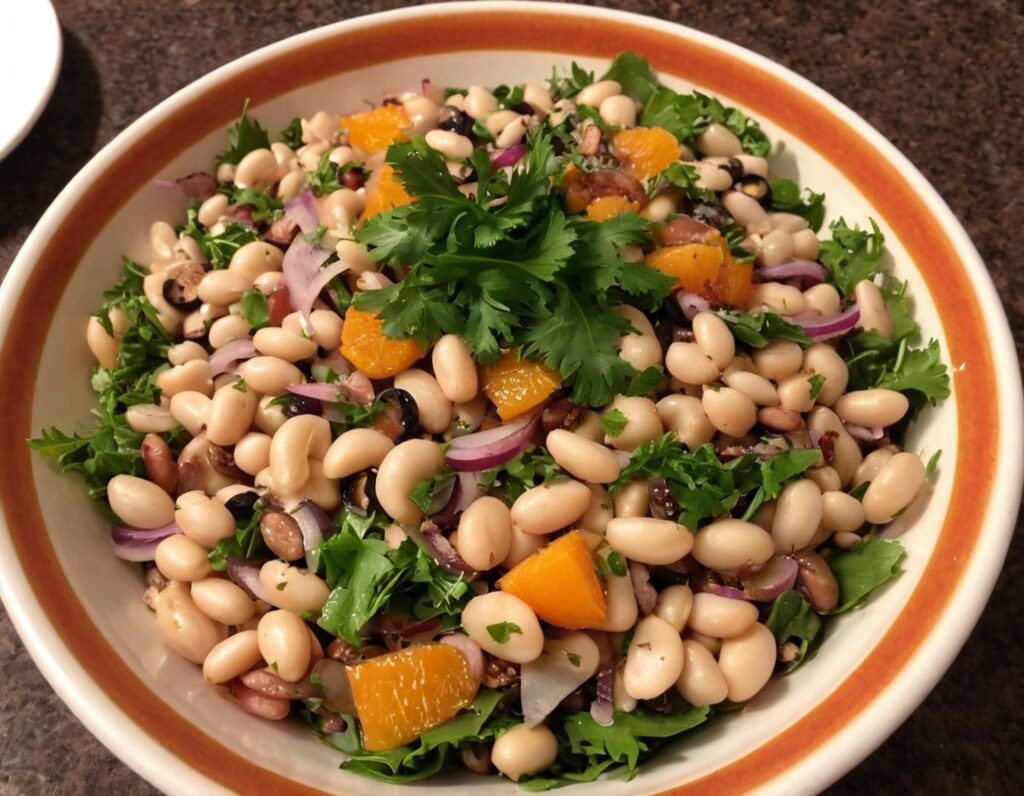Which Plant Milk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Plant-based milks—what’s best?
You asked us to look at some popular plant milks and their health properties, and we said we’d do a main feature, so here it is!
We’ll also give a quick nod to environmental considerations at the end too (they might not be quite what you expect!). That said, as a health and productivity newsletter, we’ll be focusing on the health benefits.
While we can give a broad overview, please note that individual brands may vary, especially in two important ways:
- Pro: many (most?) brands of plant milks fortify their products with extra vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin D and calcium.
- Con: some brands also add sugar.
So, by all means use this guide to learn about the different plants’ properties, and/but still do check labels later.
Alternatively, consider making your own!
- Pros: no added sugar + cheaper
- Cons: no added vitamins and minerals + some equipment required
Almond milk
Almond milk is low in carbs and thus good for a carb-controlled diet. It’s also high in vitamin E and a collection of minerals.
Oat milk
Oats are one of the healthiest “staple foods” around, and while drinking oat milk doesn’t convey all the benefits, it does a lot. It also has one of the highest soluble fiber contents of any milk, which is good for reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
See for example: Consumption of oat milk for 5 weeks lowers serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in free-living men with moderate hypercholesterolemia
Coconut milk
Coconut has a higher fat content than most plant milks, but also contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). These raise HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
Read the study: How well do plant based alternatives fare nutritionally compared to cow’s milk?
Hemp milk
Being made from hemp seeds that contain a lot of protein and healthy fats (including omega-3 and omega-6), hemp milk packs a nutritious punch. It’s carb-free. It’s also THC-free, in case you were wondering, which means no, it does not have psychoactive effects.
Pea milk
It’s very high in protein, and contains an array of vitamins and minerals. It’s not very popular yet, so there isn’t as much research about it. This 2021 study found that it had the nutritional profile the closest to cow’s milk (beating soy by a narrow margin) and praised it as a good alternative for those with a soy allergy.
This is Research Review Monday so we try to stick to pure science, but for your interest… here’s an interesting pop-science article (ostensibly in affiliation with the pea milk brand, Ripple) about the nutritional qualities of their pea milk specifically, which uses particularly nutrient-dense yellow peas, plus some extra vitamin and mineral fortifications:
Read: Ripple Milk: 6 Reasons Why You Should Try Pea Milk
Soy milk
Perhaps the most popular plant milk, and certainly usually the cheapest in stores. It’s high in protein, similar to cow’s milk. In fact, nutritionally, it’s one of the closest to cow’s milk without involving cows as a middleman. (Did you know three quarters of all soy in the world is grown to feed to livestock, not humans? Now you do).
And no, gentlemen-readers, it won’t have any feminizing effects. The human body can’t use the plant estrogens in soy for that. It does give some isoflavone benefits though, which are broadly good for everyone’s health. See for example this research review with 439 sources of its own:
Read: Soy and Health Update: Evaluation of the Clinical and Epidemiologic Literature
Quick note on flavor: nut milks have the flavor of the nut they were made from. Coconut milk tastes of coconut. The other milks listed above don’t have much of a flavor—which in many cases may be what you want.
Note on environmental considerations:
A lot of us try to be as socially responsible as reasonably possible in our choices, so this may be an influencing factor. In a nutshell:
- Oats and Soy are generally grown as vast monocrops, and these are bad for the environment
- They are still better for the environment than cow’s milk though, as for example most soy is grown to feed to cows, not humans. So including cows in the process means four times as much monocrop farming, plus adds several other environmental issues that are beyond the scope of this newsletter.
- Almonds are particularly resource-intensive when it comes to water use.
- Still nowhere near as much as cows, though.
- Peas are grown in places that naturally have very high rainfall, so are a good option here. Same generally goes for rice, which didn’t make the cut today. (Nor did hazelnuts, sorry—we can only include so much!)
- Hemp is by far and away the most environmentally friendly, assuming it is grown in a climate naturally conducive to such.
- Making plant milk at home is usually most environmentally friendly, depending on where your ingredients came from.
- Literally any plant milk is much more environmentally friendly than cow’s milk.
See the science for yourself: Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers
See also (if you like graphs and charts): Environmental footprints of dairy and plant-based milks
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rethinking Drinking
When we’re looking at certain health risks, there are often five key lifestyle factors that have a big impact; they are:
- Have a good diet
- Get good exercise
- Get good sleep
- Reduce (or eliminate) alcohol
- Don’t smoke
Today, we’re focussing the alcohol bit. Maybe you’d like to quit, maybe just cut down, maybe the topic just interests you… So, here’s a quick rundown of some things that will help make that a lot easier:
With a big enough “why”, you can overcome any “how”
Research and understand the harm done by drinking, including:
And especially as we get older, memory problems:
Alcohol-related dementia: an update of the evidence
And as for fear of missing out, or perhaps even of no longer being relaxed/fun… Did you ever, while sober, have a very drunk person try to converse with you, and you thought “I wish that were me”?
Probably not
Know your triggers
Why do you drink? If your knee-jerk response is “because I like it”, dig deeper. What events prompt you to have a drink?
- Some will be pure habit born of convention—perhaps with a meal, for example
- Others may be stress-management—after work, perhaps
- Others may be pseudo-medicinal—a nightcap for better* sleep, for instance
*this will not work. Alcohol may make us sleepy but it will then proceed to disrupt that very sleep and make it less restorative
Become mindful
Now that you know why you’d like to drink less (or quit entirely), and you know what triggers you to drink, you can circumvent that a little, by making deals with yourself, for example
- “I can drink alcohol, if and only if I have consumed a large glass of water first” (cuts out being thirsty as a trigger to drink)
- “I can drink alcohol, if and only if I meditate for at least 5 minutes first” (reduces likelihood of stress-drinking)
- “I can drink alcohol, if and only if it is with the largest meal of the day” (minimizes total alcohol consumption)
Note that these things also work around any FOMO, “Fear Of Missing Out”. It’s easier to say “no” when you know you can have it later if you still want it.
Get a good replacement drink
There are a lot of alcohol-free alcohol-like drinks around these days, and many of them are very good. Experiment and see. But!
It doesn’t even have to be that. Sometimes what we need is not even an alcohol-like drink, but rather, drinkable culinary entertainment.
If you like “punch-in-the-face” flavors (as this writer does), maybe strong black coffee is the answer. If you like “crisp and clear refreshment” (again, same), maybe your favorite herbal tea will do it for you. Or maybe for you it’ll be lemon-water. Or homemade ginger ale.
Whatever it is… make it fun, and make it yours!
Bonus item: find replacement coping strategies
This one goes if you’ve been using alcohol to cope with something. Stress, depression, anxiety, whatever it may be for you.
The thing is, it feels like it helps briefly in the moment, but it makes each of those things progressively worse in the long-run, so it’s not sustainable.
Consider instead things like therapy, exercise, and/or a new hobby to get immersed in; whatever works for you!
Share This Post
-
The Liver Cure – by Dr. Russell Blaylock
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver, but there’s a lot more that can be said in a book that we couldn’t fit into our article.
In this book, Dr. Blaylock looks at the causes and symptoms of liver disease, the mechanisms behind such, and how we can adjust our dietary habits (and other things) to do better for ourselves.
While the book’s primary focus is on diet, he does also look at medications (especially: those that hinder liver health, which are many, including simple/common stuff like Tylenol and similar), and the effects of different lifestyle choices, including ones that aren’t diet-related.
Because most people’s knowledge of liver disease starts and ends at “don’t drink yourself to death”, this book is an important tome of knowledge for actually keeping this critical organ in good order—especially since symptoms of liver disease can initially be subtle, and slow to show, often escaping notice until it’s already far, far worse than it could have been.
Many people find out by experiencing liver failure.
The writing style is… A little repetitive for this reviewer’s preference, but it does make sure that you won’t miss things. Also, when it comes to supplements, he repeatedly recommends a particular company, and it’s not clear whether he has a financial interest there. But the actual medical information is good and important and comprehensive.
Bottom line: if you’d like to keep your liver in good health, this is a book that will help you to do just that.
Click here to check out The Liver Cure, and keep yours working well!
Share This Post
-
The “Yes I Can” Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, we are given to ask ourselves: “Can I produce a healthy and tasty salad out of what I have in?” and today we show how, with a well-stocked pantry, the answer is “yes I can”, regardless of what is (or isn’t) in the fridge.
You will need
- 1 can cannellini beans, drained
- 1 can sardines (if vegetarian/vegan, substitute ½ can chickpeas, drained)
- 1 can mandarin segments
- 1 handful pitted black olives, from a jar (or from a can, if you want to keep the “yes I can” theme going)
- ½ red onion, thinly sliced (this can be from frozen, defrosted—sliced/chopped onion is always a good thing to have in your freezer, by the way; your writer here always has 1–6 lbs of chopped onions in hers, divided into 1lb bags)
- 1 oz lemon juice
- 1 tbsp chopped parsley (this can be freeze-dried, but fresh is good if you have it)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp honey (omit if you don’t care for sweetness; substitute with agave nectar if you do like sweetness but don’t want to use honey specifically)
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the onion and the lemon juice in a small bowl, massaging gently
2) Mix (in another bowl) the miso paste with the chili flakes, chia seeds, honey, olive oil, and the spare juice from the can of mandarin segments, and whisk it to make a dressing.
3) Add the cannellini beans, sardines (break them into bite-size chunks), mandarin segments, olives, and parsley, tossing them thoroughly (but gently) in the dressing.
4) Top with the sliced onion, discarding the excess lemon juice, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Life After Death? (Your Life; A Loved One’s Death)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Show Must Go On
We’ve previously written about the topics of death and dying. It’s not cheery, but it is important to tackle.
Sooner is better than later, in the case of:
Preparations For Managing Your Own Mortality
And for those who are left behind, of course it is hardest of all:
What Grief Does To Your Body (And How To Manage It)
But what about what comes next? For those who are left behind, that is.
Life goes on
In cases when the death is that of a close loved one, the early days after death can seem like a surreal blur. How can the world go ticking on as normal when [loved one] is dead?
But incontrovertibly, it does, so we can only ask again: how?
And, we get to choose that, to a degree. The above-linked article about grief gives a “101” rundown, but it’s (by necessity, for space) a scant preparation for one of the biggest challenges in life that most of us will ever face.
For many people, processing grief involves a kind of “saying goodbye”. For others, it doesn’t, as in the following cases of grieving the loss of one’s child—something no parent should ever have to face, but it happens:
Dr. Ken Druck | The Love That Never Dies
(with warning, the above article is a little heavy)
In short: for those who choose not to “say goodbye” in the case of the death of a loved one, it’s more often not a case of cold neglect, but rather the opposite—a holding on. Not in the “denial” sense of holding on, but rather in the sense of “I am not letting go of this feeling of love, no matter how much it might hurt to hold onto; it’s all I have”.
What about widows, and love after death?
Note: we’ll use the feminine “widow” here as a) it’s the most common and b) most scientific literature focuses on widows, but there is no reason why most of the same things won’t also apply to widowers.
We say “most”, as society does tend to treat widows and widowers differently, having different expectations about a respectful mourning period, one’s comportment during same, and so on.
As an aside: most scientific literature also assumes heterosexuality, which is again statistically reasonable, and for the mostpart the main difference is any extra challenges presented by non-recognition of marriages, and/or homophobic in-laws. But otherwise, grief is grief, and as the saying goes, love is love.
One last specificity before we get into the meat of this: we are generally assuming marriages to be monogamous here. Polyamorous arrangements will likely sidestep most of these issues completely, but again, they’re not the norm.
Firstly, there’s a big difference between remarrying (or similar) after being widowed, and remarrying (or similar) after a divorce, and that largely lies in the difference of how they begin. A divorce is (however stressful it may often be) more often seen as a transition into a new period of freedom, whereas bereavement is almost always felt as a terrible loss.
The science, by the way, shows the stats for this; people are less likely to remarry, and slower to remarry if they do, in instances of bereavement rather than divorce, for example:
Timing of Remarriage Among Divorced and Widowed Parents
Love after death: the options
For widows, then, there seem to be multiple options:
- Hold on to the feelings for one’s deceased partner; never remarry
- Grieve, move on, find new love, relegating the old to history
- Try to balance the two (this is tricky but can be done*)
*Why is balancing the two tricky, and how can it be done?
It’s tricky because ultimately there are three people’s wishes at hand:
- The deceased (“they would want me to be happy” vs “I feel I would be betraying them”—which two feelings can also absolutely come together, by the way)
- Yourself (whether you actually want to get a new partner, or just remain single—this is your 100% your choice either way, and your decision should be made consciously)
- The new love (how comfortable are they with your continued feelings for your late love, really?)
And obviously only two of the above can be polled for opinions, and the latter one might say what they think we want to hear, only to secretly and/or later resent it.
One piece of solid advice for the happily married: talk with your partner now about how you each would feel about the other potentially remarrying in the event of your death. Do they have your pre-emptive blessing to do whatever, do you ask a respectable mourning period first (how long?), would the thought just plain make you jealous? Be honest, and bid your partner be honest too.
One piece of solid advice for everyone: make sure you, and your partner(s), as applicable, have a good emotional safety net, if you can. Close friends or family members that you genuinely completely trust to be there through thick and thin, to hold your/their hand through the emotional wreck that will likely follow.
Because, while depression and social loneliness are expected and looked out for, it’s emotional loneliness that actually hits the hardest, for most people:
Longitudinal Examination of Emotional Functioning in Older Adults After Spousal Bereavement
…which means that having even just one close friend or family member with whom one can be at one’s absolute worst, express emotions without censure, not have to put on the socially expected appearance of emotional stability… Having that one person (ideally more, but having at least one is critical) can make a huge difference.
But what if a person has nobody?
That’s definitely a hard place to be, but here’s a good starting point:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Professional-Style Dental Cleaning At Home?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You know the scene: your dentist is rummaging around inside your mouth with an implement that looks like a medieval torture device; you wince at a sudden sharp pain, only to be told “if you flossed, you wouldn’t be bleeding now”.
For most of us, going to the dentist isn’t near the top of our “favorite things to do” list, but it is of course a necessity of (healthy) life.
So, what can we do to minimize suffering in the dentist’s chair?
First, the basics
Of course, good oral hygiene is the absolute baseline, but with so many choices out there, which is best? We examined an array of options in this three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing Without Flossing?
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options ← we recommend the miswak! Not only does it clean the teeth as well as or better than traditional brushing, but also it changes the composition of saliva to improve the oral microbiome, effectively turning your saliva into a biological mouthwash that kills unwanted microbes and is comfortable for the ones that should be there.
In fact, caring for the composition of one’s saliva, and thus one’s oral microbiome, is so important that we did a main feature on that, a little later:
Make Your Saliva Better For Your Teeth ← this is especially important if you take any meds that affect the composition of your saliva (scroll down to the table of meds). Your medications’ leaflets won’t tell you that it does that directly, but they will list “dry mouth” as one of the potential side effects (and you’ll probably know if you have a medication that gives you a dry mouth).
Next, level up
For this one, we’ll drop some links to some videos we’ve featured (for those who prefer text, worry not, your faithful writer has added text-based overviews):
- How To Regrow Receding Gums
- Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
- Tartar Removal At Home & How To Prevent Tartar
Now, that last one sounds slightly more exciting than it is—it is about using chemical processes to gradually lessen the tartar over time, with a six-month timeframe.
So, what if you want to do one better than that?
Finally… Buckle up, this one’s fun
Ok, so “fun” and “dental care” don’t usually go hand-in-hand, and maybe your sense of fun differs from this writer’s, but hey. The thing is, we’re going to get hands-on with dental tools.
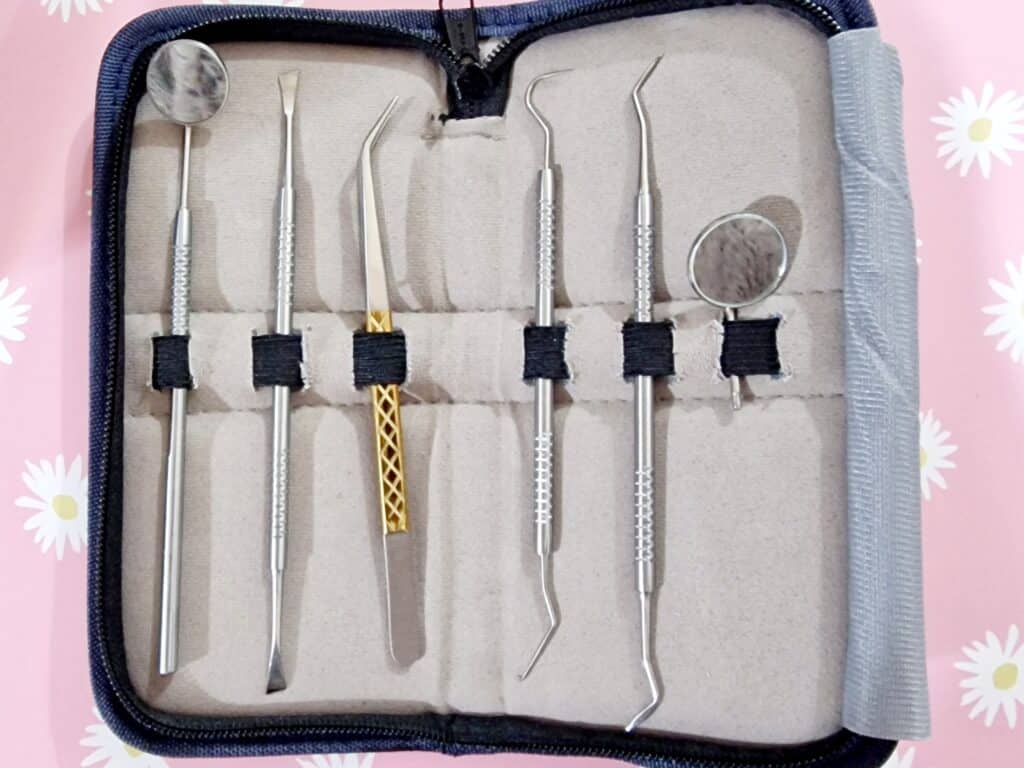
Specifically, these dental tools:
👆 these are literally the tools this writer has; if you look in the specula (the round mirror bits), you can see the reflection of the fluffy gray bathrobe I was wearing when I took the picture!
You can get tools like these easily online; here’s an example product on Amazon; do also shop around of course, and we recommend checking the reviews to ensure good quality.
Writer’s story on why I have these: once upon a time, a wisdom tooth came through at 45°, ploughing through the molar next to it, which then needed removing.
However, my teeth have the interesting anatomical quirk that I have hooked/barbed roots, which does not make tooth extraction easy; it had to come out sidewise, and the process was somewhat bungled by an inexperienced dental surgeon.
When the anesthetic wore off, it was the most pain I’ve ever been in in my life.
After that, I wasn’t a very regular returner to the dentist, and in 2013, I fell into a very deep depression for unrelated reasons, and during that period, I got some plaque/tartar buildup on some of my teeth due to lack of care, that then just stayed until I decided to take care of it more recently, which I am happy to say, I’ve now done (my teeth are the happiest and healthiest they’ve ever been), and I’m going to share how, with you.
So, here’s how to do it… First, you’ll need those tools, of course.
You will also want a good quality backlit magnifying mirror. Again, here’s an example product on Amazon ← this is the exact kind this writer has, and it’s very good.
You may be thinking: “wait a minute, this is scary, those are dangerous and I’m not a dentist!”
If so, then a few quick things to bear in mind:
- If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
- These things do look scarier than they are once you get used to them. Do you use metal silverware when eating? Technically you could stab yourself with a fork any time, or damage your teeth with it, but when was the last time you did that?
- With regard to manual dexterity, if you have the manual dexterity required to paint your nails, floss your teeth, sew by hand, or write with a pen, then you have the manual dexterity to do this, too.
Now, about the tools:
- Speculum / magnifying speculum: the one with the mirror. This is useful for looking at the backs of teeth.
- Tweezers: the one with the gold grip in the photo above. You probably won’t need to use these, but we’re sure you know how to use tweezers in general.
- Dental explorer: the one with the big wicked-looking hook on one end, and a tiny (almost invisible in the photo) hook on the other end. This is for examining cavities, not for manipulating things. Best leave that to your dentist if you have cavities.
- Dental pick: this is the one to the right of the dental explorer, and it is for cleaning in the crevices between teeth. One end is quite blunt; the other is pointier, and you can choose which end to use depending on what fits into the shape of the crevice between your teeth.
- Dental scraper: this is the one with chisel ends. One end curves very slightly to the left, the other, very slightly to the right. This is for ergonomics depending on which hand you’re using, and which side you’re scraping (you’ll become very aware that your teeth, even if they look straight, curve very slightly at the edges.
You’ll be using these last two for the actual tartar removal, selecting the tool appropriate to cleaning the flat surface of a tooth, or the crevice where the teeth meet (not like flossing! That part, yes, but under no circumstances is this thing going all the way through to the other side, it’s just for getting into to nook that the scraper can’t so easily clean, that’s all).
A word on using metal against your teeth: a scary prospect, initially! However…
While steel is indeed harder than the enamel of your teeth, the enamel of your teeth is much harder than the plaque/tartar/calculus that you will be removing. Therefore, the technique to use is very gently scrape, starting as gently as humanly possible until you get a feel for it.
Unlike the dentist, you will have an advantage here in that you have biofeedback, and bone conduction of the sounds in your mouth, so you can exercise much more restraint than your dentist can. With the correct minimum of pressure, the tool should glide smoothly down enamel, but when it’s scraping tartar, it should make a very fine sandpapery noise.
This is why “or write with a pen” was one of the skills we mentioned earlier; it’s the same thing; you don’t press with a pen so hard that it goes through the paper, so don’t press so hard with the tool that it damages your enamel, that’s all.
Because of the differential in hardness between the tartar and the enamel, it’s really very easy to remove the tartar without harming the enamel, provided one is gentle.
Final word of warning; we’ll repeat: If you’re not comfortable doing it, don’t do it. As ever, our medical/legal disclaimer applies, and we share information for your interest only, and not as an exhortation to take any particular action. By all means confer with your dentist, too, and see whether they support the idea.
Also, while this kind of cleaning can be done safely at home, we recommend against doing anything more complicated than that.
See for example: Can You Repair Your Own Teeth At Home? ← the short answer is “no”, or not beyond tooth remineralization, anyway, and kits that say otherwise are potentially misleading, or stop-gap solutions at best.
One last time: always consult with a professional and get their advice (ours is not advice; it’s just information).
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Is More Likely Than You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): More Likely Than You Think
COPD is not so much one disease, as rather a collection of similar (and often overlapping) diseases. The main defining characteristic is that they are progressive lung diseases. Historically the most common have been chronic bronchitis and emphysema, though Long COVID and related Post-COVID conditions appear to have been making inroads.
Lung cancer is generally considered separately, despite being a progressive lung disease, but there is crossover too:
COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history
COPD can be quite serious:
“But I don’t smoke”
Great! In fact we imagine our readership probably has disproportionately few smokers compared to the general population, being as we all are interested in our health.
But, it’s estimated that 30,000,000 Americans have COPD, and approximately half don’t know it. Bear in mind, the population of the US is a little over 340,000,000, so that’s a little under 9% of the population.
Click here to see a state-by-state breakdown (how does your state measure up?)
How would I know if I have it?
It typically starts like any mild respiratory illness. Likely shortness of breath, especially after exercise, a mild cough, and a frequent need to clear your throat.
Then it will get worse, as the lungs become more damaged; each of those symptoms might become stronger, as well as chest tightness and a general lack of energy.
Later stages, you guessed it, the same but worse, and—tellingly—weight loss.
The reason for the weight loss is because you are getting less oxygen per breath, making carrying your body around harder work, meaning you burn more calories.
What causes it?
Lots of things, with smoking being up at the top, or being exposed to a lot of second-hand smoke. Working in an environment with a lot of air pollution (for example, working around chemical fumes) can cause it, as can inhaling dust. New Yorkers: yes, that dust too. It can also develop from other respiratory illnesses, and some people even have a genetic predisposition to it:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: a commonly overlooked cause of lung disease
Is it treatable?
Treatment varies depending on what form of it you have, and most of the medical interventions are beyond the scope of this article. Suffice it to say, there are medications that can be taken (including bronchodilators taken via an inhaler device), corticosteroids, antibiotics and antivirals of various kinds if appropriate. This is definitely a “see your doctor” item though, because there are is far too much individual variation for us to usefully advise here.
However!
There are habits we can do to a) make COPD less likely and b) make COPD at least a little less bad if we get it.
Avoiding COPD:
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.
- Avoid second-hand smoke if you can
- Avoid inhaling other chemicals/dust that may be harmful
- Breathe through your nose, not your mouth; it filters the air in a whole bunch of ways
- Seriously, we know it seems like nostril hairs surely can’t do much against tiny particles, but tiny particles are attracted to them and get stuck in mucous and dealt with by our immune system, so it really does make a big difference
Managing COPD:
- Continue the above things, of course
- Exercise regularly, even just light walking helps; we realize it will be difficult
- Maintain a healthy weight if you can
- This means both ways; COPD causes weight loss and that needs to be held in check. But similarly, you don’t want to be carrying excessive weight either; that will tire you even more.
- Look after the rest of your health; everything else will now hit you harder, so even small things need to be taken seriously
- If you can, get someone to help / do your household cleaning for you, ideally while you are not in the room.
Where can I get more help/advice?
As ever, speak to your doctor if you are concerned this may be affecting you. You can also find a lot of resources via the COPD Foundation’s website.
Take care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Don’t smoke. Just don’t.