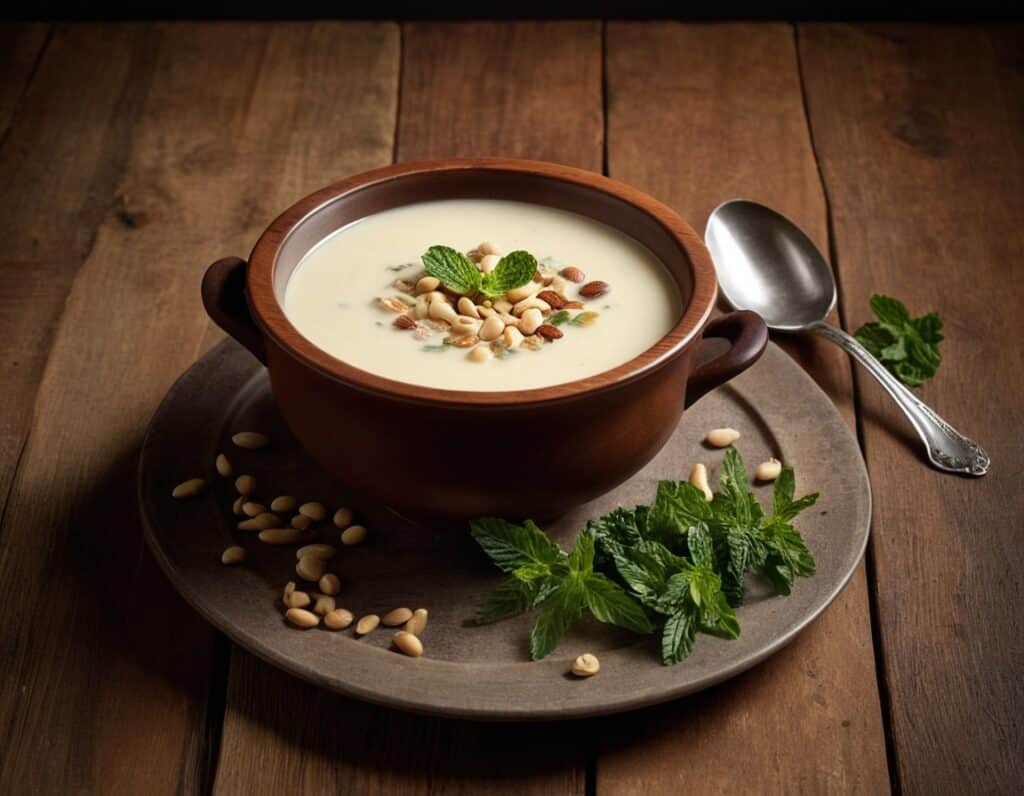
Wholesome Threesome Protein Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This soup has two protein– and fiber-rich pseudo-grains, one real wholegrain, and nutrient-dense cashews for yet even more protein, and all of the above are full of many great vitamins and minerals. All in all, a well-balanced and highly-nutritious light meal!
You will need
- ⅓ cup quinoa
- ⅓ cup green lentils
- ⅓ cup wholegrain rice
- 5 cups low-sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from offcuts of vegetables, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought in most large supermarkets)
- ¼ cup cashews
- 1 tbsp dried thyme
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Optional topping:
- ⅓ cup pine nuts
- ⅓ cup finely chopped fresh mint leaves
- 2 tbsp coconut oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the quinoa, lentils, and rice.
2) Boil 4 cups of the stock and add the grains and seasonings (MSG/salt, pepper, thyme); simmer for about 25 minutes.
3) Blend the cashews with the other cup of vegetable stock, until smooth. Add the cashew mixture to the soup, stirring it in, and allow to simmer for another 5 minutes.
4) Heat the coconut oil in a skillet and add the pine nuts, stirring until they are golden brown.
5) Serve the soup into bowls, adding the mint and pine nuts to each.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Give Us This Day Our Daily Dozen
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Red Cabbage vs Brussels Sprouts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing red cabbage to Brussels sprouts, we picked the sprouts.
Why?
First let’s note that we have an interesting comparison today, because these two plants are the exact same species (and indeed, also the exact same species as broccoli, cauliflower. and kale)—just a different cultivar. All of these plants and more are simply cultivars of Brassica oleracea.
Them being the same species notwithstanding, there are nutritional differences:
In terms of macros, the sprouts have more than 2x the protein, slightly more carbs, and nearly 2x the fiber. An easy win for sprouts here.
Looking at vitamins next, red cabbage has more vitamin A (whence the color), while Brussels sprouts have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline. Another easy win for sprouts.
In the category of minerals, red cabbage has a tiny bit more calcium, while Brussels sprouts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc—while being literally just a few mg/100g behind red cabbage on calcium anyway. So, once again, sprouts are sweeping the victory.
Both vegetables are a rich source of assorted polyphenols; for most polyphenols, Brussels sprouts scores higher—an exception being that red cabbage is very slightly higher in quercetin. So, we’ll call this category a win for Brussels sprouts, too.
In short: enjoy both; diversity is great and so is pretty much any iteration of Brassica oleracea. Standing next to Brussels sprouts made red cabbage look bad, but we assure you that cabbage in general is a nutritional powerhouse, and in this case it was hot the heels of sprouts in most of those micronutrients. If you’re going to pick one though, the Brussels sprouts are indeed the more nutritionally dense.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc ← sprout your Brassica oleracea, too!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Genius Foods – by Max Lugavere
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is a lot of seemingly conflicting (or sometimes: actually conflicting!) information out there with regard to nutrition and various aspects of health. Why, for example, are we told:
- Be sure to get plenty of good healthy fats from nuts and seeds, for metabolic health and brain health too!
- But these terrible nut and seed oils lead to heart disease and dementia! Avoid them at all costs!
Max Lugavere demystifies this and more.
His science-led approach is primarily focused on avoiding dementia, and/but is at least not bad when it comes to other areas of health too.
He takes us on a tour of different parts of our nutrition, including:
- Perhaps the clearest explanation of “healthy” vs “unhealthy” fats this reviewer has read
- Managing carbs (simple and complex) for healthy glucose management—essential for good brain health
- What foods to improve or reduce—a lot you might guess, but this is a comprehensive guide to brain health so it’d be remiss to skip it
- The role that intermittent fasting can play as a bonus extra
While the main thrust of the book is about avoiding cognitive impairment in the long-term (including later-life dementia), he makes good, evidence-based arguments for how this same dietary plan improves cognitive function in the short-term, too.
Speaking of that dietary plan: he does give a step-by-step guide in a “make this change first, then this, then this” fashion, and offers some sample recipes too. This is by no means a recipe book though—most of the book is taking us through the science, not the kitchen.
Bottom line: this is the book for getting unconfused with regard to diet and brain health, making a lot of good science easy to understand. Which we love!
Click here to check out “Genius Foods” on Amazon today, give your brain a boost!
Share This Post
-
‘Noisy’ autistic brains seem better at certain tasks. Here’s why neuroaffirmative research matters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pratik Raul, University of Canberra; Jeroen van Boxtel, University of Canberra, and Jovana Acevska, University of Canberra
Autism is a neurodevelopmental difference associated with specific experiences and characteristics.
For decades, autism research has focused on behavioural, cognitive, social and communication difficulties. These studies highlighted how autistic people face issues with everyday tasks that allistic (meaning non-autistic) people do not. Some difficulties may include recognising emotions or social cues.
But some research, including our own study, has explored specific advantages in autism. Studies have shown that in some cognitive tasks, autistic people perform better than allistic people. Autistic people may have greater success in identifying a simple shape embedded within a more complex design, arranging blocks of different shapes and colours, or spotting an object within a cluttered visual environment (similar to Where’s Wally?). Such enhanced performance has been recorded in babies as young as nine months who show emerging signs of autism.
How and why do autistic individuals do so well on these tasks? The answer may be surprising: more “neural noise”.
What is neural noise?
Generally, when you think of noise, you probably think of auditory noise, the ups and downs in the amplitude of sound frequencies we hear.
A similar thing happens in the brain with random fluctuations in neural activity. This is called neural noise.
This noise is always present, and comes on top of any brain activity caused by things we see, hear, smell and touch. This means that in the brain, an identical stimulus that is presented multiple times won’t cause exactly the same activity. Sometimes the brain is more active, sometimes less. In fact, even the response to a single stimulus or event will fluctuate continuously.
Neural noise in autism
There are many sources of neural noise in the brain. These include how the neurons become excited and calm again, changes in attention and arousal levels, and biochemical processes at the cellular level, among others. An allistic brain has mechanisms to manage and use this noise. For instance, cells in the hippocampus (the brain’s memory system) can make use of neural noise to enhance memory encoding and recall.
Evidence for high neural noise in autism can be seen in electroencephalography (EEG) recordings, where increased levels of neural fluctuations were observed in autistic children. This means their neural activity is less predictable, showing a wider range of activity (higher ups and downs) in response to the same stimulus.
In simple terms, if we imagine the EEG responses like a sound wave, we would expect to see small ups and downs (amplitude) in allistic brains each time they encounter a stimulus. But autistic brains seem to show bigger ups and downs, demonstrating greater amplitude of neural noise.
Many studies have linked this noisy autistic brain with cognitive, social and behavioural difficulties.
But could noise be a bonus?
The diagnosis of autism has a long clinical history. A shift from the medical to a more social model has also seen advocacy for it to be reframed as a difference, rather than a disorder or deficit. This change has also entered autism research. Neuroaffirming research can examine the uniqueness and strengths of neurodivergence.
Psychology and perception researcher David Simmons and colleagues at the University of Glasgow were the first to suggest that while high neural noise is generally a disadvantage in autism, it can sometimes provide benefits due to a phenomenon called stochastic resonance. This is where optimal amounts of noise can enhance performance. In line with this theory, high neural noise in the autistic brain might enhance performance for some cognitive tasks.
Our 2023 research explores this idea. We recruited participants from the general population and investigated their performance on letter-detection tasks. At the same time, we measured their level of autistic traits.
We performed two letter-detection experiments (one in a lab and one online) where participants had to identify a letter when displayed among background visual static of various intensities.
By using the static, we added additional visual noise to the neural noise already present in our participants’ brains. We hypothesised the visual noise would push participants with low internal brain noise (or low autistic traits) to perform better (as suggested by previous research on stochastic resonance). The more interesting prediction was that noise would not help individuals who already had a lot of brain noise (that is, those with high autistic traits), because their own neural noise already ensured optimal performance.
Indeed, one of our experiments showed people with high neural noise (high autistic traits) did not benefit from additional noise. Moreover, they showed superior performance (greater accuracy) relative to people with low neural noise when the added visual static was low. This suggests their own neural noise already caused a natural stochastic resonance effect, resulting in better performance.
It is important to note we did not include clinically diagnosed autistic participants, but overall, we showed the theory of enhanced performance due to stochastic resonance in autism has merits.
Why this is important?
Autistic people face ignorance, prejudice and discrimination that can harm wellbeing. Poor mental and physical health, reduced social connections and increased “camouflaging” of autistic traits are some of the negative impacts that autistic people face.
So, research underlining and investigating the strengths inherent in autism can help reduce stigma, allow autistic people to be themselves and acknowledge autistic people do not require “fixing”.
The autistic brain is different. It comes with limitations, but it also has its strengths.
Pratik Raul, PhD candidiate, University of Canberra; Jeroen van Boxtel, Associate professor, University of Canberra, and Jovana Acevska, Honours Graduate Student, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Shedding Some Obesity Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s shed some obesity myths!
There are a lot of myths and misconceptions surrounding obesity… And then there are also reactive opposite myths and misconceptions, which can sometimes be just as harmful!
To tackle them all would take a book, but in classic 10almonds style, we’re going to put a spotlight on some of the ones that might make the biggest difference:
True or False: Obesity is genetically pre-determined
False… With caveats.
Some interesting results have been found from twin studies and adoption studies, showing that genes definitely play some role, but lifestyle is—for most people—the biggest factor:
- The body-mass index of twins who have been reared apart
- An adoption study of human obesity
- Using a sibling-adoption design to parse genetic and environmental influences on children’s body mass index
In short: genes predispose; they don’t predetermine. But that predisposition alone can make quite a big difference, if it in turn leads to different lifestyle factors.
But upon seeing those papers centering BMI, let’s consider…
True or False: BMI is a good, accurate measure of health in the context of bodyweight
False… Unless you’re a very large group of thin white men of moderate height, which was the demographic the system was built around.
Bonus information: it was never intended to be used to measure the weight-related health of any individual (not even an individual thin white man of moderate height), but rather, as a tool to look at large-scale demographic trends.
Basically, as a system, it’s being used in a way it was never made for, and the results of that misappropriation of an epidemiological tool for individual health are predictably unhelpful.
To do a deep-dive into all the flaws of the BMI system, which are many, we’d need to devote a whole main feature just to that.
Update: we have now done so!
Here it is: When BMI Doesn’t Measure Up
True or False: Obesity does not meaningfully impact more general health
False… In more ways than one (but there are caveats)
Obesity is highly correlated with increased risk of all-cause mortality, and weight loss, correspondingly, correlates with a reduced risk. See for example:
So what are the caveats?
Let’s put it this way: owning a horse is highly correlated with increased healthy longevity. And while owning a horse may come with some exercise and relaxation (both of which are good for the health), it’s probably mostly not the horse itself that conveys the health benefits… it’s that someone who has the resources to look after a horse, probably has the resources to look after their own health too.
So sometimes there can be a reason for a correlation (it’s not a coincidence!) but the causative factor is partially (or in some cases, entirely) something else.
So how could this play out with obesity?
There’s a lot of discrimination in healthcare settings, unfortunately! In this case, it often happens that a thin person goes in with a medical problem and gets treated for that, while a fat person can go in with the same medical problem and be told “you should try losing some weight”.
Top tip if this happens to you… Ask: “what would you advise/prescribe to a thin person with my same symptoms?”
Other things may be more systemic, for example:
When a thin person goes to get their blood pressure taken, and that goes smoothly, while a fat person goes to get their blood pressure taken, and there’s not a blood pressure cuff to fit them, is the problem the size of the person or the size of the cuff? It all depends on perspective, in a world built around thin people.
That’s a trivial-seeming example, but the same principle has far-reaching (and harmful) implications in healthcare in general, e.g:
- Surgeons being untrained (and/or unwilling) to operate on fat people
- Getting a one-size-fits-all dose that was calculated using average weight, and now doesn’t work
- MRI machines are famously claustrophobia-inducing for thin people; now try not fitting in it in the first place
…and so forth. So oftentimes, obesity will be correlated with a poor healthcare outcome, where the problem is not actually the obesity itself, but rather the system having been set up with thin people in mind.
It would be like saying “Having O- blood type results in higher risks when receiving blood transfusions”, while omitting to add “…because we didn’t stock O- blood”.
True or False: to reduce obesity, just eat less and move more!
False… Mostly.
Moving more is almost always good for most people. When it comes to diet, quality is much more important than quantity. But these factors alone are only part of the picture!
But beyond diet and exercise, there are many other implicated factors in weight gain, weight maintenance, and weight loss, including but not limited to:
- Disrupted sleep
- Chronic stress
- Chronic pain
- Hormonal imbalances
- Physical disabilities that preclude a lot of exercise
- Mental health issues that add (and compound) extra levels of challenge
- Medications that throw all kinds of spanners into the works with their side effects
…and even just those first two things, diet and exercise, are not always so correlated to weight as one might think—studies have found that the difference for exercise especially is often marginal:
Read: Widespread misconceptions about obesity ← academic article in the Journal of the College of Family Physicians of Canada
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Good Life – by Robert Waldinger, MD, and Marc Schulz, PhD
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For any who have thought “there must be some middle-ground between entirely subjective self-help books advising how to feel better, and sifting through clinical data on what actually affects people’s moods“, this book is exactly that middle-ground!
Drs. Waldinger and Schultz went through the 80-year-long Harvard Study of Adult Development with a fine-toothed comb, and this book details—more readably—what they found.
There are frequent references to data from the study. Not just numbers, though, people’s answers to questions, too. And how different factors about people’s lives affected their answers to the same questions.
We hear from all ages, from young adults to octagenarians, and learn how attitudes (including: of the same people) change over time. Not because people are fickle, but because people grow… or become disillusioned. Or sometimes, both.
We learn about the importance of money… And where that importance ends.
We learn importance of relationships of various kinds, and this is certainly a recurring theme throughout the study—and thus, throughout the book.
The book doesn’t just present data, though, it also presents actionable insights along the way.
Bottom line: the combined wisdom and life-experiences of a lot of people provide a very “big picture” view of life, and what makes us happy, really. We highly recommend it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Where to Get Turmeric?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
“I liked the info on Turmeric. The problem for me is that I do not like black pepper which should be ingested with the turmeric for best results. Is black pepper sold in capsule form?”
Better than just black pepper being sold in capsule form, it’s usually available in the same capsules as the turmeric. As in: if you buy turmeric capsules, there is often black pepper in them as well, for precisely that reason. Check labels, of course, but here’s an example on Amazon.
“I would like to read more on loneliness, meetup group’s for seniors. Thank you”
Well, 10almonds is an international newsletter, so it’s hard for us to advise about (necessarily: local) meetup groups!
But a very popular resource for connecting to your local community is Nextdoor, which operates throughout the US, Canada, Australia, and large parts of Europe including the UK.
In their own words:
Get the most out of your neighborhood with Nextdoor
It’s where communities come together to greet newcomers, exchange recommendations, and read the latest local news. Where neighbors support local businesses and get updates from public agencies. Where neighbors borrow tools and sell couches. It’s how to get the most out of everything nearby. Welcome, neighbor.
Curious? Click here to check it out and see if it’s of interest to you
“It was superb !! Just loved that healthy recipe !!! I would love to see one of those every day, if possible !! Keep up the fabulous work !!!”
We’re glad you enjoyed! We can’t promise a recipe every day, but here’s one just for you:
! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: