Mythbusting Moldy Food
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most Food Should Not Be Fuzzy
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your policy when it comes to mold on food (aside from intentional mold, e.g. blue cheese etc), and the responses were interesting:
- About 49% said “throw the whole thing away no matter what it is; it is dangerous”
- About 24% said “cut the mold off and eat the rest of whatever it is”
- The remainder were divided equally between “eat it all; keep the immune system on its toes” and “cut the mold off bread, but moldy animal products are dangerous”
So what does the science say?
Some molds are safe to eat: True or False?
True! We don’t think this is contentious so we’ll not spend much time on it, but just for the sake of being methodical: foods that are supposed to have mold on, including many kinds of cheese and even some kinds of cured meat (salami is an example; that powdery coating is mold).
We could give a big list of safe and unsafe molds, but that would be a list of names and let’s face it, they don’t introduce themselves by name.
However! The litmus test of “is it safe to eat” is:
Did you acquire it with this mold already in place and exactly as expected and advertised?
- If so, it is safe to eat (unless you have an allergy or such)
- If not, it is almost certainly not safe to eat
(more on why, later)
The “sniff test” is a good way to tell if moldy food is bad: True or False?
False. Very false. Because of how the sense of smell works.
You may feel like smell is a way of knowing about something at a distance, but the only way you can smell something is if particles of it are physically connecting with your olfactory receptors inside you. Yes, that has unfortunate implications about bathroom smells, but for now, let’s keep our attention in the kitchen.
If you sniff a moldy item of food, you will now have its mold spores inside your respiratory system. You absolutely do not want them there.
If we cut off the mold, the rest is safe to eat: True or False?
True or False, depending on what it is:
- Hard vegetables (e.g carrots, cabbage), and hard cheeses (e.g. Gruyère, Gouda) – cut off with an inch margin, and it should be safe
- Soft vegetables (e.g. tomatoes, and any vegetables that were hard but are now soft after cooking) – discard entirely; it is unsafe
- Anything else – discard entirely; it is unsafe
The reason for this is because in the case of the hard products mentioned, the mycelium roots of the mold cannot penetrate far.
In the case of the soft products mentioned, the surface mold is “the tip of the iceberg”, and the mycelium roots, which you will not usually be able to see, will penetrate the rest of it.
“Anything else” seems like quite a sweeping statement, but fruits, soft cheeses, yogurt, liquids, jams and jellies, cooked grains and pasta, meats, and yes, bread, are all things where the roots can penetrate deeply and easily. Regardless of you only being able to see a small amount, the whole thing is probably moldy.
The USDA has a handy downloadable factsheet:
Molds On Food: Are They Dangerous?
Eating a little mold is good for the immune system: True or False?
False, generally. There are of course countless types of mold, but not only are many of them pathogenic (mycotoxins), but also, a food that has mold will usually also have pathogenic bacteria along with the mold.
See for example: Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food
Food poisoning will never make you healthier.
But penicillin is safe to eat: True or False?
False, and also penicillin is not the mold on your bread (or other foods).
Penicillin, an antibiotic* molecule, is produced by some species of Penicillium sp., a mold. There are hundreds of known species of Penicillium sp., and most of them are toxic, usually in multiple ways. Take for example:
Penicillium roqueforti PR toxin gene cluster characterization
*it is also not healthy to consume antibiotics unless it is seriously necessary. Antibiotics will wipe out most of your gut’s “good bacteria”, leaving you vulnerable. People have died from C. diff infections for this reason. So obviously, if you really need to take antibiotics, take them as directed, but if not, don’t.
See also: Four Ways Antibiotics Can Kill You
One last thing…
It may be that someone reading this is thinking “I’ve eaten plenty of mold, and I’m fine”. Or perhaps someone you tell about this will say that.
But there are two reasons this logic is flawed:
- Survivorship bias (like people who smoke and live to 102; we just didn’t hear from the 99.9% of people who smoke and die early)
- Being unaware of illness is not being absent of illness. Anyone who’s had an alarming diagnosis of something that started a while ago will know this, of course. It’s also possible to be “low-level ill” often and get used to it as a baseline for health. It doesn’t mean it’s not harmful for you.
Stay safe!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
A Guide to Rational Living – by Drs. Albert Ellis and Robert Harper
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked before about the evidence-based benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and this book is indeed about CBT. In fact, it’s in many ways the book that popularized Third Wave CBT—in other words, CBT in its modern form.
Dr. Ellis’s specific branch of CBT is Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy, (REBT). What this means is using rationality to rewire emotions so that we’re not constantly sabotaging ourselves and our lives.
This is very much a “for the masses” book and doesn’t assume any prior knowledge of psychology, therapy, or psychotherapy. Or, for that matter, philosophy, since Stoic philosopher Epictetus had a lot to say that influenced Dr. Ellis’s work, too!
This book has also been described as “a self-help book for people who don’t like self-help books”… and certainly that Stoicism we mentioned does give the work a very different feel than a lot of books on the market.
The authors kick off with an initial chapter “How far can you go with self-therapy?”, and the answer is: quite far, even if it’s not a panacea. Everything has its limitations, and this book is no exception. On the other hand…
What the book does offer is a whole stack of tools, resources, and “How to…” chapters. In fact, there are so many “How to…” items in this book that, while it can be read cover-to-cover, it can also be used simply as a dip-in reference guide to refer to in times of need.
Bottom line: this book is highly recommendable to anyone and everyone, and if you don’t have it on your bookshelf, you should.
Click here to check out “A Guide To Rational Living” on Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gluten: What’s The Truth?
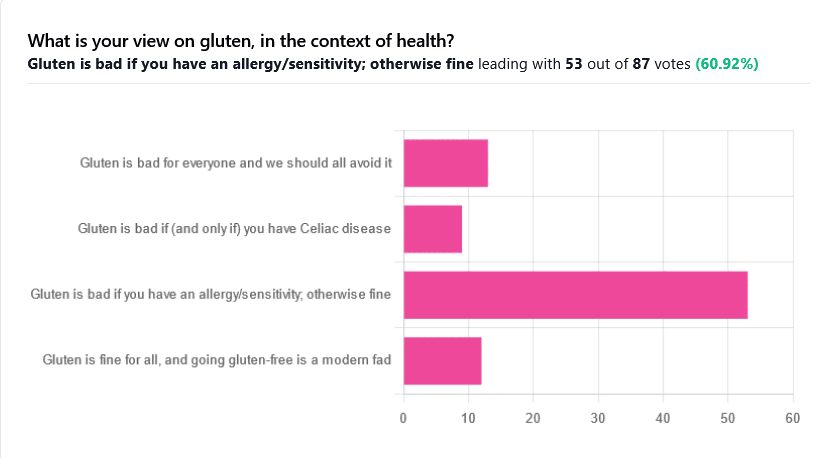
We asked you for your health-related view of gluten, and got the above spread of results. To put it simply:
Around 60% of voters voted for “Gluten is bad if you have an allergy/sensitivity; otherwise fine”
The rest of the votes were split fairly evenly between the other three options:
- Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it
- Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease
- Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad
First, let’s define some terms so that we’re all on the same page:
What is gluten?
Gluten is a category of protein found in wheat, barley, rye, and triticale. As such, it’s not one single compound, but a little umbrella of similar compounds. However, for the sake of not making this article many times longer, we’re going to refer to “gluten” without further specification.
What is Celiac disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease. Like many autoimmune diseases, we don’t know for sure how/why it occurs, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors have been strongly implicated, with the latter putatively including overexposure to gluten.
It affects about 1% of the world’s population, and people with Celiac disease will tend to respond adversely to gluten, notably by inflammation of the small intestine and destruction of enterocytes (the cells that line the wall of the small intestine). This in turn causes all sorts of other problems, beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but suffice it to say, it’s not pleasant.
What is an allergy/intolerance/sensitivity?
This may seem basic, but a lot of people conflate allergy/intolerance/sensitivity, so:
- An allergy is when the body mistakes a harmless substance for something harmful, and responds inappropriately. This can be mild (e.g. allergic rhinitis, hayfever) or severe (e.g. peanut allergy), and as such, responses can vary from “sniffly nose” to “anaphylactic shock and death”.
- In the case of a wheat allergy (for example), this is usually somewhere between the two, and can for example cause breathing problems after ingesting wheat or inhaling wheat flour.
- An intolerance is when the body fails to correctly process something it should be able to process, and just ejects it half-processed instead.
- A common and easily demonstrable example is lactose intolerance. There isn’t a well-defined analog for gluten, but gluten intolerance is nonetheless a well-reported thing.
- A sensitivity is when none of the above apply, but the body nevertheless experiences unpleasant symptoms after exposure to a substance that should normally be safe.
- In the case of gluten, this is referred to as non-Celiac gluten sensitivity
A word on scientific objectivity: at 10almonds we try to report science as objectively as possible. Sometimes people have strong feelings on a topic, especially if it is polarizing.
Sometimes people with a certain condition feel constantly disbelieved and mocked; sometimes people without a certain condition think others are imagining problems for themselves where there are none.
We can’t diagnose anyone or validate either side of that, but what we can do is report the facts as objectively as science can lay them out.
Gluten is fine for all, and going gluten-free is a modern fad: True or False?
Definitely False, Celiac disease is a real autoimmune disease that cannot be faked, and allergies are also a real thing that people can have, and again can be validated in studies. Even intolerances have scientifically measurable symptoms and can be tested against nocebo.
See for example:
- Epidemiology and clinical presentations of Celiac disease
- Severe forms of food allergy that can precipitate allergic emergencies
- Properties of gluten intolerance: gluten structure, evolution, and pathogenicity
However! It may not be a modern fad, so much as a modern genuine increase in incidence.
Widespread varieties of wheat today contain a lot more gluten than wheat of ages past, and many other molecular changes mean there are other compounds in modern grains that never even existed before.
However, the health-related impact of these (novel proteins and carbohydrates) is currently still speculative, and we are not in the business of speculating, so we’ll leave that as a “this hasn’t been studied enough to comment yet but we recognize it could potentially be a thing” factor.
Gluten is bad if (and only if) you have Celiac disease: True or False?
Definitely False; allergies for example are well-evidenced as real; same facts as we discussed/linked just above.
Gluten is bad for everyone and we should avoid it: True or False?
False, tentatively and contingently.
First, as established, there are people with clinically-evidenced Celiac disease, wheat allergy, or similar. Obviously, they should avoid triggering those diseases.
What about the rest of us, and what about those who have non-Celiac gluten sensitivity?
Clinical testing has found that of those reporting non-Celiac gluten sensitivity, nocebo-controlled studies validate that diagnosis in only a minority of cases.
In the following study, for example, only 16% of those reporting symptoms showed them in the trials, and 40% of those also showed a nocebo response (i.e., like placebo, but a bad rather than good effect):
This one, on the other hand, found that positive validations of diagnoses were found to be between 7% and 77%, depending on the trial, with an average of 30%:
Re-challenge Studies in Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
In other words: non-Celiac gluten sensitivity is a thing, and/but may be over-reported, and/but may be in some part exacerbated by psychosomatic effect.
Note: psychosomatic effect does not mean “imagining it” or “all in your head”. Indeed, the “soma” part of the word “psychosomatic” has to do with its measurable effect on the rest of the body.
For example, while pain can’t be easily objectively measured, other things, like inflammation, definitely can.
As for everyone else? If you’re enjoying your wheat (or similar) products, it’s well-established that they should be wholegrain for the best health impact (fiber, a positive for your health, rather than white flour’s super-fast metabolites padding the liver and causing metabolic problems).
Wheat itself may have other problems, for example FODMAPs, amylase trypsin inhibitors, and wheat germ agglutinins, but that’s “a wheat thing” rather than “a gluten thing”.
That’s beyond the scope of today’s main feature, but you might want to check out today’s featured book!
For a final scientific opinion on this last one, though, here’s what a respected academic journal of gastroenterology has to say:
From coeliac disease to noncoeliac gluten sensitivity; should everyone be gluten-free?
Share This Post
-
Peanuts vs Pistachios – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peanuts to pistachios, we picked the peanuts.
Why?
The choice might be surprising; after all, peanuts are usually the cheapest and most readily available nuts, popularly associated with calories and not much else. However! This one was super-close, and peanuts won very marginally, as you’ll see.
In terms of macros, peanuts have slightly more protein and fats, while pistachios have slightly more fiber and nearly 2x the carbs. What we all as individuals might prioritize more there is subjective, but this could arguably be considered a tie. About the fiber and carbs: peanuts have the lower glycemic index, but not by much. And about those fats: yes, they are healthy, and the fat breakdown for each is almost identical: peanuts have 53% monounsaturated, 34% polyunsaturated, and 14% saturated, while pistachios have 53% monounsaturated, 33% polyunsaturated, and 14% saturated, while. Yes, that adds up to 101% in the case of peanuts, but that’s what happens with rounding things to integers. However, the point is clear: both of these nuts have almost identical fats.
In the category of vitamins, peanuts have more of vitamins B3, B5, B9, E, and choline, while pistachios have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and C. So, a 5:5 tie on vitamins.
When it comes to minerals, peanuts have more iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, and zinc, while pistachios have more calcium, copper, phosphorus, and potassium, So, a marginal victory for peanuts (and yes, the margins of difference were similarly small in each case).
Adding up the tie, the other tie, and the marginal victory for peanuts, means a marginal victory for peanuts in total.
A quick note in closing though: this was comparing raw unsalted nuts in both cases, so do take that into account when buying nuts, and at the very least, skip the salted, unless you are deficient in sodium. Or if you’re using them for cooking, then buying salted nuts because they’re usually cheaper is fine; just soak and rinse them to remove the salt.
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Children with traumatic experiences have a higher risk of obesity – but this can be turned around
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Children with traumatic experiences in their early lives have a higher risk of obesity. But as our new research shows, this risk can be reduced through positive experiences.
Childhood traumatic experiences are alarmingly common. Our analysis of data from nearly 5,000 children in the Growing Up in New Zealand study revealed almost nine out of ten (87%) faced at least one significant source of trauma by the time they were eight years old. Multiple adverse experiences were also prevalent, with one in three children (32%) experiencing at least three traumatic events.
Childhood trauma includes a range of experiences such as physical and emotional abuse, peer bullying and exposure to domestic violence. It also includes parental substance abuse, mental illness, incarceration, separation or divorce and ethnic discrimination.
We found children from financially disadvantaged households and Māori and Pasifika had the highest prevalence of nearly all types of adverse experiences, as well as higher overall numbers of adversities.
The consequences of these experiences were far-reaching. Children who experienced at least one adverse event were twice as likely to be obese by age eight. The risk increased with the number of traumatic experiences. Children with four or more adverse experiences were nearly three times more likely to be obese.
Notably, certain traumatic experiences (including physical abuse and parental domestic violence) related more strongly to obesity than others. This highlights the strong connection between early-life adversity and physical health outcomes.
PickPik, CC BY-SA Connecting trauma to obesity
One potential explanation could be that the accumulation of early stress in children’s family, school and social environments is associated with greater psychological distress. This in turn makes children more likely to adopt unhealthy weight-related behaviours.
This includes consuming excessive high-calorie “comfort” foods such as fast food and sugary drinks, inadequate intake of nutritious foods, poor sleep, excessive screen time and physical inactivity. In our research, children who experienced adverse events were more likely to adopt these unhealthy behaviours. These, in turn, were associated with a higher risk of obesity.
Despite these challenges, our research also explored a promising area: the protective and mitigating effects of positive experiences.
We defined positive experiences as:
- parents in a committed relationship
- mothers interacting well with their children
- mothers involved in social groups
- children engaged in enriching experiences and activities such as visiting libraries or museums and participating in sports and community events
- children living in households with routines and rules, including those regulating bedtime, screen time and mealtimes
- children attending effective early childhood education.
The findings were encouraging. Children with more positive experiences were significantly less likely to be obese by age eight.
For example, those with five or six positive experiences were 60% less likely to be overweight or obese compared to children with zero or one positive experience. Even two positive experiences reduced the likelihood by 25%.
Positive childhood experiences such as playing sports or visiting libraries can lower the risk of obesity. Getty Images How positive experiences counteract trauma
Positive experiences can help mitigate the negative effects of childhood trauma. But a minimum of four positive experiences was required to significantly counteract the impact of adverse events.
While nearly half (48%) of the study participants had at least four positive experiences, a concerning proportion (more than one in ten children) reported zero or only one positive experience.
The implications are clear. Traditional weight-loss programmes focused solely on changing behaviours are not enough to tackle childhood obesity. To create lasting change, we must also address the social environments, life experiences and emotional scars of early trauma shaping children’s lives.
Fostering positive experiences is a vital part of this holistic approach. These experiences not only help protect children from the harmful effects of adversity but also promote their overall physical and mental wellbeing. This isn’t just about preventing obesity – it’s about giving children the foundation to thrive and reach their full potential.
Creating supportive environments for vulnerable children
Policymakers, schools and families all have a role to play. Community-based programmes, such as after-school activities, healthy relationship initiatives and mental health services should be prioritised to support vulnerable families.
Trauma-informed care is crucial, particularly for children from disadvantaged households who face higher levels of adversity and fewer positive experiences. Trauma-informed approaches are especially crucial for addressing the effects of domestic violence and other adverse childhood experiences.
Comprehensive strategies should prioritise both safety and emotional healing by equipping families with tools to create safe, nurturing environments and providing access to mental health services and community support initiatives.
At the family level, parents can establish stable routines, participate in social networks and engage children in enriching activities. Schools and early-childhood education providers also play a key role in fostering supportive environments that help children build resilience and recover from trauma.
Policymakers should invest in resources that promote positive experiences across communities, addressing inequalities that leave some children more vulnerable than others. By creating nurturing environments, we can counterbalance the impacts of trauma and help children lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
When positive experiences outweigh negative ones, children have a far greater chance of thriving – physically, emotionally and socially.
Ladan Hashemi, Senior Research Fellow in Health Sciences, University of Auckland, Waipapa Taumata Rau
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lobster vs Crab – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing lobster to crab, we picked the crab.
Why?
Generally speaking, most seafood is healthy in moderation (assuming it’s well-prepared, not poisonous, and you don’t have an allergy), and for most people, these two sea creatures are indeed considered a reasonable part of a healthy balanced diet.
In terms of macros, they’re comparable in protein, and technically crab has about 2x the fat, but in both cases it’s next to nothing, so 2x almost nothing is still almost nothing. And, if we break down the lipids profiles, crab has a sufficiently smaller percentage of saturated fat (compared to monounsaturated and polyunsaturated), that crab actually has less saturated fat than lobster. In balance, the category of macros is either a tie or a slight win for crab, depending on your personal priorities.
When it comes to vitamins, crab wins easily with more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, B9, B12, and C, in most cases by considerable margins (we’re talking multiples of what lobster has). Lobster, meanwhile, has more of vitamin B3 (tiny margin) and vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid, as in, the vitamin that’s in basically everything edible, and thus almost impossible to be deficient in unless literally starving).
The minerals scene is more balanced; lobster has more calcium, copper, manganese, and selenium, while crab has more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. The margins are comparable from one creature to another, so all in all the 4:5 score means a modest win for crab.
Both of these creatures are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, but crab is better.
Lobster and crab are both somewhat high in cholesterol, but crab is the relatively lower of the two.
In short: for most people most of the time, both are fine to enjoy in moderation, but if picking one, crab is the healthier by most metrics.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Shrimp vs Caviar – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Heal Your Stressed Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rochelle Walsh, therapist, explains the problem and how to fix it:
Not all brain damage is from the outside
Long-term stress and burnout cause brain damage; it’s not just a mindset issue—it impacts the brain physiologically. To compound matters, it also increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. While the brain can indeed grow new neurons and regenerate itself, chronic stress damages specific regions, and inhibits that.
There are some effects of chronic stress that can seem positive—the amygdalae and hypothalamus are seen to grow larger and stronger, for instance—but this is, unfortunately, “all the better to stress you with”. In compensation for this, chronic stress deprioritizes the pre-frontal cortex and hippocampi, so there goes your reasoning and memory.
This often results in people not managing chronic stress well. Just like a weak heart and lungs might impede the exercise that could make them stronger, the stressed brain is not good at permitting you to do the things that would heal it—preferring to keep you on edge all day, worrying and twitchy, mind racing and body tense. It also tends to lead to autoimmune diseases, due to the increased inflammation (because the body’s threat-detection system as at “jumping at own shadow” levels so it’s deploying every defense it has, including completely inappropriate ones).
Notwithstanding the “Heal Your Stressed Brain” thumbnail, she doesn’t actually go into this in detail and bids us sign up for her masterclass. We at 10almonds however like to deliver, so you can find useful advice and free resources in our links-drop at the bottom of this article.
Meanwhile, if you’d like to hear more about the neurological woes described above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
- How To Manage/Reduce Chronic Stress
- Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
- How Healthy People Regulate Their Emotions
- Sleep: Yes, You Really Do Still Need It!
- Give Your Adrenal Glands A Chance
- The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: