What’s the difference between burnout and depression?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If your summer holiday already feels like a distant memory, you’re not alone. Burnout – a state of emotional, physical and mental exhaustion following prolonged stress – has been described in workplaces since a 5th century monastery in Egypt.
Burnout and depression can look similar and are relatively common conditions. It’s estimated that 30% of the Australian workforce is feeling some level of burnout, while almost 20% of Australians are diagnosed with depression at some point in their lives.
So what’s the difference between burnout and depression?
Burnout is marked by helplessness and depression by hopelessness. They can have different causes and should also be managed differently.

What is burnout?
The World Health Organization defines burnout as an “occupational phenomenon” resulting from excessively demanding workload pressures. While it is typically associated with the workplace, carers of children or elderly parents with demanding needs are also at risk.
Our research created a set of burnout symptoms we captured in the Sydney Burnout Measure to assist self-diagnosis and clinicians undertaking assessments. They include:
- exhaustion as the primary symptom
- brain fog (poor concentration and memory)
- difficulty finding pleasure in anything
- social withdrawal
- an unsettled mood (feeling anxious and irritable)
- impaired work performance (this may be result of other symptoms such as fatigue).
People can develop a “burning out” phase after intense work demands over only a week or two. A “burnout” stage usually follows years of unrelenting work pressure.
What is depression?
A depressive episode involves a drop in self-worth, increase in self-criticism and feelings of wanting to give up. Not everyone with these symptoms will have clinical depression, which requires a diagnosis and has an additional set of symptoms.
Clinically diagnosed depression can vary by mood, how long it lasts and whether it comes back. There are two types of clinical depression:
- melancholic depression has genetic causes, with episodes largely coming “out of the blue”
- non-melancholic depression is caused by environmental factors, often triggered by significant life events which cause a drop in self-worth.
When we created our burnout measure, we compared burnout symptoms with these two types of depression.
Burnout shares some features with melancholic depression, but they tend to be general symptoms, such as feeling a loss of pleasure, energy and concentration skills.
We found there were more similarities between burnout and non-melancholic (environmental) depression. This included a lack of motivation and difficulties sleeping or being cheered up, perhaps reflecting the fact both have environmental causes.
Looking for the root cause
The differences between burnout and depression become clearer when we look at why they happen.
Personality comes into play. Our work suggests a trait like perfectionism puts people at a much higher risk of burnout. But they may be less likely to become depressed as they tend to avoid stressful events and keep things under control.

Those with burnout generally feel overwhelmed by demands or deadlines they can’t meet, creating a sense of helplessness.
On the other hand, those with depression report lowered self-esteem. So rather than helpless they feel that they and their future is hopeless.
However it is not uncommon for someone to experience both burnout and depression at once. For example, a boss may place excessive work demands on an employee, putting them at risk of burnout. At the same time, the employer may also humiliate that employee and contribute to an episode of non-melancholic depression.
What can you do?
A principal strategy in managing burnout is identifying the contributing stressors. For many people, this is the workplace. Taking a break, even a short one, or scheduling some time off can help.
Australians now have the right to disconnect, meaning they don’t have to answer work phone calls or emails after hours. Setting boundaries can help separate home and work life.
Burnout can be also be caused by compromised work roles, work insecurity or inequity. More broadly, a dictatorial organisational structure can make employees feel devalued. In the workplace, environmental factors, such as excessive noise, can be a contributor. Addressing these factors can help prevent burnout.
As for managing symptoms, the monks had the right idea. Strenuous exercise, meditation and mindfulness are effective ways to deal with everyday stress.

Deeper contributing factors, including traits such as perfectionism, should be managed by a skilled clinical psychologist.
For melancholic depression, clinicians will often recommend antidepressant medication.
For non-melancholic depression, clinicians will help address and manage triggers that are the root cause. Others will benefit from antidepressants or formal psychotherapy.
While misdiagnosis between depression and burnout can occur, burnout can mimic other medical conditions such as anemia or hypothyroidism.
For the right diagnosis, it’s best to speak to your doctor or clinician who should seek to obtain a sense of “the whole picture”. Only then, once a burnout diagnosis has been affirmed and other possible causes ruled out, should effective support strategies be put in place.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Correction: This article originally stated that depression is marked by helplessness and burnout by hopelessness, when in fact it is vice versa. This has been amended.
Gordon Parker, Scientia Professor of Psychiatry, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Sweetener That Interferes With Hunger/Satiety Signals
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Non-sugar sweeteners came under fire from the World Health Organization a couple of years ago:
The Problem With Sweeteners ← this is mostly about how they prompt cravings of increasingly sweeter foods/drinks, but there are other considerations discussed too
And sucralose (which is technically a sugar, but isn’t processed by the body as sugar, so it “doesn’t count” as such; the body treats it as a dietary fiber instead) got some bad press of its own:
The Sucralose News: Scaremongering Or Serious? ← the answer is both, by the way, but there’s nuance here, so do read the article!
And now, there’s more news about how sucralose specifically interferes with the brain’s hunger/satiety signals:
The study
A medium-sized (n=75) study of adults looked at the brain’s responses to, varyingly,
- Water
- Sucralose in water
- Sucrose in water (matched to be the same sweetness as the sucralose)
…using MRI, focusing on hunger-related regions like the hypothalamus.
Additionally, blood samples were taken to measure glucose, insulin, and satiety hormone (GLP-1) levels.
As for what they found:
- Sucralose kept hunger signals active in the brain for up to 35 minutes, unlike sucrose, which reduced hunger activity quickly.
- There was increased hypothalamic blood flow after sucralose intake, which meant heightened hunger signaling.
- Participants felt hungrier after consuming sucralose compared to sugar
- Sugar intake increased blood glucose (obviously), suppressing hunger, whereas sucralose had no such effect (again, reasonable, though it was worth checking, because if sucralose had an effect on insulin response, that would indirectly affect blood sugar levels one way or the other, depending on the effect on insulin levels—but that didn’t happen, so for now we may assume sucralose doesn’t affect insulin or insulin signalling).
- Women exhibited twice the hypothalamic response to sucralose compared to men, reinforcing sex-based differences in appetite control. Specifically, it was most likely hormonal differences that drove this, since the study’s participants were young adults (ages 18–35); it’s possible that if older adults had been included, untreated menopause could have changed these stats. But that latter’s just a hypothesis for now.
- Sucralose enhanced brain connectivity between the hypothalamus and motivation/reward-processing areas, potentially increasing cravings.
You can read the paper itself here:
The practical takeaway? Sucralose interferes with the brain’s “full” signals, keeping you hungrier for longer, which will (all else being equal) incline you to eat more than you would otherwise.
So, it might be worth skipping sucralose, unless you specifically want to increase how much you eat.
Want to learn more?
You might want to check out:
Carbonated Water: For Weight Loss, Satiety, Or Just Gas?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Cancer is increasingly survivable – but it shouldn’t depend on your ability to ‘wrangle’ the health system
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One in three of us will develop cancer at some point in our lives. But survival rates have improved to the point that two-thirds of those diagnosed live more than five years.
This extraordinary shift over the past few decades introduces new challenges. A large and growing proportion of people diagnosed with cancer are living with it, rather than dying of it.
In our recently published research we examined the cancer experiences of 81 New Zealanders (23 Māori and 58 non-Māori).
We found survivorship not only entailed managing the disease, but also “wrangling” a complex health system.
Surviving disease or surviving the system
Our research focused on those who had lived longer than expected (four to 32 years since first diagnosis) with a life-limiting or terminal diagnosis of cancer.
Common to many survivors’ stories was the effort it took to wrangle the system or find others to advocate on their behalf, even to get a formal diagnosis and treatment.
By wrangling we refer to the practices required to traverse complex and sometimes unwelcoming systems. This is an often unnoticed but very real struggle that comes on top of managing the disease itself.
The common focus of the healthcare system is on symptoms, side effects of treatment and other biological aspects of cancer. But formal and informal care often falls by the wayside, despite being key to people’s everyday experiences.
Survival is often linked to someone’s social connections and capacity to access funds. Getty Images The inequities of cancer survivorship are well known. Analyses show postcodes and socioeconomic status play a strong role in the prevalence of cancer and survival.
Less well known, but illustrated in our research, is that survival is also linked to people’s capacity to manage the entire healthcare system. That includes accessing a diagnosis or treatment, or identifying and accessing alternative treatments.
Survivorship is strongly related to material resources, social connections, and understandings of how the health system works and what is available. For instance, one participant who was contemplating travelling overseas to get surgery not available in New Zealand said:
We don’t trust the public system. So thankfully we had private health insurance […] But if we went overseas, health insurance only paid out to $30,000 and I think the surgery was going to be a couple of hundred thousand. I remember Dad saying and crying and just being like, I’ll sell my business […] we’ll all put in money. It was really amazing.
Assets of survivorship
In New Zealand, the government agency Pharmac determines which medications are subsidised. Yet many participants were advised by oncologists or others to “find ways” of taking costly, unsubsidised medicines.
This often meant finding tens of thousands of dollars with no guarantees. Some had the means, but for others it meant drawing on family savings, retirement funds or extending mortgages. This disproportionately favours those with access to assets and influences who survives.
But access to economic capital is only one advantage. People also have cultural resources – often described as cultural capital.
In one case, a participant realised a drug company was likely to apply to have a medicine approved. They asked their private oncologist to lobby on their behalf to obtain the drug through a compassionate access scheme, without having to pay for it.
Others gained community support through fundraising from clubs they belonged to. But some worried about where they would find the money, or did not want to burden their community.
I had my doctor friend and some others that wanted to do some public fundraising. But at the time I said, “Look, most of the people that will be contributing are people from my community who are poor already, so I’m not going to do that option”.
Accessing alternative therapies, almost exclusively self-funded, was another layer of inequity. Some felt forced to negotiate the black market to access substances such as marijuana to treat their cancer or alleviate the side effects of orthodox cancer treatment.
Cultural capital is not a replacement for access to assets, however. Māori survivorship was greatly assisted by accessing cultural resources, but often limited by lack of material assets.
Persistence pays
The last thing we need when faced with the possibility of cancer is to have to push for formal diagnosis and care. Yet this was a common experience.
One participant was told nothing could be found to explain their abdominal pain – only to find later they had pancreatic cancer. Another was told their concerns about breathing problems were a result of anxiety related to a prior mental health history, only to learn later their earlier breast cancer had spread to their lungs.
Persistence is another layer of wrangling and it often causes distress.
Once a diagnosis was given, for many people the public health system kicked in and delivered appropriate treatment. However, experiences were patchy and variable across New Zealand.
Issues included proximity to hospitals, varying degrees of specialisation available, and the requirement of extensive periods away from home and whānau. This reflects an ongoing unevenness and lack of fairness in the current system.
When facing a terminal or life-limiting diagnosis, the capacity to wrangle the system makes a difference. We shouldn’t have to wrangle, but facing this reality is an important first step.
We must ensure it doesn’t become a continuing form of inequity, whereby people with access to material resources and social and cultural connections can survive longer.
Kevin Dew, Professor of Sociology, Te Herenga Waka — Victoria University of Wellington; Alex Broom, Professor of Sociology & Director, Sydney Centre for Healthy Societies, University of Sydney; Chris Cunningham, Professor of Maori & Public Health, Massey University; Elizabeth Dennett, Associate Professor in Surgery, University of Otago; Kerry Chamberlain, Professor of Social and Health Psychology, Massey University, and Richard Egan, Associate Professor in Health Promotion, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How does cancer spread to other parts of the body?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All cancers begin in a single organ or tissue, such as the lungs or skin. When these cancers are confined in their original organ or tissue, they are generally more treatable.
But a cancer that spreads is much more dangerous, as the organs it spreads to may be vital organs. A skin cancer, for example, might spread to the brain.
This new growth makes the cancer much more challenging to treat, as it can be difficult to find all the new tumours. If a cancer can invade different organs or tissues, it can quickly become lethal.
When cancer spreads in this way, it’s called metastasis. Metastasis is responsible for the majority (67%) of cancer deaths.
Cells are supposed to stick to surrounding tissue
Our bodies are made up of trillions of tiny cells. To keep us healthy, our bodies are constantly replacing old or damaged cells.
Each cell has a specific job and a set of instructions (DNA) that tells it what to do. However, sometimes DNA can get damaged.
This damage might change the instructions. A cell might now multiply uncontrollably, or lose a property known as adherence. This refers to how sticky a cell is, and how well it can cling to other surrounding cells and stay where it’s supposed to be.
If a cancer cell loses its adherence, it can break off from the original tumour and travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to almost anywhere. This is how metastasis happens.
Many of these travelling cancer cells will die, but some will settle in a new location and begin to form new cancers.
Some cells settle in a new location.
Scipro/ShutterstockParticular cancers are more likely to metastasise to particular organs that help support their growth. Breast cancers commonly metastasise to the bones, liver, and lungs, while skin cancers like melanomas are more likely to end up in the brain and heart.
Unlike cancers which form in solid organs or tissues, blood cancers like leukaemia already move freely through the bloodstream, but can escape to settle in other organs like the liver or brain.
When do cancers metastasise?
The longer a cancer grows, the more likely it is to metastasise. If not caught early, a patient’s cancer may have metastasised even before it’s initially diagnosed.
Metastasis can also occur after cancer treatment. This happens when cancer cells are dormant during treatment – drugs may not “see” those cells. These invisible cells can remain hidden in the body, only to wake up and begin growing into a new cancer months or even years later.
For patients who already have cancer metastases at diagnosis, identifying the location of the original tumour – called the “primary site” – is important. A cancer that began in the breast but has spread to the liver will probably still behave like a breast cancer, and so will respond best to an anti-breast cancer therapy, and not anti-liver cancer therapy.
As metastases can sometimes grow faster than the original tumour, it’s not always easy to tell which tumour came first. These cancers are called “cancers of unknown primary” and are the 11th most commonly diagnosed cancers in Australia.
One way to improve the treatment of metastatic cancer is to improve our ways of detecting and identifying cancers, to ensure patients receive the most effective drugs for their cancer type.
What increases the chances of metastasis and how can it be prevented?
If left untreated, most cancers will eventually acquire the ability to metastasise.
While there are currently no interventions that specifically prevent metastasis, cancer patients who have their tumours surgically removed may also be given chemotherapy (or other drugs) to try and weed out any hidden cancer cells still floating around.
The best way to prevent metastasis is to diagnose and treat cancers early. Cancer screening initiatives such as Australia’s cervical, bowel, and breast cancer screening programs are excellent ways to detect cancers early and reduce the chances of metastasis.
The best way to prevent cancer spreading is to diagnose and treat them early.
Peakstock/ShutterstockNew screening programs to detect cancers early are being researched for many types of cancer. Some of these are simple: CT scans of the body to look for any potential tumours, such as in England’s new lung cancer screening program.
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to help examine patient scans is also possible, which might identify new patterns that suggest a cancer is present, and improve cancer detection from these programs.
More advanced screening methods are also in development. The United States government’s Cancer Moonshot program is currently funding research into blood tests that could detect many types of cancer at early stages.
One day there might even be a RAT-type test for cancer, like there is for COVID.
Will we be able to prevent metastasis in the future?
Understanding how metastasis occurs allows us to figure out new ways to prevent it. One idea is to target dormant cancer cells and prevent them from waking up.
Directly preventing metastasis with drugs is not yet possible. But there is hope that as research efforts continue to improve cancer therapies, they will also be more effective at treating metastatic cancers.
For now, early detection is the best way to ensure a patient can beat their cancer.
Sarah Diepstraten, Senior Research Officer, Blood Cells and Blood Cancer Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and John (Eddie) La Marca, Senior Resarch Officer, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Lymphatic System Against Cancer & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ask Not What Your Lymphatic System Can Do For You…
Just kidding; we’ll cover that first, as it’s definitely not talked about enough.
The lymphatic system is the system in the body that moves lymph around. It’s made of glands, nodes, and vessels:
- The glands (such as the tonsils and the adenoids) and nodes filter out bacteria and produce white blood cells. Specific functions may be, well, specialized—beyond the scope of today’s article—but that’s the broad function.
- The vessels are the tubes that allow those things to be moved around, suspended in lymph.
What’s lymph? It’s a colorless water-like liquid that transports immune cells, nutrients (and waste) around the body (through the lymphatic system).
Yes, it works alongside your vasculature; when white blood cells aren’t being deployed en masse into your bloodstream to deal with some threat, they’re waiting in the wings in the lymphatic system.
While your blood is pumped around by your heart, lymph moves based on a variety of factors, including contractions of small specialized lymphatic muscles, the pressure gradient created by the combination of those and gravity, and the movements of your body itself.
Here’s a larger article than we have room for, with diagrams we also don’t have room for:
Modelling the lymphatic system
To oversimplify it in few words for the sake of moving on: you can most of the time: think of it as an ancillary network supporting your circulatory system that unlike blood, doesn’t deal with oxygen or sugars, but does deal with a lot of other things, including:
- water and salt balance
- immune cells and other aspects of immune function
- transports fats (and any fat-soluble vitamins in them) into circulation
- cleans up stuff that gets stuck between cells
- general detoxification
There’s a lot that can go wrong if lymph isn’t flowing as it should
Too much to list here, but to give an idea:
- Arthritis and many autoimmune diseases
- Cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome
- Obesity, diabetes, and organ failure
- Alzheimer’s and other dementias
- Lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, and lymphedenopathy
- Lymphomas and Hodgkin’s disease (both are types of lymphatic cancer)
- Cancers of other kinds, because of things not being cleaned up where and when they should be
Yikes! That’s a lot of important things for a mostly-forgotten system to be taking care of protecting us from!
What you can do for your lymphatic system, to avoid those things!
Happily, there are easy things we can do to give our lymph some love, such as:
Massage therapy (and foam rolling)
This is the go-to that many people/publications recommend. It’s good! It’s certainly not the most important thing to do, but it’s good.
You can even use a simple gadget like this one to help move the lymph around, without needing to learn arcane massage techniques.
Exercise (move your body!)
This is a lot more important. The more we move our body, the more lymph moves around. The more lymph moves around today, the more easily it will move around tomorrow. A healthy constant movement of lymph throughout the lymphatic system is key to keeping everything running smoothly.
If you pick only one kind of exercise, make it High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
If for some reason you really can’t do that, just spend as much of your waking time as reasonably possible, moving, per:
For ideas on how to do that, check out…
Get thee to a kitchen
This is about getting healthy food that gives your body’s clean-up crew (the lymphatic system) an easier time of it.
Rather than trying to “eat clean” which can be a very nebulous term and it’s often not at all clear (and/or hotly debated) what counts as “clean”, instead, stick to foods that constitute an anti-inflammatory diet:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
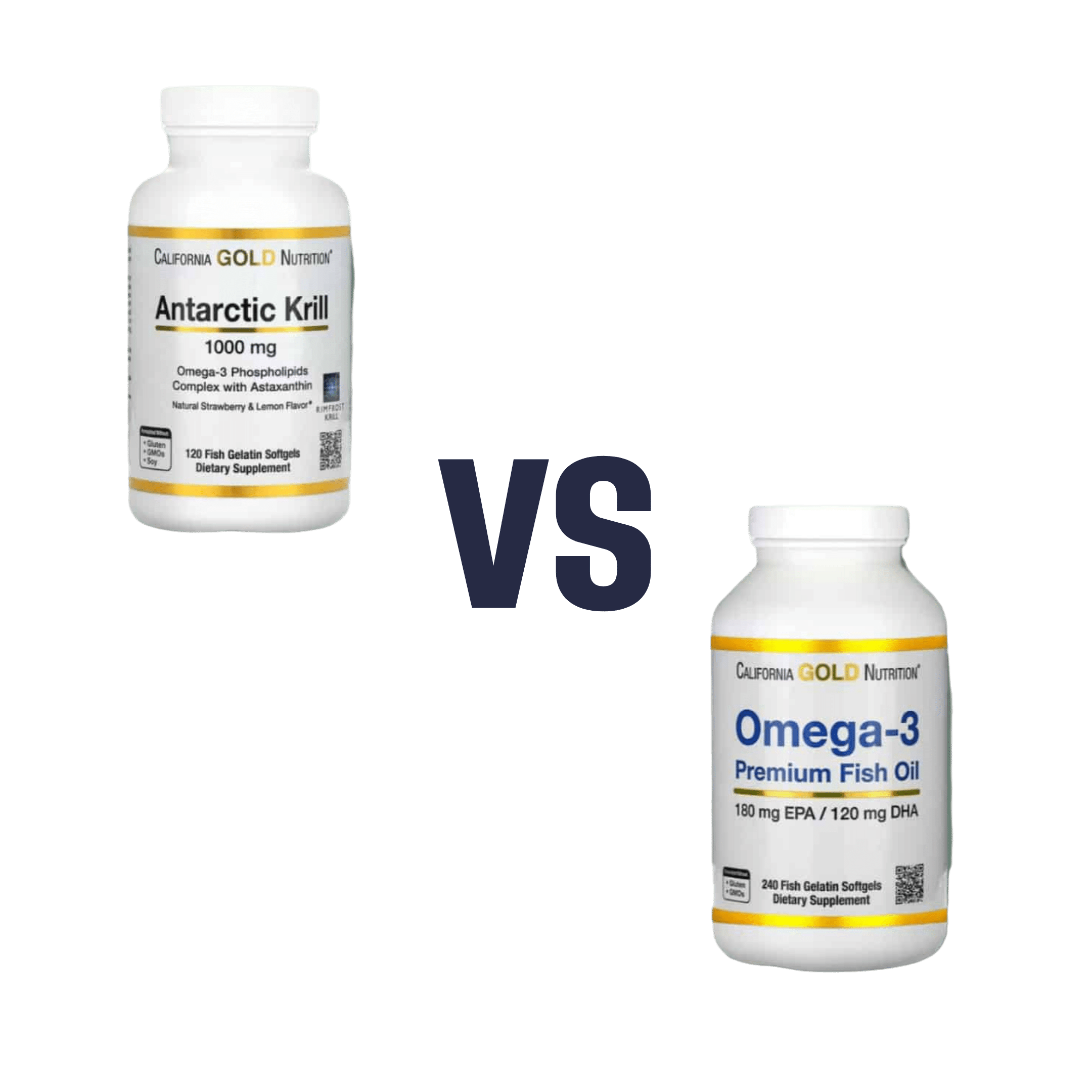
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing krill oil to fish oil, we picked the krill oil.
Why?
Both of these products are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and for the specific brand depicted above, in both cases 2 softgels will give you the recommended daily amount (which is generally held to be 250–500mg combined omega-3s per day).
This brand’s fish oil gives more (640mg combined omega-3s per 2 softgels, to the same brand’s krill oil’s 480mg per 2 softgels), but since the krill oil is already in the high end of RDA territory, the excess beyond the RDA is not helpful, and not a huge factor. More quantity is not always better, when the body can only process so much at a time.
However, the krill oil gives some extra things that the fish oil doesn’t:
- Astaxanthin, a “super-antioxidant”
- and neuroprotectant, heart-healthy phospholipids
Additional considerations
We have declared “the winner” based on health considerations only. That’s a sticking point for us in all our writings; we’ll occasionally look at and mention other factors, but we know that health is what you’re here for, so that’s what we’ll always treat as most critical.
However, in case these factors may interest you and/or influence you to one or the other:
• The fish oil is about 30% cheaper financially
• The krill oil is a lot more sustainable environmentallyBack to the health science…
Read more:
• What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
• Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & NeuroprotectantWant some? Here for your convenience are some example products on Amazon:
(brands available will vary per region, but now you know what to look out for on the labels!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Wandering Mind – by Dr. Michael Corballis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our mind’s tendency to wander can be a disability, but could it also be a superpower? Dr. Corballis makes the case for such.
While many authors focus on, well, how to focus, Dr. Corballis argues in this book that our wandering imagination can be more effective at problem-solving and creative tasks, than a focused, blinkered mind.
The book’s a quick read (184 pages of quite light reading), and yet still quite dense with content. He takes us on a tour of the brain, theory of mind, the Default Mode Network (where a lot of the brain’s general ongoing organization occurs), learning, memory, forgetting, and creativity.
Furthermore, he cites (and explains) studies showing what kinds of “breaks” from mental work allow the wandering mind to do its thing at peak efficiency, and what kinds of breaks are counterproductive. Certainly this has practical applications for all of us!
Bottom line: if you’d like to be less frustrated by your mind’s tendency to wander, this is a fine book to show how to leverage that trait to your benefit.
Click here to check out The Wandering Mind, and set yours onto more useful tracks!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: