Why We Remember – by Dr. Charan Ranganath
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, forgetfulness can become more of a spectre; the threat that one day it could be less “where did I put my sunglasses?” and more “who is this person claiming to be my spouse?”.
Dr. Ranganath explores in this work the science of memory, from a position of neurobiology, but also in application. How and why we remember, and how and why we forget, and how and why both are important.
There is a practical element to the book too; we read about things that increase our tendency to remember (and things that increase our tendency to forget), and how we can leverage that information to curate our memory in an active, ongoing basis.
The style of the book is quite casual in tone for such a serious topic, but there’s plenty of hard science too; indeed there are 74 pages of bibliography cited.
Bottom line: while filled with a lot of science, this is also a very human book, and a helpful guide to building and preserving our memory.
Click here to check out “Why We Remember”, and learn how to hold on to what matters the most!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Captivate – by Vanessa van Edwards
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book isn’t just for one area of human interactions. It covers everything from the boardroom to the bedroom (not necessarily a progression with the same person!), business associates, friends, partners, kids, and more.
She presents information in a layered manner, covering for example, chapter-by-chapter:
- the first five minutes
- the first five hours
- the first five days
She also covers such things as:
- starting conversations in a way that makes you memorable (without making it weird!)
- the importance of really listening (and how to do that)
- collecting like-minded people appropriately
- introducing other people! Because a) it’s not all about you, but also b) you’re the person who knows everybody now
- where to stand at parties / networking events!
- dating and early-days dating messages
- reading the room, reading the people
All in all, a great resource for anyone who wants to make (and maintain!) meaningful relationships with those around you.
Share This Post
-
Broad Beans vs Green Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broad beans to green beans, we picked the broad.
Why?
It’s quite a straightforward one today:
In terms of macros, broad beans have 2.5x the protein, and slightly more fiber and carbs, so we pick the broad beans as the more nutrient-dense option here.
In the category of vitamins, broad beans have more of vitamins B1, B3, B9, and C, while green beans have more of vitamins A and B6 (with comparable margins of difference for both beans’ winning vitamins), so another win for broad beans, based on the 4:2 numerical advantage.
When it comes to minerals, broad beans have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while green beans have more calcium and manganese. Again, comparable mostly margins of difference (except for broad beans bing 5x richer in selenium, which is a bit of an outlier, but it’s not because broad beans are an amazing source of selenium, but rather, that green beans have only a tiny amount), so it’s a clear 7:2 win for broad beans.
Adding up the three wins for broad beans makes an overall win for them, but by all means, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Podiatrists Debunk 11 Feet Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Podiatrists Dr. Sarah Haller and Dr. Brad Schaeffer put us on a better path:
Don’t get wrong-footed
We’ll not keep the 11 myths a mystery; they are…
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
False! Warts are caused by a virus, not dirt. Viruses can be picked up from surfaces like yoga mats, pools, gyms, and showers. - “Bunions are caused by wearing heels.”
False! Bunions are genetic deformities where the bone behind the big toe shifts. Heels might worsen them but don’t cause them. - “Cutting the sides of my toenail will prevent an ingrown toenail.”
False! Toenails should be cut straight across. Cutting the sides can make ingrown toenails worse. - “Pedicures gave me toenail fungus.”
Partially true! You can get fungus from many places, but safe, sterile pedicures are generally fine. - “Only athletes get athlete’s foot.”
False! Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection caused by warm, moist environments. Anyone can get it, not just athletes. - “My feet are fine because I trained them to walk in stilettos.”
False! You can get used to stilettos, but they aren’t healthy long-term. They shorten the Achilles tendon and put pressure on the foot. - “You can’t do anything for a broken toe.”
False! Broken toes can be treated and should be checked by a doctor. They may need to be set for proper healing. - “It’s normal for your feet to hurt from standing all day.”
False! Foot pain isn’t normal and can be prevented with proper footwear, support, and compression socks. - “All inserts are the same.”
False! Everyone’s feet are different. Some may benefit from over-the-counter insoles, but others need custom orthotics. - “Sprained ankles are no big deal.”
False! Sprains can damage ligaments and lead to instability or arthritis if untreated. Proper stabilization is essential. - “If I can walk after an injury, I don’t need to see a doctor.”
False! You can still have serious injuries like fractures even if you can walk. Always get checked after an injury.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
- “You have warts because your feet are dirty.”
Related Posts
-
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recent, large (n=72,269) 8-year prospective* observational study of adults aged 40-79 has found an association between irregular sleep and major cardiovascular events.
*this means they started the study at a given point, and measured what happened for the next eight years—as opposed to a retrospective study, which would look at what had happened during the previous 8 years.
As to what qualifies as major cardiovascular events, they counted:
- Heart attack
- Cardiac arrest
- Stroke
- Cardiovascular death (any)
Irregular sleep, meanwhile, was defined per a bell curve of participants. Based on a sleep regularity index (SRI) score, those with a score of 87 or more were on the “regular” side of the curve, and those with a score of 72 or lower were on the “irregular” side of the curve.
What they found is that irregular sleep is associated with major cardiovascular events, regardless of the actual amount of sleep that people got. So in other words, you could be sleeping 9 hours per day, but if it’s a different 9 hours each day, your cardiovascular risk will still be higher.
How much higher?
- For those in the middle of the curve (so, moderate irregularity), it was 8% higher than those on the “regular” side.
- For those on the “irregular” side of the curve, it was 26% higher than those on the “regular” side.
All of the above is after taking into account confounding variables such as age, physical activity levels, discretionary screen time, fruit, vegetable, and coffee intake, alcohol consumption, smoking, mental health issues, medication use, and shift work. Which is quite something, given that shift work is a very common reason for irregular sleep schedules in a lot of people.
Limitations
While, as noted above, they did their best to account for a lot of things, this was an observational study, not an interventional study or a randomized controlled trial, and as such, it cannot truly establish cause and effect.
For example, an observational study in the 90s found that the sport most strongly associated with longevity was polo. For any unfamiliar, it’s a game played on horseback with mallets and balls. Why was this game so much better than, say, swimming? And the answer is most likely that polo is played almost entirely by very rich people. It wasn’t the sport that enhanced longevity—it was the wealth.
So similarly here, it could be for example that people who are predisposed to heart conditions, are prone to having irregular schedules. We won’t know for sure until we have interventional studies (and we probably can’t get RCTs for this, for practical reasons).
Still, it seems likely that the association is indeed causal, in which case, having a regular sleep schedule if at all possible seems like a very good way to look after one’s health.
You can read more about the study here:
Irregular sleep may elevate risk of major cardiovascular events
Practical take-away
This study strongly suggests that sleep regularity is even more important than sleep duration.
This means that there is extra reason to not sleep in past one’s normal getting-up time, even if one had a less restful night.
That’s the end of sleep that’s the most important in practical terms, too, because we can control our getting-up time, whereas we can’t really control our going-to-sleep time, because it’s perfectly possible to just lie there awake.
So, controlling the getting-up time is really the key to the whole thing. See also:
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
And for scope, you might enjoy reading:
Morning Larks vs Night Owls: How Much Can We Control Our Sleep Schedule?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dealing With Back Acne
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Lately I’ve increasingly been getting zits on my back, I don’t think my shower habits have changed at all, is this just an age thing or is there something I can do about it?❞
Well, we cannot diagnose from afar, so definitely consider seeing a dermatologist if it persists and/or it’s more than a small nuisance to you, but…
Yes and no, with regard to age.
Rather, it’s not really about age, but (in most cases, anyway) hormonal fluctuations. That’s why teenagers often get it; it’s also why acne breakouts can occur during pregnancy, and it can happen again in perimenopause, menopause, or in the postmenopause climb-down, due to imbalanced hormones during the change, and while it’s less likely for men undergoing the andropause (the noticeable drop of testosterone levels after a certain age), it can absolutely occur if taking certain androgenic supplements, including simply taking testosterone (or conversely, if taking something to dial down antagonistic hormones). It can also happen if you’re taking something that throws out your free testosterone to DHT ratio.
As for what to do in this case? The usual process is: just wait it out. At some point your hormones will become stable again (nature loves equilibrium, and the body is mostly a self-righting system if given what it needs to do that), and your skin will return to normal. To be clear: the acne occurs because of the change, not necessarily the end place. So whatever hormone levels you have, be they medicated or otherwise, you just need to keep them stable now (assuming the levels are fine; if not, get them fine, and then keep them stable—speak to an endocrinologist for that) in order to come out the other side acne-free.
However, that’s “the usual process”, and obviously we cannot guarantee it’s not something else. It can also be caused by stress:
The Impact of Pyschological Stress on Acne ← teehee, a typo made it into the publication title
…in which case, of course, simply manage your stress (we know, often easier said than done, but the point is, that’s the remedy in this case).
See also: How To Reduce Chronic Stress
Diet is not the cause (or cure), but enjoying an anti-inflammatory diet will be beneficial, and consuming inflammatory things, exacerbatory:
Effects of Diet on Acne and Its Response to Treatment
Hygiene is also rarely to blame, but it can make a difference, so: do wash gently, wear clean clothes, and wash your bedsheets more often than you think necessary. And about that showering:
Body Scrubs: Benefits, Risks, and Guidance
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
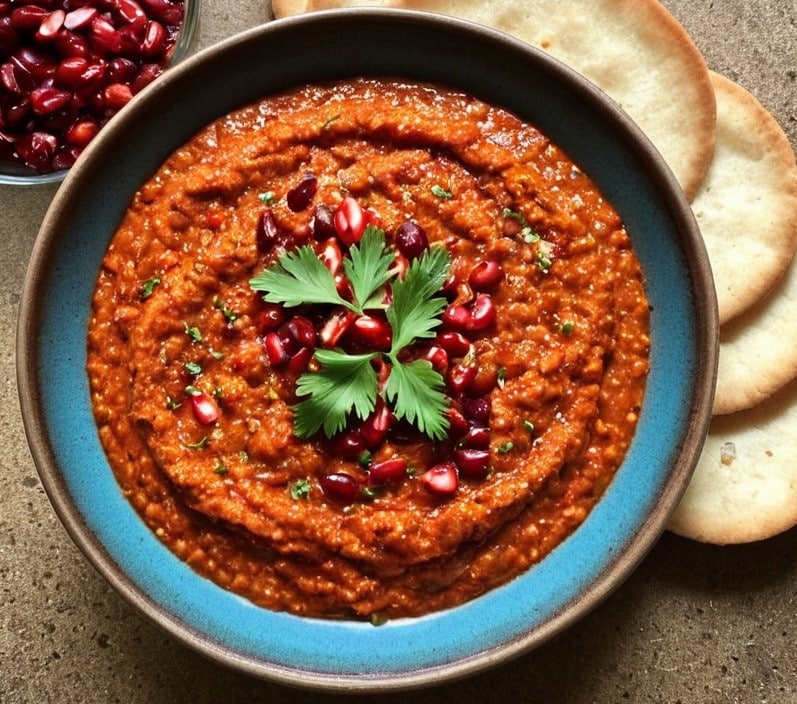
Muhammara
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a Levantine dish, Syrian in origin (although Lebanese cuisine uses it plenty too) and popularly enjoyed all the way up to Turkey, down to Egypt, and across to Armenia. And today, perhaps rather further afield! It’s first and foremost a spicy dip/spread, though it can be lengthened into a sauce, and/or made more substantial by adding an extra protein. We’ll give you the basic recipe though, and let you see where it takes you! Healthwise, it’s very nutritionally dense, mostly thanks to the walnuts and red peppers, though spices and olive oil bring their healthy benefits too.
You will need
- ½ cup chopped walnuts (ideally: toasted)
- 3 red peppers, from a jar (jarred over fresh not only improves the consistency, but also makes it extra gut-healthy due to the fermentation bacteria present; if you must use fresh, roast them first)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp pomegranate molasses (you can omit if you don’t like sweetness, but this is traditional)
- 1 tbsp tomato purée
- 1 tbsp Aleppo pepper flakes (less, if you don’t like heat) (substitute another hot pepper if necessary)
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tsp ground smoked paprika
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Juice of 1 lemon
- Optional: handful of pomegranate seeds
- Optional: herb garnish, e.g. cilantro or parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add everything except the pomegranate seeds and herbs to a blender, and blend to a smooth consistency.
2) Add the pomegranate seeds and herbs, as a garnish.
3) Serve! Can be enjoyed as a dip (perhaps using our Homemade Healthy Flatbreads recipe), or as a spread, or used as a sauce poured over chickpeas or some other bulky protein, to make a more substantial dish.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Walnuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Red Bell Peppers vs Tomatoes – Which is Healthier?
- Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: