The Compass of Pleasure – by Dr. David Linden
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are a lot of books about addiction, so what sets this one apart?
Mostly, it’s that this one maintains that addiction is neither good nor bad per se—just, some behaviors and circumstances are. Behaviors and circumstances caused, directly or indirectly, by addiction.
But, Dr. Linden argues, not every addiction has to be so. Especially behavioral addictions; the rush of dopamine one gets from a good session at the gym or learning a new language, that’s not a bad thing, even if they can fundamentally be addictions too.
Similarly, we wouldn’t be here as a species without some things that rely on some of the same biochemistry as addictions; orgasms and eating food, for example. Yet, those very same urges can also inconvenience us, and in the case of foods and other substances, can harm our health.
In this book, the case is made for shifting our addictive tendencies to healthier addictions, and enough information is given to help us do so.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand what is going on when you get waylaid by some temptation, and how to be tempted to better things, this book can give the understanding to do just that.
Click here to check out The Compass of Pleasure, and make yours work in your favor!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between a food allergy and an intolerance?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
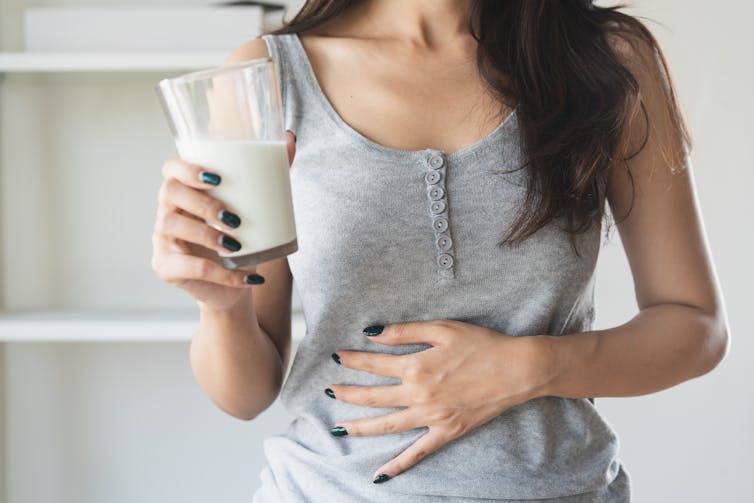
At one time or another, you’ve probably come across someone who is lactose intolerant and might experience some unpleasant gut symptoms if they have dairy. Maybe it’s you – food intolerances are estimated to affect up to 25% of Australians.
Meanwhile, cow’s milk allergy is one of the most common food allergies in infants and young children, affecting around one in 100 infants.
But what’s the difference between food allergies and food intolerances? While they might seem alike, there are some fundamental differences between the two.
Feel good studio/Shutterstock What is an allergy?
Australia has one of the highest rates of food allergies in the world. Food allergies can develop at any age but are more common in children, affecting more than 10% of one-year-olds and 6% of children at age ten.
A food allergy happens when the body’s immune system mistakenly reacts to certain foods as if they were dangerous. The most common foods that trigger allergies include eggs, peanuts and other nuts, milk, shellfish, fish, soy and wheat.
Mild to moderate signs of food allergy include a swollen face, lips or eyes; hives or welts on your skin; or vomiting. A severe allergic reaction (called anaphylaxis) can cause trouble breathing, persistent dizziness or collapse.
What is an intolerance?
Food intolerances (sometimes called non-allergic reactions) are also reactions to food, but they don’t involve your immune system.
For example, lactose intolerance is a metabolic condition that happens when the body doesn’t produce enough lactase. This enzyme is needed to break down the lactose (a type of sugar) in dairy products.
Food intolerances can also include reactions to natural chemicals in foods (such as salicylates, found in some fruits, vegetables, herbs and spices) and problems with artificial preservatives or flavour enhancers.
Lactose intolerance is caused by a problem with breaking down lactose in milk. Pormezz/Shutterstock Symptoms of food intolerances can include an upset stomach, headaches and fatigue, among others.
Food intolerances don’t cause life-threatening reactions (anaphylaxis) so are less dangerous than allergies in the short term, although they can cause problems in the longer term such as malnutrition.
We don’t know a lot about how common food intolerances are, but they appear to be more commonly reported than allergies. They can develop at any age.
It can be confusing
Some foods, such as peanuts and tree nuts, are more often associated with allergy. Other foods or ingredients, such as caffeine, are more often associated with intolerance.
Meanwhile, certain foods, such as cow’s milk and wheat or gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye and barley), can cause both allergic and non-allergic reactions in different people. But these reactions, even when they’re caused by the same foods, are quite different.
For example, children with a cow’s milk allergy can react to very small amounts of milk, and serious reactions (such as throat swelling or difficulty breathing) can happen within minutes. Conversely, many people with lactose intolerance can tolerate small amounts of lactose without symptoms.
There are other differences too. Cow’s milk allergy is more common in children, though many infants will grow out of this allergy during childhood.
Lactose intolerance is more common in adults, but can also sometimes be temporary. One type of lactose intolerance, secondary lactase deficiency, can be caused by damage to the gut after infection or with medication use (such as antibiotics or cancer treatment). This can go away by itself when the underlying condition resolves or the person stops using the relevant medication.
Whether an allergy or intolerance is likely to be lifelong depends on the food and the reason that the child or adult is reacting to it.
Allergies to some foods, such as milk, egg, wheat and soy, often resolve during childhood, whereas allergies to nuts, fish or shellfish, often (but not always) persist into adulthood. We don’t know much about how likely children are to grow out of different types of food intolerances.
How do you find out what’s wrong?
If you think you may have a food allergy or intolerance, see a doctor.
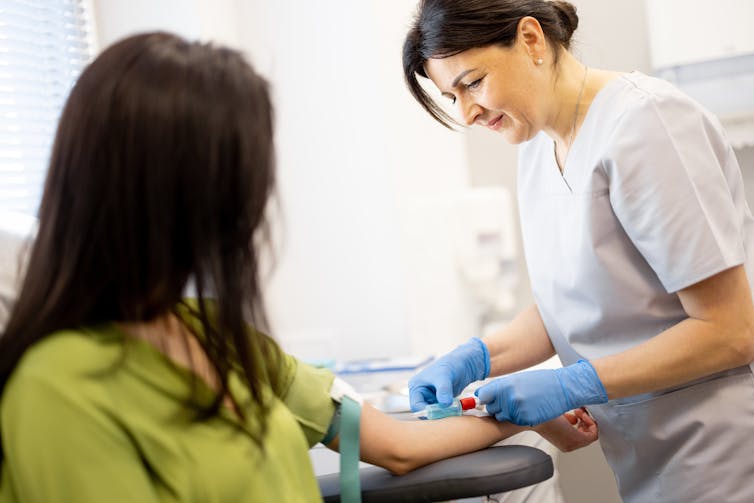
Allergy tests help doctors find out which foods might be causing your allergic reactions (but can’t diagnose food intolerances). There are two common types: skin prick tests and blood tests.
In a skin prick test, doctors put tiny amounts of allergens (the things that can cause allergies) on your skin and make small pricks to see if your body reacts.
A blood test checks for allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your blood that show if you might be allergic to a particular food.
Blood tests can help diagnose allergies. RossHelen/Shutterstock Food intolerances can be tricky to figure out because the symptoms depend on what foods you eat and how much. To diagnose them, doctors look at your health history, and may do some tests (such as a breath test). They may ask you to keep a record of foods you eat and timing of symptoms.
A temporary elimination diet, where you stop eating certain foods, can also help to work out which foods you might be intolerant to. But this should only be done with the help of a doctor or dietitian, because eliminating particular foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies, especially in children.
Is there a cure?
There’s currently no cure for food allergies or intolerances. For allergies in particular, it’s important to strictly avoid allergens. This means reading food labels carefully and being vigilant when eating out.
However, researchers are studying a treatment called oral immunotherapy, which may help some people with food allergies become less sensitive to certain foods.
Whether you have a food allergy or intolerance, your doctor or dietitian can help you to make sure you’re eating the right foods.
Victoria Gibson, a Higher Degree by Research student and Research Officer at the School of Nursing, Midwifery and Social Work at the University of Queensland, and Rani Scott-Farmer, a Senior Research Assistant at the University of Queensland, contributed to this article.
Jennifer Koplin, Group Leader, Childhood Allergy & Epidemiology, The University of Queensland and Desalegn Markos Shifti, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Child Health Research Centre, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Spoon-Fed – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Spector looks at widespread beliefs about food, and where those often scientifically disproven beliefs come from. Hint, there’s usually some manner of “follow the money”.
From calorie-counting to cholesterol content, from fish to bottled water, to why of all the people who self-report having an allergy, only around half turn out to actually have one when tested, Dr. Spector sets the record straight.
The style is as very down-to-earth and not at all self-aggrandizing; the author acknowledges his own mistakes and limitations along the way. In terms of pushing any particular agenda, his only agenda is clear: inform the public about bad science, so that we demand better science going forwards. Along the way, he gives us lots of information that can inform our personal health choices based on better science than indiscriminate headlines wildly (and sometimes intentionally) misinterpreting results.
Read this book, and you may find yourself clicking through to read the studies for yourself, next time you see a bold headline.
Bottom line: this book looks at a lot of what’s wrong with what a lot of people believe about healthy eating. Regular 10almonds readers might not find a lot that’s new here, but it could be a great gift for a would-be health-conscious friend or relative
Share This Post
-
What Are Nootropics, Really?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What are nootropics, really?
A nootropic is anything that functions as a cognitive enhancer—in other words, improves our brainpower.
These can be sensationalized as “smart drugs”, misrepresented excitingly in science fiction, meme-ified in the mundane (“but first, coffee”), and reframed entirely, (“exercise is the best nootropic”).
So, clearly, “nootropics” can mean a lot of different things. Let’s look at some of the main categories…
The neurochemical modulators
These are what often get called “smart drugs”. They are literally drugs (have a chemical effect on the body that isn’t found in our diet), and they affect the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as by:
- Adding more of that neurotransmitter (simple enough)
- Decreasing the rate at which we lose that neurotransmitter (re-uptake inhibitors)
- Antagonizing an unhelpful neurotransmitter (doing the opposite thing to it)
- Blocking an unhelpful neurotransmitter (stopping the receptors from receiving it)
“Unhelpful” here is relative and subjective, of course. We need all the neurotransmitters that are in our brain, after all, we just don’t need all of them all the time.
Examples: modafinil, a dopamine re-uptake inhibitor (mostly prescribed for sleep disorders), reduces the rate at which our brains scrub dopamine, resulting in a gradual build-up of dopamine that we naturally produced, so we get to enjoy that dopamine for longer. This will tend to promote wakefulness, and may also help with problem-solving and language faculties—as well as giving a mood boost. In other words, all things that dopamine is used for. Mirtazaрine, an adrenoreceptor agonist (mostly prescribed as an antidepressant), increases noradrenergic neurotransmission, thus giving many other brain functions a boost.
Why it works: our brains need healthy levels of neurotransmitters, in order to function well. Those levels are normally self-regulating, but can become depleted in times of stress or fatigue, for example.
The metabolic brain boosters
These are the kind of things that get included in nootropic stacks (stack = a collection of supplements and/or drugs that complement each other and are taken together—for example, a multivitamin tablet could be described as a vitamin stack) even though they have nothing specifically relating them to brain function. Why are they included?
The brain needs so much fuel. Metabolically speaking, it’s a gas-guzzler. It’s the single most resource-intensive organ of our body, by far. So, metabolic brain boosters tend to:
- Increase blood flow
- Increase blood oxygenation
- Increase blood general health
- Improve blood pressure (this is relative and subjective, since very obviously there’s a sweet spot)
Examples: B-vitamins. Yep, it can be that simple. A less obvious example might be Co-enzyme Q10, which supports energy production on a cellular level, and good cardiovascular health.
Why it works: you can’t have a healthy brain without a healthy heart!
We are such stuff as brains are made of
Our brains are made of mostly fat, water, and protein. But, not just any old fat and protein—we’re at least a little bit special! So, brain-food foods tend to:
- Give the brain the fats and proteins it’s made of
- Give the brain the stuff to make the fats and proteins it’s made of (simpler fats, and amino acids)
- Give the brain hydration! Just having water, and electrolytes as appropriate, does this
Examples: healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and seafood; also, a lot of phytonutrients from greens and certain fruits. Long-time subscribers may remember our article “Brain Food: The Eyes Have It!” on the importance of dietary lutein in reducing Alzheimer’s risk, for example
Why it works: this is matter of structural upkeep and maintenance—our brains don’t work fabulously if deprived of the very stuff they’re made of! Especially hydration is seriously underrated as a nootropic factor, by the way. Most people are dehydrated most of the time, and the brain dehydrates quickly. Fortunately, it rehydrates quickly as well when we take hydrating liquids.
Weird things that sound like ingredients in a witch’s potion
These are too numerous and too varied in how they work to cover here, but they do appear a lot in nootropic stacks and in popular literature on the subject.
Often they work by one of the mechanisms described above; sometimes we’re not entirely sure how they work, and have only measured their effects sufficiently to know that, somehow, they do work.
Examples: panax ginseng is one of the best-studied examples that still remains quite mysterious in many aspects of its mechanism. Lion’s Mane (the mushroom, not the jellyfish or the big cat hairstyle), meanwhile, is known to contain specific compounds that stimulate healthy brain cell growth.
Why it works: as we say, it varies so much from on ingredient to another in this category, so… Watch out for our Research Review Monday features, as we’ll be covering some of these in the coming weeks!
(PS, if there’s any you’d like us to focus on, let us know! We always love to hear from you. You can hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom)
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Plant-Based Diet Revolution – by Dr. Alan Desomond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is this just another gut-healthy cooking guide? Not entirely…
For a start, it’s not just about giving you a healthy gut; it also covers a healthy heart and a healthy brain. There’s lots of science in here!
It’s also aimed as a transitional guide to eating more plants and fewer animal products, if you so choose. And if you don’t so choose, at least having the flexibility to cook both ways.
The recipes themselves (organized into basics, breakfasts, lunches, mains, desserts) are clear and easy while also being calculated to please readers (and their families) who are used to eating more meat. There are, for instance, plenty of healthy proteins, healthy fats, and comfort foods.
The “28 days” of the title refers to a meal plan using the recipes from the book; it’s not a big feature of the book though, so use it or don’t, but the cooking advice itself is more than worth the price of the book and the recipes are certainly great.
Bottom line: if you’re thinking of taking a “Meatless Mondays” approach to making your diet healthier, this book can help you do that in style!
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Diet Revolution, and upgrade your culinary repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
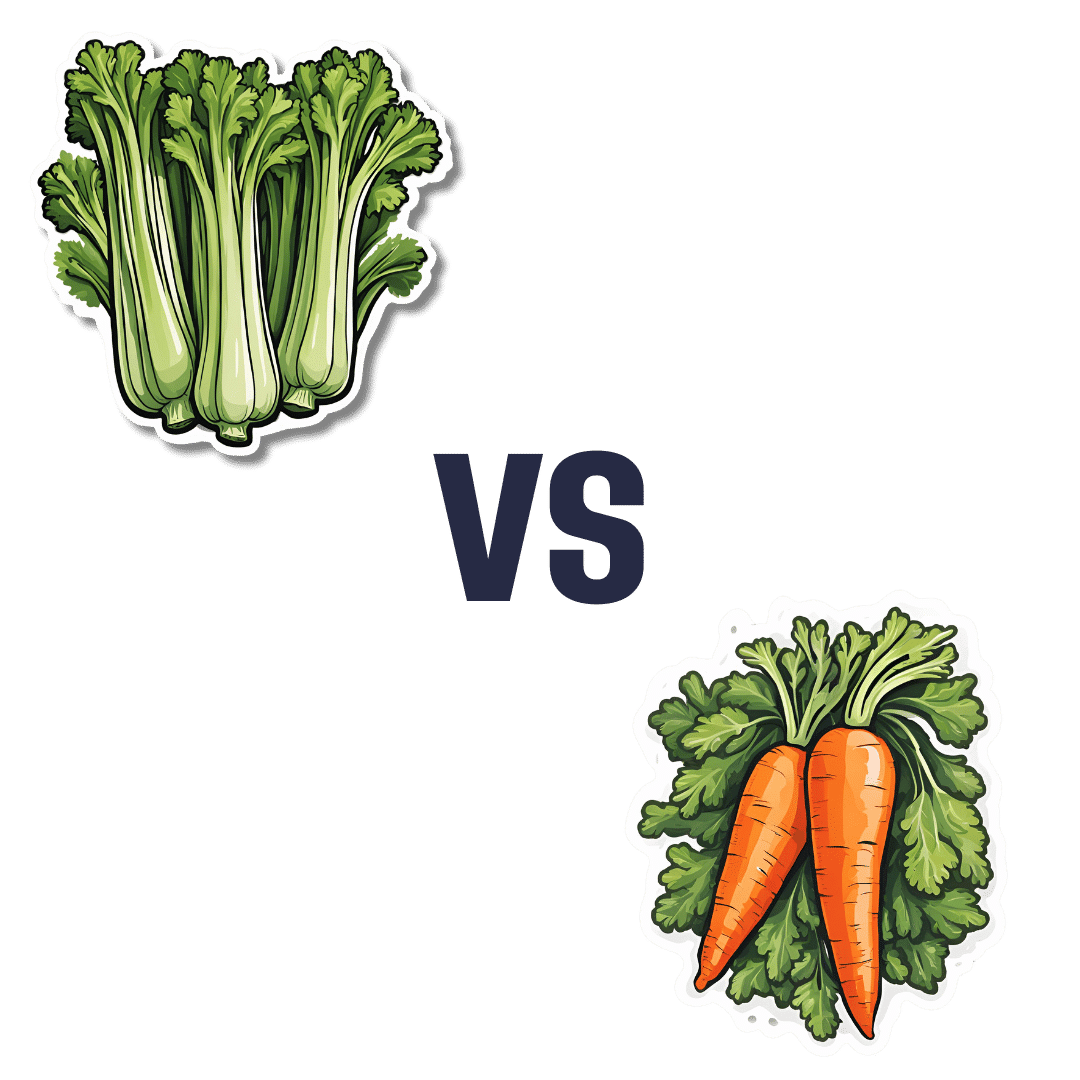
Celery vs Carrot – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to carrot, we picked the carrot.
Why?
In terms of macros, carrot has more protein, carbs, and fiber, and is thus the “most food per food” option. The carb:fiber ratio is such that they have about the same glycemic index (when raw, anyway).
In the category of vitamins, celery has more of vitamins B9 and K, while carrot has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, E, and choline. An easy win for carrot here.
When it comes to minerals, celery has more calcium and selenium, while carrot has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Another clear win for carrot.
In short, both are very respectable foods, but carrot simply has more in it, and it’s all good.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat to Your Heart’s Content – by Dr. Sat Bains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Making food heart-healthy and tasty is a challenge that vexes many, but it doesn’t have to be so difficult.
Dr. Sat Bains, a professional chef with multiple Michelin stars to his name, is an expert on “tasty”, and after surviving a heart attack himself, he’s become an expert on “heart-healthy” since then.
The book contains not only the recipes (of which there are 68, by the way), but also large sections of explanation of what makes various ingredients or methods heart-healthy or heart-unhealthy.
There’s science in there too, and these sections were written under the guidance of Dr. Neil Williams, a lecturer in physiology and nutrition.
You may be wondering as to why the author himself has a doctorate too; in fact he has three, none of which are relevant:
- Doctor of Arts
- Doctor of Laws
- Doctor of Hospitality (Honorary)
…but we prefix “Dr.” when people are that and he is that. The expertise we’re getting here though is really his culinary skill and extracurricular heart-healthy learning, plus Dr. Williams’ actual professional health guidance.
Bottom line: if you’d like heart-healthy recipes with restaurant-level glamour, this book is a fine choice.
Click here to check out Eat To Your Heart’s Content, and look after yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: