You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This time of year, most fridges are stocked up with food and drinks to share with family and friends. Let’s not make ourselves and our guests sick by getting things wrong when preparing and serving food.
As the weather warms up, so does the environment for micro-organisms in foods, potentially allowing them to multiply faster to hazardous levels. So put the drinks on ice and keep the fridge for the food.
But what are some of those food safety myths we’ve long come to believe that aren’t actually true?
Myth 1: if you’ve defrosted frozen meat or chicken you can’t refreeze it
From a safety point of view, it is fine to refreeze defrosted meat or chicken or any frozen food as long as it was defrosted in a fridge running at 5°C or below. Some quality may be lost by defrosting then refreezing foods as the cells break down a little and the food can become slightly watery.
Another option is to cook the defrosted food and then divide into small portions and refreeze once it has stopped steaming. Steam in a closed container leads to condensation, which can result in pools of water forming. This, combined with the nutrients in the food, creates the perfect environment for microbial growth. So it’s always best to wait about 30 minutes before refrigerating or freezing hot food.
Plan ahead so food can be defrosted in the fridge, especially with large items such as a frozen turkey or roll of meat. If left on the bench, the external surface could be at room temperature and micro-organisms could be growing rapidly while the centre of the piece is still frozen!
Myth 2: Wash meat before you prepare and/or cook it
It is not a good idea to wash meats and poultry when preparing for cooking. Splashing water that might contain potentially hazardous bacteria around the kitchen can create more of a hazard if those bacteria are splashed onto ready-to-eat foods or food preparation surfaces.
It is, however, a good idea to wash fruits and vegetables before preparing and serving, especially if they’re grown near or in the ground as they may carry some dirt and therefore micro-organisms.
This applies particularly to foods that will be prepared and eaten without further cooking. Consuming foods raw that traditionally have been eaten cooked or otherwise processed to kill pathogenic micro-organisms (potentially deadly to humans) might increase the risk of food poisoning.
Fruit, salad, vegetables and other ready-to-eat foods should be prepared separately, away from raw meat, chicken, seafood and other foods that need cooking.
Myth 3: Hot food should be left out to cool completely before putting it in the fridge
It’s not OK to leave perishable food out for an extended time or overnight before putting it in the fridge.
Micro-organisms can grow rapidly in food at temperatures between 5° and 60°C. Temperature control is the simplest and most effective way of controlling the growth of bacteria. Perishable food should spend as little time as possible in the 5-60°C danger zone. If food is left in the danger zone, be aware it is potentially unsafe to eat.
Hot leftovers, and any other leftovers for that matter, should go into the fridge once they have stopped steaming to reduce condensation, within about 30 minutes.
Large portions of hot food will cool faster if broken down into smaller amounts in shallow containers. It is possible that hot food such as stews or soup left in a bulky container, say a two-litre mixing bowl (versus a shallow tray), in the fridge can take nearly 24 hours to cool to the safe zone of less than 5°C.
Myth 4: If it smells OK, then it’s OK to eat
This is definitely not always true. Spoilage bacteria, yeasts and moulds are the usual culprits for making food smell off or go slimy and these may not make you sick, although it is always advisable not to consume spoiled food.
Pathogenic bacteria can grow in food and not cause any obvious changes to the food, so the best option is to inhibit pathogen growth by refrigerating foods.
Myth 5: Oil preserves food so it can be left at room temperature
Adding oil to foods will not necessarily kill bugs lurking in your food. The opposite is true for many products in oil if anaerobic micro-organisms, such as Clostridium botulinum (botulism), are present in the food. A lack of oxygen provides perfect conditions for their growth.
Outbreaks of botulism arising from consumption of vegetables in oil – including garlic, olives, mushrooms, beans and hot peppers – have mostly been attributed to the products not being properly prepared.
Vegetables in oil can be made safely. In 1991, Australian regulations stipulated that this class of product (vegetables in oil) can be safely made if the pH (a measure of acid) is less than 4.6. Foods with a pH below 4.6 do not in general support the growth of food-poisoning bacteria including botulism.
So keep food out of the danger zone to reduce your guests’ risk of getting food poisoning this summer. Check out other food safety tips and resources from CSIRO and the Food Safety Information Council, including testing your food safety knowledge.
Cathy Moir, Team leader, Microbial and chemical sciences, Food microbiologist and food safety specialist, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.

Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No-Exercise Exercise!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you love to go to the gym?
If so, today’s article might not be for you so much. Or maybe it will, because let’s face it, exercise is fun!
At least… It can be, and should be 😎
So without further ado, here’s a slew of no-exercise exercise ideas; we’re willing to bet that somewhere in the list there’s at least some you haven’t tried before, and probably some you haven’t done in a while but might enjoy making a reprise!
Walking
No surprises here: walking is great. Hopefully you have some green spaces near you, but if you don’t, [almost] any walking is better than no walking. So unless there’s some sort of environmental disaster going on outside, lace up and get stepping.
If you struggle to “walk for walking’s sake” give yourself a little mission. Walk to the shop to buy one item. Walk to the park and find a flower to photograph. Walk to the library and take out a book. Whatever works for you!
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Take the stairs
This one doesn’t need many words, just: make it a habit.
Treat the elevators as though they aren’t there!
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Dance
Dance is amazing! Any kind of dance, whatever suits your tastes. This writer loves salsa and tango, but no matter whether for you it’s zouk or zumba, breakdancing or line dancing, whatever gets you moving is going to be great for you.
If you don’t know how, online tutorials abound, and best of all is to attend local classes if you can, because they’re always a fun social experience too.
Make music
Not something often thought of as an exercise, but it is! Most instruments require that we be standing or siting with good posture, focusing intently on our movements, and often as not, breathing very mindfully too. And yes, it’s great for the brain as well!
Check out: This Is Your Brain on Music: The Science of a Human Obsession – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Take a stand
If you spend a lot of time at a desk, please consider investing in a standing desk; they can be truly life-changing. Not only is it so much better for your back, hips, neck, and internal organs, but also it burns hundreds more calories than sitting, due to the no-exercise exercise that is keeping your body constantly stabilized while on your feet.
(or, if you’re like this writer: on your foot. I do have two feet, I just spend an inordinate amount of time at my desk standing on one leg at a time; I’m a bit of a flamingo like that)
See also: Deskbound: Standing Up to a Sitting World – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
Sit, but…
Sit in a sitting squat! Sometimes called a Slav squat, or an Asian squat, or a resting squat, or various other names:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Alternatively, sitting in seiza (the traditional Japanese sitting position) is also excellent, but watch out! While it’s great once your body is accustomed to it, if you haven’t previously sat this way much, you may cut off your own circulation, hurt your knees, and (temporarily) lose feeling in your feet. So if you don’t already sit in seiza often, gradually work up the time period you spend sitting in seiza, so that your vasculature can adapt and improve, which honestly, is a very good thing for your legs and feet to have.
Breathe
Perhaps the absolute most “no-exercise exercise” there is. And yes, of course you are (hopefully) breathing all the time, but how you are breathing matters a lot:
The Inside Job Of Fixing Our Breathing: Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
Clean
This doesn’t have to mean scrubbing floors like a sailor—even merely giving your house the Marie Kondo treatment counts, because while you’re distracted with all the objects, you’re going to be going back and forth, getting up and down, etc, clocking up lots of exercise that you barely even notice!
PS, check out: The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
Garden
As with the above, it’s lots of activity that doesn’t necessarily feel like it (assuming you’re doing more pruning and weeding etc, and less digging ditches etc), and as a bonus, there are a stack of mental health benefits to being in a green natural environment and interacting with soil:
Read more: The Antidepressant In Your Garden
Climb
Depending on where you live, this might mean an indoor climbing wall, but give it a go! They have color-coded climbs from beginner to advanced, so don’t worry about being out of your depth.
And the best thing is, the beginner climbs will be as much a workout to a beginner as the advanced climbs will be to an advanced climber, because at the end of the day, you’re still clinging on for dear life, no matter whether it’s a sizeable handhold not far from the ground, or the impression of a fingernail crack in an overhang 100ft in the air.
Video games (but…)
Less in the category of Stardew Valley, and more in the category of Wii Fit.
So, dust off that old controller (or treat yourself to one if you didn’t have one already), and get doing a hundred sports and other physical activities in the comfort of your living room, with a surprisingly addictive gaming system!
Sex!
You probably don’t need instructions here, and if you do, well honestly, we’re running out of space today. But the answer to “does xyz count?” is “did it get your heart racing?” because if so, it counts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Antibiotics? Think Thrice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Antibiotics: Useful Even Less Often Than Previously Believed (And Still Just As Dangerous)
You probably already know that antibiotics shouldn’t be taken unless absolutely necessary. Not only does taking antibiotics frivolously increase antibiotic resistance (which is bad, and kills people), but also…
It’s entirely possible for the antibiotics to not only not help, but instead wipe out your gut’s “good bacteria” that were keeping other things in check.
Those “other things” can include fungi like Candida albicans.
Candida, which we all have in us to some degree, feeds on sugar (including the sugar formed from breaking down alcohol, by the way) and refined carbs. Then it grows, and puts its roots through your intestinal walls, linking with your neural system. Then it makes you crave the very things that will feed it and allow it to put bigger holes in your intestinal walls.
Don’t believe us? Read: Candida albicans-Induced Epithelial Damage Mediates Translocation through Intestinal Barriers
(That’s scientist-speak for “Candida puts holes in your intestines, and stuff can then go through those holes”)
And as for how that comes about, it’s like we said:
See also: Candida albicans as a commensal and opportunistic pathogen in the intestine
That’s not all…
And that’s just C. albicans, never mind things like C. diff. that can just outright kill you easily.
We don’t have room to go into everything here, but you might like to check out:
Four Ways Antibiotics Can Kill You
It gets worse (now comes the new news)
So, what are antibiotics good for? Surely, for clearing up chesty coughs, lower respiratory tract infections, right? It’s certainly one of the two things that antibiotics are most well-known for being good at and often necessary for (the other being preventing/treating sepsis, for example in serious and messy wounds).
But wait…
A large, nationwide (US) observational study of people who sought treatment in primary or urgent care settings for lower respiratory tract infections found…
(drumroll please)
…the use of antibiotics provided no measurable impact on the severity or duration of coughs even if a bacterial infection was present.
Read for yourself:
And in the words of the lead author of that study,
❝Lower respiratory tract infections tend to have the potential to be more dangerous, since about 3% to 5% of these patients have pneumonia. But not everyone has easy access at an initial visit to an X-ray, which may be the reason clinicians still give antibiotics without any other evidence of a bacterial infection.❞
So, what’s to be done about this? On a large scale, Dr. Merenstein recommends:
❝Serious cough symptoms and how to treat them properly needs to be studied more, perhaps in a randomized clinical trial as this study was observational and there haven’t been any randomized trials looking at this issue since about 2012.❞
This does remind us that, while not a RCT, there is a good ongoing observational study that everyone with a smartphone can participate in:
Dr. Peter Small’s medical AI: “The Cough Doctor”
In the meantime, he advises that when COVID and SARS have been ruled out, then “basic symptom-relieving medications plus time brings a resolution to most people’s infections”.
You can read a lot more detail here:
Antibiotics aren’t effective for most lower tract respiratory infections
In summary…
Sometimes, antibiotics really are a necessary and life-saving medication. But most of the time they’re not, and given their great potential for harm, they may be best simultaneously viewed as the very dangerous threat they also are, and used only when those “heavy guns” are truly what’s required.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Tomatoes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tomatoes to carrots, we picked the carrots.
Why?
Both known for being vitamin-A heavyweights, there is nevertheless a clear winner:
In terms of macros, carrots have a little over 2x the carbs, and/but also a little over 2x the fiber, so we consider category this a win for carrots.
In the category of vitamins, tomatoes have more vitamin C, while carrots have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, E, K, and choline. And about that vitamin A specifically: carrots have over 20x the vitamin A of tomatoes. An easy win for carrots here!
When it comes to minerals, tomatoes have a little more copper, while carrots have more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Another clear win for carrots.
Looking at polyphenols, carrots are good but tomatoes have more, including a good healthy dose of quercetin; they also have more lycopene, not technically a polyphenol by virtue of its chemical structure (it’s a carotenoid), but a powerful phytochemical nonetheless (and much more prevalent in sun-dried tomatoes, in any case, which is not what we were looking at today—perhaps another day we’ll do sun-dried tomatoes and carrots head-to-head!).
Still, a) carrots are not short of carotenoids either (including lycopene), and b) we don’t think the moderate win on polyphenols is enough to outdo carrots having won all the other categories.
All in all, carrots win the day, but of course, do enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Garlic vs Ginger – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing garlic to ginger, we picked the ginger.
Why?
Both are great, and it is close!
Notwithstanding that (almost?) nobody eats garlic or ginger for the macros, let’s do a moment’s due diligence on that first: garlic has more than 3x the protein and about 2x the fiber (and slightly higher carbs). But, given the small quantities in which people usually consume these foods, these numbers aren’t too meaningful.
In the category of micronutrients, garlic has a lot more vitamins and minerals. We’ll not do a full breakdown for this though, because again, unless you’re eating it by the cupful, this won’t make a huge difference.
Which means that so far, we have two nominal wins for garlic.
Both plants have many medicinal properties. They are both cardioprotective and anticancer, and both full of antioxidants. The benefits of both are comparable in these regards.
Both have antidiabetic action also, but ginger’s effects are stronger when compared head-to head.
So that’s an actual practical win for ginger.
Each plant’s respective effects on the gastrointestinal tract sets them further apart—ginger has antiemetic effects and can be used for treating nausea and vomiting from a variety of causes. Garlic, meanwhile, can cause adverse gastrointestinal effects in some people—but it’s usually neutral for most people in this regard.
Another win for ginger in practical terms.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 things you can do if you think you sweat too much
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sweating is our body’s way of cooling down, a bit like an internal air conditioner.
When our core temperature rises (because it’s hot outside, or you’re exercising), sweat glands all over our skin release a watery fluid. As that fluid evaporates, it takes heat with it, keeping us from overheating.
But sweating can vary from person to person. Some people might just get a little dewy under the arms, others feel like they could fill a swimming pool (maybe not that dramatic, but you get the idea).
So what’s a normal amount of sweat? And what’s too much?
ERIK Miheyeu/Shutterstock Why do some people sweat more than others?
How much you sweat depends on a number of factors including:
- your age (young kids generally sweat less than adults)
- your sex (men tend to sweat more than women)
- how active you are.
The average person sweats at the rate of 300 millilitres per hour (at 30°C and about 40% humidity). But as you can’t go around measuring the volume of your own sweat (or weighing it), doctors use another measure to gauge the impact of sweating.
They ask whether sweating interferes with your daily life. Maybe you stop wearing certain clothes because of the sweat stains, or feel embarrassed so don’t go to social events or work.
If so, this is a medical condition called hyperhidrosis, which affects millions of people worldwide.
People with this condition most commonly report problematic armpit sweating, as you’d expect. But sweaty hands, feet, scalp and groin can also be an issue.
Hyperhidrosis can be a symptom of another medical condition, such as an overactive thyroid, fever or menopause.
But hyperhidrosis can have no obvious cause, and the reasons behind this so-called primary hyperhidrosis are a bit of a mystery. People have normal numbers of sweat glands but researchers think they simply over-produce sweat after triggers such as stress, heat, exercise, tobacco, alcohol and hot spices. There may also be a genetic link.
OK, I sweat a lot. What can I do?
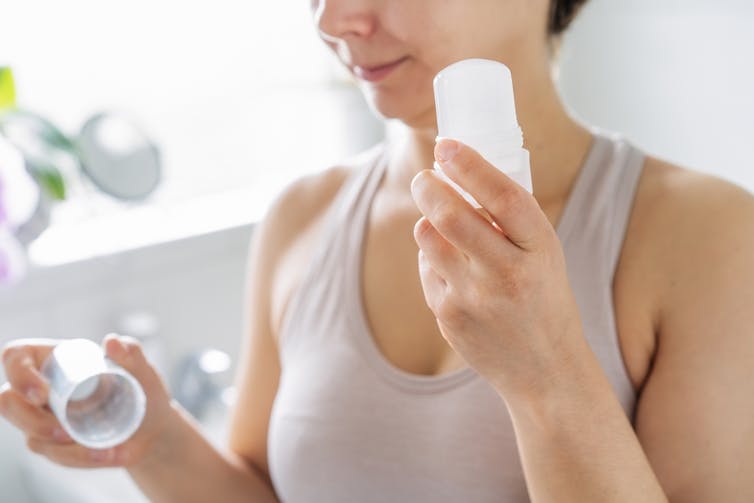
1. Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants, particularly ones with aluminium, are your first line of defence and are formulated to reduce sweating. Deodorants only stop body odour.
Aluminum chloride hexahydrate, aluminium chloride or the weaker aluminum zirconium tetrachlorohydrex glycinate react with proteins in the sweat glands, forming a plug. This plug temporarily blocks the sweat ducts, reducing the amount of sweat reaching the skin’s surface.
These products can contain up to 25% aluminium. The higher the percentage the better these products work, but the more they irritate the skin.
Make sure you’re buying antiperspirant and not deodorant. Okrasiuk/Shutterstock 2. Beat the heat
This might seem obvious, but staying cool can make a big difference. That’s because you have less heat to lose, so the body makes less sweat.
Avoid super-hot, long showers (you will have more heat to loose), wear loose-fitting clothes made from breathable fabrics such as cotton (this allows any sweat you do produce to evaporate more readily), and carry a little hand fan to help your sweat evaporate.
When exercising try ice bandanas (ice wrapped in a scarf or cloth, then applied to the body) or wet towels. You can wear these around the neck, head, or wrists to reduce your body temperature.
Try also to modify the time or place you exercise; try to find cool shade or air-conditioned areas when possible.
If you have tried these first two steps and your sweating is still affecting your life, talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out the best way to manage it.
3. Medication
Some medications can help regulate your sweating. Unfortunately some can also give you side effects such as a dry mouth, blurred vision, stomach pain or constipation. So talk to your doctor about what’s best for you.
Your GP may also refer you to a dermatologist – a doctor like myself who specialises in skin conditions – who might recommend different treatments, including some of the following.
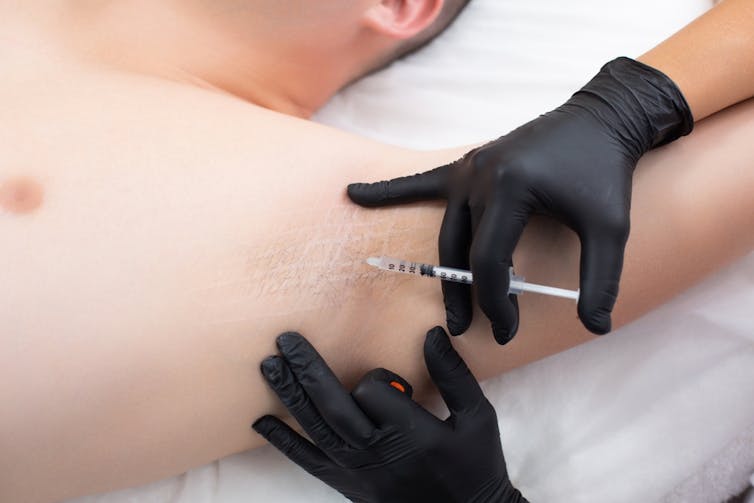
4. Botulinum toxin injections
Botulinum toxin injections are not just used for cosmetic reasons. They have many applications in medicine, including blocking the nerves that control the sweat glands. They do this for many months.
A dermatologist usually gives the injections. But they’re only subsidised by Medicare in Australia for the armpits and if you have primary hyperhidrosis that hasn’t been controlled by the strongest antiperspirants. These injections are given up to three times a year. It is not subsidised for other conditions, such as an overactive thyroid or for other areas such as the face or hands.
If you don’t qualify, you can have these injections privately, but it will cost you hundreds of dollars per treatment, which can last up to six months.
Injections are available on Medicare in some cases. Satyrenko/Shutterstock 5. Iontophoresis
This involves using a device that passes a weak electrical current through water to the skin to reducing sweating in the hands, feet or armpits. Scientists aren’t sure exactly how it works.
But this is the only way to control sweating of the hands and feet that does not require drugs, surgery or botulinum toxin injections.
This treatment is not subsidised by Medicare and not all dermatologists provide it. However, you can buy and use your own device, which tends to be cheaper than accessing it privately. You can ask your dermatologist if this is the right option for you.
6. Surgery
There is a procedure to cut certain nerves to the hands that stop them sweating. This is highly effective but can cause sweating to occur elsewhere.
There are also other surgical options, which you can discuss with your doctor.
7. Microwave therapy
This is a newer treatment that zaps your sweat glands to destroy them so they can’t work any more. It’s not super common yet, and it is quite painful. It’s available privately in a few centres.
Michael Freeman, Associate Professor of Dermatology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Artichoke vs Heart of Palm– Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to heart of palm, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
If you were thinking “isn’t heart of palm full of saturated fat?” then no… Palm oil is, but heart of palm itself has 0.62g/100g fat, of which, 0.13g saturated fat. So, negligible.
As for the rest of the macros, artichoke has more protein, carbs, and fiber, thus being the “more food per food” option. Technically heart of palm has the lower glycemic index, but they are both low-GI foods, so it’s really not a factor here.
Vitamins are where artichoke shines; artichoke has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while heart of palm is not higher in any vitamins.
The minerals situation is more balanced: artichoke has more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium, while heart of palm has more iron, manganese, selenium, and zinc.
Adding up the categories, the winner of this “vegetables with a heart” face-off is clearly artichoke.
Fun fact: in French, “to have the heart of an artichoke” (avoir le coeur d’un artichaut) means to fall in love easily. Perfect vegetable for a romantic dinner, perhaps (especially with all those generous portions of B-vitamins)!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Artichoke vs Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: