154 million lives saved in 50 years: 5 charts on the global success of vaccines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know vaccines have been a miracle for public health. Now, new research led by the World Health Organization has found vaccines have saved an estimated 154 million lives in the past 50 years from 14 different diseases. Most of these have been children under five, and around two-thirds children under one year old.
In 1974 the World Health Assembly launched the Expanded Programme on Immunization with the goal to vaccinate all children against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), measles, polio, tuberculosis and smallpox by 1990. The program was subsequently expanded to include several other diseases.
The modelling, marking 50 years since this program was established, shows a child aged under ten has about a 40% greater chance of living until their next birthday, compared to if we didn’t have vaccines. And these positive effects can be seen well into adult life. A 50-year-old has a 16% greater chance of celebrating their next birthday thanks to vaccines.
What the study did
The researchers developed mathematical and statistical models which took in vaccine coverage data and population numbers from 194 countries for the years 1974–2024. Not all diseases were included (for example smallpox, which was eradicated in 1980, was left out).
The analysis includes vaccines for 14 diseases, with 11 of these included in the Expanded Programme on Immunization. For some countries, additional vaccines such as Japanese encephalitis, meningitis A and yellow fever were included, as these diseases contribute to major disease burden in certain settings.
The models were used to simulate how diseases would have spread from 1974 to now, as vaccines were introduced, for each country and age group, incorporating data on increasing vaccine coverage over time.
Children are the greatest beneficiaries of vaccines
Since 1974, the rates of deaths in children before their first birthday has more than halved. The researchers calculated almost 40% of this reduction is due to vaccines.
The effects have been greatest for children born in the 1980s because of the intensive efforts made globally to reduce the burden of diseases like measles, polio and whooping cough.
Some 60% of the 154 million lives saved would have been lives lost to measles. This is likely due to its ability to spread rapidly. One person with measles can spread the infection to 12–18 people.
The study also found some variation across different parts of the world. For example, vaccination programs have had a much greater impact on the probability of children living longer across low- and middle-income countries and settings with weaker health systems such as the eastern Mediterranean and African regions. These results highlight the important role vaccines play in promoting health equity.
Vaccine success is not assured
Low or declining vaccine coverage can lead to epidemics which can devastate communities and overwhelm health systems.
Notably, the COVID pandemic saw an overall decline in measles vaccine coverage, with 86% of children having received their first dose in 2019 to 83% in 2022. This is concerning because very high levels of vaccination coverage (more than 95%) are required to achieve herd immunity against measles.
In Australia, the coverage for childhood vaccines, including measles, mumps and rubella, has declined compared to before the pandemic.
This study is a reminder of why we need to continue to vaccinate – not just against measles, but against all diseases we have safe and effective vaccines for.
The results of this research don’t tell us the full story about the impact of vaccines. For example, the authors didn’t include data for some vaccines such as COVID and HPV (human papillomavirus). Also, like with all modelling studies, there are some uncertainties, as data was not available for all time periods and countries.
Nonetheless, the results show the success of global vaccination programs over time. If we want to continue to see lives saved, we need to keep investing in vaccination locally, regionally and globally.
Meru Sheel, Associate Professor and Epidemiologist, Infectious Diseases, Immunisation and Emergencies Group, Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney and Alexandra Hogan, Mathematical epidemiologist, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Regular Nail Polish vs Gel Nail Polish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing regular nail polish to gel nail polish, we picked the regular.
Why?
This one’s less about what’s in the bottle, and more about what gets done to your hands:
- Regular nail polish application involves carefully brushing it on.
- Regular nail polish removal involves wiping with acetone.
…whereas:
- Gel nail polish application involves deliberately damaging (roughing up) the nail to allow the color coat to adhere, then when the top coat is applied, holding the nails (and thus, the attached fingers) under a UV light to set it. That UV lamp exposure is very bad for the skin.
- Gel nail polish removal involves soaking in acetone, which is definitely worse than wiping with acetone. Failure to adequately soak it will result in further damage to the nail while trying to get the base coat off the nail that you already deliberately damaged when first applying it.
All in all, regular nail polish isn’t amazing for nail health (healthiest is for nails to be free and naked), but for those of us who like a little bit of color there, regular is a lot better than gel.
Gel nail polish damages the nail itself by necessity, and presents a cumulative skin cancer risk and accelerated aging of the skin, by way of the UV lamp use.
For your interest, here are the specific products that we compared, but the above goes for any of this kind:
Regular nail polish | Gel nail polish
If you’d like to read more about nail health, you might enjoy reading:
The Counterintuitive Dos and Don’ts of Nail Health
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Chiropractors have been banned again from manipulating babies’ spines. Here’s what the evidence actually says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chiropractors in Australia will not be able to perform spinal manipulation on children under the age of two once more, following health concerns from doctors and politicians.
But what is the spinal treatment at the centre of the controversy? Does it work? Is there evidence of harm?
We’re a team of researchers who specialise in evidence-based musculoskeletal health. I (Matt) am a registered chiropractor, Joshua is a registered physiotherapist and Giovanni trained as a physiotherapist.
Here’s what the evidence says.
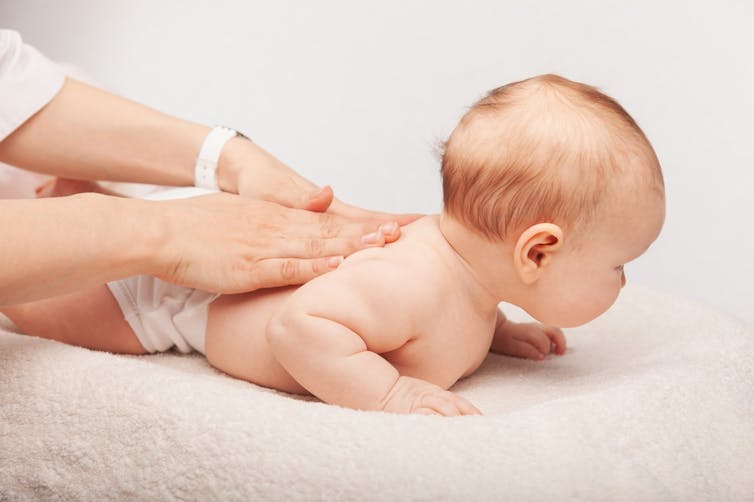
Dmitry Naumov/Shutterstock Remind me, how did this all come about?
A Melbourne-based chiropractor posted a video on social media in 2018 using a spring-loaded device (known as the Activator) to manipulate the spine of a two-week-old baby suspended upside down by the ankles.
The video sparked widespread concerns among the public, medical associations and politicians. It prompted a ban on the procedure in young children. The Victorian health minister commissioned Safer Care Victoria to conduct an independent review of spinal manipulation techniques on children.
Recently, the Chiropractic Board of Australia reinstated chiropractors’ authorisation to perform spinal manipulation on babies under two years old. But this week, it backflipped, following heavy criticism from medical associations and politicians.
What is spinal manipulation?
Spinal manipulation is a treatment used by chiropractors and other health professionals such as doctors, osteopaths and physiotherapists.
It is an umbrella term that includes popular “back cracking” techniques.
It also includes more gentle forms of treatment, such as massage or joint mobilisations. These involve applying pressure to joints without generating a “cracking” sound.
Does spinal manipulation in babies work?
Several international guidelines for health-care professionals recommend spinal manipulation to treat adults with conditions such as back pain and headache as there is an abundance of evidence on the topic. For example, spinal manipulation for back pain is supported by data from nearly 10,000 adults.
For children, it’s a different story. Safer Care Victoria’s 2019 review of spinal manipulation found very few studies testing whether this treatment was safe and effective in children.
Studies were generally small and were of poor quality. Some of those small, poor-quality studies, suggest spinal manipulation provides a very small benefit for back pain, colic and potentially bedwetting – some common reasons for parents to take their child to see a chiropractor. But overall, the review found the overall body of evidence was very poor.
Spinal manipulation doesn’t seem to help young children with an ear infection. MIA Studio/Shutterstock However, for most other children’s conditions chiropractors treat – such as headache, asthma, otitis media (a type of ear infection), cerebral palsy, hyperactivity and torticollis (“twisted neck”) – there did not appear to be a benefit.
The number of studies investigating the effectiveness of spinal manipulation on babies under two years of age was even smaller.
There was one high-quality study and two small, poor quality studies. These did not show an appreciable benefit of spinal manipulation on colic, otitis media with effusion (known as glue ear) or twisted neck in babies.
Is spinal manipulation on babies safe?
In terms of safety, most studies in the review found serious complications were extremely rare. The review noted one baby or child dying (a report from Germany in 2001 after spinal manipulation by a physiotherapist). The most common complications were mild in nature such as increased crying and soreness.
However, because studies were very small, they cannot tell us anything about the safety of spinal manipulation in a reliable way. Studies that are designed to properly investigate if a treatment is safe typically include thousands of patients. And these studies have not yet been done.
Why do people see chiropractors?
Safer Care Victoria also conducted surveys with more than 20,000 people living in Australia who had taken their children under 12 years old to a chiropractor in the past ten years.
Nearly three-quarters said that was for treatment of a child aged two years or younger.
Nearly all people surveyed reported a positive experience when they took their child to a chiropractor and reported that their child’s condition improved with chiropractic care. Only a small number of people (0.3%) reported a negative experience, and this was mostly related to cost of treatment, lack of improvement in their child’s condition, excessive use of x-rays, and perceived pressure to avoid medications.
Many of the respondents had also consulted their GP or maternity/child health nurse.
What now for spinal manipulation in children?
At the request of state and federal ministers, the Chiropractic Board of Australia confirmed that spinal manipulation on babies under two years old will continue to be banned until it discusses the issue further with health ministers.
Many chiropractors believe this is unfair, especially considering the strong consumer support for chiropractic care outlined in the Safer Care Victoria report, and the rarity of serious reported harms in children.
Others believe that in the absence of evidence of benefit and uncertainty around whether spinal manipulation is safe in children and babies, the precautionary principle should apply and children and babies should not receive spinal manipulation.
Ultimately, high quality research is urgently needed to better understand whether spinal manipulation is beneficial for the range of conditions chiropractors provide it for, and whether the benefit outweighs the extremely small chance of a serious complication.
This will help parents make an informed choice about health care for their child.
Matt Fernandez, Senior lecturer and researcher in chiropractic, CQUniversity Australia; Giovanni E. Ferreira, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Institute of Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney, and Joshua Zadro, NHMRC Emerging Leader Research Fellow, Sydney Musculoskeletal Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Stress-Proof Brain – by Dr. Melanie Greenberg
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of the book is as stated in the subtitle: using mindfulness and neuroplasticity to manage our stress response.
As such, it’s divided into three parts:
- Understanding your stress (and different types of stressors)
- Calming your amygdalae (thus, dealing with your stress response while the stressor is stressing you)
- Moving forward with your prefrontal cortex (and thus, gradually improving automatic stress responses over time, as we learn new, better responses to do automatically)
The content ranges from the neurophysiological to “therapist’s couch” stuff; Dr. Greenberg having her PhD in psychology has prepared her to write both of those different-but-touching fields with equal competence. In-line citations are given throughout, for those who want to look up studies.
The style is direct and informative, with little to no attention given to making it an entertaining read. As a result, it’s information dense (which is good), and/but not necessarily a “couldn’t put it down” page-turner.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your ability to deal with stress, this book is as good as any.
Click here to check out The Stress-Proof Brain, and stress-proof yours!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance Is Useful!
At 10almonds we talk a lot about the importance of regular moderate exercise (e.g. walking, gardening, housework, etc), and with good reason: getting in those minutes (at least 150 minutes per week, so, a little over 20 minutes per day, or 25 minutes per day with one day off) is the exericise most consistently linked to better general health outcomes and reduced mortality risk.
We also often come back to mobility, because at the end of the day, being able to reach for something from a kitchen cabinet without doing oneself an injury is generally more important in life than being able to leg-press a car.
Today though, we’re going to talk about resistance training.
What is resistance training?
It can be weight-lifting, or it can be bodyweight exercises. In those cases, what you’re resisting is gravity. It can also be exercises with resistance bands or machines. In all cases, it’s about building and/or maintaining strength.
Why does it matter?
Let’s say you’re not an athlete, soldier, or laborer, and the heaviest thing you have to pick up is a bag of groceries. Strength still matters, for two main reasons:
- Muscle strength correlates to bone strength. You can’t build (or maintain) strong muscles on weak bones, so if you take care of your muscles, then your body will keep your bones strong too.
- That’s assuming you have a good diet as well—but today’s not about that. If you’d like to know more about eating for bone health though, do check out this previous article about that!
- Muscle strength correlates to balance and stability. You can’t keep yourself from falling over if you are physically frail.
Both of those things matter, because falls and fractures often have terrible health outcomes (e.g., slower recovery and more complications) the older we get. So, we want to:
- Ideally, not fall in the first place
- If we do fall, have robust bones
See also: Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health
How much should we do?
Let’s go to the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research on this one:
❝There is strong evidence to support the benefits of resistance exercise for countering many age-related processes of sarcopenia, muscle weakness, mobility loss, chronic disease, disability, and even premature mortality.
In addition, this Position Statement provides specific evidence-based practice recommendations to aid in the implementation of resistance exercise programs for healthy older adults and those with special considerations.
While there are instances where low-intensity, low-volume programs are appropriate (i.e., beginning programs for individuals with frailty or CVDs), the greatest benefits are possible with progression to moderate to higher intensity programs.❞
~ Fragala et al
Read the statement in full:
There’s a lot of science there and it’s well worth reading if you have the time. It’s particularly good at delineating how much is not enough vs how much is too much, and the extent to which we should (or shouldn’t) train to exhaustion.
If you don’t fancy that, though, and/or just want to start with something accessible and work your way up, the below is a very good (and also evidence-based) start-up plan:
Healthline’s Exercise Plan For Seniors—For Strength, Balance, & Flexibility
(it has a weekly planner, step-by-step guides to the exercises, and very clear illustrative animations of each)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Muscle strength correlates to bone strength. You can’t build (or maintain) strong muscles on weak bones, so if you take care of your muscles, then your body will keep your bones strong too.
-
Future-Proof Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Kimberly Wilson. She’s a psychologist, not a doctor, and/but her speciality is neurophysiology and brain health.
Here’s what she wants us to know…
Avoid this very common killer
As you’re probably aware, the #1 killer in the US is heart disease, followed by COVID, which effectively pushed everything down a place. Thereafter, we see cancer, followed by accidental injuries, stroke, and dementia (including Alzheimer’s).
Over in the UK, where Wilson is from, dementia (including Alzheimer’s disease) is the #1 killer, followed by heart disease and then respiratory diseases (including COVID), and then stroke, then cancer.
As ever, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain, so many of the same interventions will help avoid both. With regard to some of the other differences in order, the reasons are mostly due to differences in the two countries’ healthcare systems and firearms laws.
It’s worth noting, though, that the leading cause of death in young people (aged 15–19) is suicide in the UK; in the US it’s nominally accidental injuries first (e.g. accidental shootings) with intentional suicide in the second spot.
In other words… Young or old, mental health is a serious health category that kills literally the most people in the UK, and also makes the top spots in the US.
Avoid the early killer
Given the demographics of most of our readership, chances are you’ve already lived past your teens and twenties. That’s not to say that suicide is no longer a risk, though, and it’s also worth noting that while mental health issues are invisible, they’re still physical illnesses (the brain is also an organ, after all!), so this isn’t something where you can simply “decide not to” and that’s you set, safe for life. So, please do continue to take good care in that regard.
We wrote about this previously, here:
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
Avoid the later killer
Wilson talks about how a recent survey found that…
- while nearly half of adults say dementia is the disease they fear most,
- only a third of those thought you could do anything to avoid it, and
- just 1% could name the 7 known risk factors.
Quick test: can you name the 7 known risk factors?
Please take a moment to actually try (this kind of mental stimulation is good in any case), and count them out on your fingers (or write them down), and then…
When you’re ready: click here to see the answer!
How many did you get? If you got them all, well done. If not, then well, now you know, so that’s good.
So, with those 7 things in mind, the first obvious advice is to take care of those things.
Taking an evidence-based medicine approach, Wilson recommends some specific interventions that will each improve one or more of those things, directly or indirectly:
Eating right
Wilson is a big fan of “nutritional psychiatry” and feeding one’s brain properly. We wrote about this, here:
The 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry
As well as agreeing with the obvious “eat plenty of fiber, different-colored plants, and plenty of greens and beans”, Wilson specifically also champions getting enough of vitamins B9, B12, and D, as well as getting a healthy dose of omega-3 fatty acids.
She also recommends intermittent fasting, if that’s a reasonable option for you—but advocates for not worrying about it, if it’s not easy for you. For example, if you are diabetic, or have (or have a history with) some kind of eating disorder(s), then it’s probably not usefully practicable. But for most people, it can reduce systemic inflammation, which means also reducing neuroinflammation.
Managing stress right
Here she advocates for three main things:
- Mindful meditation (see: Evidence-Based, No-Frills Mindfulness)
- Psychological resilience (see: Building Psychological Resilience)
- Mindful social media use (see: Making Social Media Work For Your Mental Health)
Managing money right
Not often we talk about this in a health science publication as opposed to a financial planning publication, but the fact is that a lot of mental distress, which goes on to have a huge impact on the brain, is rooted in financial stresses.
And, of course, it’s good to be able to draw on financial resources to directly fund one’s good health, but that is the secondary consideration here—the financial stress is the biggest issue, and you can’t CBT your way out of debt, for example.
Therapists often face this, and what has been referred to informally by professionals in the field as “Shit Life Syndrome”—and there’s only so much that therapy can do about that.
We’re not a financial publication, but one recommendation we’ll drop is that if you don’t currently have budgeting software that you use, this writer personally uses and swears by YNAB (You Need A Budget), so maybe check that out if you don’t already have everything covered in that regard. It’s not free, but there is a 34-day free trial.
Therapy can be very worthwhile nonetheless
Wilson notes that therapy is like non-invasive brain surgery (because of neuroplasticity, it’s literally changing physical things in your brain).
It’s not a magic bullet and it’s not the right choice for everyone, but it’s worth considering, and even self-therapy can yield benefits for many:
The Gym For Your Mental Health: Getting The Most Out Of Therapy
Sleeping right
Sleep is not only critical for health in general and brain health in particular, it’s also most of when our glymphatic system does clean-up in the brain (essential for avoiding Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s, amongst other diseases):
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
Want to know more from Kimberley Wilson?
We reviewed a book of hers recently, here:
Unprocessed: What your Diet Is Doing To Your Brain – by Kimberley Wilson
However, much of what we shared today was sourced from another book of hers that we haven’t reviewed yet but probably will do one of these days:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Half of Australians in aged care have depression. Psychological therapy could help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While many people maintain positive emotional wellbeing as they age, around half of older Australians living in residential aged care have significant levels of depression. Symptoms such as low mood, lack of interest or pleasure in life and difficulty sleeping are common.
Rates of depression in aged care appear to be increasing, and without adequate treatment, symptoms can be enduring and significantly impair older adults’ quality of life.
But only a minority of aged care residents with depression receive services specific to the condition. Less than 3% of Australian aged care residents access Medicare-subsidised mental health services, such as consultations with a psychologist or psychiatrist, each year.
Cochrane AustraliaInstead, residents are typically prescribed a medication by their GP to manage their mental health, which they often take for several months or years. A recent study found six in ten Australian aged care residents take antidepressants.
While antidepressant medications may help many people, we lack robust evidence on whether they work for aged care residents with depression. Researchers have described “serious limitations of the current standard of care” in reference to the widespread use of antidepressants to treat frail older people with depression.
Given this, we wanted to find out whether psychological therapies can help manage depression in this group. These treatments address factors contributing to people’s distress and provide them with skills to manage their symptoms and improve their day-to-day lives. But to date researchers, care providers and policy makers haven’t had clear information about their effectiveness for treating depression among older people in residential aged care.
The good news is the evidence we published today suggests psychological therapies may be an effective approach for people living in aged care.
We reviewed the evidence
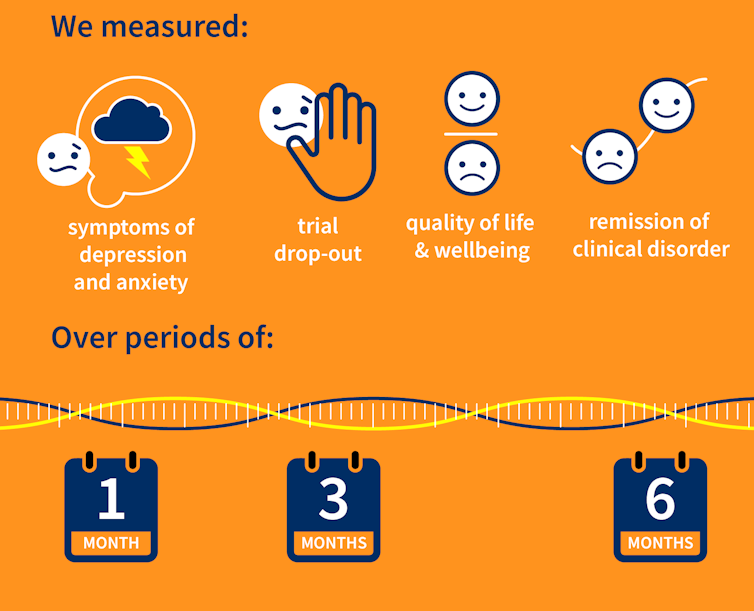
Our research team searched for randomised controlled trials published over the past 40 years that were designed to test the effectiveness of psychological therapies for depression among aged care residents 65 and over. We identified 19 trials from seven countries, including Australia, involving a total of 873 aged care residents with significant symptoms of depression.
The studies tested several different kinds of psychological therapies, which we classified as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), behaviour therapy or reminiscence therapy.
CBT involves teaching practical skills to help people re-frame negative thoughts and beliefs, while behaviour therapy aims to modify behaviour patterns by encouraging people with depression to engage in pleasurable and rewarding activities. Reminiscence therapy supports older people to reflect on positive or shared memories, and helps them find meaning in their life history.
The therapies were delivered by a range of professionals, including psychologists, social workers, occupational therapists and trainee therapists.
Cochrane AustraliaIn these studies, psychological therapies were compared to a control group where the older people did not receive psychological therapy. In most studies, this was “usual care” – the care typically provided to aged care residents, which may include access to antidepressants, scheduled activities and help with day-to-day tasks.
In some studies psychological therapy was compared to a situation where the older people received extra social contact, such as visits from a volunteer or joining in a discussion group.
What we found
Our results showed psychological therapies may be effective in reducing symptoms of depression for older people in residential aged care, compared with usual care, with effects lasting up to six months. While we didn’t see the same effect beyond six months, only two of the studies in our review followed people for this length of time, so the data was limited.
Our findings suggest these therapies may also improve quality of life and psychological wellbeing.
Psychological therapies mostly included between two and ten sessions, so the interventions were relatively brief. This is positive in terms of the potential feasibility of delivering psychological therapies at scale. The three different therapy types all appeared to be effective, compared to usual care.
However, we found psychological therapy may not be more effective than extra social contact in reducing symptoms of depression. Older people commonly feel bored, lonely and socially isolated in aged care. The activities on offer are often inadequate to meet their needs for stimulation and interest. So identifying ways to increase meaningful engagement day-to-day could improve the mental health and wellbeing of older people in aged care.
Some limitations
Many of the studies we found were of relatively poor quality, because of small sample sizes and potential risk of bias, for example. So we need more high-quality research to increase our confidence in the findings.
Many of the studies we reviewed were also old, and important gaps remain. For example, we are yet to understand the effectiveness of psychological therapies for people from diverse cultural or linguistic backgrounds.
Separately, we need better research to evaluate the effectiveness of antidepressants among aged care residents.
What needs to happen now?
Depression should not be considered a “normal” experience at this (or any other) stage of life, and those experiencing symptoms should have equal access to a range of effective treatments. The royal commission into aged care highlighted that Australians living in aged care don’t receive enough mental health support and called for this issue to be addressed.
While there have been some efforts to provide psychological services in residential aged care, the unmet need remains very high, and much more must be done.
The focus now needs to shift to how to implement psychological therapies in aged care, by increasing the competencies of the aged care workforce, training the next generation of psychologists to work in this setting, and funding these programs in a cost-effective way.
Tanya Davison, Adjunct professor, Health & Ageing Research Group, Swinburne University of Technology and Sunil Bhar, Professor of Clinical Psychology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: