Vodka vs Beer – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing vodka to beer, we picked the vodka.
Why?
As you might have guessed, neither are exactly healthy. But one of them is relatively, and we stress relatively, less bad than the other.
In the category of nutrients, vodka is devoid of nutrients, and beer has small amounts of some vitamins and minerals—but the amounts are so small, that you would need to drink yourself to death before benefiting from them meaningfully. And while beer gets touted as “liquid bread”, it really isn’t. A thousand years ago it will have been a lot less alcoholic and more carby, but even then, it wasn’t a health product aside from that it provided a way of making potentially contaminated water safer to drink.
In the category of carbohydrates, vodka nominally has none, due to the distillation process, and beer has some. Glycemic index websites often advise that the GI of beers, wines, and spirits can’t be measured as their carb content is not sufficient to get a meaningful sample, but diabetes research tells a more useful story:
Any alcoholic drink will generally cause a brief drop in blood sugars, followed by a spike. This happens because the liver prioritises metabolizing alcohol over producing glycogen, so it hits pause on the sugar metabolism and then has a backlog to catch up on. In the case of alcoholic drinks that have alcohol and carbs, this will be more pronounced—so this means that the functional glycemic load of beer is higher.
That’s a point in favor of vodka.
Additionally, in terms of the alcohol content, correctly-distilled vodka’s alcohol is pure ethanol, while beer will contain an amount of methanol that will vary per beer, but an illustrative nominal figure could be about 16mg/L. Methanol is more harmful than ethanol.
So that’s another point in favor of vodka.
Once again, neither drink is healthy; both are distinctly unhealthy. But unit for unit, beer is the least healthy of the two, making vodka the lesser of two evils.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health? (answer: we cannot, but this was about alcohol’s proposed heart-healthy benefits)
- Guinness Is Good For You* (it isn’t, but this was the long-time slogan and marketing campaign that fooled many)
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
5 Surprising Benefits Of Exercise After 50 (More Than Just Fitness)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to want to do less as we get older, but the benefits of continuing to actively exercise, pushing oneself even just a little, can be far-reaching.
Direct and indirect benefits
As well as the obvious fitness benefits, keeping up good levels of exercise can also offer:
Healthy Skin
Exercise improves circulation, bringing growth factors (thus: regeneration, because it’s replacing cells), oxygen, and nutrients to the skin. Accordingly, it can lead to healthier, more youthful-looking skin as a low-cost alternative to a lot of skincare products. That said, it also encourages good skin habits, like daily sunscreen use.
Bone Health
Weight-bearing and resistance exercises (which between them, encompasses most forms of exercise) improve bone density. This is because physical stress signals bones to strengthen, reducing the risk of fractures. This includes activities like walking, hiking, and using resistance bands or weights. Note however that it is on a “per bone” basis. So for example, hiking will improve your lower body and spine, but do nothing for your arms. On the other hand, doing a daily groceries trip on foot, if local geography makes that practicable, can do the whole body, if one is then carrying groceries home (this writer lives about 2 miles from where she buys groceries, and does this pretty much daily).
Mental Health
Exercise, especially outdoors, has well-established positive effects on mental well-being, and can relieve stress and improve mood. As a bonus, community engagement and shared experiences can enhance mental health benefits for many people—but if you prefer it as peaceful time for yourself, that’s beneficial in its own way too!
Better Sleep
Physical activity helps promote better sleep quality, which is important for so many aspects of health—because fatiguing the body through exercise can lead to a more restful night, which is often harder to achieve with age.
Visibility and Confidence
Staying active and taking on challenges (e.g. training for some event) can boost visibility in social and family settings, countering “invisibility” often felt from midlife onwards. And even if one doesn’t do those things, exercise fosters confidence and helps people carry themselves with more self-assurance, which has a lot of knock-on benefits too.
For more on all of these things, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Are There Any Sensible Age Limits To Exercise?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Cooling Bulgarian Tarator
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The “Bulgarian” qualifier is important here because the name “tarator” is used to refer to several different dishes from nearby-ish countries, and they aren’t the same. Today’s dish (a very healthy and deliciously cooling cucumber soup) isn’t well-known outside of Bulgaria, but it should be, and with your help we can share it around the world. It’s super-easy and takes only about 10 minutes to prepare:
You will need
- 1 large cucumber, cut into small (¼” x ¼”) cubes or small (1″ x ⅛”) batons (the size is important; any smaller and we lose texture; any larger and we lose the balance of the soup, and also make it very different to eat with a spoon)
- 2 cups plain unsweetened yogurt (your preference what kind; live-cultured of some kind is best, and yes, vegan is fine too)
- 1½ cup water, chilled but not icy (fridge-temperature is great)
- ½ cup chopped walnuts (substitutions are not advised; omit if allergic)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 3 tbsp fresh dill, chopped
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG* or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the cucumber, garlic, 2 tbsp of the dill, oil, MSG-or-salt and pepper in a big bowl
2) Add the yogurt and mix it in too
3) Add the cold water slowly and stir thoroughly; it may take a minute to achieve smooth consistency of the liquid—it should be creamy but thin, and definitely shouldn’t stand up by itself
4) Top with the chopped nuts, and the other tbsp of dill as a garnish
5) Serve immediately, or chill in the fridge until ready to serve. It’s perfect as a breakfast or a light lunch, by the way.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- How To Really Look After Your Joints ← this is about how cucumber has phytochemicals that outperform glucosamine and chondroitin by 200%, at 1/135th of the dose
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Is Dairy Scary? ← short answer in terms of human health is “not if it’s fermented”
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk? ← *for those who are worried about the health aspects of MSG; it is healthier and safer than table salt
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Comfort Book – by Matt Haig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book “is what it says on the tin”. Matt Haig, bestselling author of “Reasons to Stay Alive” (amongst other works) is here with “a hug in a book”.
The format of the book is an “open it at any page and you’ll find something of value” book. Its small chapters are sometimes a few pages long, but often just a page. Sometimes just a line. Always deep.
All of us, who live long enough, will ponder our mortality sometimes. The feelings we may have might vary on a range from “afraid of dying” to “despairing of living”… but Haig’s single biggest message is that life is full of wonder; each moment precious.
- That hope is an incredible (and renewable!) resource.
- That we are more than a bad week, or month, or year, or decade.
- That when things are taken from us, the things that remain have more value.
Bottom line: you might cry (this reviewer did!), but it’ll make your life the richer for it, and remind you—if ever you need it—the value of your amazing life.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Which Style Of Yoga Is Best For You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For you personally, that is—so let’s look at some options, their benefits, and what kind of person is most likely to benefit from each.
Yoga is, of course, an ancient practice, and like any ancient practice, especially one with so many practitioners (and thus also: so many teachers), there are very many branches to the tree of variations, that is to say, different schools and their offshoots.
Since we cannot possibly cover all of them, we’ll focus on five broad types that are popular (and thus, likely available near to you, unless you live in a very remote place):
Hatha Yoga
This is really the broadest of umbrella categories for yoga as a physical practice of the kind that most immediately comes to mind in the west:
- Purpose: energizes the practitioner through controlled postures and breath.
- Practice: non-heated, slow asanas held for about a minute with intentional transitions
- Benefits: reduces stress, improves flexibility, tones muscles, and boosts circulation.
- Best for: beginners with an active lifestyle.
Vinyasa Yoga
You may also have heard of this called simply “Flow”, without reference to the Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi sense of the word. Rather, it is about a flowing practice:
- Purpose: builds heat and strength through continuous, flowing movement paired with breath.
- Practice: dynamic sequences of the same general kind as the sun salutation, leading to a final resting pose.
- Benefits: enhances heart health, strengthens core, tones muscles, and improves flexibility.
- Best for: beginner to intermediate yogis seeking a cardio-based practice.
Hot Yoga
This one’s well-known and the clue is in the name; it’s yoga practised in a very hot room:
- Purpose: uses heat to increase heart rate, and loosen muscles.
- Practice: heated studio (32–42℃, which is 90–108℉), often with vinyasa flows, resulting in heavy sweating*
- Benefits: burns calories, improves mood, enhances skin, and builds bone density.
- Best for: intermediate yogis comfortable with heat; not recommended for certain health conditions.
*and also sometimes heat exhaustion / heat stroke. This problem arises most readily when the ambient temperature is higher than human body temperature, because that is the point at which sweating ceases to fulfil its biological function of cooling us down.
Noteworthily, a study found that doing the same series of yoga postures in the same manner, but without the heat, produced the same health benefits without the risk:
❝The primary finding from this investigation is that the hatha yoga postures in the Bikram yoga series produce similar enhancements in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in healthy, middle-aged adults regardless of environmental temperature. These findings highlight the efficacy of yoga postures in producing improvements in vascular health and downplay the necessity of the heated practice environment in inducing vascular adaptations.❞
(“Bikram yoga” is simply the brand name of a particular school of hot yoga)
Yin Yoga
This is a Chinese variation, and is in some ways the opposite of the more vigorous forms, being gentler in pretty much all ways:
- Purpose: promotes deep tissue stretching and circulation by keeping muscles cool.
- Practice: passive, floor-based asanas held for 5–20 minutes in a calming environment.
- Benefits: increases flexibility, enhances circulation, improves mindfulness, and emotional release.
- Best for: all levels, regardless of health or flexibility.
Restorative Yoga
This is often tailored to a specific condition, but it doesn’t have to be:
- Purpose: encourages relaxation and healing through supported, restful poses.
- Practice: reclined, prop-supported postures in a soothing, low-lit setting.
- Benefits: relieves stress, reduces chronic pain, calms the nervous system, and supports healing.
- Best for: those recovering from illness/injury or managing emotional stress.
See for example: Yoga Therapy for Arthritis: A Whole-Person Approach to Movement and Lifestyle
Want to know more?
If you’re still unsure where to start, check out:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible (from scratch) in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’m feeling run down. Why am I more likely to get sick? And how can I boost my immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It has been a long winter, filled with many viruses and cost-of-living pressures, on top of the usual mix of work, study, life admin and caring responsibilities.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. In short bursts, our stress response has evolved as a survival mechanism to help us be more alert in fight or flight situations.
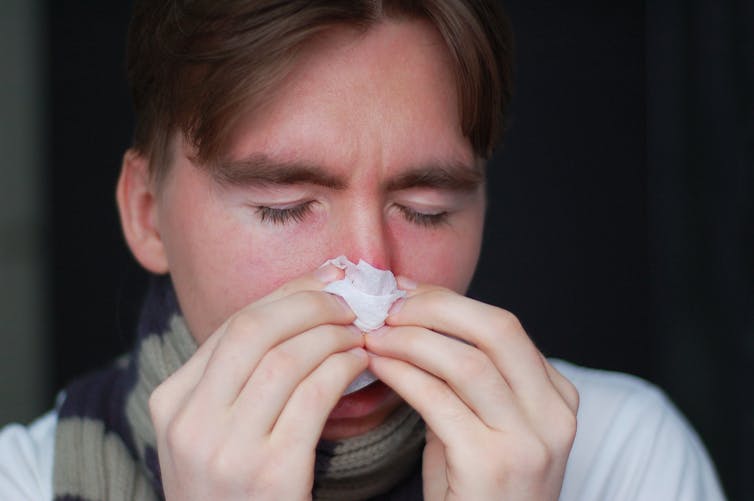
But when stress is chronic, it weakens the immune system and makes us more vulnerable to illnesses such as the common cold, flu and COVID.
Pexels/Ketut Subiyanto Stress makes it harder to fight off viruses
When the immune system starts to break down, a virus that would normally have been under control starts to flourish.
Once you begin to feel sick, the stress response rises, making it harder for the immune system to fight off the disease. You may be sick more often and for longer periods of time, without enough immune cells primed and ready to fight.
In the 1990s, American psychology professor Sheldon Cohen and his colleagues conducted a number of studies where healthy people were exposed to an upper respiratory infection, through drops of virus placed directly into their nose.
These participants were then quarantined in a hotel and monitored closely to determine who became ill.
One of the most important factors predicting who got sick was prolonged psychological stress.
Cortisol suppresses immunity
“Short-term stress” is stress that lasts for a period of minutes to hours, while “chronic stress” persists for several hours per day for weeks or months.
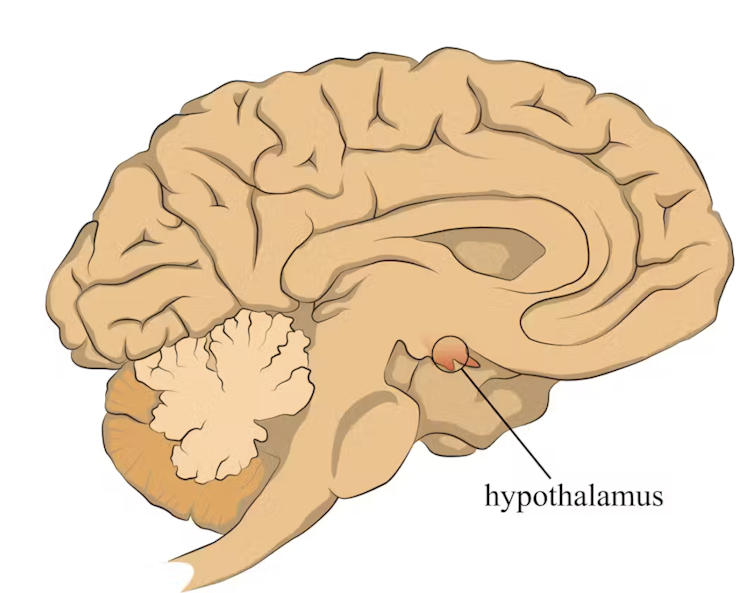
When faced with a perceived threat, psychological or physical, the hypothalamus region of the brain sets off an alarm system. This signals the release of a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol.
The hypothalamus sets off an alarm system in response to a real or perceived threat. stefan3andrei/Shutterstock In a typical stress response, cortisol levels quickly increase when stress occurs, and then rapidly drop back to normal once the stress has subsided. In the short term, cortisol suppresses inflammation, to ensure the body has enough energy available to respond to an immediate threat.
But in the longer term, chronic stress can be harmful. A Harvard University study from 2022 showed that people suffering from psychological distress in the lead up to their COVID infection had a greater chance of experiencing long COVID. They classified this distress as depression, probable anxiety, perceived stress, worry about COVID and loneliness.
Those suffering distress had close to a 50% greater risk of long COVID compared to other participants. Cortisol has been shown to be high in the most severe cases of COVID.
Stress causes inflammation
Inflammation is a short-term reaction to an injury or infection. It is responsible for trafficking immune cells in your body so the right cells are present in the right locations at the right times and at the right levels.
The immune cells also store a memory of that threat to respond faster and more effectively the next time.
Initially, circulating immune cells detect and flock to the site of infection. Messenger proteins, known as pro-inflammatory cytokines, are released by immune cells, to signal the danger and recruit help, and our immune system responds to neutralise the threat.
During this response to the infection, if the immune system produces too much of these inflammatory chemicals, it can trigger symptoms such as nasal congestion and runny nose.
Our immune response can trigger symptoms such as a runny nose. Alyona Mandrik/Shutterstock What about chronic stress?
Chronic stress causes persistently high cortisol secretion, which remains high even in the absence of an immediate stressor.
The immune system becomes desensitised and unresponsive to this cortisol suppression, increasing low-grade “silent” inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (the messenger proteins).
Immune cells become exhausted and start to malfunction. The body loses the ability to turn down the inflammatory response.
Over time, the immune system changes the way it responds by reprogramming to a “low surveillance mode”. The immune system misses early opportunities to destroy threats, and the process of recovery can take longer.
So how can you manage your stress?
We can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by managing our stress levels. Rather than letting stress build up, try to address it early and frequently by:
1) Getting enough sleep
Getting enough sleep reduces cortisol levels and inflammation. During sleep, the immune system releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
2) Taking regular exercise
Exercising helps the lymphatic system (which balances bodily fluids as part of the immune system) circulate and allows immune cells to monitor for threats, while sweating flushes toxins. Physical activity also lowers stress hormone levels through the release of positive brain signals.
3) Eating a healthy diet
Ensuring your diet contains enough nutrients – such as the B vitamins, and the full breadth of minerals like magnesium, iron and zinc – during times of stress has a positive impact on overall stress levels. Staying hydrated helps the body to flush out toxins.
4) Socialising and practising meditation or mindfulness
These activities increase endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood and have anti-inflammatory effects. Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset” and reduce cortisol levels.
Sathana Dushyanthen, Academic Specialist & Lecturer in Cancer Sciences & Digital Health| Superstar of STEM| Science Communicator, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Toe-Tapping Tip For Better Balance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Balance is critical for health especially in older age, since it’s amazing how much else can go dramatically and suddenly wrong after a fall. So, here’s an exercise to give great balance and stability:
How to do it
You will need:
- Something to hold onto, such as a countertop
- A target on the floor, such as a mark or a coin
The steps:
- Lift one leg up, bring your foot forward, and tap the object in front of you.
- Then, bring that foot back to where it started.
- Next, switch to the other leg and tap.
- Alternate between your right and left legs, shifting back and forth.
- Your goal is to do this for 10 repetitions on each leg without holding on.
How it works:
Whenever you tap, you have to lift one leg up and reach it out in front of you. Doing this requires you to stand on one leg while moving a weight (namely: your other leg), which is something many people, especially upon getting older, are hesitant to do. If you’re unable to stand on one leg, let alone move your center of gravity (per the counterbalance of the other leg) while doing so, you may end up shuffling and walking with your feet sliding across the ground—something you really want to avoid.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fall Special ← this is about not falling, or, failing that, minimizing injury if you do
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: