Life Lessons From A Brain Surgeon – by Dr. Rahul Jandial
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In the category of surgeons with a “what to put on your table to stay off mine” angle, this book packs an extra punch. As well as being an experienced brain surgeon, Dr. Jandial also does a lot of cutting edge lab research too. What does this mean for us?
This book gives, as the subtitle promises, “practical strategies for peak health and performance”—with a brain-centric bias, of course.
From diet and nootropic supplements, to exercise and brain-training, we get a good science-based view of which ones actually work, and which don’t. The style is also very readable; Dr. Jandial is a great educator, presenting genuine scientific content with very accessible language.
Bottom line: if you’d indeed like to look after your most important organ optimally, this book gives a lot of key pointers, without unnecessary fluff.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
One More Reason To Prioritize Sleep To Fight Cognitive Decline
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked sometimes at 10almonds about how important sleep is for many aspects of health, including for brain health, and including in later life.
There’s a common myth that older people require less sleep; the reality is that sleeping less and not dying of it does not equate to needing less.
See also: Sleep: Yes, You Really Do Still Need It!
And: How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
Quantity is not everything though; quality absolutely matters too. We’ve written about that here:
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter) ← duration is just one dimension out of the six
We’ve even gone into some more obscure, but still very important things, such as: How Your Sleep Position Changes Dementia Risk
We’ve also talked about the role of sleep in memory (and forgetting): How Your Brain Chooses What To Remember
With that in mind…
Some more recent science
This study was about spatial memory, but what’s important (in our opinion) is that it’s about solidifying recent learning.
Researchers measured brain activity in rats for up to 20 hours of sleep following spatial learning tasks. Initially, the neuronal patterns observed during sleep mirrored those from the learning phase. However, as sleep progressed, these patterns transformed to resemble the activity seen when the rats later recalled the locations of food rewards. Interestingly, this reorganization happened during non-REM sleep, which means it wasn’t just a case of “the rats were dreaming about their day” (which is a well-established way in which memories do get encoded), but rather, the newly-learned experiences were being actively encoded in the rest of sleep.
This is critical, because in age-related cognitive decline, it’s very common for very long-term memory (VLTM) to remain intact, while LTM and short-term memory (STM) crumble. For example, someone may remember many details of their life from 20 years ago, but forget where they currently live, or what happened in the conversation two minutes ago.
In other words, the biggest problem is not the storage of memories, but rather the encoding of them in the first place.
Which sleep facilitates!
And it’s also important to note that part about it being the rest of sleep, because when the brain is sleep-deprived, it’ll tend to prioritize REM sleep, which is important, but that means cutting back on other phases of sleep, and from this study, we can see that memory & learning will be amongst the things adversely affected by such cuts.
Here’s the paper, for those interested:
Sleep stages antagonistically modulate reactivation drift
And for those who prefer lighter reading, here’s a pop-science article about the same study, which explains it in more words than we can here:
But wait, there’s more!
Sleep resets neurons for new memories the next day, study finds
So, once again… It is absolutely critical to prioritize good sleep.
Want to know more?
Check out:
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Hawthorn For The Heart (& More)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hawthorn, The Heart-Healthy Helper
Hawthorn, a berry of the genus Crataegus (there are many species, but they seem to give more or less the same benefits), has been enjoyed for hundreds of years, if not thousands, as a herbal remedy for many ailments, mostly of the cardiovascular, digestive, and/or endocrine systems:
Crataegus pinnatifida: Chemical Constituents, Pharmacology, and Potential Applications
Antioxidant & Anti-inflammatory
Like most berries, it’s full of helpful polyphenols, with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Indeed, as Dr. Nabavi et al. wrote,
❝Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (hawthorn) is one of the most important edible plants of the Rosaceae family and is also used in traditional medicine.
Growing evidence has shown that this plant has various interesting physiological and pharmacological activities due to the presence of different bioactive natural compounds.
In addition, scientific evidence suggests that the toxicity of hawthorn is negligible. ❞
Read in full: Polyphenolic Composition of Crataegus monogyna Jacq.: From Chemistry to Medical Applications
While “the toxicity of hawthorn is negligible” may be reasonably considered a baseline for recommending an edible plant, it’s still important as just that: a baseline. It’s good to know that berries are safe, after all!
More positively, about those antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties:
This one was a mouse study, but it’s important as it about modulating liver injury after being fed a high fructose diet.
In other words: it a) helps undo the biggest cause of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, b) logically, likely guards against diabetes also (by the same mechanism)
Anti-Diabetes Potential
Curious about that latter point, we looked for studies, and found, for example:
- Hypoglycemic effect of hawthorn in type II diabetes mellitus rat model
- Molecular Mechanisms of Hawthorn Extracts in Multiple Organs Disorders in Underlying of Diabetes: A Review
- Modulation of GPC-4 and GPLD1 serum levels by improving glycemic indices in type 2 diabetes: Resistance training and hawthorn extract intervention
Noteworthily, those studies are from the past couple of years, which is probably why we’re not seeing many human trials for this yet—everything has to be done in order, and there’s a lengthy process between each.
We did find some human trials with hawthorn in diabetes patients, for example:
…but as you see, that’s testing not its antidiabetic potential, so far demonstrated only in mice and rats (so far as we could find), but rather its blood pressure lowering effects, using diabetic patients as a sample.
Blood pressure benefits
Hawthorn has been studied specifically for its hypotensive effect, for example:
As an extra bonus, did you notice in the conclusion,
❝Furthermore, a trend towards a reduction in anxiety (p = 0.094) was also observed in those taking hawthorn compared with the other groups.
These findings warrant further study, particularly in view of the low dose of hawthorn extract used.❞
…it seems that not a lot more study has been done yet, but that is promising too!
Other blood metrics
So, it has antidiabetic and antihypertensive benefits, what of blood lipids?
Hawthorn Fruit Extract Elevates Expression of Nrf2/HO-1 and Improves Lipid Profiles
And as for arterial plaque?
here it was tested alongside another herb, and performed well (also against placebo).
In summary…
Hawthorn (Crataegus sp.) is…
- a potent berry containing many polyphenols with good antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
- looking promising against diabetes, but research for this is still in early stages
- found to have other cardioprotective effects (antihypertensive, improves lipid profiles), too
- considered to have negligible toxicity
Where can I get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
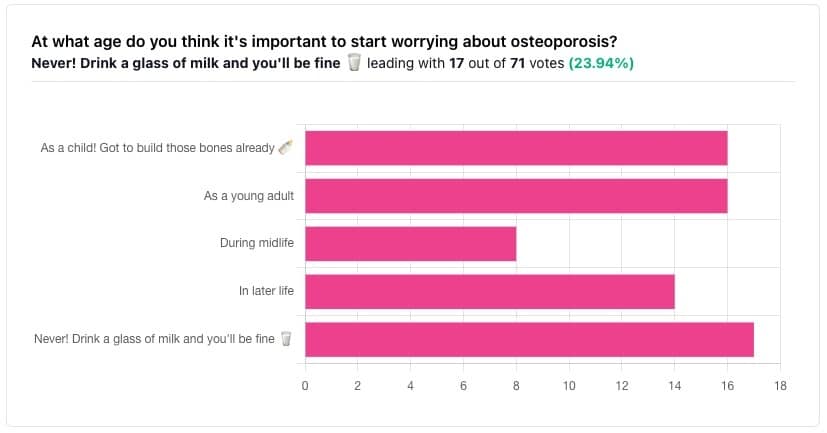
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
The Bare-bones Truth About Osteoporosis
In yesterday’s issue of 10almonds, we asked you “at what age do you think it’s important to start worrying about osteoporosis?”, and here’s the spread of answers you gave us:
At first glance it may seem shocking that a majority of respondents to a poll in a health-focused newsletter think it’ll never be an issue worth worrying about, but in fact this is partly a statistical quirk, because the vote of the strongest “early prevention” crowd was divided between “as a child” and “as a young adult”.
This poll also gave you the option to add a comment with your vote. Many subscribers chose to do so, explaining your choices… But, interestingly, not one single person who voted for “never” had any additional thoughts to add.
We loved reading your replies, by the way, and wish we had room to include them here, because they were very interesting and thought-provoking.
Let’s get to the myths and facts:
Top myth: “you will never need to worry about it; drink a glass of milk and you’ll be fine!”
The body is constantly repairing itself. Its ability to do that declines with age. Until about 35 on average, we can replace bone mineral as quickly as it is lost. After that, we lose it by up to 1% per year, and that rate climbs after 50, and climbs even more steeply for those who go through (untreated) menopause.
Losing 1% per year might not seem like a lot, but if you want to live to 100, there are some unfortunate implications!
About that menopause, by the way… Because declining estrogen levels late in life contribute significantly to osteoporosis, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be of value to many for the sake of bone health, never mind the more obvious and commonly-sought benefits.
On the topic of that glass of milk…
- Milk is a great source of calcium, which is useless to the body if you don’t also have good levels of vitamin D and magnesium.
- People’s vitamin D levels tend to directly correlate to the level of sun where they live, if supplementation isn’t undertaken.
- Plant-based milks are usually fortified with vitamin D (and calcium), by the way.
- Most people are deficient in magnesium, because green leafy things don’t form as big a part of most people’s diets as they should.
See also: An update on magnesium and bone health
Next most common myth: “bone health is all about calcium”
We spoke a little above about the importance of vitamin D and magnesium for being able to properly use that. But potassium is also critical:
Read more: The effects of potassium on bone health
While we’re on the topic…
People think of collagen as being for skin health. And it is important for that, but collagen’s benefits (and the negative effects of its absence) go much deeper, to include bone health. We’ve written about this before, so rather than take more space today, we’ll just drop the link:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Want to really maximize your bone health?
You might want to check out this well-sourced LiveStrong article:
Bone Health: Best and Worst Foods
(Teaser: leafy greens are in 2nd place, topped by sardines at #1—where do you think milk ranks?)
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What Harm Can One Sleepless Night Do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ll not bury the lede: a study found that just one night of 24-hour sleep deprivation can alter immune cell profiles in young, lean, healthy people to resemble those of people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammation, in turn, causes very many other chronic diseases, and worsens most of the ones it doesn’t outright cause.
The reason this happens is because in principle, inflammation is supposed to be good for us—it’s our body’s defenses coming to the rescue. However, if we imagine our immune cells as firefighters, then compare:
- A team of firefighters who are in great shape and ready to deploy at a moment’s notice, are mostly allowed to rest, sometimes get training, and get called out to a fire from time time, just enough to keep them on their toes. Today, something in your house caught fire, and they showed up in 5 minutes and put it out safely.
- A team of firefighters who have been pulling 24-hour shifts every day for the past 20 years, getting called out constantly for lost cats, burned toast, wrong numbers, the neighbor’s music, a broken fridge, and even the occasional fire. Today, your printer got jammed so they broke down your door and also your windows just for good measure, and blasted your general desk area with a fire hose, which did not resolve the problem but now your computer itself is broken.
Which team would you rather have?
The former team is a healthy immune system; the latter is the immune system of someone with chronic inflammation.
But if it’s one night, it’s not chronic, right?
Contingently true. However, the problem is that because the immune profile was made to be like the bad team we described (imagine that chaos in your house, now remember that for this metaphor, it’s your body that that’s happening to), the immediate strong negative health impact will already have knock-on effects, which in turn make it more likely that you’ll struggle to get your sleep back on track quickly.
For example, the next night you may oversleep “to compensate”, but then the following day your sleep schedule is now slid back considerably; one thing leads to another, and a month later you’re thinking “I really must sort my sleep out”.
See also: How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← A recent, large (n=72,269) 8-year prospective* observational study of adults aged 40-79 found a strong association between irregular sleep and major cardiovascular events, to such an extent that it was worse than undersleeping.
*this means they started the study at a given point, and measured what happened for the next eight years—as opposed to a retrospective study, which would look at what had happened during the previous 8 years.
What about sleep fragmentation?
In other words: getting sleep, but heavily disrupted sleep.
The answer is: basically the same deal as with missed sleep.
Specifically, elevated proinflammatory cytokines (in this context, that’s bad) and an increase in nonclassical monocytes—as are typically seen in people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Remember: these were young, lean, healthy participants going into the study, who signed up for a controlled sleep deprivation experiment.
This is important, because the unhealthy inflammatory profile means that people with such are a lot more likely to develop diabetes, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and many more things besides. And, famously, most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well.
Even amongst 10almonds readers, a health-conscious demographic by nature, 62% of 10almonds readers do not regularly get the prescribed 7–9 hours sleep (i.e. they get under 7 hours).
You can see the data on this one, here: Why You Probably Need More Sleep ← yes, including if you are in the older age range; we bust that myth in the article too!*
*Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that. But we also cover that in the article, and how to know whether you have it.
With regard to “most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well”, this means that most people in the industrialized world are subject to an unseen epidemic of sleep-deprivation-induced inflammation that is creating vulnerability to many other diseases. In short, the lifestyle of the industrialized world (especially: having to work certain hours) is making most of the working population sick.
Dr. Fatema Al-Rashed, lead researcher, concluded:
❝In the long term, we aim for this research to drive policies and strategies that recognize the critical role of sleep in public health.
We envision workplace reforms and educational campaigns promoting better sleep practices, particularly for populations at risk of sleep disruption due to technological and occupational demands.
Ultimately, this could help mitigate the burden of inflammatory diseases like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.❞
You can read the paper in full here: Impact of sleep deprivation on monocyte subclasses and function
What can we do about it?
With regard to sleep, we’ve written so much about this, but here are three key articles that contain a lot of valuable information:
- Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
- Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
- Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
…and with regard to inflammation, a good concise overview of how to dial it down is:
How To Prevent Or Reduce Inflammation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fast. Feast. Repeat – by Dr. Gin Stephens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed intermittent fasting books before, so what makes this one different?
The title “Fast. Feast. Repeat.” doesn’t give much away; after all, we already know that that’s what intermittent fasting is.
After taking the reader though the basics of how intermittent fasting works and what it does for the body, much of the rest of the book is given over to improvements.
That’s what the real strength of this book is: ways to make intermittent fasting more efficient, including how to avoid plateaus. After all, sometimes it can seem like the only way to push further with intermittent fasting is to restrict the eating window further. Not so!
Instead, Dr. Stephens gives us ways to keep confusing our metabolism (in a good way) if, for example, we had a weight loss goal we haven’t met yet.
Best of all, this comes without actually having to eat less.
Bottom line: if you want to be in good physical health, and/but also believe that life is for living and you enjoy eating food, then this book can resolve that age-old dilemma!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Out With The Old…
Fisetin is a flavonoid (specifically, a flavonol), but it’s a little different than most. While it has the usual antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties you might reasonably expect from flavonoids, it has an extra anti-aging trick up its sleeve that most don’t.
❝Fisetin is a flavonol that shares distinct antioxidant properties with a plethora of other plant polyphenols. Additionally, it exhibits a specific biological activity of considerable interest as regards the protection of functional macromolecules against stress which results in the sustenance of normal cells cytoprotection. Moreover, it shows potential as an anti-inflammatory, chemopreventive, chemotherapeutic and recently also senotherapeutic agent❞
~ Dr. Grynkiewicz & Dr. Demchuk
Let’s briefly do some due diligence on its expected properties, and then we’ll take a look at its bonus anti-aging effects.
The flavonol that does-it-ol
Because of the similar mechanisms involved, there are three things that often come together, which are:
- Antioxidant
- Anti-inflammatory
- Anticancer
This list often gets expanded to also include:
- Anti-aging
…although that is usually the last thing to get tested out of that list.
In today’s case, let’s kick it off with…
❝Fisetin (3,3′,4′,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a dietary flavonoid found in various fruits (strawberries, apples, mangoes, persimmons, kiwis, and grapes), vegetables (tomatoes, onions, and cucumbers), nuts, and wine that has shown strong anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-tumorigenic, anti-invasive, anti-angiogenic, anti-diabetic, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective effects❞
Read more: Fisetin and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
Understanding its anticancer mechanisms
The way that fisetin fights cancer is basically “all the ways”, and this will be important when we get to its special abilities shortly:
❝Being a potent anticancer agent, fisetin has been used to inhibit stages in the cancer cells (proliferation, invasion),prevent cell cycle progression, inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, cause polymerase (PARP) cleavage, and modulate the expressions of Bcl‐2 family proteins in different cancer cell lines (HT‐29, U266, MDA‐MB‐231, BT549, and PC‐3M‐luc‐6), respectively. Further, fisetin also suppresses the activation of the PKCα/ROS/ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, reduces the NF‐κB activation, and down‐regulates the level of the oncoprotein securin. Fisetin also inhibited cell division and proliferation and invasion as well as lowered the TET1 expression levels. ❞
Read more: Fisetin: An anticancer perspective
There’s also more about it than we even have room to quote, here:
Now For What’s New And Exciting: Senolysis
All that selectivity that fisetin exhibits when it comes to “this cell gets to live, and this one doesn’t” actions?
It makes a difference when it comes to aging, too. Because aging and cancer happen by quite similar mechanisms; they’re both DNA-copying errors that get copied forward, to our detriment.
- In the case of cancer, it’s a cell line that accidentally became immortal and so we end up with too many of them multiplying in one place (a tumor)
- In the case of aging, it’s the cellular equivalent of “a photocopy of a photocopy of a photocopy” gradually losing information as it goes
In both cases…
The cell must die if we want to live
Critically, and which quality differentiates it from a lot of other flavonoids, fisetin has the ability to selectively kill senescent cells.
To labor the photocopying metaphor, this means there’s an office worker whose job it is to say “this photocopy is barely legible, I’m going to toss this, and then copy directly from the clearest copy we have instead”, thus keeping the documents (your DNA) in pristine condition.
In fisetin’s case, this was first tested in mouse (in vivo) studies, and in human tissue (in vitro) studies, before moving to human clinical studies:
❝Of the 10 flavonoids tested, fisetin was the most potent senolytic.
The natural product fisetin has senotherapeutic activity in mice and in human tissues. Late life intervention was sufficient to yield a potent health benefit.❞
~ Dr. Matthew Yousefzadeh et al.
Read in full: Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan
There’s lots more science that’s been done to it since that first groundbreaking study though; here’s a more recent example:
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: