Escape Self-Sabotage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Stop Making The Same Mistakes
It’s easy to think that a self-destructive cycle is easy to avoid if you have no special will to self-destruction. However, the cycle is sneaky.
It’s sneaky because it can be passive, and/or omissions rather than actions, procrastinations rather than obvious acts of impulse, and so forth.
So, they’re often things that specifically aren’t there to see.
How to catch them
How often do you think “I wish I had [done xyz]” or “I wish I had [done yxz] sooner”?
Now, how often have you thought that about the same thing more than once? For example, “I should have kept up my exercise”.
For things like this, habit-trackers are a great way to, well, keep track of habits. If for example you planned to do a 10-minute exercise session daily but you’ve been postponing it since you got distracted on January the 2nd, then it’ll highlight that. See also:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Speaking of habits, this goes for other forms of procrastination, too. For example, if you are always slow to get medical check-ups, or renew your prescriptions, or get ready for some regularly-occurring thing in your schedule, then set a reminder in your preferred way (phone app, calendar on the wall, whatever) and when the appointed time arrives (to book the check-up, renew the prescription, do your taxes, whatever), do it on the day you set your reminder for, as a personal rule for you that you keep to, barring extreme calamity.
By “extreme calamity” we mean less “running late today” and more “house burned down”.
Digital traps
Bad habits can be insidious in other ways too, like getting sucked into social media scrolling (it is literally designed to do that to you; you are not immune modern programming hijacking evolutionary dopamine responses).
Setting a screentime limit (you can specify “just these apps” if you like) will help with this. On most devices, this feature includes a sticky notification in the notification bar, that’ll remind you “27 out of 30 minutes remaining” or whatever you set it for. That’ll remind you to do what you went there to do, instead of getting caught in the endless scroll (and if you went there to just browse, to do so briefly).
Here’s how to set that:
Instructions for iOS devices | Instructions for Android devices
Oh, and on the topic of social media? If you find yourself getting caught up in unproductive arguments on the Internet, try the three-response rule:
- You reply; they reply (no progress made)
- You reply; they reply (still no progress made)
- You reply; they reply (still yet no progress made)
You reply just one more time: “I have a personal rule that if I’m arguing on the Internet and no progress has been made after three replies, I don’t reply further—I find this is helpful to avoid a lot of time lost to pointless arguing that isn’t going anywhere. Best wishes.”
(and then stick to it, no matter how they try to provoke you; best is to just not look until at least the next day)
When “swept up in love” gets to one of those little whirlpools…
The same works in personal relationships, by the way. If for example you are arguing with a loved one and not making progress, it can be good if you both have a pre-arranged agreement that either of you can, up to once on any given day, invoke a “time-out” (e.g. 30 minutes, but you agree the time between you when you first make this standing policy) during which you will both keep out of the other’s way, and come back with a more productive head on (remembering that things go best when it’s you both vs the problem, rather than vs each other).
See also:
Seriously Useful Communication Skills: Conflict Resolution
What if the self-sabotaging cycle is active and apparent?
Well, that is less sneaky, but certainly no less serious, and sometimes moreso. An obvious example is drinking too much; this is often cyclical in nature. We wrote about this one previously:
That article’s alcohol-specific, but the same advices go for other harmful activities, including other substance abuse (which in turn includes binge-eating), as well psychological addictions (such as gambling, for example).
Finally…
If your destructive cycle is more of a rut you’ve got stuck in, a common advice is to change something, anything, to get out of the rut.
That can be very bad advice! Because sometimes the change you go for is absolutely not the change that was needed, and is rather just cracking under pressure and doing something impulsive.
Here’s one way to actively get out of a slump:
Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
Note: you do not have to be depressed or anxious to do this. But the point is, it’s a tool you can use even if you are depressed and/or anxious, so it’s a good thing to try for getting out of most kinds of slumps.
And really finally, here’s a resource for, well, the title speaks for itself:
When You Know What You “Should” Do (But Knowing Isn’t The Problem)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How much weight do you actually need to lose? It might be a lot less than you think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re one of the one in three Australians whose New Year’s resolution involved losing weight, it’s likely you’re now contemplating what weight-loss goal you should actually be working towards.
But type “setting a weight loss goal” into any online search engine and you’ll likely be left with more questions than answers.
Sure, the many weight-loss apps and calculators available will make setting this goal seem easy. They’ll typically use a body mass index (BMI) calculator to confirm a “healthy” weight and provide a goal weight based on this range.
Your screen will fill with trim-looking influencers touting diets that will help you drop ten kilos in a month, or ads for diets, pills and exercise regimens promising to help you effortlessly and rapidly lose weight.
Most sales pitches will suggest you need to lose substantial amounts of weight to be healthy – making weight loss seem an impossible task. But the research shows you don’t need to lose a lot of weight to achieve health benefits.
Using BMI to define our target weight is flawed
We’re a society fixated on numbers. So it’s no surprise we use measurements and equations to score our weight. The most popular is BMI, a measure of our body weight-to-height ratio.
BMI classifies bodies as underweight, normal (healthy) weight, overweight or obese and can be a useful tool for weight and health screening.
But it shouldn’t be used as the single measure of what it means to be a healthy weight when we set our weight-loss goals. This is because it:
- fails to consider two critical factors related to body weight and health – body fat percentage and distribution
- does not account for significant differences in body composition based on gender, ethnicity and age.
How does losing weight benefit our health?
Losing just 5–10% of our body weight – between 6 and 12kg for someone weighing 120kg – can significantly improve our health in four key ways.
1. Reducing cholesterol
Obesity increases the chances of having too much low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol – also known as bad cholesterol – because carrying excess weight changes how our bodies produce and manage lipoproteins and triglycerides, another fat molecule we use for energy.
Having too much bad cholesterol and high triglyceride levels is not good, narrowing our arteries and limiting blood flow, which increases the risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
But research shows improvements in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels are evident with just 5% weight loss.
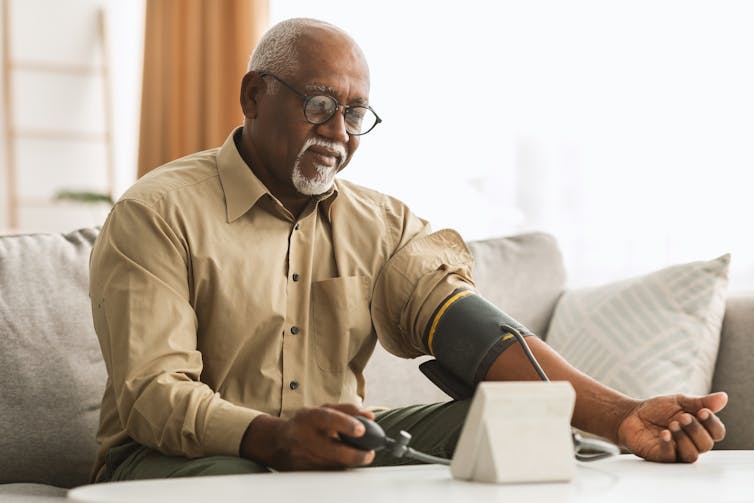
2. Lowering blood pressure
Our blood pressure is considered high if it reads more than 140/90 on at least two occasions.
Excess weight is linked to high blood pressure in several ways, including changing how our sympathetic nervous system, blood vessels and hormones regulate our blood pressure.
Essentially, high blood pressure makes our heart and blood vessels work harder and less efficiently, damaging our arteries over time and increasing our risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
Losing weight can lower your blood pressure.
Prostock-studio/ShutterstockLike the improvements in cholesterol, a 5% weight loss improves both systolic blood pressure (the first number in the reading) and diastolic blood pressure (the second number).
A meta-analysis of 25 trials on the influence of weight reduction on blood pressure also found every kilo of weight loss improved blood pressure by one point.
3. Reducing risk for type 2 diabetes
Excess body weight is the primary manageable risk factor for type 2 diabetes, particularly for people carrying a lot of visceral fat around the abdomen (belly fat).
Carrying this excess weight can cause fat cells to release pro-inflammatory chemicals that disrupt how our bodies regulate and use the insulin produced by our pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious medical conditions if it’s not carefully managed, including damaging our heart, blood vessels, major organs, eyes and nervous system.
Research shows just 7% weight loss reduces risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.
4. Reducing joint pain and the risk of osteoarthritis
Carrying excess weight can cause our joints to become inflamed and damaged, making us more prone to osteoarthritis.
Observational studies show being overweight doubles a person’s risk of developing osteoarthritis, while obesity increases the risk fourfold.
Small amounts of weight loss alleviate this stress on our joints. In one study each kilogram of weight loss resulted in a fourfold decrease in the load exerted on the knee in each step taken during daily activities.
Losing weight eases stress on joints.
Shutterstock/Rostislav_SedlacekFocus on long-term habits
If you’ve ever tried to lose weight but found the kilos return almost as quickly as they left, you’re not alone.
An analysis of 29 long-term weight-loss studies found participants regained more than half of the weight lost within two years. Within five years, they regained more than 80%.
When we lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Just as the problem is evolutionary, the solution is evolutionary too. Successfully losing weight long-term comes down to:
losing weight in small manageable chunks you can sustain, specifically periods of weight loss, followed by periods of weight maintenance, and so on, until you achieve your goal weight
making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
Setting a goal to reach a healthy weight can feel daunting. But it doesn’t have to be a pre-defined weight according to a “healthy” BMI range. Losing 5–10% of our body weight will result in immediate health benefits.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Beetroot vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing beetroot to cucumber, we picked the beetroot.
Why?
While they’re both mostly-water vegetables that can go in salads, soups, and sauces, they have some notable differences:
In terms of macros, beetroot has nearly 3x the carbs and/but also nearly 6x the fiber, so we say beetroot wins this category.
On the vitamins front, beetroot has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, C, and E, while cucumber has more of vitamins A, B5, and K. In short, a clear win for beetroot.
In the category of minerals, beetroot has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while cucumber is not richer in any minerals.
When it comes to beneficial phytochemicals, both have good things to offer, though we say beetroot has more. Notably, cucumber extract beats glucosamine and chondroitin for reducing joint inflammation, at 1/135th of the dose. On the other hand, beetroot’s phytochemical benefits are so numerous we’ll not list them here, and just recommend checking out the link below!
In short, a win in all categories for beetroot, but cucumbers are great too, so by all means enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Beetroot For More Than Just Your Blood Pressure
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Bridging The Generation Gap Over The Holidays
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often seen as a time for family connection, this same holiday period is often experienced as a time of family tension. But it doesn’t have to be that way!
Hopefully this will be of benefit to readers of all ages, but we’re going to write with the largest age-group of our readership, which is people who are most likely to have Gen-Z grandkids.
why are we writing about this?
Not only are health and happiness closely linked, and not only is mental health also just health, but… In terms of the healthy longevity secrets of the “Blue Zones”, strong intergenerational connections are usually a feature.
First, the obvious:
Any holiday tensions, of course, don’t usually start with grandkids, and are more likely amongst the adults, but some points of friction can be the same:
- Differences of opinion on political/social/economic issues
- Difference of opinion on parenting/dating choices
- Differences of opinion on life priorities
And yes, by the way, that includes even young teens (and perhaps younger) having opinions on these things—we are living in an information age, and this does mean a lot of information is a lot more accessible than it used to be, including for kids. Problems (at all ages) may occur when someone is only really exposed to views from within a certain “bias bubble”, but for better or worse, most people will have an opinion on most well-known things.
As a general rule of thumb, all of these differences of opinion can be shelved if (and only if) those involved seek to avoid conflict. And while age is no guarantee of maturity, often it’ll be the older person(s) in the strongest position to redirect things. So, have a stack of “safe” topics up your sleeve.
Bonus: you can also have non-conversational distractions up your sleeve! These may be kitchen-related, for example (time to produce something distracting, or if the nascent conflict was only between you and one other person, time to go check on something, thus removing yourself from the situation).
Next, about “family time” and technology
It can be tempting to try to have a “phones away” rule, but this will tend to only exacerbate a younger person’s withdrawal.
Better: ask (with a tone of cheerful curiosity, not accusation) about what captures their attention so. Ask about their favorite YouTubers or TikTokers or whatever it is that it is for them. Learn about that Subreddit.
Or maybe (more likely for Millennials) they were following what is going on in the world via social media, which takes on an intermediary role for the delivery of world news. Hopefully this won’t run into the differences of opinion that we mentioned up top, but it could also be a perfectly good avenue of conversation, and maybe there’s more common ground than you might expect.
Meanwhile, if you’re the older generation present, chances are your own social media use is more about the human element. That’s great, but watch out:
A common faux pas is taking pictures without asking, let alone posting them online without asking. For many people this may seem an odd thing to object to, but generationally speaking, the younger someone is (down to the upper single digits, anyway) the more likely they might feel strongly about this. So, ask first.
The reason, by the way, is that in this age of digital hypervisibility, what we choose to share online can be a deeply personal thing. And, say what you will about the pros or cons of someone carefully curating an image of how they wish to be seen, shortcutting through that for them with a candid photo posted on Facebook will not endear you to them, even if you can’t see anything wrong with the photo in question, for example.
See also: Make Social Media Work For Your Mental Health
Show an interest, but don’t interrogate
This one doesn’t take too much explanation. If people want to share about their lives, they’ll need only the smallest nudge to do so. If someone passes up an opportunity to talk about something you showed an interest in, chances are they have their own reasons for not wanting to talk about it. This might be hurtful if you feel like they’re keeping you out of their life, but the best way to get them to talk to you is just to be a good listener—not an interrogator that they have to dodge.
For some powerful tools on this, see: Listening, Better
Lastly, if things aren’t so good…
43% of people are currently experiencing some sort of familial estrangement, so if that’s you, you’re not on your own.
Sometimes, it really is too late to fix things, but sometimes it isn’t; we put together a guide that might help:
Family Estrangement & How To Fix It
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Good, The Bad, & The Vigorously Debated
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This week in health news sees some pretty varied topics:
One more reason to care about the gut-brain axis
Stroke is a top killer in much of the industrialized world, usually making it into the top-few list on a per-country basis. And, it’s rising in prevalence, too. This is partly because our longevity is increasing so age-related things kill us more often, statistically, than age-unrelated things. But that’s only part of the reason; another is that our lifestyle (on the national level) is becoming more conducive to stroke. Diet is a large contributor to that, and gut health has now been identified as a key factor.
What recent research has shown is that minutes after a stroke occurs, normal gut anatomy is disrupted, and cells responsible for gut barrier integrity are eroded, and bugs from the gut get into the blood, and arrive at the (newly damaged) brain vasculature, where the blood-brain barrier is often also compromised on account of the stroke.
Because of this, critical to reducing post-stroke neuroinflammation (something that makes stroke damage more severe and recovery a lot harder) is improving the gut’s ability to heal itself quickly.
This can be helped with a dose of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1), but there are other things that can help or hinder, and those other things are modifiable by us as individuals in our lifestyle choices (e.g. a gut-healthy diet with plenty of fiber, and avoiding gut-unhealthy things like sugar and alcohol that feed C. albicans growths that will put roots through your intestines and make holes as they do), because the better/worse your gut barrier integrity is to start with, the easier/harder it will be for your gut to repair itself quickly:
Read in full: Healing the gut can reduce long-term impact of stroke
Related: Stop Sabotaging Your Gut
How about that seasonal lead-spiced hot drink?
Lead contamination in ground spices has become a bit of an issue, ground turmeric has had quite some flak in this regard, and now the spotlight is on cinnamon.
These reports, by the way, do not specify what kind of cinnamon (i.e. cassia vs Ceylon), however, clicking through to assorted sources and then doing our own digging finds that all cinnamon products we found listed as contaminated, were cassia cinnamon. This is unsurprising, as a) it’s cheaper b) it’s the kind most readily found on shelves in the US. That said, when it comes to Ceylon (sweet) cinnamon, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, so that doesn’t mean they got the all-clear on lead contamination, but rather, that they haven’t received the same scrutiny as yet.
It’s worth noting that cinnamon sticks have been found to have less contamination than ground cinnamon, though.
It’s also worth noting that since some adulterated products have had lead added deliberately in increase the weight and darken the color, this is more likely to happen to cassia cinnamon than sweet cinnamon because cassia cinnamon is visibly darker, so adding a darkening agent to sweet cinnamon would just make it look like cassia (which no seller would want to do since cassia is the cheaper of the two).
Read in full: Why lead-tainted cinnamon products have turned up on shelves, and what questions consumers should ask
Related: Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier? ← this also covers toxicity issues, by the way
A matter of life and death
Assisted dying is currently legal in 10/40 US states, and Canada. Over in the UK, it’s being debated (and voted on) in Parliament today, at time of writing.
While bodily autonomy discussions are usually quite straightforward arguments between the very separate camps of
- “my body, my choice” vs
- “they shouldn’t be allowed to do that”,
…this one comes with a considerable middleground, because
- “people should have to right to end things without extra suffering and on their own terms”, and
- “many disabled people fear being placed in a position of having justify why they are not exercising their right to die when it might be cheaper and easier for others if they did”
…are positions with a lot of potential overlap.
In any case, we know most of our readers are in the US, but with a 10/40 split in US states (and some recent controversies in Canada), it’s likely a topic that’ll come up for most people at some point, so it’s good to understand it, and this is as good an opportunity as any:
Read in full: How would the assisted dying bill work and what issues might it create?
Related: Managing Your Mortality ← this talks about psychological/social considerations, as well as end-of-life care, palliative care (which is not quite the same thing!) and euthanasia in various forms, including the unofficial kind that you might want to be aware of if you want to avoid that happening.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Ways To Self-Soothe That Don’t Involve Food Or Drink
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If one is accustomed to comfort-eating or drowning one’s sorrows, what are the alternatives that can actually work? Holistic nutritionist Selin Bilgin has a list:
Self-Care That’s Not Self-Sabotage
You might want to make a note of these 10 things, so they can be a sort of “menu” for you when you need them:
- Give your introversion or extroversion what it needs (e.g. alone time to decompress, or social activities)
- Treat your senses: often we don’t actually need food/drink so much as culinary entertainment. So, we can sate this sensory mood in other ways, for example pleasant candles, flowers, and so forth.
- Bathe/shower nicely: it’s cliché but some personal pampering can go a long way
- Beautify yourself: it’s also cliché, but a makeover evening has its place
- Move! Go for a walk, do some yoga, whatever suits you, but move your body.
- Make movie nights luxurious: instead of making it about food/drink, focus on creating an enjoyable atmosphere
- Physically release tension: at 10almonds we recommend progressive relaxation for this!
- Create something: whether it’s art, craft, baking, or something else, creativity feels good
- Tackle things you’ve been procrastinating: this one doesn’t seem like self-soothing from the front end, but from the back end (i.e., having done it), it makes a big difference!
- Journal: expressing your thoughts and feelings can help a lot—really.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- Rebalancing Dopamine (Without “Dopamine Fasting”)
- Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Zucchini vs Okra – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing zucchini to okra, we picked the okra.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, okra has nearly 2x the protein and more than 3x the fiber (for about 2x the carbs).
In terms of vitamins, things are also quite one-sided; zucchini has a little more vitamin B2, while okra has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
Nor does the mineral situation make any compelling counterargument; zucchini is higher only in sodium, while okra has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc.
*Actually it’s only a little more potassium. But the rest are with big margins of difference.
Both of these on-the-cusp-of-being-pungent vegetables have beneficial antioxidant polyphenols (especially various forms of quercetin), but okra has more.
In short: enjoy both, of course, but there’s a clear winner here and it’s okra.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter/Astringent/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: