Make Your Vegetables Work Better Nutritionally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most people know that boiling vegetables to death is generally not best for them, but raw isn’t always best either, and if we want to not sabotage our food, then there’s more to bear in mind than “just steam them, then”.
So, what should we keep in mind?
Water solubility
Many nutrients are water-soluble, including vitamin C, vitamin B-complex (as in, the collection of B-vitamins), and flavonoids, as well as many other polyphenols.
This means that if you cook your vegetables (which includes beans, lentils, etc) in water, a lot of the nutrients will go into the water, and be lost if you then drain that.
There are, thus, options;
- Steaming, yes
- Use just enough water to slow-cook or pressure-cook things that are suitable for slow-cooking, or pressure-cooking such as those beans and lentils. That way, when it’s done, there’s no excess water to drain, and all the nutrients are still in situ.
- Use as much water as you like, but then keep the excess water to make a soup, sauce, or broth.
- Use a cooking method other than water, where appropriate. For example, roasting peppers is a much better idea than roasting dried pulses.
- Consume raw, where appropriate.
Fat solubility
Many nutrients are fat-soluble, including vitamins A, D, E, and K, as well as a lot of carotenoids (including heavy-hitters lycopene and β-carotene) and many other polyphenols.
We’re now going to offer almost the opposite advice to that we had about water solubility. This is because unless they are dried, vegetables already contain water, whereas many contain only trace amounts of fat. Consequently, the advice this time is to add fat.
There are options:
- Cook with a modest amount of your favorite healthy cooking oil (our general go-to is extra-virgin olive oil, but avocado oil is great especially for higher temperature cooking, and an argument can be made for coconut oil sometimes)
- Remember that this goes for roasting, too. Brush those vegetables with a touch of olive oil, and not only will they be delicious, they’ll be more nutritious, too.
- Drizzle some the the above, if you’re serving things raw and it’s appropriate. This goes also for things like salads, so dress them!
- Enjoy your vegetables alongside healthy fatty foods such as nuts and seeds (or fatty animal products, if you eat those; fatty fish is a fine option here, in moderation, as are eggs, or fermented dairy products).
For a deeper understanding: Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Do not, however, deep-fry your foods unless it’s really necessary and then only for an occasional indulgence that you simply accept will be unhealthy. Not only is deep-frying terrible for the health in a host of ways (ranging from an excess of oil in the resultant food, to acrylamide, to creating Advanced Glycation End-products*), but also those fat-soluble nutrients? Guess where they’ll go. And unlike with the excess vegetable-cooking water that you can turn into soup or whatever, we obviously can’t recommend doing that with deep-fryer oil.
*see also: Are You Eating AGEs?
Temperature sensitivity
Many nutrients are sensitive to temperature, including vitamin C (breaks down when exposed to high temperatures) and carotenoids (are released when exposed to higher temperatures). Another special case is ergothioneine, “the longevity vitamin” that’s not a vitamin, found in mushrooms, which is also much more bioavailable when cooked.
So, if you’re eating something for vitamin C, then raw is best if that’s a reasonable option.
And if it’s not a reasonable option? Well, then you can either a) just cope with the fact it’s going to have less vitamin C in it, or b) cook it as gently and briefly as reasonably possible.
On the other hand, if you’re eating something for carotenoids (especially including lycopene and β-carotene), or ergothioneine, then cooked is best.
Additionally, if your food is high in oxalates (such as spinach), and you don’t want it to be (for example because you have kidney problems, which oxalates can exacerbate, or would like to get more calcium out of the spinach and into your body, which which oxalic acid would inhibit), then cooked is best, as it breaks down the oxalates.
Same goes for phytates, another “anti-nutrient” found in some whole grains (such as rice and wheat); cooking breaks it down, therefore cooked is best.
This latter is not, however, applicable in the case of brown rice protein powder, for those who enjoy that—because phytates aren’t found in the part of the rice that’s extracted to make that.
And as for brown rice itself? Does contain phytates… Which can be reduced by soaking and heating, preferably both, to the point that the nutritional value is better than it would have been had there not been phytic acid present in the first place; in other words: cooked is best.
You may be wondering: “who is eating rice raw?” and the answer is: people using rice flour.
See: Brown Rice Protein: Strengths & Weaknesses
Want to know more?
Here’s a great rundown from Dr. Rosalind Gibson, Dr. Leah Perlas, and Dr. Christine Hotz:
Improving the bioavailability of nutrients in plant foods at the household level
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Immediately after we stop drinking is rarely when we feel our best. But how long is it before we can expect to see benefits, instead of just suffering?
Timeline
After stopping drinking alcohol for…
- Seconds: the liver starts making progress filtering out toxins and sugars; ethanol starts to leave the system
- 1 hour: fatigue sets in as the body uses a lot of energy to metabolize and eliminate alcohol. However, sleep quality (if one goes to sleep now) is low because alcohol disrupts the brain patterns required for restful sleep
- 6–12 hours: the immune system starts recovering from the suppression caused by alcohol
- 24 hours: immune system is back to normal; withdrawal symptoms may occur in the case of heavy drinkers
- 3–5 days: resting blood pressure begins to drop, as stress levels decrease (alcohol may seem anxiolytic, but it is actually anxiogenic; it just masks its own effect in this regard). Also, because of insulin responses improving, appetite reduces. The liver, once it has finished dealing your last drinking session (if you used to drink all the time, it probably had a backlog to clear), can now begin to make repairs on itself.
- 1 week: skin will start looking better, as antidiuretic hormone levels neutralize, leading to a healthier maintenance of hydration
- 2 weeks: cognitive abilities improve as the brain begins to make progress in repairing itself. At the same time, kidneys start to heal.
- 3–4 weeks: the liver begins to regenerate in earnest. You may wonder what took it so long given the liver’s famous regenerative abilities, but in this case, the liver was also the organ that took the most damage from drinking, so its regeneration gets off to a slow start (in contrast, if the liver had “merely” suffered physical trauma, such as being shot, stabbed,
or eaten by eagles,it’d start regenerating vigorously as soon as the immediate wound-response had been tended to). Once it is able to pick up the pace though, overall health improves, as the liver can focus on breaking down other toxins. - 1–2 months: the heart is able to repair itself, and start to become stronger again (dependent on other lifestyle factors, of course).
- 3 months and more: bodily repairs continue (for example, the damage to the liver is often so severe that it can take quite a bit longer to recover completely, and repairs in the brain are always slow, for reasons beyond the scope of this article). Looking at the big picture, at this point we also see other benefits, such as reduced cancer risks.
In short… It’s never too soon to stop, but it’s also never too late, unless you are going to die in the next few days. So long as you’ll be in the land of the living for a few days yet, there’s time to enjoy the benefits of stopping.
Most importantly: the timeline for the most important repairs is not as long as many people might think, and that itself can be very motivating.
For more detail on much of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health?
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aspirin Pros & Cons
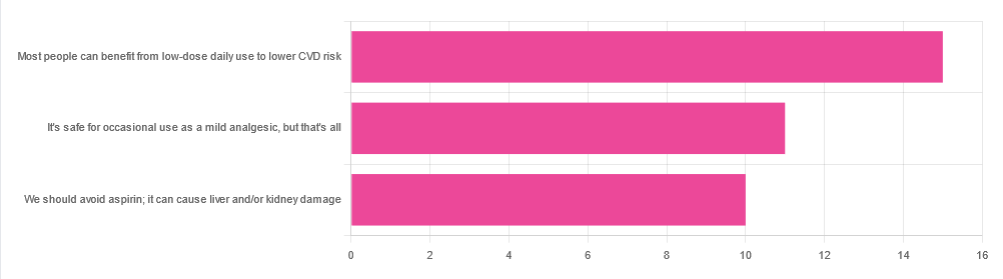
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked your health-related opinion of aspirin, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 42% said “Most people can benefit from low-dose daily use to lower CVD risk”
- About 31% said “It’s safe for occasional use as a mild analgesic, but that’s all”
- About 28% said “We should avoid aspirin; it can cause liver and/or kidney damage”
So, what does the science say?
Most people can benefit from low-dose daily aspirin use to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease: True or False?
True or False depending on what we mean by “benefit from”. You see, it works by inhibiting platelet function, which means it simultaneously:
- decreases the risk of atherothrombosis
- increases the risk of bleeding, especially in the gastrointestinal tract
When it comes to balancing these things and deciding whether the benefit merits the risk, you might be asking yourself: “which am I most likely to die from?” and the answer is: neither
While aspirin is associated with a significant improvement in cardiovascular disease outcomes in total, it is not significantly associated with reductions in cardiovascular disease mortality or all-cause mortality.
In other words: speaking in statistical generalizations of course, it may improve your recovery from minor cardiac events but is unlikely to help against fatal ones
The current prevailing professional (amongst cardiologists) consensus is that it may be recommended for secondary prevention of ASCVD (i.e. if you have a history of CVD), but not for primary prevention (i.e. if you have no history of CVD). Note: this means personal history, not family history.
In the words of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology:
❝Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) might be considered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among select adults 40 to 70 years of age who are at higher ASCVD risk but not at increased bleeding risk (S4.6-1–S4.6-8).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults >70 years of age (S4.6-9).
Low-dose aspirin (75-100 mg orally daily) should not be administered for the primary prevention of ASCVD among adults of any age who are at increased risk of bleeding (S4.6-10).❞
~ Dr. Donna Arnett et al. (those section references are where you can find this information in the document)
Read in full: Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology
Or if you’d prefer a more pop-science presentation:
Many older adults still use aspirin for CVD prevention, contrary to clinical guidance
Aspirin can cause liver and/or kidney damage: True or False?
True, but that doesn’t mean we must necessarily abstain, so much as exercise caution.
Aspirin is (at recommended doses) not usually hepatotoxic (toxic to the liver), but there is a strong association between aspirin use in children and the development of Reye’s syndrome, a disease involving encephalopathy and a fatty liver. For this reason, most places have an official recommendation that aspirin not be used by children (cut-off age varies from place to place, for example 12 in the US and 16 in the UK, but the key idea is: it’s potentially dangerous for those who are not fully grown).
Aspirin is well-established as nephrotoxic (toxic to the kidneys), however, the toxicity is sufficiently low that this is not expected to be a problem to otherwise healthy adults taking it at no more than the recommended dose.
For numbers, symptoms, and treatment, see this very clear and helpful resource:
An evidence based flowchart to guide the management of acute salicylate (aspirin) overdose
Take care!
Share This Post
-
5 Minute Posture Improvement Routine!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
McKay Lang walks us through it:
Step by Step
Breathing exercise:
- Place your hands on your lower abdomen.
- Take three deep breaths, focusing on body tension in the shoulders and neck… And release.
Shoulder squeeze:
- With your hands on your hips, inhale and squeeze your shoulders upwards.
- Hold your breath for 3–4 seconds, then exhale.
- Repeat two more times, holding the squeeze a little longer each time.
Upper shoulder massage:
- Massage your upper shoulder muscles to release tension stored there.
Overhead arm stretch:
- Raise your arms above your head, clasping each elbow with the opposite hand.
- Inhale deeply, stretch upwards, then exhale and release.
- Repeat, alternating elbows.
Neck and head push:
- Place your palms on the back of the head, and push your head into your hands (and vice versa, because of Newton’s Third Law of Motion).
- Do the same sideways (one side and then the other), to engage the other neck muscles.
Cool down:
- Gently unclasp your hands, bring your head upright, and massage your muscles. And breathe.
For variations and a visual demonstration of all, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
6 Ways To Look After Your Back
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
From Painkillers To Hunger-Killers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Here’s this week’s selection of health news discoveries, the science behind them, what they mean for you, and where you can go from there:
Killing more than pain
It’s well-known that overuse of opioids can lead to many problems, and here’s another one: messing with the endocrine system. This time, mostly well-evidenced in men—however, the researchers are keen to point out that absence of evidence is very much not evidence of absence, hence “the hidden effects” in the headline below. It’s not that the effects are hard to see—it’s that a lot of the research has yet to be done. For now, though, we know at the very least that there’s an association between opioid use and hyperprolactinemia in men. The same research also begins to shine a light on the effects of opioid use on the hypothalamic-pituitary system and bone health, too:
Read in full: The hidden effects of opioid use on the endocrine system
Related: The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
Gut microbiome dysbiosis may lead to slipping disks
These things sound quite unconnected, but the association is strong. The likely mechanism of action is that the gut dysbiosis influences systemic inflammation, and thus spinal health—because the gut-spine axis cannot really be disconnected (while you’re alive, at least). It’s especially likely if you’re over 50 and female:
Read in full: Are back problems influenced by your gut?
Related: Is Your Gut Leading You Into Osteoporosis?
The Internet is really really great (for brains)
It’s common to see many articles on the Internet telling us, paradoxically, that we should spend less time on the Internet. However… Remember when in the 90s, it was all about “the information superhighway”? It turns out, the fact that it’s more like “the information spaghetti junction” these days doesn’t change the fact that stimulation is good for our brains, and daily Internet use improves memory, because of the different way that we index and store information that came from a virtual source. While there are parts of your brain for “things at home” and “things at the local supermarket”, there are also parts for “things at 10almonds” and “things at Facebook” and so forth. You are, in effect, building a vast mental library as you surf:
Read in full: Daily internet use supercharges your memory!
Related: Make Social Media Work For Your Mental Health
Fall back
Around this time of year in many places in the Northern Hemisphere, the clocks go back an hour (it’s next weekend in the US and Canada, by the way, and this weekend in most of Europe). Many enjoy this as the potential for an extra hour’s sleep, but for night owls, it can be more of a nuisance than a benefit—throwing out what’s often an already difficult relationship with the clock, and presenting challenges both practical and physiological (different processing of melatonin, for instance). Here be science:
Read in full: Why night owls struggle more when the clocks go back
Related: Early Bird Or Night Owl? Genes vs Environment
Can you outrun your hunger?
It seems so, though benefits are strongest in women. We say “outrun”, though this study did use stationary cycling. To put it in few words, intense exercise (but not moderate exercise) significantly reduced acylated ghrelin (hunger hormone) levels, and subjective reports of hunger, especially in women:
Read in full: Study finds intense exercise may suppress appetite in healthy humans
Related: 3 Appetite Suppressants Better Than Ozempic
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Machine-Dispensed Coffee & Heart Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We have written before about the health benefits (and risks) of coffee; for most people, the benefits far outweigh the risks, but individual cases may vary:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?) ← this is a mythbusting edition
Speaking of bitterness; coffee has abundant polyphenols, which means…
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
See also: Why Bitter Is Better: Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain ← while it says foods in the title, this does cover coffee too.
For mythbusting on caffeine specifically, enjoy: Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
There are also gut health benefits from drinking coffee, and what’s good for our gut is invariably good for our heart and brain:
Coffee & Your Gut ← gut bacteria do not, by the way, have a preference about how you make your coffee or whether it is caffeinated or not
The latest science on coffee and heart health
Specifically, on coffee and cholesterol levels, so for a quick primer on cholesterol, check out: Demystifying Cholesterol
High total cholesterol, and especially high LDL (“bad” cholesterol) is generally associated with cardiovascular disease, for the reasons outlined in the link above.
Recently, researchers at Uppsala University in Sweden examined the levels of cafestol and kahweol, which are both diterpenes, substances known to increase cholesterol levels, in coffee made by various methods, including those dispensed from coffee machines in workplaces.
Two samples were taken from each machine every 2–3 weeks, and the most common kinds of machines produced the highest concentrations of diterpenes. These machines are the ones that push hot water through a small amount of ground coffee, through a wide-gauge filter, dispensing coffee into a cup in about 30 seconds.
Actual espresso machines, which work on the same principle but usually with a finer filter, higher pressure, and slower dispensing of the drink, had widely varying results, quite possibly because there is (in most machines) a human element in how tightly the ground coffee is packed into the metal filter basket.
Simple filter coffee, whether made in a coffee percolator machine or made using the pour-over method, had the lowest concentrations of diterpenes.
You can read about this study here:
However!
We were curious as to how, exactly, cafestol and kahweol increase cholesterol levels.
It turns out that research in this area has been scant, because most mice aren’t affected by it in the way that most humans are, which has limited mouse model studies.
Scant does not mean non-existent, though, and the answer came by virtue of transgenic mice (specifically, apolipoprotein (apo) E*3-Leiden transgenic mice, which do have the same reaction to cafestol as humans), the paper title sums it up nicely:
You may be wondering: what does suppression of bile acid synthesis have to do with cholesterol levels?
To oversimplify it a bit: cafestol messes with cholesterol metabolism by interfering with the enzymes involved in cholesterol metabolism (specifically, regulatory enzymes found in bile acid).
As to what it actually does in that regard: it reduces LDLR (LDL receptor) mRNA levels by 37% (that figure’s an average of the specific enzymes, sterol 27-hydroxylase and oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase, which were reduced by 32% and 48%, respectively).
Why this matters in practical terms: cafestol does not add any cholesterol to our systems, it inhibits our ability to clear LDL cholesterol, thus promoting raised LDL cholesterol levels.
In other words: if you have little or no dietary cholesterol (no dietary cholesterol, for example, if you are vegan), then your body will only have the cholesterol that it made for itself because it needed it, and as such, the body won’t need to do the same kind of clean-up job that it would if you had that coffee with a double cheeseburger with extra bacon.
As such, if you have little or no dietary cholesterol, cafestol is unlikely to have anything like the same effect on cholesterol levels.
Disclaimer: this latter is technically a hypothesis, but based on sound reasoning:
It’s the same logic that says “if you do not drink alcohol, then eating a durian fruit, which inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase, which the body uses to metabolize alcohol, will not cause alcohol-related problems for you”.
Want to know more?
We wrote previously on coffee and cafestol, along with some suggestions:
Health-Hack Your Coffee To Make Your Coffee Heart-Healthier!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tell Yourself a Better Lie – by Marissa Peer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As humans, we generally lie to ourselves constantly. Or perhaps we really believe some of the things we tell ourselves, even if they’re not objectively necessarily true:
- I’ll always be poor
- I’m destined to be alone
- I don’t deserve good things
- Etc.
Superficially, it’s easy to flip those, and choose to tell oneself the opposite. But it feels hollow and fake, doesn’t it? That’s where Marissa Peer comes in.
Our stories that we tell ourselves don’t start where we are—they’re generally informed by things we learned along the way. Sometimes good lessons, sometimes bad ones. Sometimes things that were absolutely wrong and/or counterproductive.
Peer invites the reader to ask “What if…”, unravel how the unhelpful lessons got wired into our brains in the first place, and then set about untangling them.
“Tell yourself a better lie” does not mean self-deceit. It means that we’re the authors of our own stories, so we might as well make them work for us. Many things in life are genuinely fixed; others are open to interpretation.
Sorting one from the other, and then treating them correctly in a way that’s helpful to us? That’s how we can stop hurting ourselves, and instead bring our own stories around to uplift and fortify us.
Get Your Copy of “Tell Yourself A Better Lie” on Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: