Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
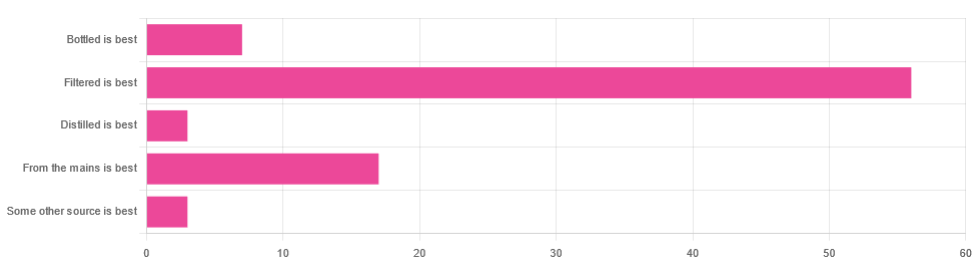
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Kidney Beans or Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kidney beans to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
First, do note that black beans are also known as turtle beans, or if one wants to hedge one’s bets, black turtle beans. It’s all the same bean. As a small linguistic note, kidney beans are known as “red beans” in many languages, so we could have called this “red beans vs black beans”, but that wouldn’t have landed so well with our largely anglophone readership. So, kidney beans vs black beans it is!
They’re certainly both great, and this is a close one today…
In terms of macros, they’re equal on protein and black beans have more carbs and/but also more fiber. So far, so equal—or rather, if one pulls ahead of the other here, it’s a matter of subjective priorities.
In the category of vitamins, they’re equal on vitamins B2, B3, and choline, while kidney beans have more of vitamins B6, B9, C, and K, and black beans have more of vitamins A, B1, B5, and E. In other words, the two beans are still tied with a 4:4 split, unless we want to take into account that that vitamin E difference is that black beans have 29x more vitamin E, in which case, black beans move ahead.
When it comes to minerals, finally the winner becomes apparent; while kidney beans have a little more manganese and zinc, on the other hand black beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. However, it should be noted that honestly, the margins aren’t huge here and kidney beans are almost as good for all of these minerals.
In short, black beans win the day, but kidney beans are very close behind, so enjoy whichever you prefer, or better yet, both! They go great together in tacos, burritos, or similar, by the way.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Kidney Beans vs Fava Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Bold Beans – by Amelia Christie-Miller ← this is a recipe book; if you’re looking to incorporate more beans into your diet and want to make it good, this cookbook can lead the way!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Balanced Energy Cake Bars
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Unlike a lot of commercially available products, these bars won’t spike your blood sugars in the same way. There’s technically plenty of sugar in them, mostly from the chopped dates, but they’re also full of fiber, protein, and healthy fats. This means they can give you an energy boost (along with lots of gut-healthy, heart-healthy, and brain-healthy ingredients) without any crash later. They’re also delicious, and make for a great afternoon snack!
You will need
- 1 cup oats
- 15 Medjool dates, pitted and soaked in hot water for 15 minutes
- 3 carrots, grated
- 4oz almond butter
- 2 tbsp tahini
- 2 tbsp flaxseeds, milled
- 1 tbsp sesame seeds, toasted
- Optional: your choice of dried fruit and/or chopped nuts (mix it up; diversity is good!)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the grated carrots for 3–4 minutes; pat dry and allow to cool
2) Drain and pat dry the dates, roughly chop them and add them to a bowl with the carrots. Because we chopped the dates rather than blended them (as many recipes do), they keep their fiber, which is important.
3) Add the oats, seeds, almond butter, and tahini. Also add in any additional dried fruit and/or chopped nuts you selected for the optional part. Mix well; the mixture should be quite firm. If it isn’t, add more oats.
4) Press the mixture into a 10″ square baking tin lined with baking paper. Refrigerate for a few hours, before cutting into bar shapes (or squares if you prefer). These can now be eaten immediately or stored for up to a week.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
PlantYou: Scrappy Cooking – by Carleigh Bodrug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book that took “whole foods plant-based diet” and ran with it.
“Whole foods”, you say? Carleigh Bodrug has you covered in this guide to using pretty much everything.
One of the greatest strengths of the book is its “Got this? Make that” section, for using up those odds and ends that you’d normally toss.
You may be thinking: “ok, but if to use this unusual ingredient I have to buy four other ingredients to make this recipe, generating waste from those other ingredients, then this was a bad idea”, but fear not.
Bodrug covers that too, and in many cases leftover “would get wasted” ingredients can get turned into stuff that can go into longer-term storage one way or another, to use at leisure.
Which also means that on the day “there’s nothing in the house to eat” and you don’t want to go grocery-shopping, or if some global disaster causes the supply lines to fail and the stores become empty (that could never happen though, right?), you will have the mystical ability to conjure a good meal out of assorted odds and ends that you stored because of this book.
Bottom line: if you love food and hate food waste, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out Scrappy Cooking, and do domestic magic!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Fasting, eating earlier in the day or eating fewer meals – what works best for weight loss?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Globally, one in eight people are living with obesity. This is an issue because excess fat increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease and certain cancers.
Modifying your diet is important for managing obesity and preventing weight gain. This might include reducing your calorie intake, changing your eating patterns and prioritising healthy food.
But is one formula for weight loss more likely to result in success than another? Our new research compared three weight-loss methods, to see if one delivered more weight loss than the others:
- altering calorie distribution – eating more calories earlier rather than later in the day
- eating fewer meals
- intermittent fasting.
We analysed data from 29 clinical trials involving almost 2,500 people.
We found that over 12 weeks or more, the three methods resulted in similar weight loss: 1.4–1.8kg.
So if you do want to lose weight, choose a method that works best for you and your lifestyle.
chalermphon_tiam/Shutterstock Eating earlier in the day
When our metabolism isn’t functioning properly, our body can’t respond to the hormone insulin properly. This can lead to weight gain, fatigue and can increase the risk of a number of chronic diseases such as diabetes.
Eating later in the day – with a heavy dinner and late-night snacking – seems to lead to worse metabolic function. This means the body becomes less efficient at converting food into energy, managing blood sugar and regulating fat storage.
In contrast, consuming calories earlier in the day appears to improve metabolic function.
However, this might not be the case for everyone. Some people naturally have an evening “chronotype”, meaning they wake up and stay up later.
People with this chronotype appear to have less success losing weight, no matter the method. This is due to a combination of factors including genes, an increased likelihood to have a poorer diet overall and higher levels of hunger hormones.
Eating fewer meals
Skipping breakfast is common, but does it hinder weight loss? Or is a larger breakfast and smaller dinner ideal?
While frequent meals may reduce disease risk, recent studies suggest that compared to eating one to two meals a day, eating six times a day might increase weight loss success.
However, this doesn’t reflect the broader research, which tends to show consuming fewer meals can lead to greater weight loss. Our research suggests three meals a day is better than six. The easiest way to do this is by cutting out snacks and keeping breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Most studies compare three versus six meals, with limited evidence on whether two meals is better than three.
However, front-loading your calories (consuming most of your calories between breakfast and lunch) appears to be better for weight loss and may also help reduce hunger across the day. But more studies with a longer duration are needed.
Fasting, or time-restricted eating
Many of us eat over a period of more than 14 hours a day.
Eating late at night can throw off your body’s natural rhythm and alter how your organs function. Over time, this can increase your risk of type 2 diabetes and other chronic diseases, particularly among shift workers.
Time-restricted eating, a form of intermittent fasting, means eating all your calories within a six- to ten-hour window during the day when you’re most active. It’s not about changing what or how much you eat, but when you eat it.
Some people limit their calories to a six hour window, while others opt for ten hours. Shutterstock/NIKS ADS Animal studies suggest time-restricted eating can lead to weight loss and improved metabolism. But the evidence in humans is still limited, especially about the long-term benefits.
It’s also unclear if the benefits of time-restricted eating are due to the timing itself or because people are eating less overall. When we looked at studies where participants ate freely (with no intentional calorie limits) but followed an eight-hour daily eating window, they naturally consumed about 200 fewer calories per day.
What will work for you?
In the past, clinicians have thought about weight loss and avoiding weight gain as a simile equation of calories in and out. But factors such as how we distribute our calories across the day, how often we eat and whether we eat late at night may also impact our metabolism, weight and health.
There are no easy ways to lose weight. So choose a method, or combination of methods, that suits you best. You might consider
- aiming to eat in an eight-hour window
- consuming your calories earlier, by focusing on breakfast and lunch
- opting for three meals a day, instead of six.
The average adult gains 0.4 to 0.7 kg per year. Improving the quality of your diet is important to prevent this weight gain and the strategies above might also help.
Finally, there’s still a lot we don’t know about these eating patterns. Many existing studies are short-term, with small sample sizes and varied methods, making it hard to make direct comparisons.
More research is underway, including well-controlled trials with larger samples, diverse populations and consistent methods. So hopefully future research will help us better understand how altering our eating patterns can result in better health.
Hayley O’Neill, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University and Loai Albarqouni, Assistant Professor | NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop The World…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some news highlights from this week:
“US vs Them”?
With the US now set to lose its WHO membership, what does that mean for Americans? For most, the consequences will be indirect:
- the nation’s scientists and institutions will be somewhat “left out in the cold” when it comes to international scientific collaboration in the field of health
- the US will no longer enjoy a position of influence and power within the WHO, which organization’s reports and position statements have a lot of sway over the world’s health practices
Are there any benefits (of leaving the WHO) for Americans? Yes, there is one: the US will no longer be paying into the WHO’s budget, which means:
- the US will save the 0.006% of the Federal budget that it was paying into the WHO annually
- for the average American’s monthly budget, that means (if the saving is passed on) you’ll have an extra dime
However, since US scientific institutions will still need access to international data, likely that access will need to be paid separately, at a higher rate than US membership in WHO cost.
In short: it seems likely to go the way that Brexit did: “saving” on membership fees and then paying more for access to less.
Why is the US leaving again? The stated reasons were mainly twofold:
- the cost of US membership (the US’s contribution constituted 15% of the the overall WHO budget)
- holding the US’s disproportionately high COVID death rate (especially compared to countries such as China) to be a case of WHO mismanagement
Read in full: What losing WHO membership means for the U.S.
Related: What Would a Second Trump Presidency Look Like for Health Care? ← this was a speculative post by KFF Health News, last year
Halt, You’re Under A Breast
More seriously, this is about halting the metastasis of cancerous tumors in the breast. It is reasonable to expect the same principle and thus treatment may apply to other cancers too, but this is where the research is at for now (breast cancer research gets a lot of funding).
And, what principle and treatment is this, you ask? It’s about the foxglove-derived drug digoxin, and how it stops cancerous cells from forming clusters, and even actively dissolves clusters that have already formed. No clusters means no new tumors, which means no metastasis. No metastasis, in turn, means the cancer becomes much more treatable because it’s no longer a game of whack-a-mole; instead of spreading to other places, it’s a much more manageable case of “here’s the tumor, now let’s kill it with something”.
Note: yes, that does mean the tumor still needs killing by some other means—digoxin won’t do that, it “just” stops it from spreading while treatment is undertaken.
Read in full: Proof-of-concept study dissolves clusters of breast cancer cells to prevent metastases
Related: The Hormone Therapy That Reduces Breast Cancer Risk & More
Force Of Habit
“It takes 21 days to make a habit”, says popular lore. Popular is not, however, evidence-based:
❝This systematic review of 20 studies involving 2601 participants challenges the prevailing notion of rapid habit formation, revealing that health-related habits typically require 2–5 months to develop, with substantial individual variability ranging from 4 to 335 days. The meta-analysis demonstrated significant improvements in habit scores across various health behaviours, with key determinants including morning practices, personal choice, and behavioural characteristics❞
So, this is not a lottery, “maybe it will take until Tuesday, maybe it will take nearly a year”, so much as “there are important factors that seriously change how long a habit takes to become engrained, and here is what those factors are”.
Read in full: Study reveals healthy habits take longer than 21 days to set in
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Can You Reverse Gray Hair? A Dermatologist Explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Betteridge’s Law of Headlines states “any headline that ends in a question mark can be answered by the word no“—it’s not really a universal truth, but it’s true surprisingly often, and, as board certified dermatologist “The Beauty MD” Dr. Sam Ellis explains, it’s true in this case.
But, all is not lost.
Physiological Factors
Hair color is initially determined by genes and gene expression, instructing the body to color it with melanin (brown and black) and/or pheomelanin (blonde and red). If and when the body produces less of those pigments, our hair will go gray.
Factors that affect if/when our hair will go gray include:
- Genetics: primary determinant, essentially a programmed change
- Age: related to the above, but critically, the probability of going gray in any given year increases with age
- Ethnicity: the level of melanin in our skin is an indicator of how long we are likely to maintain melanin in our hair. Black people with the darkest skintones will thus generally go gray last, whereas white people with the lightest skintones will generally go gray first, and so on for a spectrum between the two.
- Medical conditions: immune conditions such as vitiligo, thyroid disease, and pernicious anemia promote an earlier loss of pigmentation
- Stress: oxidative stress, mainly, so factors like smoking will cause earlier graying. But yes, also chronic emotional stress does lead to oxidative stress too. Interestingly, this seems to be more about norepinephrine than cortisol, though.
- Nutrient deficiencies: the body can make a lot of things, but it needs the raw ingredients. Not having the right amounts of important vitamins and minerals will result in a loss of pigmentation (amongst other more serious problems). Vitamins B6, B9, and B12 are talked about in the video, as are iron and zinc. Copper is also needed for some hair colors. Selenium is needed for good hair health in general (but not too much, as an excess of selenium paradoxically causes hair loss), and many related things will stop working properly without adequate magnesium. Hair health will also benefit a lot from plenty of vitamin B7.
So, managing the above factors (where possible; obviously some of the above aren’t things we can influence) will result in maintaining one’s hair pigment for longer. As for texture, by the way, the reason gray hair tends to have a rougher texture is not for the lack of pigment itself, but is due to decreased sebum production. Judicious use of exogenous hair oils (e.g. argan oil, coconut oil, or whatever your preference may be) is a fine way to keep your grays conditioned.
However, once your hair has gone gray, there is no definitive treatment with good evidence for reversing that, at present. Dye it if you want to, or don’t. Many people (including this writer, who has just a couple of streaks of gray herself) find gray hair gives a distinguished look, and such harmless signs of age are a privilege not everyone gets to reach, and thus may be reasonably considered a cause for celebration
For more on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: