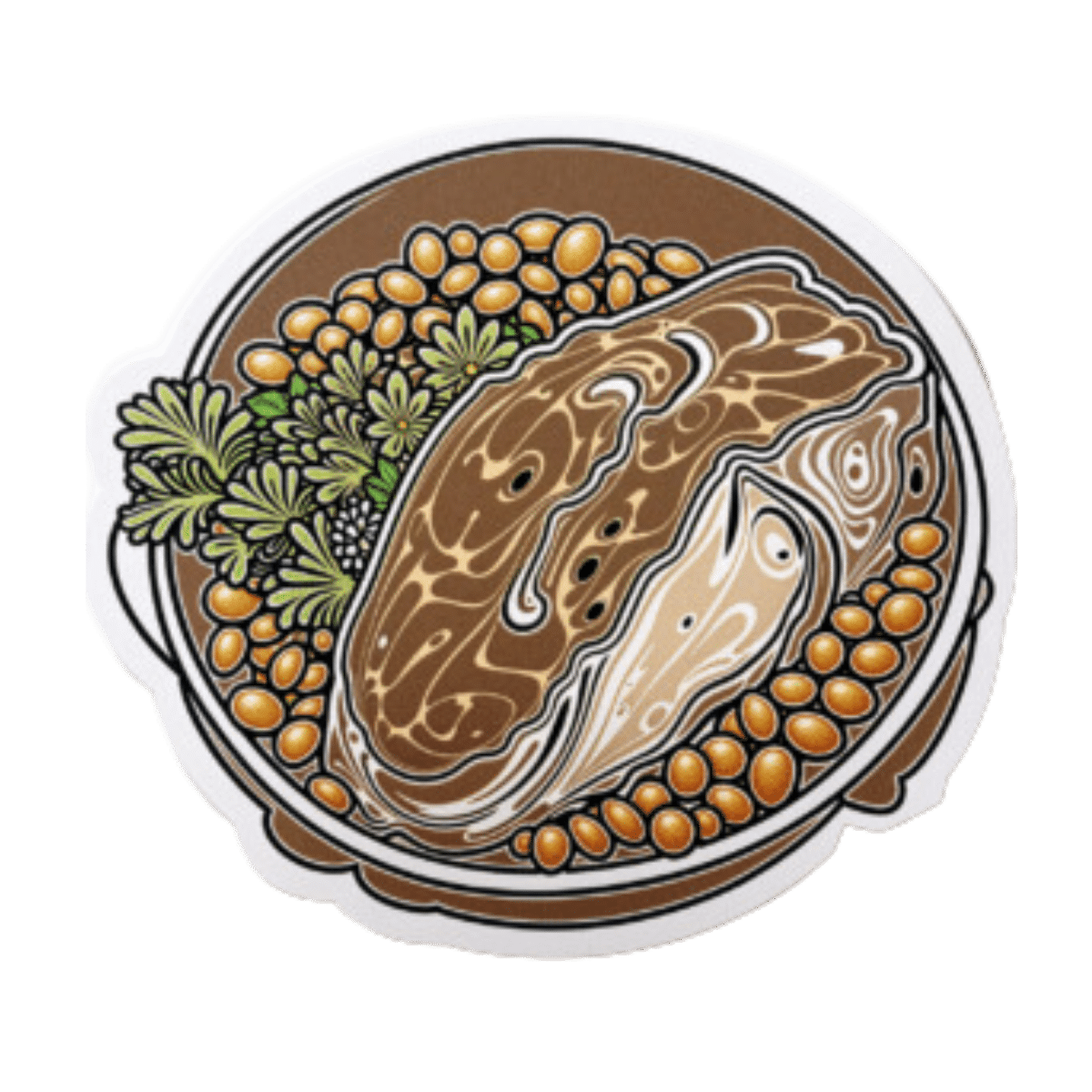
Tuna Steak with Protein Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yes, it’s protein on protein today, and it’s all healthy.
You will need (per person)
- 1 tuna steak
- 1 400g/12oz can mixed beans, drained & rinsed
- 1 tsp capers
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 red chili, chopped
- 1 lime, cut into wedges
- ½ tsp white wine vinegar
- Extra virgin olive oil, for cooking
- Garnish: chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the beans in a bowl, mixing in the capers, vinegar, and 1 tsp of the black pepper
2) Gently rub a little olive oil onto each side of the tuna steak, and season with the remainder of the black pepper (as in, the other tsp, not the rest of what you have in the house).
3) Heat a ridged grill pan until hot, and then cook the tuna for around 3 minutes on each side. Do not jiggle it! Do not slide it, and definitely do not stir it. Just gently turn it over when necessary. The edges should be cooked, and the inside should still be pink (it’s easy to forget when it comes from a can, but remember tuna is usually eaten raw)
4) Serve, sprinkling with the chopped chili and garnishing with the parsley. The lime wedges go on the side for squeezing at the table.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
- Salmon vs Tuna – Which is Healthier?
- Cilantro vs Parsley – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are You Making This Alcohol Mistake?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The famous “small glass of red per day” is, as is quite well-established now in science, but not so much in popular culture, known to be not a good idea.
What most people don’t know
Rethinking “One Drink a Day”:
- Outdated beliefs and flawed studies:
- The idea that “one drink a day is healthy” stems from flawed associative studies that included…
- unhealthy former heavy drinkers in the zero-drinks category, and
- healthy older individuals who continued light drinking due to good health, not because alcohol contributed to it, in the drinkers category
- In other words, they looked at former alcoholics whose health was ruined by drinking and said “aha, non-drinkers have bad health”, and looked at the survivors of survivorship bias and said “aha, light drinking is the key to good health”. Which of course is terrible science propped up by terrible abuse of statistics propped up by shoddy methodology.
- The idea that “one drink a day is healthy” stems from flawed associative studies that included…
- New research findings:
- A 2022 UK Biobank Study showed that even one drink a day leads to brain shrinkage, neuron death, and cognitive decline.
- Another study on CVD disproved the notion that light drinking benefits heart health once confounding variables were removed.
- There are plenty more, and at 10almonds we’ve done a main feature about it, but for now, you get the idea.
Some other things you should know:
Ethanol and acetaldehyde damage neurons responsible for impulse control, judgment, motor coordination, and memory formation, leading to cognitive decline. The feeling of being drunk results from the suppression and damage of these neurons. But while the drunk feeling wears off, the damage to neurons does not.
Alcohol causes cumulative DNA damage in neurons, accelerates brain aging, and prevents the formation of new neurons, similar to a slow, gradual stroke.
Broader Health Impacts of Alcohol
We’ve said it before, and we’ll say it again: alcohol is bad for pretty much everything.
Here are some examples mentioned in the video:
- Neurodegenerative diseases: heavy drinking increases the risk of Alzheimer’s, particularly in those genetically predisposed.
- Sleep disruption: alcohol reduces deep, restful sleep and hampers the brain’s natural detox process overnight, contributing to morning grogginess.
- Inflammation and immune suppression: alcohol increases inflammation, exacerbates autoimmune diseases (like psoriasis and arthritis), and weakens immune function.
- Cancer risk: alcohol is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, linked to various cancers, especially breast cancer. Even light drinking increases breast cancer risk.
- Hormonal imbalances: in women, alcohol heightens PMS symptoms, reduces fertility, and increases testosterone. In men, it lowers sperm quality and disrupts hormones.
For more on all of these and more, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health? ← this is mostly about red wine and heart health
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol ← this is about the more general reasons to quit, and how to do so
- What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol ← a realistic timeline of recovery
Take care!
Share This Post
- Outdated beliefs and flawed studies:
-
Popcorn vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing air-popped popcorn to peanuts (without an allergy), we picked the peanuts.
Why?
Peanuts, if we were to list popular nuts in order of healthfulness, would not be near the top of the list. Many other nuts have more nutrients and fewer/lesser drawbacks.
But the comparison to popcorn shines a different light on it:
Popcorn has very few nutrients. It’s mostly carbs and fiber; it’s just not a lot of carbs because the manner of its consumption makes it a very light snack (literally). You can eat a bowlful and it was perhaps 30g. It has some small amounts of some minerals, but nothing that you could rely on it for. It’s mostly fresh air wrapped in fiber.
Peanuts, in contrast, are a much denser snack. High in calories yes, but also high in protein, their fats are mostly healthy, and they have not only a fair stock of vitamins and minerals, but also a respectable complement of beneficial phytochemicals: mostly assorted antioxidant polyphenols, but also oleic acid (as in olives, good for healthy triglyceride levels).
Another thing worth a mention is their cholesterol-reducing phytosterols (these reduce the absorption of dietary cholesterol, “good” and “bad”, so this is good for most people, bad for some, depending on the state of your cholesterol and what you ate near in time to eating the nuts)
Peanuts do have their clear downsides too: its phytic acid content can reduce the bioavailability of iron and zinc taken at the same time.
In summary: while popcorn’s greatest claim to dietary beneficence is its fiber content and that it’s close to being a “zero snack”, peanuts (eaten in moderation, say, the same 30g as the popcorn) have a lot to contribute to our daily nutritional requirements.
We do suggest enjoying other nuts though!
Read more: Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Share This Post
-
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time to go nuts for nuts!
Nuts, in popular perception, range from “basically the healthiest food anyone can eat” to “basically high calorie salty snacks”. And, they can be either!
Some notes, then:
- Raw is generally better that not
- Dry roasted is generally better than the kind with added oils
- Added salt is neither necessary nor good
Quick tip: if “roasted salted” are the cheapest or most convenient to buy, you can at least mitigate that by soaking them in warm water for 5 minutes, before rinsing and (if you don’t want wet nuts) drying.
You may be wondering: who does want wet nuts? And the answer is, if for example you’re making a delicious cashew and chickpea balti, the fact you didn’t dry them before throwing them in won’t make a difference.
Now, let’s do a quick run-down; we don’t usually do “listicles” but it seemed a good format here, so we’ve picked a top 5 for nutritional potency:
Almonds
We may have a bias. We accept it. But almonds are also one of the healthiest nuts around, and generally considered by most popular metrics the healthiest.
Not only are they high in protein, healthy fat, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, but they’re even a natural prebiotic that increases the populations of healthy gut bacteria, while simultaneously keeping down the populations of gut pathogens—what more can we ask of a nut?
Read more: Prebiotic effects of almonds and almond skins on intestinal microbiota in healthy adult humans
Pistachios
Not only are these super tasty and fun to eat (and mindful eating is all but guaranteed, as shelling them by hand slows us down and makes us more likely to eat them one at a time rather than by the handful), but also they contain lots of nutrients and are lower in calories than most nuts, so they’re a great option for anyone who’d like to eat more nuts but is doing a calorie-controlled diet and doesn’t want to have half a day’s calories in a tiny dish of nuts.
Walnuts
Popularly associated with brain health (perhaps easy to remember because of their appearance), they really are good for the brain:
Check it out: Beneficial Effects of Walnuts on Cognition and Brain Health
Cashews
A personal favorite of this writer for their versatility in cooking, food prep, or just as a snack, they also do wonders for metabolic health:
Brazil nuts
The most exciting thing about these nuts is that they’re an incredibly potent source of selenium, which is important not just for hair/skin/nails as popularly marketed, but also for thyroid hormone production and DNA synthesis.
But don’t eat too many, because selenium is definitely one of those “you can have too much of a good thing” nutrients, and selenium poisoning can make your hair (however beautiful and shiny it got because of the selenium) fall out if you take too much.
Know the numbers: Brazil nuts and selenium—health benefits and risks
Bottom line on nuts:
- Nuts are a great and healthful part of almost anyone’s diet
- Obviously, if you have a nut allergy, then we’re sorry; this one won’t have helped you so much
- Almonds are one of the most healthful nuts out there
- Brazil nuts are incredibly potent, to the point where moderation is recommended
- A handful of mixed nuts per day is a very respectable option—when it comes to food and health, diversity is almost always good!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
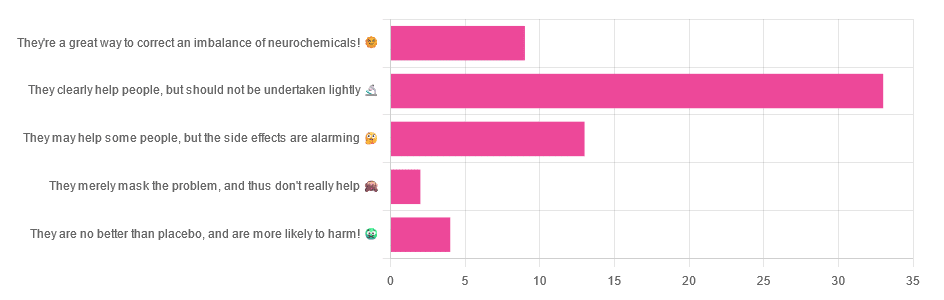
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on antidepressants, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- Just over half of respondents said “They clearly help people, but should not be undertaken lightly”
- Just over a fifth of respondents said “They may help some people, but the side effects are alarming”
- Just under a sixth of respondents said “They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals”
- Four respondents said “They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm”
- Two respondents said “They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help”
So what does the science say?
❝They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm? True or False?❞
True or False depending on who you are and what you’re taking. Different antidepressants can work on many different systems with different mechanisms of action. This means if and only if you’re not taking the “right” antidepressant for you, then yes, you will get only placebo benefits:
- Placebo Effect in the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety ← randomly assigned antidepressants are, shockingly, luck of the draw in usefulness
- Antidepressants versus placebo in major depression: an overview ← “wow this science is messy”
- Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs: a systematic review and network meta-analysis ← “oh look, it makes a difference which antidepressant we give to people”
Rather than dismissing antidepressants as worthless, therefore, it is a good idea to find out (by examination or trial and error) what kind of antidepressant you need, if you indeed do need such.
Otherwise it is like getting a flu shot and being surprised when you still catch a cold!
❝They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help: True or False?❞
False, categorically.
The problem in depressed people is the depressed mood. This may be influenced by other factors, and antidepressants indeed won’t help directly with those, but they can enable the person to better tackle them (more on this later).
❝They may help some people, but the side-effects are alarming: True or False?❞
True or False depending on more factors than we can cover here.
Side-effects vary from drug to drug and person to person, of course. As does tolerability and acceptability, since to some extent these things are subjective.
One person’s dealbreaker may be another person’s shrugworthy minor inconvenience at most.
❝They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals: True or False?❞
True! Contingently.
That is to say: they’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals if and only if your problem is (at least partly) an imbalance of neurochemicals. If it’s not, then your brain can have all the neurotransmitters it needs, and you will still be depressed, because (for example) the other factors* influencing your depression have not changed.
*common examples include low self-esteem, poor physical health, socioeconomic adversity, and ostensibly bleak prospects for the future.
For those for whom the problem is/was partly a neurochemical imbalance and partly other factors, the greatest help the antidepressants give is getting the brain into sufficient working order to be able to tackle those other factors.
Want to know more about the different kinds?
Here’s a helpful side-by-side comparison of common antidepressants, what type they are, and other considerations:
Mind | Comparing Antidepressants
Want a drug-free approach?
You might like our previous main feature:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How much time should you spend sitting versus standing? New research reveals the perfect mix for optimal health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People have a pretty intuitive sense of what is healthy – standing is better than sitting, exercise is great for overall health and getting good sleep is imperative.
However, if exercise in the evening may disrupt our sleep, or make us feel the need to be more sedentary to recover, a key question emerges – what is the best way to balance our 24 hours to optimise our health?
Our research attempted to answer this for risk factors for heart disease, stroke and diabetes. We found the optimal amount of sleep was 8.3 hours, while for light activity and moderate to vigorous activity, it was best to get 2.2 hours each.
Finding the right balance
Current health guidelines recommend you stick to a sensible regime of moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity 2.5–5 hours per week.
However mounting evidence now suggests how you spend your day can have meaningful ramifications for your health. In addition to moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity, this means the time you spend sitting, standing, doing light physical activity (such as walking around your house or office) and sleeping.
Our research looked at more than 2,000 adults who wore body sensors that could interpret their physical behaviours, for seven days. This gave us a sense of how they spent their average 24 hours.
At the start of the study participants had their waist circumference, blood sugar and insulin sensitivity measured. The body sensor and assessment data was matched and analysed then tested against health risk markers — such as a heart disease and stroke risk score — to create a model.
Using this model, we fed through thousands of permutations of 24 hours and found the ones with the estimated lowest associations with heart disease risk and blood-glucose levels. This created many optimal mixes of sitting, standing, light and moderate intensity activity.
When we looked at waist circumference, blood sugar, insulin sensitivity and a heart disease and stroke risk score, we noted differing optimal time zones. Where those zones mutually overlapped was ascribed the optimal zone for heart disease and diabetes risk.
You’re doing more physical activity than you think
We found light-intensity physical activity (defined as walking less than 100 steps per minute) – such as walking to the water cooler, the bathroom, or strolling casually with friends – had strong associations with glucose control, and especially in people with type 2 diabetes. This light-intensity physical activity is likely accumulated intermittently throughout the day rather than being a purposeful bout of light exercise.
Our experimental evidence shows that interrupting our sitting regularly with light-physical activity (such as taking a 3–5 minute walk every hour) can improve our metabolism, especially so after lunch.
While the moderate-to-vigorous physical activity time might seem a quite high, at more than 2 hours a day, we defined it as more than 100 steps per minute. This equates to a brisk walk.
It should be noted that these findings are preliminary. This is the first study of heart disease and diabetes risk and the “optimal” 24 hours, and the results will need further confirmation with longer prospective studies.
The data is also cross-sectional. This means that the estimates of time use are correlated with the disease risk factors, meaning it’s unclear whether how participants spent their time influences their risk factors or whether those risk factors influence how someone spends their time.
Australia’s adult physical activity guidelines need updating
Australia’s physical activity guidelines currently only recommend exercise intensity and time. A new set of guidelines are being developed to incorporate 24-hour movement. Soon Australians will be able to use these guidelines to examine their 24 hours and understand where they can make improvements.
While our new research can inform the upcoming guidelines, we should keep in mind that the recommendations are like a north star: something to head towards to improve your health. In principle this means reducing sitting time where possible, increasing standing and light-intensity physical activity, increasing more vigorous intensity physical activity, and aiming for a healthy sleep of 7.5–9 hours per night.
Beneficial changes could come in the form of reducing screen time in the evening or opting for an active commute over driving commute, or prioritising an earlier bed time over watching television in the evening.
It’s also important to acknowledge these are recommendations for an able adult. We all have different considerations, and above all, movement should be fun.
Christian Brakenridge, Postdoctoral research fellow at Swinburne University Centre for Urban Transitions, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
America’s Health System Isn’t Ready for the Surge of Seniors With Disabilities
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The number of older adults with disabilities — difficulty with walking, seeing, hearing, memory, cognition, or performing daily tasks such as bathing or using the bathroom — will soar in the decades ahead, as baby boomers enter their 70s, 80s, and 90s.
But the health care system isn’t ready to address their needs.
That became painfully obvious during the covid-19 pandemic, when older adults with disabilities had trouble getting treatments and hundreds of thousands died. Now, the Department of Health and Human Services and the National Institutes of Health are targeting some failures that led to those problems.
One initiative strengthens access to medical treatments, equipment, and web-based programs for people with disabilities. The other recognizes that people with disabilities, including older adults, are a separate population with special health concerns that need more research and attention.
Lisa Iezzoni, 69, a professor at Harvard Medical School who has lived with multiple sclerosis since her early 20s and is widely considered the godmother of research on disability, called the developments “an important attempt to make health care more equitable for people with disabilities.”
“For too long, medical providers have failed to address change in society, changes in technology, and changes in the kind of assistance that people need,” she said.
Among Iezzoni’s notable findings published in recent years:
Most doctors are biased. In survey results published in 2021, 82% of physicians admitted they believed people with significant disabilities have a worse quality of life than those without impairments. Only 57% said they welcomed disabled patients.
“It’s shocking that so many physicians say they don’t want to care for these patients,” said Eric Campbell, a co-author of the study and professor of medicine at the University of Colorado.
While the findings apply to disabled people of all ages, a larger proportion of older adults live with disabilities than younger age groups. About one-third of people 65 and older — nearly 19 million seniors — have a disability, according to the Institute on Disability at the University of New Hampshire.
Doctors don’t understand their responsibilities. In 2022, Iezzoni, Campbell, and colleagues reported that 36% of physicians had little to no knowledge of their responsibilities under the 1990 Americans With Disabilities Act, indicating a concerning lack of training. The ADA requires medical practices to provide equal access to people with disabilities and accommodate disability-related needs.
Among the practical consequences: Few clinics have height-adjustable tables or mechanical lifts that enable people who are frail or use wheelchairs to receive thorough medical examinations. Only a small number have scales to weigh patients in wheelchairs. And most diagnostic imaging equipment can’t be used by people with serious mobility limitations.
Iezzoni has experienced these issues directly. She relies on a wheelchair and can’t transfer to a fixed-height exam table. She told me she hasn’t been weighed in years.
Among the medical consequences: People with disabilities receive less preventive care and suffer from poorer health than other people, as well as more coexisting medical conditions. Physicians too often rely on incomplete information in making recommendations. There are more barriers to treatment and patients are less satisfied with the care they do get.
Egregiously, during the pandemic, when crisis standards of care were developed, people with disabilities and older adults were deemed low priorities. These standards were meant to ration care, when necessary, given shortages of respirators and other potentially lifesaving interventions.
There’s no starker example of the deleterious confluence of bias against seniors and people with disabilities. Unfortunately, older adults with disabilities routinely encounter these twinned types of discrimination when seeking medical care.
Such discrimination would be explicitly banned under a rule proposed by HHS in September. For the first time in 50 years, it would update Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, a landmark statute that helped establish civil rights for people with disabilities.
The new rule sets specific, enforceable standards for accessible equipment, including exam tables, scales, and diagnostic equipment. And it requires that electronic medical records, medical apps, and websites be made usable for people with various impairments and prohibits treatment policies based on stereotypes about people with disabilities, such as covid-era crisis standards of care.
“This will make a really big difference to disabled people of all ages, especially older adults,” said Alison Barkoff, who heads the HHS Administration for Community Living. She expects the rule to be finalized this year, with provisions related to medical equipment going into effect in 2026. Medical providers will bear extra costs associated with compliance.
Also in September, NIH designated people with disabilities as a population with health disparities that deserves further attention. This makes a new funding stream available and “should spur data collection that allows us to look with greater precision at the barriers and structural issues that have held people with disabilities back,” said Bonnielin Swenor, director of the Johns Hopkins University Disability Health Research Center.
One important barrier for older adults: Unlike younger adults with disabilities, many seniors with impairments don’t identify themselves as disabled.
“Before my mom died in October 2019, she became blind from macular degeneration and deaf from hereditary hearing loss. But she would never say she was disabled,” Iezzoni said.
Similarly, older adults who can’t walk after a stroke or because of severe osteoarthritis generally think of themselves as having a medical condition, not a disability.
Meanwhile, seniors haven’t been well integrated into the disability rights movement, which has been led by young and middle-aged adults. They typically don’t join disability-oriented communities that offer support from people with similar experiences. And they don’t ask for accommodations they might be entitled to under the ADA or the 1973 Rehabilitation Act.
Many seniors don’t even realize they have rights under these laws, Swenor said. “We need to think more inclusively about people with disabilities and ensure that older adults are fully included at this really important moment of change.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: