Why ’10almonds’? Newsletter Name Explained
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Nudge – by Richard Thaler & Cass Sunstein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How often in life do we make a suboptimal decision that ends up plaguing us for a long time afterwards? Sometimes, a single good or bad decision can even directly change the rest of our life.
So, it really is important that we try to optimize the decisions we do make.
Professors Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein look at all kinds of decision-making in this book. Their goal, as per the subtitle, is “improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness”.
For the most part, the book concentrates on “nudges”. Small factors that influence our decisions one way or another.
Most importantly: that some of them are very good reasons to be nudged; others, very bad ones. And they often look similar.
Where this book excels is in highlighting the many ways we make decisions without even thinking about it… or we think about it, but only down a prescribed, foreseen track, to an externally expected conclusion (for example, an insurance company offering three packages, but two of them exist only to direct you to the “correct” choice).
A weakness of the book is that in some aspects it’s a little inconsistent. The authors describe their economic philosophy as “libertarian paternalism”, and as libertarians they’re against mandates, except when as paternalists they’re for them. But, if we take away their labels, this boils down to “some mandates can be good and some can be bad”, which would not be so inconsistent after all.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand your own decision-making processes through the eyes of policy-setting economists (especially Sunstein, who worked for the White House Office of Information & Regulatory Affairs) whose job it is to make sure you make the “right” decisions, then this is a very enlightening book.
Click here to check out Nudge and improve your decision-making clarity!
Share This Post
-
Nanotechnology vs Alcohol Damage!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One Thing That Does Pair Well With Alcohol…
Alcohol is not a healthy thing to consume. That shouldn’t be a controversial statement, but there is a popular belief that it can be good for the heart:
Red Wine & The Heart: Can We Drink To Good Health?
The above is an interesting and well-balanced article that examines the arguments for health benefits (including indirectly, e.g. social aspects).
Ultimately, though, as the World Health Organization puts it:
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
There is some good news:
We can somewhat reduce the harm done by alcohol by altering our habits slightly:
How To Make Drinking Less Harmful
…and we can also, of course, reduce our alcohol consumption (ideally to zero, but any reduction is an improvement already):
And, saving the best news (in this section, anyway) for last, it is almost always possible to undo the harm done specifically to one’s liver:
Nanotechnology to the rescue?
Remember when we had a main feature about how colloidal gold basically does nothing by itself (and that that’s precisely why gold is used in medicine, when it is used)?
Now it has an extra bit of nothing to do, for our benefit (if we drink alcohol, anyway), as part of a gel that detoxifies alcohol before it can get to our liver:
Gold is one of the “ingredients” in a gel containing a nanotechnology lattice of protein fibrils coated with iron (and the gold is there as an inert catalyst, which is chemistry’s way of saying it doesn’t react in any way but it does cheer the actual reagents on). There’s more chemistry going on than we have room to discuss in our little newsletter, so if you like the full details, you can read about that here:
Single-site iron-anchored amyloid hydrogels as catalytic platforms for alcohol detoxification
The short and oversimplified explanation is that instead of alcohol being absorbed from the gut and transported via the bloodstream to the liver, where it is metabolized (poisoning the liver as it goes, and poisoning the rest of the body too, including the brain), the alcohol is degraded while it is still in the gastrointestinal tract, converted by the gel’s lattice into acetic acid (which is at worst harmless, and actually in moderation a good thing to have).
Even shorter and even more oversimplified: the gel turns the alcohol into vinegar in the stomach and gut, before it can get absorbed into the blood.
But…
Of course there’s a “but”…
There are some limitations:
It doesn’t get it all (tests so far found it only gets about half of the alcohol), and so far it’s only been tested on mice, so it’s not on the market yet—while the researchers are sufficiently confident about it that a patent application has now been made, though, so it’ll probably show up on the market in the near future.
You can read a pop-science article about it (with diagrams!) here:
New gel breaks down alcohol in the body
Want to read more…
…about how to protect your organs (including your brain) from alcohol completely?
We’ve reviewed quite a number of books about quitting alcohol, so it’s hard to narrow it down to a single favorite, but after some deliberation, we’ll finish today with recommending:
Quit Drinking – by Rebecca Dolton ← you can read our review here
Take care!
Share This Post
-
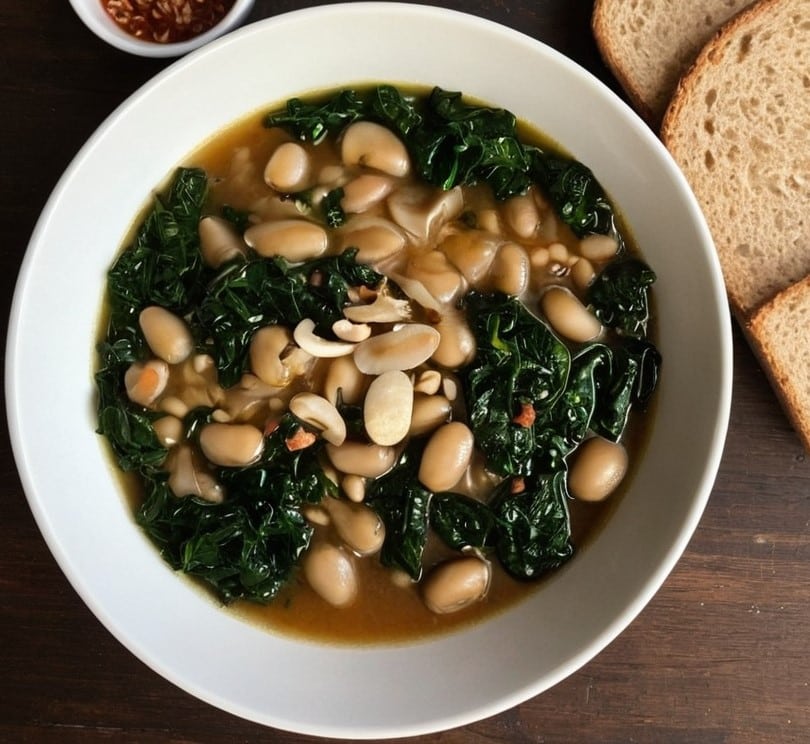
Brothy Beans & Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Eat beans and greens”, we say, “but how”, you ask. Here’s how! Tasty, filling, and fulfilling, this dish is full of protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and assorted powerful phytochemicals.
You will need
- 2½ cups low-sodium vegetable stock
- 2 cans cannellini beans, drained and rinsed
- 1 cup kale, stems removed and roughly chopped
- 4 dried shiitake mushrooms
- 2 shallots, sliced
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp white miso paste
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp rosemary leaves
- 1 tsp thyme leaves
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp red chili flakes
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Optional: your favorite crusty bread, perhaps using our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a skillet and fry the shallots for 2–3 minutes.
2) Add the nutritional yeast, garlic, herbs, and spices, and stir for another 1 minute.
3) Add the beans, vegetable stock, and mushrooms. Simmer for 10 minutes.
4) Add the miso paste, stirring well to dissolve and distribute evenly.
5) Add the kale until it begins to wilt, and remove the pot from the heat.
6) Add the lemon juice and stir.
7) Serve; we recommend enjoying it with crusty wholegrain bread.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen ← beans and greens up top!
- The Magic of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Plant-Based Salmon Recipe
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Tofu to Salmon
This video (below) by SweetPotatoSoul isn’t just a recipe tutorial; it’s an inspiring journey into the world of vegan cooking, proving that reducing animal products doesn’t have to mean sacrificing flavor.
The key to her vegan salmon is the tofu. However, there’s a trick to the tofu – you have to press it.
Essentially, this involved putting some paper towel on either side of the tofu, and then placing a heavy object on top; this removes excess water and, more importantly, primes the tofu to absorb the flavor of your marinade!
(You’ll want to press the tofu for around 1 hour)
Find the rest of the recipe in the 12-minute video below!
Other Plant-Based Recipes
With there being so many benefits of cutting meat out of your diet, we’ve spent the time reviewing some of the top books on vegan recipes, including The Green Roasting Tin and The Vegan Instant Pot Cookbook. We hope you enjoy them as much as you’ll enjoy this recipe:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mental Health Courts Can Struggle to Fulfill Decades-Old Promise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
GAINESVILLE, Ga. — In early December, Donald Brown stood nervously in the Hall County Courthouse, concerned he’d be sent back to jail.
The 55-year-old struggles with depression, addiction, and suicidal thoughts. He worried a judge would terminate him from a special diversion program meant to keep people with mental illness from being incarcerated. He was failing to keep up with the program’s onerous work and community service requirements.
“I’m kind of scared. I feel kind of defeated,” Brown said.
Last year, Brown threatened to take his life with a gun and his family called 911 seeking help, he said. The police arrived, and Brown was arrested and charged with a felony of firearm possession.
After months in jail, Brown was offered access to the Health Empowerment Linkage and Possibilities, or HELP, Court. If he pleaded guilty, he’d be connected to services and avoid prison time. But if he didn’t complete the program, he’d possibly face incarceration.
“It’s almost like coercion,” Brown said. “‘Here, sign these papers and get out of jail.’ I feel like I could have been dealt with a lot better.”
Advocates, attorneys, clinicians, and researchers said courts such as the one Brown is navigating can struggle to live up to their promise. The diversion programs, they said, are often expensive and resource-intensive, and serve fewer than 1% of the more than 2 million people who have a serious mental illness and are booked into U.S. jails each year.
People can feel pressured to take plea deals and enter the courts, seeing the programs as the only route to get care or avoid prison time. The courts are selective, due in part to political pressures on elected judges and prosecutors. Participants must often meet strict requirements that critics say aren’t treatment-focused, such as regular hearings and drug screenings.
And there is a lack of conclusive evidence on whether the courts help participants long-term. Some legal experts, like Lea Johnston, a professor of law at the University of Florida, worry the programs distract from more meaningful investments in mental health resources.
Jails and prisons are not the place for individuals with mental disorders, she said. “But I’m also not sure that mental health court is the solution.”
The country’s first mental health court was established in Broward County, Florida, in 1997, “as a way to promote recovery and mental health wellness and avoid criminalizing mental health problems.” The model was replicated with millions in funding from such federal agencies as the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration and the Department of Justice.
More than 650 adult and juvenile mental health courts were operational as of 2022, according to the National Treatment Court Resource Center. There’s no set way to run them. Generally, participants receive treatment plans and get linked to services. Judges and mental health clinicians oversee their progress.
Researchers from the center found little evidence that the courts improve participants’ mental health or keep them out of the criminal justice system. “Few studies … assess longer-term impacts” of the programs “beyond one year after program exit,” said a 2022 policy brief on mental health courts.
The courts work best when paired with investments in services such as clinical treatment, recovery programs, and housing and employment opportunities, said Kristen DeVall, the center’s co-director.
“If all of these other supports aren’t invested in, then it’s kind of a wash,” she said.
The courts should be seen as “one intervention in that larger system,” DeVall said, not “the only resource to serve folks with mental health needs” who get caught up in the criminal justice system.
Resource limitations can also increase the pressures to apply for mental health court programs, said Lisa M. Wayne, executive director of the National Association of Criminal Defense Lawyers. People seeking help might not feel they have alternatives.
“It’s not going to be people who can afford mental health intervention. It’s poor people, marginalized folks,” she said.
Other court skeptics wonder about the larger costs of the programs.
In a study of a mental health court in Pennsylvania, Johnston and a University of Florida colleague found participants were sentenced to longer time under government supervision than if they’d gone through the regular criminal justice system.
“The bigger problem is they’re taking attention away from more important solutions that we should be investing in, like community mental health care,” Johnston said.
When Melissa Vergara’s oldest son, Mychael Difrancisco, was arrested on felony gun charges in Queens in May 2021, she thought he would be an ideal candidate for the New York City borough’s mental health court because of his diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder and other behavioral health conditions.
She estimated she spent tens of thousands of dollars to prepare Difrancisco’s case for consideration. Meanwhile, her son sat in jail on Rikers Island, where she said he was assaulted multiple times and had to get half a finger amputated after it was caught in a cell door.
In the end, his case was denied diversion into mental health court. Difrancisco, 22, is serving a prison sentence that could be as long as four years and six months.
“There’s no real urgency to help people with mental health struggles,” Vergara said.
Critics worry such high bars to entry can lead the programs to exclude people who could benefit the most. Some courts don’t allow those accused of violent or sexual crimes to participate. Prosecutors and judges can face pressure from constituents that may lead them to block individuals accused of high-profile offenses.
And judges often aren’t trained to make decisions about participants’ care, said Raji Edayathumangalam, senior policy social worker with New York County Defender Services.
“It’s inappropriate,” she said. “We’re all licensed to practice in our different professions for a reason. I can’t show up to do a hernia operation just because I read about it or sat next to a hernia surgeon.”
Mental health courts can be overly focused on requirements such as drug testing, medication compliance, and completing workbook assignments, rather than progress toward recovery and clinical improvement, Edayathumangalam said.
Completing the programs can leave some participants with clean criminal records. But failing to meet a program’s requirements can trigger penalties — including incarceration.
During a recent hearing in the Clayton County Behavioral Health Accountability Court in suburban Atlanta, one woman left the courtroom in tears when Judge Shana Rooks Malone ordered her to report to jail for a seven-day stay for “being dishonest” about whether she was taking court-required medication.
It was her sixth infraction in the program — previous consequences included written assignments and “bench duty,” in which participants must sit and think about their participation in the program.
“I don’t like to incarcerate,” Malone said. “That particular participant has had some challenges. I’m rooting for her. But all the smaller penalties haven’t worked.”
Still, other participants praised Malone and her program. And, in general, some say such diversion programs provide a much-needed lifeline.
Michael Hobby, 32, of Gainesville was addicted to heroin and fentanyl when he was arrested for drug possession in August 2021. After entry into the HELP Court program, he got sober, started taking medication for anxiety and depression, and built a stable life.
“I didn’t know where to reach out for help,” he said. “I got put in handcuffs, and it saved my life.”
Even as Donald Brown awaited his fate, he said he had started taking medication to manage his depression and has stayed sober because of HELP Court.
“I’ve learned a new way of life. Instead of getting high, I’m learning to feel things now,” he said.
Brown avoided jail that early December day. A hearing to decide his fate could happen in the next few weeks. But even if he’s allowed to remain in the program, Brown said, he’s worried it’s only a matter of time before he falls out of compliance.
“To try to improve myself and get locked up for it is just a kick in the gut,” he said. “I tried really hard.”
KFF Health News senior correspondent Fred Clasen-Kelly contributed to this report.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: