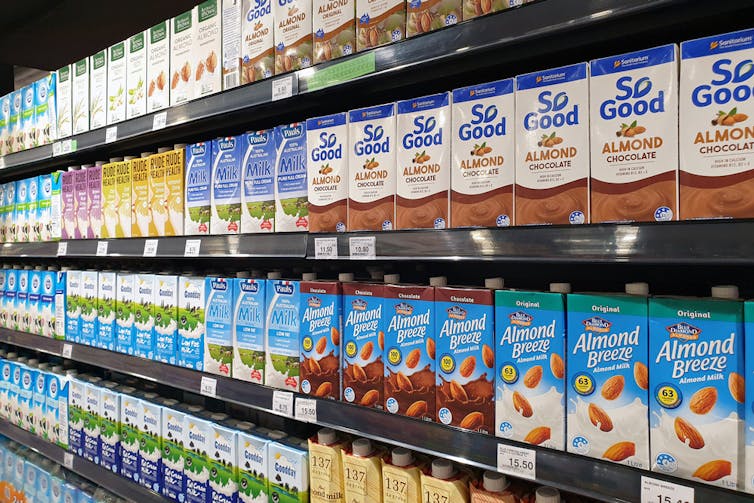
What about plant-based milks?
Some 70% of the plant-based milks we audited were fortified with calcium, a nutrient important for bone health.
This is good news as a 2019-2020 audit of 115 plant-based milks from Melbourne and Sydney found only 43% of plant-based milks were fortified with calcium.
Of the fortified milks in our audit, almost three-quarters (73%) contained the recommended amount of calcium – at least 100mg per 100mL.
We also looked at the saturated fat content of plant-based milks.
Coconut-based milks had on average up to six times higher saturated fat content than almond, oat or soy milks.
Previous audits also found coconut-based milks were much higher in saturated fat than all other categories of milks.

TY Lim/Shutterstock
A first look at cheese and yoghurt alternatives
Our audit is the first study to identify the range of cheese and yoghurt alternatives available in Australian supermarkets.
Calcium was only labelled on a third of plant-based yoghurts, and only 20% of supermarket options met the recommended 100mg of calcium per 100g.
For plant-based cheeses, most (92%) were not fortified with calcium. Their sodium content varied from 390mg to 1,400mg per 100g, and saturated fat ranged from 0g to 28g per 100g.
So, what should we consider when shopping?
As a general principle, try to choose whole plant foods, such as unprocessed legumes, beans or tofu. These foods are packed with vitamins and minerals. They’re also high in dietary fibre, which is good for your gut health and keeps you fuller for longer.
If opting for a processed plant-based food, here are five tips for choosing a healthier option.
1. Watch the sodium
Plant-based meat alternatives can be high in sodium, so look for products that have around 150-250mg sodium per 100g.
2. Pick canned beans and legumes
Canned chickpeas, lentils and beans can be healthy and low-cost additions to many meals. Where you can, choose canned varieties with no added salt, especially when buying baked beans.
3. Add herbs and spices to your tofu
Tofu can be a great alternative to meat. Check the label and pick the option with the highest calcium content. We found flavoured tofu was higher in salt and sugar content than minimally processed tofu. So it’s best to pick an unflavoured option and add your own flavours with spices and herbs.
4. Check the calcium
When choosing a non-dairy alternative to milk, such as those made from soy, oat, or rice, check it is fortified with calcium. A good alternative to traditional dairy will have at least 100mg of calcium per 100g.
5. Watch for saturated fat
If looking for a lower saturated fat option, almond, soy, rice and oat varieties of milk and yoghurt alternatives have much lower saturated fat content than coconut options. Pick those with less than 3g per 100g.
Laura Marchese, PhD Student at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University and Katherine Livingstone, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Older Americans Say They Feel Trapped in Medicare Advantage Plans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2016, Richard Timmins went to a free informational seminar to learn more about Medicare coverage.
“I listened to the insurance agent and, basically, he really promoted Medicare Advantage,” Timmins said. The agent described less expensive and broader coverage offered by the plans, which are funded largely by the government but administered by private insurance companies.
For Timmins, who is now 76, it made economic sense then to sign up. And his decision was great, for a while.
Then, three years ago, he noticed a lesion on his right earlobe.
“I have a family history of melanoma. And so, I was kind of tuned in to that and thinking about that,” Timmins said of the growth, which doctors later diagnosed as malignant melanoma. “It started to grow and started to become rather painful.”
Timmins, though, discovered that his enrollment in a Premera Blue Cross Medicare Advantage plan would mean a limited network of doctors and the potential need for preapproval, or prior authorization, from the insurer before getting care. The experience, he said, made getting care more difficult, and now he wants to switch back to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
But he can’t. And he’s not alone.
“I have very little control over my actual medical care,” he said, adding that he now advises friends not to sign up for the private plans. “I think that people are not understanding what Medicare Advantage is all about.”
Enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans has grown substantially in the past few decades, enticing more than half of all eligible people, primarily those 65 or older, with low premium costs and perks like dental and vision insurance. And as the private plans’ share of the Medicare patient pie has ballooned to 30.8 million people, so too have concerns about the insurers’ aggressive sales tactics and misleading coverage claims.
Enrollees, like Timmins, who sign on when they are healthy can find themselves trapped as they grow older and sicker.
“It’s one of those things that people might like them on the front end because of their low to zero premiums and if they are getting a couple of these extra benefits — the vision, dental, that kind of thing,” said Christine Huberty, a lead benefit specialist supervising attorney for the Greater Wisconsin Agency on Aging Resources.
“But it’s when they actually need to use it for these bigger issues,” Huberty said, “that’s when people realize, ‘Oh no, this isn’t going to help me at all.’”
Medicare pays private insurers a fixed amount per Medicare Advantage enrollee and in many cases also pays out bonuses, which the insurers can use to provide supplemental benefits. Huberty said those extra benefits work as an incentive to “get people to join the plan” but that the plans then “restrict the access to so many services and coverage for the bigger stuff.”
David Meyers, assistant professor of health services, policy, and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, analyzed a decade of Medicare Advantage enrollment and found that about 50% of beneficiaries — rural and urban — left their contract by the end of five years. Most of those enrollees switched to another Medicare Advantage plan rather than traditional Medicare.
In the study, Meyers and his co-authors muse that switching plans could be a positive sign of a free marketplace but that it could also signal “unmeasured discontent” with Medicare Advantage.
“The problem is that once you get into Medicare Advantage, if you have a couple of chronic conditions and you want to leave Medicare Advantage, even if Medicare Advantage isn’t meeting your needs, you might not have any ability to switch back to traditional Medicare,” Meyers said.
Traditional Medicare can be too expensive for beneficiaries switching back from Medicare Advantage, he said. In traditional Medicare, enrollees pay a monthly premium and, after reaching a deductible, in most cases are expected to pay 20% of the cost of each nonhospital service or item they use. And there is no limit on how much an enrollee may have to pay as part of that 20% coinsurance if they end up using a lot of care, Meyers said.
To limit what they spend out-of-pocket, traditional Medicare enrollees typically sign up for supplemental insurance, such as employer coverage or a private Medigap policy. If they are low-income, Medicaid may provide that supplemental coverage.
But, Meyers said, there’s a catch: While beneficiaries who enrolled first in traditional Medicare are guaranteed to qualify for a Medigap policy without pricing based on their medical history, Medigap insurers can deny coverage to beneficiaries transferring from Medicare Advantage plans or base their prices on medical underwriting.
Only four states — Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, and New York — prohibit insurers from denying a Medigap policy if the enrollee has preexisting conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Paul Ginsburg is a former commissioner on the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, also known as MedPAC. It’s a legislative branch agency that advises Congress on the Medicare program. He said the inability of enrollees to easily switch between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare during open enrollment periods is “a real concern in our system; it shouldn’t be that way.”
The federal government offers specific enrollment periods every year for switching plans. During Medicare’s open enrollment period, from Oct. 15 to Dec. 7, enrollees can switch out of their private plans to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
Medicare Advantage enrollees can also switch plans or transfer to traditional Medicare during another open enrollment period, from Jan. 1 to March 31.
“There are a lot of people that say, ‘Hey, I’d love to come back, but I can’t get Medigap anymore, or I’ll have to just pay a lot more,’” said Ginsburg, who is now a professor of health policy at the University of Southern California.
Timmins is one of those people. The retired veterinarian lives in a rural community on Whidbey Island just north of Seattle. It’s a rugged, idyllic landscape and a popular place for second homes, hiking, and the arts. But it’s also a bit remote.
While it’s typically harder to find doctors in rural areas, Timmins said he believes his Premera Blue Cross plan made it more challenging to get care for a variety of reasons, including the difficulty of finding and getting in to see specialists.
Nearly half of Medicare Advantage plan directories contained inaccurate information on what providers were available, according to the most recent federal review. Beginning in 2024, new or expanding Medicare Advantage plans must demonstrate compliance with federal network expectations or their applications could be denied.
Amanda Lansford, a Premera Blue Cross spokesperson, declined to comment on Timmins’ case. She said the plan meets federal network adequacy requirements as well as travel time and distance standards “to ensure members are not experiencing undue burdens when seeking care.”
Traditional Medicare allows beneficiaries to go to nearly any doctor or hospital in the U.S., and in most cases enrollees do not need approval to get services.
Timmins, who recently finished immunotherapy, said he doesn’t think he would be approved for a Medigap policy, “because of my health issue.” And if he were to get into one, Timmins said, it would likely be too expensive.
For now, Timmins said, he is staying with his Medicare Advantage plan.
“I’m getting older. More stuff is going to happen.”
There is also a chance, Timmins said, that his cancer could resurface: “I’m very aware of my mortality.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Good Is Your Sleep, Really?
This is Dr. Marie-Pierre St-Onge, Director of Columbia University’s Center of Excellence for Sleep and Circadian Research.
The focus of Dr. St-Onge’s research is the study of the impact of lifestyle, especially sleep and diet, on cardio-metabolic risk factors.
She conducts clinical research combining her expertise on sleep, nutrition, and energy regulation.
What kind of things do her studies look at?
Her work focuses on questions about…
- The role of circadian rhythms (including sleep duration and timing)
- Meal timing and eating patterns
…and their impact on cardio-metabolic risk.
What does she want us to know?
First things first, when not to worry:
❝Getting a bad night’s sleep once in a while isn’t anything to worry about. That’s what we would describe as transient insomnia. Chronic insomnia occurs when you spend three months or more without regular sleep, and that is when I would start to be concerned.❞
But… as prevention is (as ever) better than cure, she also advises that we do pay attention to our sleep! And, as for how to do that…
The Six Dimensions of Sleep
One useful definition of overall sleep health is the RU-Sated framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
You’ll notice that some of these things you can only really know if you use a sleep-monitoring app. She does recommend the use of those, and so do we!
We reviewed and compared some of the most popular sleep-monitoring apps! You can check them out here: Time For Some Pillow Talk
You also might like…
We’re not all the same with regard to when is the best time for us to sleep, so:
Use This Sleep Cycle Calculator To Figure Out the Optimal Time for You To Go to Bed and Wake Up
AROUND THE WEB
What’s happening in the health world…
- Aspirin may make your breathing worse
- Taking naps for more than 30 minutes may raise your metabolic disease risk
- How to ease back into exercise after surgery
- Study provides evidence that breathing exercises may reduce your Alzheimer’s risk
- No one in movies knows how to swallow a pill
More to come tomorrow!
Share This Post
-
The Brain Alarm Signs That Warn Of Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Turmeric (Curcumin) Dos and Don’ts With Dr. Kim
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Turmeric is a fabulous spice, most well-known for its anti-inflammatory powers; its antioxidant effects benefit all of the body, including the brain. While it fights seemingly everything from arthritis to atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s and more, it also boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor, looks after your cardiovascular health, holds back diabetes, reduces the risk of cancer, fights depression, slows aging, and basically does everything short of making you sing well too.
Dr. Leonid Kim goes over the scientific evidence for these, and also talks about some of the practicalities of taking turmeric, and safety considerations.
For the most part, turmeric is very safe even at high doses (up to 8g at least); indeed, at smaller doses (e.g. 500mg) it largely does the same job as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, with fewer problems.
It also does the job of several antidiabetic medications, by increasing uptake of glucose (thus reducing blood sugar levels) while simultaneously decreasing the glucose secretion from the liver. It does this by regulating the AMPK signalling pathway, just like metformin—while again, being safer.
Dr. Kim also looks at the (good!) evidence for turmeric in managing PCOS and undoing NAFLD; so far, so good.
Dosage: he bids us pay attention whether we’re taking it as turmeric itself or as curcumin standardized extract. The latter is the active compound, and in principle more powerful, but in practice it can get metabolized too quickly and easily—before it can have its desired effect. So, turmeric itself is a very good choice.
Absorption: since we do want it to be absorbed well, though, he does recommend taking it with piperine (as in black pepper).
You may be thinking: isn’t this going to cause the same problem you were just talking about, and cause it to be metabolized too quickly? And the answer is: no! How piperine works is almost the opposite; it protects the curcumin in the turmeric from our digestive enzymes, and thus allows them to get absorbed without being broken down too quickly—thus increasing the bioavailability by slowing the process down.
Lipophilia: no, that’s not a disease (or a fetish), rather it means that curcumin is soluble in fats, so we should take it near in time to a meal that contains at least a tablespoon of oil in total (so if you’re cooking a curry with your turmeric, this need is covered already, for example).
Supplement provenance: he recommends picking a supplement that’s been tested by a reputable 3rd party, as otherwise turmeric can be quite prone to impurities (which can include lead and arsenic, so, not great).
Contraindications: for some people, curcumin can cause gastrointestinal issues (less likely if taking with meals), and also, it can interact with blood-thinners. While taking aspirin or curcumin alone might help avoid circulatory problems, taking both could increase the bleeding risk for some people, for example. Similarly, if taking curcumin and metformin while diabetic, one must watch out for the combination being too effective at lowering blood sugar levels, and thus causing hypoglycemia instead. Similar deal with blood pressure medications.
There’s more in the video though (yes really; we know we wrote a lot but it’s information-dense), so do check it out:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Want to know more?
You can also check out our related articles:
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Parent Effectiveness Training – by Dr. Thomas Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you want your home (or workplace, for that matter) to be a place of peace? This book literally got the author nominated for a Nobel Peace Prize. Can’t really get much higher praise than that.
The title is “Parent Effectiveness Training”, but in reality, the advice in the book is applicable to all manner of relationships, including:
- romantic relationships
- friends
- colleagues
- …and really any human interaction.
It covers some of the same topics we did today (and more) in much more detail than we ever could in a newsletter. It lays out formulae to use, gives plenty of examples, and/but is free from undue padding.
- Pros: this isn’t one of those “should have been an article” books. It has so much valuable content.
- Cons: It is from the 1970s* so examples may feel “dated” now.
In addition to going into much more detail on some of the topics covered in today’s issue of 10almonds, Dr. Gordon also talks in-depth about the concept of “problem-ownership”.
In a nutshell, that means: whose problem is a given thing? Who “has” what problem? Everyone needs to be on the same page about everyone else’s problems in the situation… as well as their own, which is not always a given!
Dr. Gordon presents, in short, tools not just to resolve conflict, but also to pre-empt it entirely. With these techniques, we can identify and deal with problems (together!) well before they arise.
Everybody wins.
Get your copy of “Parent Effectiveness Training” from Amazon today!
*Note: There is an updated edition on the market, and that’s what you’ll find upon following the above link. This reviewer (hi!) has a battered old paperback from the 1970s and cannot speak for what was changed in the new edition. However: if the 70s one is worth more than its weight in gold (and it is), the new edition is surely just as good, if not better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A new study has highlighted the importance of lifestyle factors in shaping the oral microbiome—that is to say, how the things we do affect the bacteria that live in our mouths:
Nepali oral microbiomes reflect a gradient of lifestyles from traditional to industrialized
Neither the study title nor the abstract elucidate how, exactly, one impacts the other, but the study itself does (of course) contain that information; we read it, and the short version is:
In terms of the extremes of “most traditional” to “most industrialized”, foragers have the most diverse oral microbiomes (that’s good), and people with an American industrialized lifestyle had the least diverse oral microbiomes (that’s bad). Between the two extremes, we see the gradient promised by the title.
If you do feel like checking it out, Figure 3 in the paper illustrates this nicely.
Also illustrated in the above-linked Figure 3 is oral microbiome composition. In other words (and to oversimplify it rather), how good or bad our mouth bacteria are for us, independent of diversity (so for example, are there more of this or that kind of bacteria).
Once again, there is a gradient, only this time, the ends of it are even more polarized: foragers have a diverse oral microbiome rich with healthy-for-humans bacteria, while people with an American industrialized lifestyle might not have the diversity, but do have a large number of bad-for-humans bacteria.
While many lifestyle factors are dietary or quasi-dietary, e.g. what kinds of foods people eat, whether they drink alcohol, whether they smoke or use gum, etc, many lifestyle factors were examined, including everything from medications and exercise, to things like kitchen location and what fuel is predominantly used, to education and sexual activity and many other things that we don’t have room for here.
You can see how each lifestyle factor stacked up, in Figure 5.
Why it matters
Our oral microbiome affects many aspects of health, including:
- Locally: caries, periodontal diseases, mucosal diseases, oral cancer, and more
- Systemically: gastrointestinal diseases in general, IBS in particular, nervous system diseases, Alzheimer’s disease, endocrine diseases, all manner of immune/autoimmune diseases, and more
Nor are the effects it has mild; oral microbiome health can be a huge factor, statistically, for many of the above. You can see information and data pertaining to all of the above and more, here:
Oral microbiomes: more and more importance in oral cavity and whole body
What to do about it
Take care of your oral microbiome, to help it to take care of you. As well as the above-mentioned lifestyle factors, it’s worth noting that when it comes to oral hygiene, not all oral hygiene products are created equal:
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Kinds Help, And Which Kinds Harm?
Additionally, you might want to consider gentler options, but if you do, take care to opt for things that science actually backs., rather than things that merely trended on social media.
This writer (hi, it’s me) is particularly excited about the science and use of the miswak stick, which comes from the Saladora persica tree, and has phytochemical properties that (amongst many other health-giving effects) improve the quality of saliva (i.e., improve its pH and microbiome composition). In essence, your own saliva gets biochemically nudged into being the safest, most effective mouthwash.
There’s a lot of science for the use of S. persica, and we’ve discussed it before in more detail than we have room to rehash today, here:
Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
If you’d like to enjoy these benefits (and also have the equivalent of a toothbrush that you can carry with you at all times and does not require water*), then here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
*don’t worry, it won’t feel like dry-brushing your teeth. Remember what we said about what it does to your saliva. Basically, you chomp it once, and your saliva a) increases and b) becomes biological tooth-cleaning fluid. The stick itself is fibrous, so the end of it frays in a way that makes a natural little brush. Each stick is about 5”×¼” and you can carry it in a little carrying case (you’ll get a couple with each pack of miswak sticks), so you can easily use it in, say, the restroom of a restaurant or before your appointment somewhere, just as easily as you could use a toothpick, but with much better results. You may be wondering how long a stick lasts; well, that depends on how much you use it, but in this writer’s experience, each stick lasts about a month maybe, using it at least 2–3 times per day, probably rather more since I use it after each meal/snack and upon awakening.
(the above may read like an ad, but we promise you it’s not sponsored and this writer’s just enthusiastic, and when you read the science, you will be too)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: