The Dopa-Bean
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mucuna pruriens, also called the “magic velvet bean”, is an established herbal drug used for the management of male infertility, nervous disorders, and also as an aphrodisiac:
The Magic Velvet Bean of Mucuna pruriens
How it works is more interesting than that, though.
It’s about the dopamine
M. pruriens contains levodopa (L-dopa). That’s right, the same as the dopaminergic medication most often prescribed for Parkinson’s disease. Furthermore, it might even be better than synthetic L-dopa, because:
❝M. pruriens seed extract demonstrated acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, while synthetic L-dopa enhanced the activity of the enzyme. It can be concluded that the administration of M. pruriens seed might be effective in protecting the brain against neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.
M. pruriens seed extract containing L-dopa has shown less acetylcholinesterase activity stimulation compared with L-dopa, suggesting that the extract might have a superior benefit for use in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.❞
~ Dr. Narisa Kamkaen et al.
Indeed, it has been tested specifically in (human!) Parkinson’s disease patients, which RCT found:
❝The rapid onset of action and longer on time without concomitant increase in dyskinesias on mucuna seed powder formulation suggest that this natural source of l-dopa might possess advantages over conventional l-dopa preparations in the long term management of Parkinson’s disease❞
~ Dr. Regina Katzenschlager et al.
Read more: Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind clinical and pharmacological study
Beyond Parkinson’s disease
M. pruriens has also been tested and found beneficial in cases of disease other than Parkinson’s, thus:
Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: recent advancement and future prospective
…but the science is less well-established for things not generally considered related to dopamine, such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiometabolic disorders.
Note, however, that the science for it being neuroprotective is rather stronger.
Against depression
Depression can have many causes, and (especially on a neurological level) diverse presentations. As such, sometimes what works for one person’s depression won’t touch another person’s, because the disease and treatment are about completely different neurotransmitter dysregulations. So, if a person’s depression is due to a shortage of serotonin, for example, then perking up the dopamine won’t help much, and vice versa. See also:
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
When it comes to M. pruriens and antidepressant activity, then predictably it will be more likely to help if your depression is due to too little dopamine. Note that this means that even if your depression is dopamine-based, but the problem is with your dopamine receptors and not the actual levels of dopamine, then this may not help so much, depending on what else you have going on in there.
The science for M. pruriens and depression is young, and we only found non-human animal studies so far, for example:
In summary
It’s good against Parkinson’s in particular and is good against neurodegeneration in general.
It may be good against depression, depending on the kind of depression you have.
Is it safe?
That’s a great question! And the answer is: it depends. For most people, in moderation, it should be fine (but, see our usual legal/medical disclaimer). Definitely don’t take it if you have bipolar disorder or any kind of schizoid/psychotic disorder; it is likely to trigger a manic/psychotic episode if you do.
For more on this, we discussed it (pertaining to L-dopa in general, not M. pruriens specifically) at greater length here:
An Accessible New Development Against Alzheimer’s ← scroll down to the heading that reads “Is there a catch?”
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
7 Essential Devices For Hand Arthritis: Regain Control of Your Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Diana Girnita is a double board-certified physician in rheumatology and internal medicine. With a PhD in immunology (on top of her MD), and training at Harvard and top universities, she founded Rheumatologist OnCall, offering integrative medicine to broaden rheumatology access. Here’s what she has to say about things that make life easier:
Get your hands on these…
The seven devices that Dr. Girnita recommends are:
- Hand grip strengthener: helps build grip strength with a spring-loaded mechanism. Regular use can improve strength and reduce pain.
- Finger exerciser: different device; similar principle: it strengthens hand and finger muscles using resistance, enhancing hand function.
- Moisturizing paraffin bath: a heated paraffin wax bath that soothes hands, providing heat therapy and moisturizing the skin.
- Weighted silverware: weighted utensils (knives, forks, spoons) make gripping easier and provide stability for eating.
- Foam tubing grips: foam covers to make kitchen tools, toothbrushes, and hairbrushes easier to grip.
- Electric can-opener: reduces strain in opening cans, making meal preparation more accessible.
- Compression gloves: provide gentle compression to reduce swelling and pain, improving hand flexibility and circulation.
- Door knob cover grips: make it easier to turn doorknobs by providing a larger surface to grip.
- Wider-grip pens: ergonomically designed pens with a larger diameter and softer grip reduce hand strain while writing.
This writer, who does not have arthritis but also does not have anything like the grip strength she used to, also recommends a jar opener like this one.
As a bonus, if you spend a lot of time writing at a computer, an ergonomic split keyboard like this one goes a long way to avoiding carpal tunnel syndrome, and logically must be better for arthritis than a regular keyboard; another excellent thing to have (that again this writer uses and swears by) is an ergonomic vertical mouse like this one (aligns the wrist bones correctly; the “normal” horizontal version is woeful for the carpal bones). These things are both also excellent to help avoid worsening peripheral neuropathy (something that troubles this writer’s wrists if she’s not careful, due to old injuries there).
For more on the seven things otherwise listed above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is A Visible Six-Pack Obtainable Regardless Of Genetic Predisposition?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it possible for anyone to get 6-pack abs (even if genetics makes it easier or harder) and how much does it matter for health e.g. waist size etc?❞
Let’s break it down into two parts:
Is it possible for anyone to get 6-pack abs (even if genetics makes it easier or harder)?
Short answer: no
First, a quick anatomy lesson: while “abs” (abdominal muscles) are considered in the plural and indeed they are, what we see as a six-pack is actually only one muscle, the rectus abdominis, which is nestled in between other abdominal muscles that are beyond the scope of our answer here.
The reason that the rectus abdominis looks like six muscles is because there are bands of fascia (connective tissue) lying over it, so we see where it bulges between those bands.
The main difference genes make are as follows:
- Number of fascia bands (and thus the reason that some people get a four-, six-, eight-, or rarely, even ten-pack). Obviously, no amount of training can change this number, any more than doing extra bicep curls will grow you additional arms.
- Density of muscle fibers. Some people have what has been called “superathlete muscle type”, which, while prized by Olympians and other athletes, is on bodybuilding forums less glamorously called being a “hard gainer”. What this means is that muscle fibers are denser, so while training will make muscles stronger, you won’t see as much difference in size. This means that size for size, the person with this muscle type will always be stronger than someone the same size without it, but that may be annoying if you’re trying to build visible definition.
- Twitch type of muscle fibers. Some people have more fast-twitch fibers, some have more slow-twitch fibers. Fast-twitch fibers are better suited for visible abs (and, as the name suggests, quick changes between contracting and relaxing). Slow-twitch fibers are better for endurance, but yield less bulky muscles.
- Inclination to subcutaneous fat storage. This is by no means purely genetic; hormones make the biggest difference, followed by diet. But, genes are an influencing factor, and if your body fat percentage is inclined to be higher than someone else’s, then it’ll take more work to see muscle definition under that fat.
The first of those items is why our simple answer is “no”; because some people are destined to, if muscle is visible, have a four-, eight, or (rarely) ten-pack, making a six-pack unobtainable.
It’s worth noting here that while a bigger number is more highly prized aesthetically, there is literally zero difference healthwise or in terms of performance, because it’s nothing to do with the muscle, and is only about the fascia layout.
The density of muscle fibers is again purely genetic, but it only makes things easier or harder; this part’s not impossible for anyone.
The inclination to subcutaneous fat storage is by far the most modifiable factor, and the thus most readily overcome, if you feel so inclined. That doesn’t mean it will necessarily be easy! But it does mean that it’s relatively less difficult than the others.
How much does it matter for health, e.g. waist size etc?
As you may have gathered from the above, having a six-pack (or indeed a differently-numbered “pack”, if that be your genetic lot) makes no important difference to health:
- The fascia layout is completely irrelevant to health
- The muscle fiber types do make a difference to athletic performance, but not general health when at rest
- The subcutaneous fat storage is a health factor, but probably not how most people think
Healthy body fat percentages are (assuming normal hormones) in the range of 20–25% for women and 15–20% for men.
For most people, having clearly visible abs requires going below those healthy levels. For most people, that’s not optimally healthy. And those you see on magazine covers or in bodybuilding competitions are usually acutely dehydrated for the photo, which is of course not good. They will rehydrate after the shoot.
However, waist size (especially as a ratio, compared to hip size) is very important to health. This has less to do with subcutaneous fat, though, and is more to do with visceral belly fat, which goes under the muscles and thus does not obscure them:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
One final note: fat notwithstanding, and aesthetics notwithstanding, having a strong core is very good for general health; it helps keeps one’s internal organs in place and well-protected, and improves stability, making falls less likely as we get older. Additionally, having muscle improves our metabolic base rate, which is good for our heart. Abs are just one part of core strength (the back being important too, for example), but should not be neglected.
Top-tier exercises to do include planks, and hanging leg raises (i.e. hang from some support, such as a chin-up bar, and raise your legs, which counterintuitively works your abs a lot more than your legs).
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Kidney Beans vs Pinto Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kidney beans to pinto beans, we picked the pinto.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, pinto beans have slightly more protein and carbs, and a lot more fiber, making them the all-round “more food per food” choice.
In the vitamins category, kidney beans have more of vitamins B3, C, and K, while pinto beans have more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, E, and choline; another win for pinto beans. In kidney beans’ defense though, with the exception of vitamin E (31x more in pinto beans) the margins of difference are small for the rest of these vitamins, making kidney beans a close runner-up. Still, at least a nominal win for pinto beans here, by the numbers.
When it comes to minerals, kidney beans are not higher in any minerals, while pinto beans have more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. In kidney beans’ defense, though, with the exception of selenium (5–6x more in pinto beans) the margins of difference are small for the rest of these minerals, making kidney beans a fine choice here too. Once again though, a winner is declarable here by the numbers, and it’s pinto beans.
Adding up the three wins makes for one big win for pinto beans. Still, enjoy either or both, because kidney beans are great too, and so is diversity!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Healthy Butternut Macaroni Cheese
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A comfort food classic, healthy and plant-based, without skimping on the comfort.
You will need
- ½ butternut squash, peeled and cut into small pieces (if buying ready-chopped, this should be about 1 lb)
- 1 onion, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 12 oz (or thereabouts) wholegrain macaroni, or similar pasta shape (even penne works fine—which is good, as it’s often easier to buy wholegrain penne than wholegrain macaroni) (substitute with a gluten-free pasta such as buckwheat pasta, if avoiding gluten)
- 6 oz (or thereabouts) cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 15 minutes (but longer is better)
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend hazelnut for its mellow nutty flavor)
- 3 tbsp nutritional yeast
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: smoked paprika, to serve
Note: if you are allergic to nuts, please accept our apologies that there’s no substitution available in this one. Simply put, removing the cashews would mean changing most of the rest of the recipe to compensate, so there’s no easy “or substitute with…” that we can mention. We’ll have to find/develop a good healthy plant-based no-nuts recipe for you at a later date.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the butternut squash, onion, and garlic with the olive oil, in a large roasting tin, tossing thoroughly to ensure an even coat of oil. Roast them for about 25 minutes until soft.
3) Cook the macaroni while you wait (this should take about 10 minutes or so in salted water), drain, and rinse thoroughly in cold water, before setting aside. This cooling increases the pasta’s resistant starch content (that’s good, for your gut and for your blood sugars, and thus also for your heart and brain), and it will maintain this benefit even when we reheat it later.
4) Drain the cashews, and tip them into a high-speed blender with the milk, and process until smooth. Add the roasted vegetables and the remaining ingredients apart from the pasta, and continue to process until again smooth. You can add a little more milk if you need to, but go easy with it.
5) Heat the sauce (that you just made in the food processor) gently in a saucepan, and refresh the pasta by pouring a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander.
6) Optional: combine the pasta and sauce in an ovenproof dish or cast iron pan, and give it a few minutes under the hottest grill (or browning iron, if you have such) your oven can muster. Alternatively, use a culinary blowtorch, if you have one.
7) Serve; and if you didn’t do the optional step above, this means combining the pasta and sauce. You can also dust the top with some extra seasonings if you like. Smoked paprika works well for this.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Butternut Squash vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
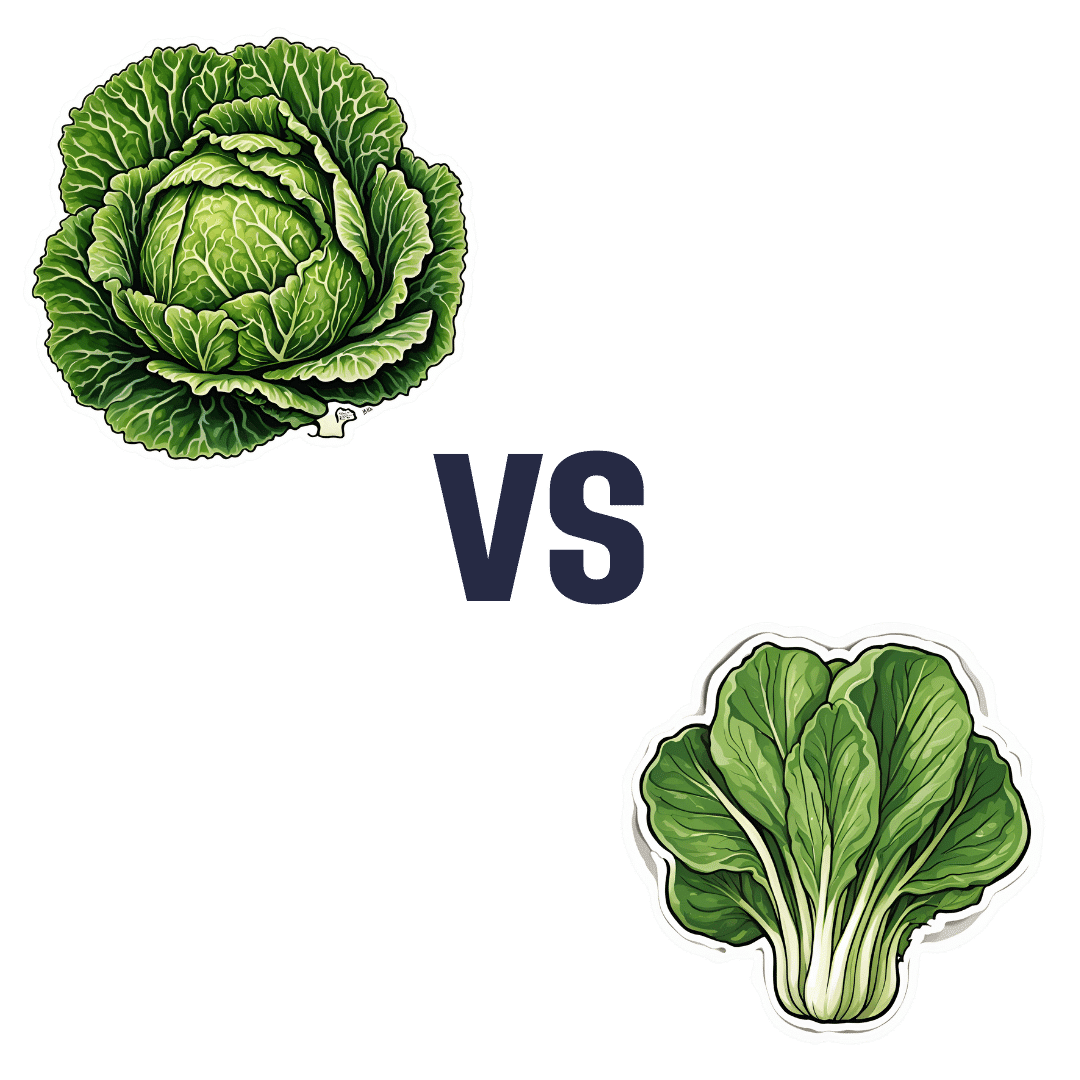
Savoy Cabbage vs Pak Choi – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing savoy cabbage to pak choi, we picked the savoy.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, the savoy has a little more protein, just under 3x the carbs, and just over 3x the fiber. A modest yet respectable win for savoy.
In terms of vitamins, savoy has more of vitamins B1, B5, B9, E, K, and choline, while pak choi has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and C. Thus, a 6:4 win for savoy.
When it comes to minerals, savoy has more copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pak choi has more calcium, iron, and potassium. So this time, a 7:3 win for savoy.
On the other hand, pak choi scores higher on the polyphenols side, especially in the categories of kaempferol and quercetin.
Still, adding up the sections, we conclude this one’s an overall win for savoy cabbage. Of course, enjoy either or both, though!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Fight Inflammation & Protect Your Brain, With Quercetin
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Awakening Your Ikigai – by Dr. Ken Mogi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s been well-established in supercentenarian studies that one of the key factors beyond diet or exercise or suchlike (important as those things definitely are), is having a purpose to one’s life.
Neuroscientist Dr. Ken Mogi explains in this very easy-to-read book, how we can bring ikigai into our lives.
From noticing the details of the small things in life, to reorienting one’s life around what’s most truly most important to us, Dr. Mogi gives us not just a “this is ikigai” exposé, but rather, a practical and readily applicable how-to guide.
Bottom line: if you’ve so far been putting off ikigai as “I’ll get to that”, the time to start is today.
Click here to check out Awakening Your Ikigai, and actually awaken yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: