You Are the One You’ve Been Waiting For – by Dr. Richard Schwartz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As self-therapy approaches go, the title here could be read two ways: as pop-psychology fluff, or a suggestion of something deeper. And, while written in a way to make it accessible to all, we’re happy to report the content consists of serious therapeutic ideas, presented clearly.
Internal Family Systems (IFS) is a large, internationally recognized, and popular therapeutic approach. It’s also an approach that lends itself quite well to self-therapy, as this book illustrates.
Dr. Schwartz kicks off by explaining not IFS, but the problem that it solves… We (most of us, anyway) have over the course of our lives tried to plug the gaps in our own unmet psychological needs. And, that can cause resentment, strain, and can even be taken out on others if we’re not careful.
The real meat of the book, however, is in its illustrative explanations of how IFS works, and can be applied by an individual. The goal is to recognize all the parts that make us who we are, understand what they need in order to be at peace, and give them that. Spoiler: most what they will need is just being adequately heard, rather than locked in a box untended.
One of the benefits of using this book for self-therapy, of course, is that it requires a lot less vulnerability with a third party.
But, speaking of which, what of these intimate relationships the subtitle of the book referenced? Mostly the benefits to such come from a “put your own oxygen mask on first” angle… but the book does also cover discussions between intimate partners, and approaches to love, including what the author calls “courageous love”.
Bottom line: this is a great book if you want to do some “spring-cleaning of the soul” and live a little more lightly as a result.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep: yes, you really do still need it!
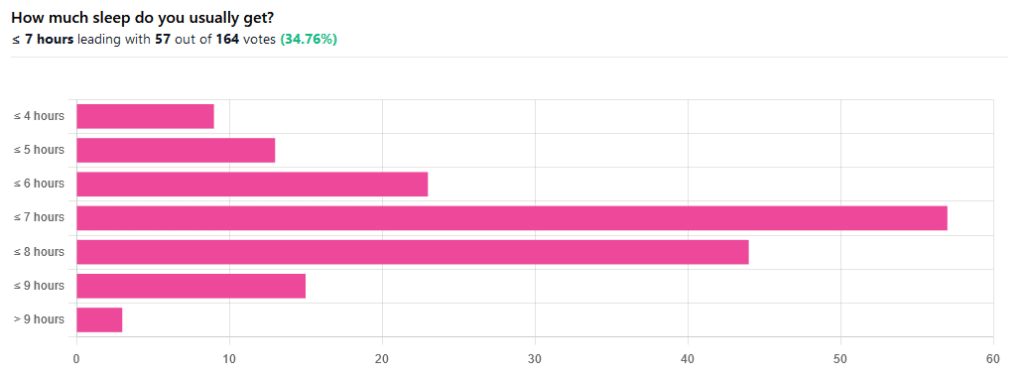
We asked you how much sleep you usually get, and got the above-pictured, below-described set of responses:
- A little of a third of all respondents selected the option “< 7 hours”
- However, because respondents also selected options such as < 6 hours, < 5 hours, and < 4 hours, so if we include those in the tally, the actual total percentage of respondents who reported getting under 7 hours, is actually more like 62%, or just under two thirds of all respondents.
- Nine respondents, which was about 5% of the total, reported usually getting under 4 hours sleep
- A little over quarter of respondents reported usually getting between 7 and 8 hours sleep
- Fifteen respondents, which was a little under 10% of the total, reported usually getting between 8 and 9 hours of sleep
- Three respondents, which was a little under 2% of the total, reported getting over 9 hours of sleep
- In terms of the classic “you should get 7–9 hours sleep”, approximately a third of respondents reported getting this amount.
You need to get 7–9 hours sleep: True or False?
True! Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that.
The way to know whether you have this, without genomic testing to know for sure, is: do you regularly get under 6.5 hours sleep, and yet continue to go through life bright-eyed and bushy-tailed? If so, you probably have that gene. If you experience daytime fatigue, brain fog, and restlessness, you probably don’t.
About that mutated ADRB1 gene:
NIH | Gene identified in people who need little sleep
Quality of sleep matters as much as duration, and a lot of studies use the “RU-Sated” framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity / usual hours
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
But, that doesn’t mean that you can skimp on the last one if the others are in order. In fact, getting a good 7 hours sleep can reduce your risk of getting a cold by three or four times (compared with six or fewer hours):
Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold
^This study was about the common cold, but you may be aware there are more serious respiratory viruses freely available, and you don’t want those, either.
Napping is good for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on how you’re doing it!
If you’re trying to do it to sleep less in total (per polyphasic sleep scheduling), then no, this will not work in any sustainable fashion and will be ruinous to the health. We did a Mythbusting Friday special on specifically this, a while back:
Could Just Two Hours Sleep Per Day Be Enough?
PS: you might remember Betteridge’s Law of Headlines
If you’re doing it as a energy-boosting supplement to a reasonable night’s sleep, napping can indeed be beneficial to the health, and can give benefits such as:
- Increased alertness
- Helps with learning
- Improved memory
- Boost to immunity
- Enhance athletic performance
However! There is still a right and a wrong way to go about it, and we wrote about this previously, for a Saturday Life Hacks edition of 10almonds:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
As we get older, we need less sleep: True or False
False, with one small caveat.
The small caveat: children and adolescents need 9–12 hours sleep because, uncredited as it goes, they are doing some seriously impressive bodybuilding, and that is exhausting to the body. So, an adult (with a normal lifestyle, who is not a bodybuilder) will tend to need less sleep than a child/adolescent.
But, the statement “As we get older, we need less sleep” is generally taken to mean “People in the 65+ age bracket need less sleep than younger adults”, and this popular myth is based on anecdotal observational evidence: older people tend to sleep less (as our survey above shows! For any who aren’t aware, our readership is heavily weighted towards the 60+ demographic), and still continue functioning, after all.
Just because we survive something with a degree of resilience doesn’t mean it’s good for us.
In fact, there can be serious health risks from not getting enough sleep in later years, for example:
Sleep deficiency promotes Alzheimer’s disease development and progression
Want to get better sleep?
What gets measured, gets done. Sleep tracking apps can be a really good tool for getting one’s sleep on a healthier track. We compared and contrasted some popular ones:
The Head-To-Head Of Google and Apple’s Top Apps For Getting Your Head Down
Take good care of yourself!
Share This Post
-
Ideal Blood Pressure Numbers Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Maybe I missed it but the study on blood pressure did it say what the 2 numbers should read ideally?❞
We linked it at the top of the article rather than including it inline, as we were short on space (and there was a chart rather than a “these two numbers” quick answer), but we have a little more space today, so:
Category Systolic (mm Hg) Diastolic (mm Hg) Normal < 120 AND < 80 Elevated 120 – 129 AND < 80 Stage 1 – High Blood Pressure 130 – 139 OR 80 – 89 Stage 2 – High Blood Pressure 140 or higher OR 90 or higher Hypertensive Crisis Above 180 AND/OR Above 120 To oversimplify for a “these two numbers” answer, under 120/80 is generally considered good, unless it is under 90/60, in which case that becomes hypotension.
Hypotension, the blood pressure being too low, means your organs may not get enough oxygen and if they don’t, they will start shutting down.
To give you an idea how serious this, this is the closed-circuit equivalent of the hypovolemic shock that occurs when someone is bleeding out onto the floor. Technically, bleeding to death also results in low blood pressure, of course, hence the similarity.
So: just a little under 120/80 is great.
Share This Post
-
From Cucumbers To Kindles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
Q: Where do I get cucumber extract?
A: You can buy it from BulkSupplements.com (who, despite their name, start at 100g packs)
Alternatively: you want it as a topical ointment (for skin health) rather than as a dietary supplement (for bone and joint health), you can extract it yourself! No, it’s not “just juice cucumbers”, but it’s also not too tricky.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Zucchini vs Okra – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing zucchini to okra, we picked the okra.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, okra has nearly 2x the protein and more than 3x the fiber (for about 2x the carbs).
In terms of vitamins, things are also quite one-sided; zucchini has a little more vitamin B2, while okra has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
Nor does the mineral situation make any compelling counterargument; zucchini is higher only in sodium, while okra has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc.
*Actually it’s only a little more potassium. But the rest are with big margins of difference.
Both of these on-the-cusp-of-being-pungent vegetables have beneficial antioxidant polyphenols (especially various forms of quercetin), but okra has more.
In short: enjoy both, of course, but there’s a clear winner here and it’s okra.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter/Astringent/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 Self-Care Trends That Are Actually Ruining Your Mental Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ok, some of these are trends; some are more perennial to human nature. For example, while asceticism is not a new idea, the “dopamine detox” is, and “bed rotting” is not a trend that this writer has seen recommended anywhere, but on the other hand, there are medieval illustrations of it—there was no Netflix in sight in the medieval illustrations, but perhaps a label diagnosing it as “melancholy”, for example.
So without further ado, here are five things to not do…
Don’t fall into these traps
The 5 things to watch out for are:
- Toxic positivity: constantly promoting positivity regardless of the reality of a situation can shame or invalidate genuine emotions, preventing people from processing their real feelings and leading to negative mental health outcomes—especially if it involves a “head in sand” approach to external problems as well as internal ones (because then those problems will never actually get dealt with).
- Self-indulgence: excessive focus on personal desires can make you more self-centered, less disciplined, and ultimately dissatisfied, which hinders personal growth and mental wellness.
- Bed rotting: spending prolonged time in bed for relaxation or entertainment can decrease motivation, productivity, and lead to (or worsen) depression rather than promoting genuine rest and rejuvenation.
- Dopamine detox: abstaining from pleasurable activities to “reset” the brain simply does not work and can lead to loneliness, boredom, and worsen mental health, especially when done excessively.
- Over-reliance on self-help: consuming too much self-help content or relying on material possessions for well-being can lead to information overload, unrealistic expectations, and the constant need for self-fixing, rather than fostering self-acceptance and authentic growth. Useful self-help can be like taking your car in for maintenance—counterproductive self-help is more like having your car always in for maintenance and never actually on the road.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read, and yes these are pretty much one-for-one with the 5 items above, doing a deeper dive into each in turn,
- How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
- Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- The Dopamine Myth
- Behavioral Activation Against Depression & Anxiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Night School – by Dr. Richard Wiseman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep is a largely neglected part of health for most people. Compared to factors like food and exercise, it’s something that experientially we’re mostly not present for! Little wonder then that we also often feel like it’s outside of our control.
While Dr. Wiseman does cover the usual advices with regard to getting good sleep, this book has a lot more than that.
Assuming that they go beyond the above, resources about sleep can usually be divided into one of two categories:
- Hard science: lots about brainwaves, sleep phases, circadian rhythms, melatonin production, etc… But nothing very inspiring!
- Fantastical whimsy: lots about dreams, spiritualism, and not a scientific source to be found… Nothing very concrete!
This book does better.
We get the science and the wonder. When it comes to lucid dreaming, sleep-learning, sleep hypnosis, or a miraculously reduced need for sleep, everything comes with copious scientific sources or not at all. Dr. Wiseman is well-known in his field for brining scientific skepticism to paranormal claims, by the way—so it’s nice to read how he can do this without losing his sense of wonder. Think of him as the Carl Sagan of sleep, perhaps.
Style-wise, the book is pop-science and easy-reading. Unsurprising, for a professional public educator and science-popularizer.
Structurally, the main part of the book is divided into lessons. Each of these come with background science and principles first, then a problem that we might want to solve, then exercises to do, to get the thing we want. It’s at once a textbook and an instruction manual.
Bottom line: this is a very inspiring book with a lot of science. Whether you’re looking to measurably boost your working memory or heal trauma through dreams, this book has everything.
Click here to check out Night School and learn what your brain can do!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: