Vegetarian & Vegan Diets: Good Or Bad For Brain Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-established that most people should eat more plants, and generally speaking, less meat. But what about abstaining from meat completely? And what about abstaining from all animal products?
For a more general overview (rather than specifically brain health), check out: Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
Now, about brains…
Before Homo sapiens was a thing, our precursors such as Homo habilis developed language (thus: greatly enhanced collaborative teamwork) and cooking, resulting in Homo ergaster (who came approximately next in line, give or take taxonomical quibbles) having twice the cranial capacity, generally attributed to being able to acquire and—where appropriate—cook calorie-dense food, which included meat, and also tubers that can’t be safely eaten raw. It’s estimated (based on forensic examination of tooth wear, mineralization, microdeposits of various kinds, etc) that our consumption of animal products in that era was around 10% of our diet (fluctuating by region, of course), but it likely was an important one.
By the time we got to Homo erectus, our skulls (including our cranial cavities, and thus it is presumed, our brains) were actually larger than in Homo sapiens. You may be wondering about Homo neanderthalensis; our cousins (or in some cases, ancestors—but that is beyond the scope of today’s article) also had larger cranial cavities than us, and certainly enjoyed comparatively advanced culture, arts, religion, etc.
Fast-forward to the present day. Nothing is going to meaningfully change our skull size, as individuals. Brain size? Well, keep hydrated or it’ll shrink. Don’t overhydrate or it’ll swell. Neuroplasticity means we can increase (or lose) volume in specific areas of the brain, according to what we do most of. For example, if you were to scan this writer’s brain, you’d probably find overdevelopment in the various areas pertaining to language and memory, as that’s been “my thing” for as long as I can remember (which is a long way). See also: An Underrated Tool Against Alzheimer’s
The impact of diet in the modern day
Unlike our distant ancestors, if we want a high-calorie snack we can buy some nuts from the supermarket, and if anything, this can be a problem (as many people’s go-to high-calorie snack may be a lot less healthy than that), and in turn cause problems for the brain, because too many pizzas, cheeseburgers, tater tots, and so forth cause chronic inflammation, and thus, neuroinflammation.
See also: 6 Worst Foods That Cause Dementia
So much for “calories for the brain”. Yes, the brain definitely needs calories (it expends a very large portion of our daily calorie intake), but you can have too much of a good thing.
In any case, the brain needs more than just calories!
For example, you may remember the “6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry”, which are:
- Be whole; eat whole
- Eat the rainbow
- The greener, the better
- Tap into your body intelligence
- Consistency & balance are key
- Avoid anxiety-triggering foods
For more on all of those, see Dr. Uma Naidoo’s 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry ← She’s a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, professional chef graduating with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry.
When it comes to any potential nutritional deficiencies of a vegetarian or vegan diet, it’s a matter of planning.
Properly planned vegetarian diets are rich in essential nutrients like carbohydrates, fiber, magnesium, potassium, folate, vitamins C and E, and an abundance of phytochemicals, which support brain health (and overall health too, but today is about brain health).
However, if not well-planned, they can indeed lack certain nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are critical for brain function.
In essence, there’s a difference between a “whole foods plant-based diet” and junk food that just happens to be vegetarian or vegan.
Vitamin B12 is usually supplemented by vegans, but it can also be enjoyed from nutritional yeast used in cooking (it adds a cheesy flavor to dishes for which that’d be appropriate).
Iron is a fascinating beast, because while everyone thinks of red meat (which is indeed rich in iron), not only are there good plant-based sources of iron, but there are important considerations when it comes to bioavailability differences between heme and non-heme iron. In few words, heme iron (from blood etc) is more bioavailable by 1.8x, but all iron, including non-heme iron (from beans, greens, etc) can have its bioavailability multiplied by 5x just by having it with vitamin C:
Avoiding Anemia (More Than Just “Get More Iron”)
Omega-3 fatty acids, for vegetarians that mostly means eggs. See: Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
For vegans, we must look to nuts and seeds, for the most part. Or supplement—many omega 3 supplements are vegan, made from algae, or seaweed (that in turn is composed partially or entirely of algae):
So really, it comes down to “make sure you still get these things”, and once you’re used to it, it’s easy.
For those who prefer to keep some meat in their diet
Our summary in our top-linked article (Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?) concluded:
- Most of us can live healthily and happily on just plants if we so choose.
- Some people cannot, and will require varying kinds (and quantities) of animal products.
- As for red and/or processed meats, we’re not the boss of you, but from a health perspective, the science is clear: unless you have a circumstance that really necessitates it, just don’t.
- Same goes for pork, which isn’t red and may not be processed, but metabolically it’s associated with the same problems.
- The jury is out on poultry, but it strongly appears to be optional, healthwise, without making much of a difference either way
- Fish is roundly considered healthful in moderation. Enjoy it if you want, don’t if you don’t.
And the paper from which we’ve largely been working from today included such comments as:
❝ Evidence suggests that vegan and vegetarian diets, when well planned, can be rich in phytonutrients and antioxidants, which have been associated with lower levels of inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These findings indicate a potential role in reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are linked to neurodegenerative diseases.
However, deficiencies in critical nutrients such as vitamin B12, DHA, EPA, and iron have been consistently associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline, mood disturbances, and neurodegenerative disorders.
While plant-based diets provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, their neurological implications depend on nutrient adequacy. Proper planning, supplementation, and food preparation techniques are essential to mitigate risks and enhance cognitive health.❞
Source: Impact of Vegan and Vegetarian Diets on Neurological Health: A Critical Review ← you can see that they also cover the same nutrients that we do
One final note, not discussed above
We often say “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain”, because the former feeds the latter (with oxygen and nutrients) and assists in cleanup (of detritus that otherwise brings about cognitive decline).
So with that in mind…
What Matters Most For Your Heart? ← hint: it’s fiber. So whether you eat animal products or not, please do eat plenty of plants!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Stress-Proof Brain – by Dr. Melanie Greenberg
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of the book is as stated in the subtitle: using mindfulness and neuroplasticity to manage our stress response.
As such, it’s divided into three parts:
- Understanding your stress (and different types of stressors)
- Calming your amygdalae (thus, dealing with your stress response while the stressor is stressing you)
- Moving forward with your prefrontal cortex (and thus, gradually improving automatic stress responses over time, as we learn new, better responses to do automatically)
The content ranges from the neurophysiological to “therapist’s couch” stuff; Dr. Greenberg having her PhD in psychology has prepared her to write both of those different-but-touching fields with equal competence. In-line citations are given throughout, for those who want to look up studies.
The style is direct and informative, with little to no attention given to making it an entertaining read. As a result, it’s information dense (which is good), and/but not necessarily a “couldn’t put it down” page-turner.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your ability to deal with stress, this book is as good as any.
Click here to check out The Stress-Proof Brain, and stress-proof yours!
Share This Post
-
Codependency Isn’t What Most People Think It Is
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Codependency isn’t what most people think it is
In popular parlance, people are often described as “codependent” when they rely on each other to function normally. That’s interdependent mutualism, and while it too can become a problem if a person is deprived of their “other half” and has no idea how to do laundry and does not remember to take their meds, it’s not codependency.
Codependency finds its origins in the treatment and management of alcoholism, and has been expanded to encompass other forms of relationships with dependence on substances and/or self-destructive behaviors—which can be many things, including the non-physical, for example a pattern of irresponsible impulse-spending, or sabotaging one’s own relationship(s).
We’ll use the simplest example, though:
- Person A is (for example) an alcoholic. They have a dependency.
- Person B, married to A, is not an alcoholic. However, their spouse’s dependency affects them greatly, and they do what they can to manage that, and experience tension between wanting to “save” their spouse, and wanting their spouse to be ok, which latter, superficially, often means them having their alcohol.
Person B is thus said to be “codependent”.
The problem with codependency
The problems of codependency are mainly twofold:
- The dependent partner’s dependency is enabled and thus perpetuated by the codependent partner—they might actually have to address their dependency, if it weren’t for their partner keeping them from too great a harm (be it financially, socially, psychologically, medically, whatever)
- The codependent partner is not having a good time of it either. They have the stress of two lives with the resources (e.g. time) of one. They are stressing about something they cannot control, understandably worrying about their loved one, and, worse: every action they might take to “save” their loved one by reducing the substance use, is an action that makes their partner unhappy, and causes conflict too.
Note: codependency is often a thing in romantic relationships, but it can appear in other relationships too, e.g. parent-child, or even between friends.
See also: Development and validation of a revised measure of codependency
How to deal with this
If you find yourself in a codependent position, or are advising someone who is, there are some key things that can help:
- Be a nurturer, not a rescuer. It is natural to want to “rescue” someone we care about, but there are some things we cannot do for them. Instead, we must look for ways to build their strength so that they can take the steps that only they can take to fix the problem.
- Establish boundaries. Practise saying “no”, and also be clear over what things you can and cannot control—and let go of the latter. Communicate this, though. An “I’m not the boss of you” angle can prompt a lot of people to take more personal responsibility.
- Schedule time for yourself. You might take some ideas from our previous tangentially-related article:
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
Want to read more?
That’s all we have space for today, but here’s a very useful page with a lot of great resources (including questionnaires and checklist and things, in case you’re thinking “is it, or…?”)
Share This Post
-
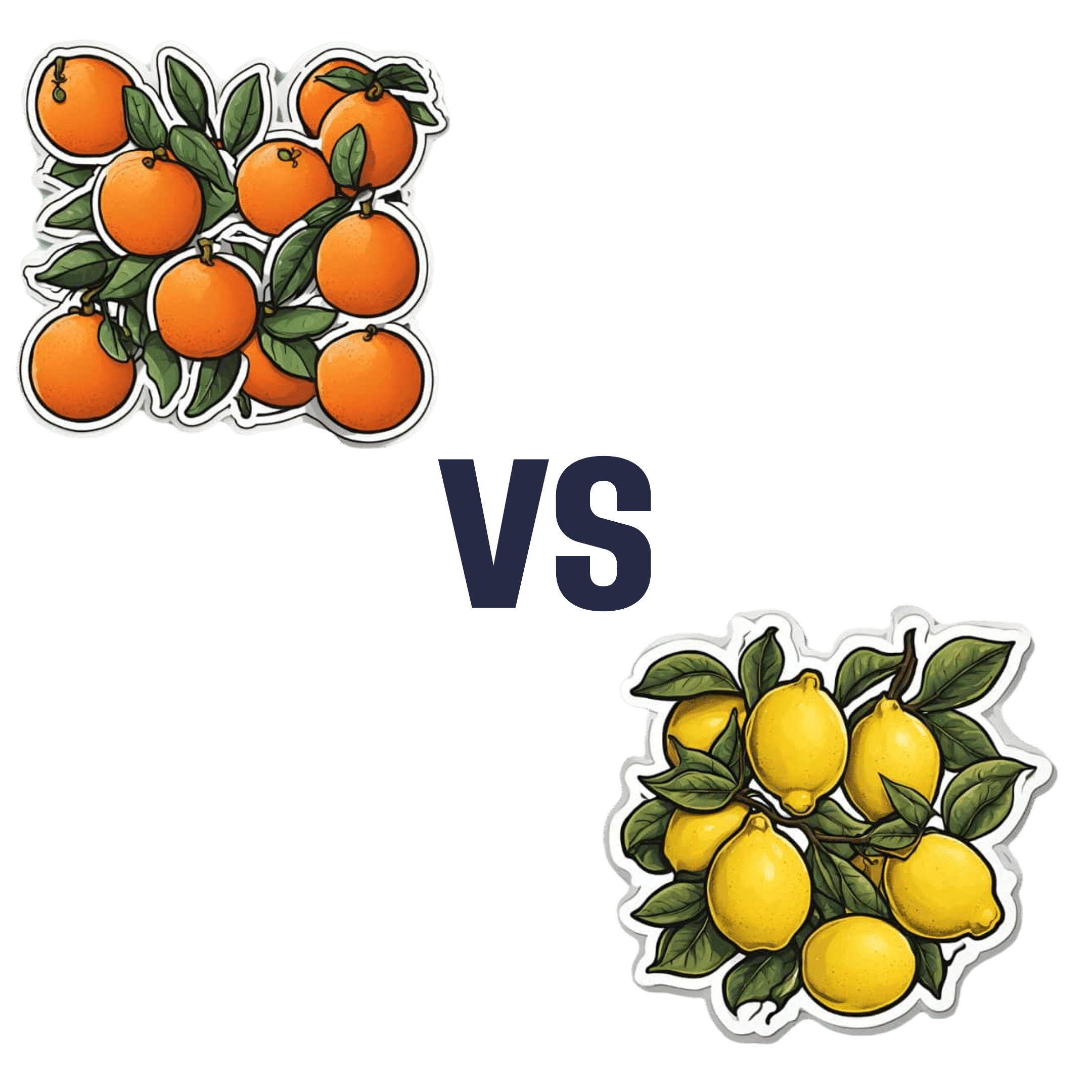
Oranges vs Lemons – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing oranges to lemons, we picked the oranges.
Why?
In the battle of these popular citrus fruits, there is a clear winner on the nutritional front.
Things were initially promising for lemons when looking at the macros—lemons have a little more fiber while oranges are slightly higher in carbs, but the differences are small and both are very healthy in this regard.
However, alas for this writer who prefers sour fruits to sweet ones (I’m sweet enough already), the micronutrient profiles tell a different story:
In terms of vitamins, oranges have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B9, E, and choline. In contrast, lemons have a (very) little more vitamin B6. You might be wondering about vitamin C, since both fruits are famous for that—they’re equal on vitamin C. But, with that stack we listed above, oranges clearly win the vitamin category easily.
As for minerals, oranges boast more calcium, copper, magnesium, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while lemons have more iron, manganese, and phosphorus.
Technically lemons also have more sodium, but the numbers are truly miniscule (by coincidence, we discover upon grabbing a calculator, you’d need to eat approximately your own bodyweight in whole lemons to get to the RDA of sodium—and that’s to reach the RDA, not the upper healthy limit) so we’ll overlook the tiny sodium difference as irrelevant. Which means, while closer than the vitamins category, oranges win on minerals with a 6:3 lead over lemons.
Both fruits offer generous helpings of flavonoids and other polyphenols such as naringenin and hesperidin, which have anti-inflammatory properties and more specifically can also reduce allergy symptoms (unless, of course, you are allergic to citrus fruits, which is a relatively rare but extant allergy).
In short: as ever, enjoy both; diversity is great for the health. But if you want to maximize the nutrients you get, it’s oranges.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Lemons vs Limes – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
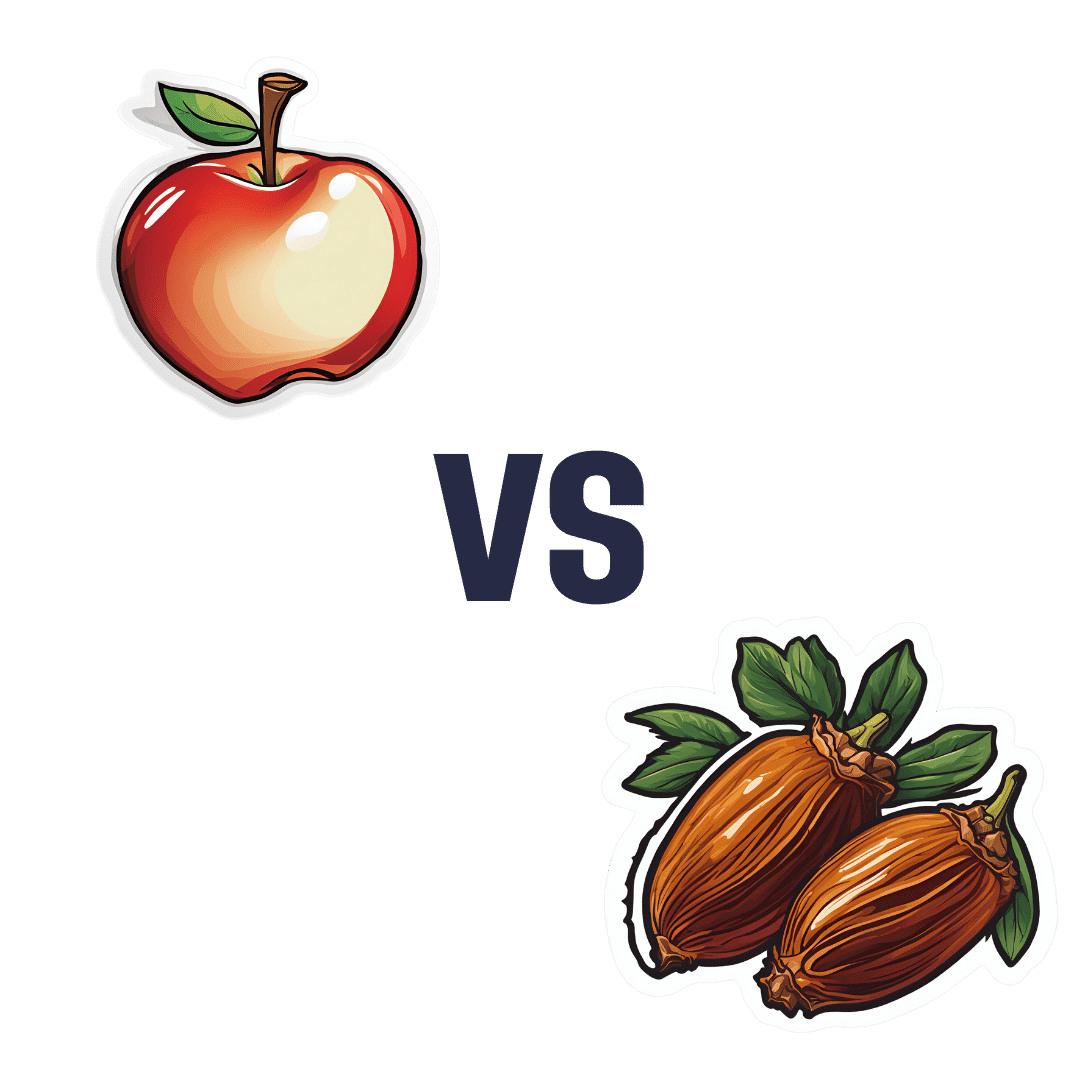
Apples vs Dates – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apples to dates, we picked the dates.
Why?
Both have their strengths, but ultimatley, it wasn’t close:
In terms of macros, dates have more fiber and carbs, for an approximately equal glycemic index. Thus, we say dates win this category as the more nutritionally dense option.
In the category of vitamins, apples have more of vitamins A, C, and E, while dates have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, K, and choline. A clear win for dates.
When it comes to minerals, it’s even more one-sided: apples are not richer in any minerals, while dates have a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. An overwhelming win for dates.
Of course, enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but if you want the most nutrients per bite, it’s dates.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blueberries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blueberries to cranberries, we picked the blueberries.
Why?
It’s close!
In terms of macros, blueberries have slightly more protein and carbs, while cranberries have slightly more fiber. We say the extra fiber’s more important than the (even more minimally) extra protein, so this is the slightest of marginal wins for cranberries in this category.
In the category of vitamins, blueberries have much more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B9, K, and choline, while cranberries have slightly more of vitamins A, B5, B6, C, and E. That’s a 6:5 win for blueberries, and also, the margins of difference were much greater for blueberries’ vitamins, making this a clearer win for blueberries.
When it comes to minerals, blueberries have slightly more iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, while cranberries have slightly more calcium. The margins of difference are small in both cases, but this is a 4:1 win for blueberries.
Both of these berries are famously full of antioxidants; blueberries have more antioxidant power overall, though cranberries have some specific benefits such as being better than antibiotics against UTIs—though there are some contraindications too; check out the link below for more on that!
All in all, meanwhile, we say that adding up the sections here makes for a win for blueberries, but by all means, enjoy either or both (unless one of the contraindications below applies to you).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Everyone You Don’t Like Is A Narcissist
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about how psychiatry tends to name disorders after how they affect other people, rather than how they affect the bearer, and this is most exemplified when it comes to personality disorders. For example:
“You have a deep insecurity about never being good enough, and you constantly mess up in your attempt to overcompensate? You may have Evil Bastard Disorder!”
“You have a crippling fear of abandonment and that you are fundamentally unloveable, so you do all you can to try to keep people close? You must have Manipulative Bitch Disorder!”
See also: Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
Antisocial DiagnosesThese days, it is easy to find on YouTube countless videos of how to spot a narcissist, with a list of key traits that all mysteriously describe exactly the exes of everyone in the comments.
And these days it is mostly “narcissist”, because “psychopath” and “sociopath” have fallen out of popular favor a bit:
- perhaps for coming across as overly sensationalized, and thus lacking credibility
- perhaps because “Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD)” exists in the DSM-5 (the US’s latest “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders”), while psychopathy and sociopathy are not mentioned as existing.
You may be wondering: what do “psychopathy” and “sociopathy” mean?
And the answer is: they mean whatever the speaker wants them to mean. Their definitions and differences/similarities have been vigorously debated by clinicians and lay enthusiasts alike for long enough that the scientific world has pretty much given up on them and moved on.
Stigma vs pathology
Because of the popular media (and social media) representation of NPD, it is easy to armchair diagnose one’s relative/ex/neighbor/in-law/boss/etc as being a narcissist, because the focus is on “narcissists do these bad things that are mean to people”.
If the focus were instead on “narcissists have cripplingly low self-esteem, and are desperate to not show weakness in a world they have learned is harsh and predatory”, then there may not be so many armchair diagnoses—or at the very least, the labels may be attached with a little more compassion, the same way we might with other mental health issues such as depression.
Not that those with depression get an easy time of it socially either—society’s response is generally some manner of “aren’t you better yet, stop being lazy”—but at the very least, depressed people are not typically viewed with hatred.
A quick aside: if you or someone you know is struggling with depression, here are some things that actually help:
The Mental Health First-Aid You’ll Hopefully Never Need
The disorder is not the problem
Maybe your relative, ex, neighbor, etc really is clinically diagnosable as a narcissist. There are still two important things to bear in mind:
- After centuries of diagnosing people with mental health maladies that we now know don’t exist per se (madness, hysteria, etc), and in recent decades countless revisions to the DSM and similar tomes, thank goodness we now have the final and perfect set of definitions that surely won’t be re-written in the next few years or so ← this is irony; it will absolutely be re-written numerous times yet because of course it’s still not a magically perfect descriptor of the broad spectrum of human nature
- The disorder is not the problem; the way they treat (or have treated) you is the problem.
For example, let’s take a key thing generally attributed to narcissists: a lack of empathy
Now, empathy can be divided into:
- affective empathy: the ability to feel what other people are feeling
- cognitive empathy: the ability to intellectually understand what other people are feeling (akin to sympathy, which is the same but with the requisite of having experienced the thing in question oneself)
A narcissist (as well as various other people without NPD) will typically have negligible affective empathy, and their cognitive empathy may be a little sluggish too.
Sluggish = it may take them a beat longer than most people, to realize what an external signifier of emotions means, or correctly guess how something will be felt by others. This can result in gravely misspeaking (or inappropriately emoting), after failing to adequately quickly “read the room” in terms of what would be a socially appropriate response. To save face, they may then either deny/minimize the thing they just said/did, or double-down on it and go on [what for them feels like] the counterattack.
As to why this shutting off of empathy happens: they have learned that the world is painful, and that people are sources of pain, and so—to avoid further pain—have closed themselves off to that, often at a very early age. This will also apply to themselves; narcissists typically have negligible self-empathy too, which is why they will commonly make self-destructive decisions, even while trying to put themselves first.
Important note on how this impacts other people: the “Golden Rule” of “treat others as you would wish to be treated” becomes intangible, as they have no more knowledge of their own emotional needs than they do of anyone else’s, so cannot make that comparison.
Consider: if instead of being blind to empathy, they were colorblind… You would probably not berate them for buying green apples when you asked for red. They were simply incapable of seeing that, and consequently made a mistake. So it is when it’s a part of the brain that’s not working normally.
So… Since the behavior does adversely affect other people, what can be done about it? Even if “hate them for it and call for their eradication from the face of the Earth” is not a reasonable (or compassionate) option, what is?
Take the bull by the horns
Above all, and despite all appearances, a narcissist’s deepest desire is simply to be accepted as good enough. If you throw them a life-ring in that regard, they will generally take it.
So, communicate (gently, because a perceived attack will trigger defensiveness instead, and possibly a counterattack, neither of which are useful to anyone) what behavior is causing a problem and why, and ask them to do an alternative thing instead.
And, this is important, the alternative thing has to be something they are capable of doing. Not merely something that you feel they should be capable of doing, but that they are actually capable of doing.
- So not: “be a bit more sensitive!” because that is like asking the colorblind person to “be a bit more observant about colors”; they are simply not capable of it and it is folly to expect it of them, because no matter how hard they try, they can’t.
- But rather: “it upsets me when you joke about xyz; I know that probably doesn’t make sense to you and that’s ok, it doesn’t have to. I am asking, however, if you will please simply refrain from joking about xyz. Would you do that for me?”
Presented with such, it’s much more likely that the narcissist will drop their previous attempt to be good enough (by joking, because everyone loves someone with a sense of humor, right?) for a new, different attempt to be good enough (by showing “behold, look, I am a good person and doing the thing you asked, of which I am capable”).
That’s just one example, but the same methodology can be applied to most things.
For tricks pertaining to how to communicate such things without causing undue resistance, see:
Seriously Useful Communication Skills
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: