Your Brain Is Always Listening – by Dr. Daniel Amen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of books on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), so what makes this one different?
While many CBT books have a focus (as this one also does) on controlling Automatic Negative Thoughts (ANTs), this one stands out in two ways:
Firstly: Dr. Amen, a medical doctor and psychiatrist, looks not just as the thoughts and feelings side of things… but also the neurological underpinnings. This makes a difference because it gives a much more tangible handle on some of the problems that we might face.
We wouldn’t tell someone with Type 1 Diabetes that they are “just blaming their pancreas” for blood sugar woes. So what’s with the notion of “this person is just blaming their brain”? Why would be harder on ourselves (or others) for having amygdalae that are a little out of whack, or a sluggish prefrontal cortex, or an overactive anterior cingulate gyrus?
So, Dr. Amen’s understanding and insights help us look at how we can give those bits of brain what they need to perk them up or calm them down.
Secondly, rather than picture-perfect easily-solved neat-and-tidy made-up scenarios as illustrations, he uses real (messy, human) case studies.
This means that we get to see how the methods advised work in the case of, for example, a business executive who has a trauma response to public speaking, because at the age of 12 he had to stand in court and argue for why his father should not receive the death penalty.
Bottom line: if these methods can ease situations like that, maybe we can apply them usefully in our own lives, too.
Click here to check out Your Brain Is Always Listening, and take control of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Treat Your Own Back – by Robin McKenzie
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A quick note about the author first: he’s a physiotherapist and not a doctor, but with over 40 years of practice to his name and 33 letters after his name (CNZM OBE FCSP (Hon) FNZSP (Hon) Dip MDT Dip MT), he seems to know his stuff. And certainly, if you visit any physiotherapist, they will probably have some of his books on their own shelves.
This book is intended for the layperson, and as such, explains everything that you need to know, in order to diagnose and treat your back. To this end, he includes assorted tests to perform, a lot of details about various possible back conditions, and then exercises to fix it, i.e. fix whatever you have now learned that the problem is, in your case (if indeed you didn’t know for sure already).
Of course, not everything can be treated by exercises, and he does point to what other things may be necessary in those cases, but for the majority, a significant improvement (if not outright symptom-free status) can be enjoyed by applying the techniques described in this book.
Bottom line: for most people, this book gives you the tools required to do exactly what the title says.
Click here to check out Treat Your Own Back, and treat your own back!
PS: if your issue is not with your back, we recommend you check out his other books in the series (neck, shoulder, hip, knee, ankle) 😎
Share This Post
-
Do We Need Supplements, And Do They Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does our diet need a little help?
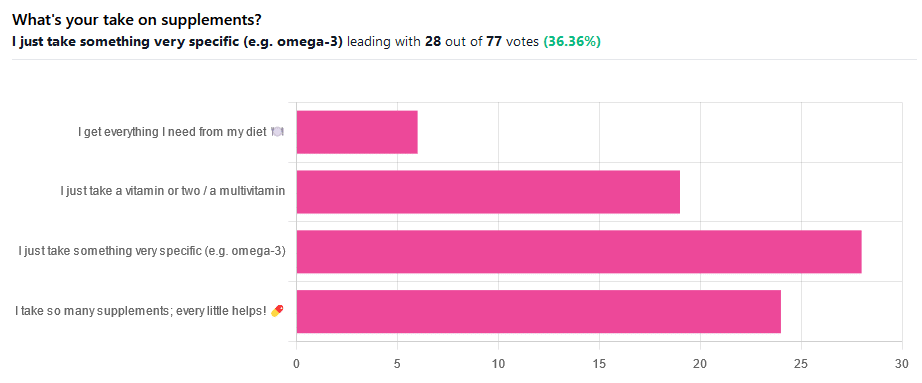
We asked you for your take on supplements, and got the above-illustrated, below-described set of results.
- The largest minority of respondents (a little over a third) voted for “I just take something very specific”
- The next most respondents voted for “I take so many supplements; every little helps!”
- Almost as many voted for “I just take a vitamin or two / a multivitamin”
- Fewest, about 8%, voted for “I get everything I need from my diet”
But what does the science say?
Food is less nutritious now than it used to be: True or False?
True or False depending on how you measure it.
An apple today and an apple from a hundred years ago are likely to contain the same amounts of micronutrients per apple, but a lower percentage of micronutrients per 100g of apple.
The reason for this is that apples (and many other food products; apples are just an arbitrary example) have been selectively bred (and in some cases, modified) for size, and because the soil mineral density has remained the same, the micronutrients per apple have not increased commensurate to the increase in carbohydrate weight and/or water weight. Thus, the resultant percentage will be lower, despite the quantity remaining the same.
We’re going to share some science on this, and/but would like to forewarn readers that the language of this paper is a bit biased, as it looks to “debunk” claims of nutritional values dropping while skimming over “yes, they really have dropped percentage-wise” in favor of “but look, the discrete mass values are still the same, so that’s just a mathematical illusion”.
The reality is, it’s no more a mathematical illusion than is the converse standpoint of saying the nutritional value is the same, despite the per-100g values dropping. After all, sometimes we eat an apple as-is; sometimes we buy a bag of frozen chopped fruit. That 500g bag of chopped fruit is going to contain less copper (for example) than one from decades past.
Here’s the paper, and you’ll see what we mean:
Supplements aren’t absorbed properly and thus are a waste of money: True or False?
True or False depending on the supplement (and your body, and the rest of your diet)
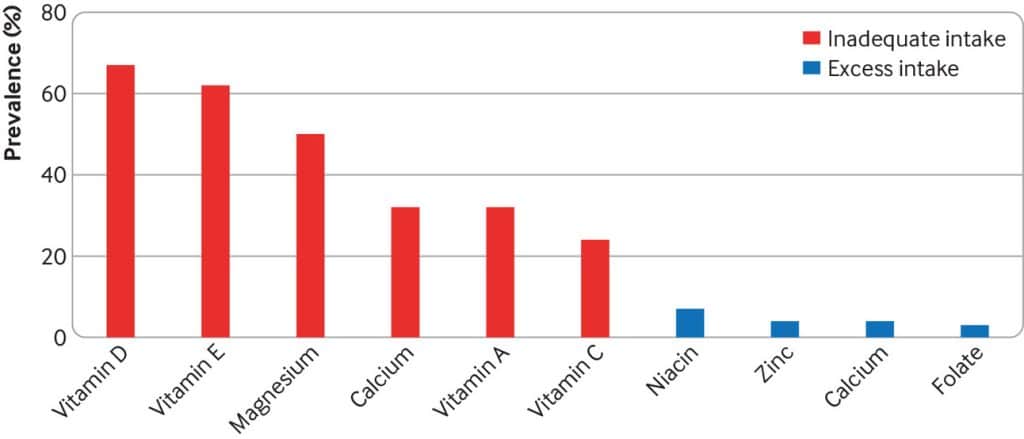
Many people are suffering from dietary deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, that could be easily correctable by supplementation:
However, as this study by Dr. Fang Fang Zhang shows, a lot of vitamin and mineral supplementation does not appear to have much of an effect on actual health outcomes, vis-à-vis specific diseases. She looks at:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoporosis
Her key take-aways from this study were:
- Randomised trial evidence does not support use of vitamin, mineral, and fish oil supplements to reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases
- People using supplements tend to be older, female, and have higher education, income, and healthier lifestyles than people who do not use them
- Use of supplements appreciably reduces the prevalence of inadequate intake for most nutrients but also increases the prevalence of excess intake for some nutrients
- Further research is needed to assess the long term effects of supplements on the health of the general population and in individuals with specific nutritional needs, including those from low and middle income countries
Read her damning report: Health effects of vitamin and mineral supplements
On the other hand…
This is almost entirely about blanket vitamin-and-mineral supplementation. With regard to fish oil supplementation, many commercial fish oil supplements break down in the stomach rather than the intestines, and don’t get absorbed well. Additionally, many people take them in forms that aren’t pleasant, and thus result in low adherence (i.e., they nominally take them, but in fact they just sit on the kitchen counter for a year).
One thing we can conclude from this is that it’s good to check the science for any given supplement before taking it, and know what it will and won’t help for. Our “Monday Research Review” editions of 10almonds do this a lot, although we tend to focus on herbal supplements rather than vitamins and minerals.
We can get everything we need from our diet: True or False?
Contingently True (but here be caveats)
In principle, if we eat the recommended guideline amounts of various macro- and micro-nutrients, we will indeed get all that we are generally considered to need. Obviously.
However, this may come with:
- Make sure to get enough protein… Without too much meat, and also without too much carbohydrate, such as from most plant sources of protein
- Make sure to get enough carbohydrates… But only the right kinds, and not too much, nor at the wrong time, and without eating things in the wrong order
- Make sure to get enough healthy fats… Without too much of the unhealthy fats that often exist in the same foods
- Make sure to get the right amount of vitamins and minerals… We hope you have your calculators out to get the delicate balance of calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and vitamin D right.
That last one’s a real pain, by the way. Too much or too little of one or another and the whole set start causing problems, and several of them interact with several others, and/or compete for resources, and/or are needed for the others to do their job.
And, that’s hard enough to balance when you’re taking supplements with the mg/µg amount written on them, never mind when you’re juggling cabbages and sardines.
On the topic of those sardines, don’t forget to carefully balance your omega-3, -6, and -9, and even within omega-3, balancing ALA, EPA, and DHA, and we hope you’re juggling those HDL and LDL levels too.
So, when it comes to getting everything we need from our diet, for most of us (who aren’t living in food deserts and/or experiencing food poverty, or having a medical condition that restricts our diet), the biggest task is not “getting enough”, it’s “getting enough of the right things without simultaneously overdoing it on the others”.
With supplements, it’s a lot easier to control what we’re putting in our bodies.
And of course, unless our diet includes things that usually can’t be bought in supermarkets, we’re not going to get the benefits of taking, as a supplement, such things as:
Etc.
So, there definitely are supplements with strong science-backed benefits, that probably can’t be found on your plate!
Share This Post
-
Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resveratrol & Healthy Aging
Resveratrol is the compound found in red grapes, and thus in red wine, that have resulted in red wine being sometimes touted as a heart-healthy drink.
However, at the levels contained in red wine, you’d need to drink 100–1000 glasses of wine per day (depending on the wine) to get the dose of resveratrol that was associated with heart health benefits in mouse studies.
Which also means: if you are not a mouse, you might need to drink even more than that!
Further reading: can we drink to good health?
Resveratrol supplementation
Happily, resveratrol supplements exist. But what does resveratrol do?
It lowers blood pressure:
Effect of resveratrol on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
It improves blood lipid levels:
It improves insulin sensitivity:
It has neuroprotective effects too:
Resveratrol promotes clearance of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta peptides
Is it safe?
For most people, it is generally recognized as safe. However, if you are on blood-thinners or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, you might want to skip it:
Antiplatelet activity of synthetic and natural resveratrol in red wine
You also might want to check with your pharmacist/doctor, if you’re on blood pressure meds, anxiety meds, or immunosuppressants, as it can increase the amount of these drugs that will then stay in your system:
Resveratrol modulates drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes in a healthy volunteer study
And as ever, of course, if unsure just check with your pharmacist/doctor, to be on the safe side.
Where to get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Gut Revolution – by Dr. Christine Bishara
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: what sets this apart from other books about gut health?
And one answer is: the author discusses her own published study, with regard to the connection between a deficiency in Bifidobacterium sp., and COVID infection risk/severity. However, this is not an entire book to say “supplement Bifidobacterium sp.”; rather, there are many other things at hand too.
And indeed, supplementing with probiotics will be useless if your gut is not an environment conducive to them thriving. If you take probiotics on an otherwise “Standard American Diet”, then this is approximately the equivalent of paradropping firefighters naked into a raging fire. It will not help. It isn’t the thought that counts.
Instead, Dr. Bishara talks us through what is required for beneficial gut bacteria to thrive, and how to go about making our gut an ideal place for them. In return, they will produce important biochemical metabolites for us, they will improve our immune response, regulate our emotions, help us maintain a healthy weight, heal our skin, and make us smell nice too. In short, they’re a trillions-strong clean-up and maintenance team, if only we treat our workforce well.
Another thing that Dr. Bishara brings of value here that’s not found in a lot of gut health books is the benefits (for gut health) of intermittent fasting, and specifically, a very useful timeline of what happens when, to ensure we do not sabotage our efforts by breaking our fast too early or too late.
The style is easy-reading pop-science, albeit with scientific references throughout for those who want to delve deeper.
Bottom line: this is a gut health book that stands out from the crowd in several ways, and is well worth the investment of reading it!
Click here to check out Gut Revolution, and help yours to help you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fruit, Fiber, & Leafy Greens… On A Low-FODMAP Diet!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber For FODMAP-Avoiders
First, let’s quickly cover: what are FODMAPs?
FODMAPs are fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols.
In plainer English: they’re carbohydrates that are resistant to digestion.
This is, for most people most of the time, a good thing, for example:
When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber? When It’s A Resistant Starch.
Not for everyone…
However, if you have inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS), including ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, or similar, then suddenly a lot of common dietary advice gets flipped on its head:
While digestion-resistant carbohydrates making it to the end parts of our digestive tract are good for our bacteria there, in the case of people with IBS or similar, it can be a bit too good for our bacteria there.
Which can mean gas (a natural by-product of bacterial respiration) accumulation, discomfort, water retention (as the pseudo-fiber draws water in and keeps it), and other related symptoms, causing discomfort, and potentially disease such as diarrhea.
Again: for most people this is not so (usually: quite the opposite; resistant starches improve things down there), but for those for whom it’s a thing, it’s a Big Bad Thing™.
Hold the veg? Hold your horses.
A common knee-jerk reaction is “I will avoid fruit and veg, then”.
Superficially, this can work, as many fruit & veg are high in FODMAPs (as are fermented dairy products, by the way).
However, a diet free from fruit and veg is not going to be healthy in any sustainable fashion.
There are, however, options for low-FODMAP fruit & veg, such as:
Fruits: bananas (if not overripe), kiwi, grapefruit, lemons, limes, melons, oranges, passionfruit, strawberries
Vegetables: alfalfa, bell peppers, bok choy, carrots, celery, cucumbers, eggplant, green beans, kale, lettuce, olives, parsnips, potatoes (and sweet potatoes, yams etc), radishes, spinach, squash, tomatoes*, turnips, zucchini
*our stance: botanically it’s a fruit, but culinarily it’s a vegetable.
For more on the science of this, check out:
Strategies for Producing Low FODMAPs Foodstuffs: Challenges and Perspectives ← table 2 is particularly informative when it comes to the above examples, and table 3 will advise about…
Bonus
Grains: oats, quinoa, rice, tapioca
…and wheat if the conditions in table 3 (linked above) are satisfied
(worth mentioning since grains also get a bad press when it comes to IBS, but that’s mostly because of wheat)
See also: Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat More, Live Well – by Dr. Megan Rossi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Often, eating healthily can feel restrictive. Don’t eat this, skip that, eliminate the other. Where is the joy?
Dr. Megan Rossi brings a scientific angle on positive dieting, that is to say, looking at what to add, rather than what to subtract. Now, the idea isn’t to have sugar-laden chocolate cake with berries on top and call it a net positive because of the berries, though. Rather, Dr. Rossi lays out how to include as many diverse vegetables and fruits as possible, with tasty recipes so that we’re too busy with those to crave junk food.
Speaking of recipes, there are 80, and they are easy to follow. She describes them as “plant-based”, and by this what she really means is “plant-centric” or such; she does include the use of some animal products.
This is important to note, because general convention is to use “plant-based” to mean functionally vegan, but being about the food rather than the ideology; a relevant distinction in both society and science. In the case of this book, it’s neither, but it is very healthy.
Bottom line: if you’d like to introduce more healthy diversity to your diet, rather than eating the same three fruits and five vegetables, but you’re not sure how, this book will get you where you need to be.
Click here to check out Eat More, Live Well, and diversify your diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: