The 7-Minute Morning Routine That Eliminates Stiffness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The video title says “65+”, but honestly, if you are younger than that, and wait until you are 65 to attend to such things as mobility maintenance, then you’ll wish you’d started a long time previously!
So, today is always a good day to start, whatever your age.
A good way to start the day
The exercises do not, in fact, include the forwards bend depicted in the thumbnail. Rather, they are:
Exercise 1: toe wiggles (1 minute):
- while lying in bed, open and close your toes to improve foot mobility.
- this may seem silly and/or trivial, but it’s vital for overall mobility as foot health impacts daily movement, and your toes are responsible for a surprising amount when it comes to your posture, gait, etc.
Exercise 2: calf and hamstring stretch (1 minute):
- use a rolled-up towel (or similar non-stretchy long thing) to pull one foot towards you while straightening your leg.
- hold the stretch for 30 seconds per leg to relieve tightness in the calf or hamstring.
Exercise 3: knee flexion (1 minute):
- bend your knee as much as possible and pull your shin towards you.
- perform for 30 seconds per leg, gently easing into stiffness if necessary to improve knee mobility (i.e. if this is difficult at first).
Exercise 4: knee extension (1 minute):
- straighten one leg on the bed and press your knee down while pulling the toes up.
- hold for 5 seconds, repeat six times per leg, improving knee extension and strengthening the quads.
Exercise 5: hip flexion mobilization (1 minute):
- with your knees bent, pull one knee towards your chest and release in a rhythmic motion (see video for differences from #3)
- do 30 seconds per leg to improve hip mobility and loosen stiffness, especially beneficial for those with hip arthritis.
exercise 6: cat-cow stretch (1 minute):
- on all fours, alternate between arching your back (cat) and dipping it (cow).
- improves mobility in the neck, mid-back, and lower back.
exercise 7: shoulder and upper back stretch (1 minute):
- stand facing a wall, place your hands on the wall, and hinge at the hips to drop your torso between your arms.
- stretches lats, shoulders, and the upper back; do two 30-second holds..
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Over 50? Do These 3 Stretches Every Morning To Avoid Pain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
ADHD… As An Adult?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ADHD—not just for kids!
Consider the following:
- If a kid has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, ADHD!”
- If a young adult has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, a disinterested ne’er-do-well!”
- If an older adult has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, a senior moment!”
Yet, if we recognize that ADHD is fundamentally a brain difference in children (and we do; there are physiological characteristics that we can test), and we can recognize that as people get older our brains typically have less neuroplasticity (ability to change) than when we are younger rather than less, then… Surely, there are just as many adults with ADHD as kids!
After all, that rather goes with the linear nature of time and the progressive nature of getting older.
So why do kids get diagnoses so much more often than adults?
Parents—and schools—can find children’s ADHD challenging, and it’s their problem, so they look for an explanation, and ADHD isn’t too difficult to find as a diagnosis.
Meanwhile, adults with ADHD have usually developed coping mechanisms, have learned to mask and/or compensate for their symptoms, and we expect adults to manage their own problems, so nobody’s rushing to find an explanation on their behalf.
Additionally, the stigma of neurodivergence—especially something popularly associated with children—isn’t something that many adults will want for themselves.
But, if you have an ADHD brain, then recognizing that (even if just privately to yourself) can open the door to much better management of your symptoms… and your life.
So what does ADHD look like in adults?
ADHD involves a spread of symptoms, and not everyone will have them all, or have them in the same magnitude. However, very commonly most noticeable traits include:
- Lack of focus (ease of distraction)
- Conversely: high focus (on the wrong things)
- To illustrate: someone with ADHD might set out to quickly tidy the sock drawer, and end up Marie Kondo-ing their entire wardrobe… when they were supposed to doing something else
- Conversely: high focus (on the wrong things)
- Poor time management (especially: tendency to procrastinate)
- Forgetfulness (of various kinds—for example, forgetting information, and forgetting to do things)
Want To Take A Quick Test? Click Here ← this one is reputable, and free. No sign in required; the test is right there.
Wait, where’s the hyperactivity in this Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder?
It’s often not there. ADHD is simply badly-named. This stems from how a lot of mental health issues are considered by society in terms of how much they affect (and are observable by) other people. Since ADHD was originally noticed in children (in fact being originally called “Hyperkinetic Reaction of Childhood”), it ended up being something like:
“Oh, your brain has an inconvenient relationship with dopamine and you are driven to try to correct that by shifting attention from boring things to stimulating things? You might have trouble-sitting-still disorder”
Hmm, this sounds like me (or my loved one); what to do now at the age of __?
Some things to consider:
- If you don’t want medication (there are pros and cons, beyond the scope of today’s article), you might consider an official diagnosis not worth pursuing. That’s fine if so, because…
- More important than whether or not you meet certain diagnostic criteria, is whether or not the strategies recommended for it might help you.
- Whether or not you talk to other people about it is entirely up to you. Maybe it’s a stigma you’d rather avoid… Or maybe it’ll help those around you to better understand and support you.
- Either way, you might want to learn more about ADHD in adults. Today’s article was about recognizing it—we’ll write more about managing it another time!
In the meantime… We recommended a great book about this a couple of weeks ago; you might want to check it out:
Click here to see our review of “The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults”!
Note: the review is at the bottom of that page. You’ll need to scroll past the video (which is also about ADHD) without getting distracted by it and forgetting you were there to see about the book. So:
- Click the above link
- Scroll straight to the review!
Share This Post
-
How Are You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Answering The Most Difficult Question: How Are You?
Today’s feature is aimed at helping mainly two kinds of people:
- “I have so many emotions that I don’t always know what to do with them”
- “What is an emotion, really? I think I felt one some time ago”
So, if either those describe you and/or a loved one, read on…
Alexithymia
Alexi who? Alexithymia is an umbrella term for various kinds of problems with feeling emotions.
That could be “problems feeling emotions” as in “I am unable to feel emotions” or “problems feeling emotions” as in “feeling these emotions is a problem for me”.
It is most commonly used to refer to “having difficulty identifying and expressing emotions”.
There are a lot of very poor quality pop-science articles out there about it, but here’s a decent one with good examples and minimal sensationalist pathologization:
Alexithymia Might Be the Reason It’s Hard to Label Your Emotions
A somatic start
Because a good level of self-awareness is critical for healthy emotional regulation, let’s start there. We’ll write this in the first person, but you can use it to help a loved one too, just switching to second person:
Simplest level first:
Are my most basic needs met right now? Is this room a good temperature? Am I comfortable dressed the way I am? Am I in good physical health? Am I well-rested? Have I been fed and watered recently? Does my body feel clean? Have I taken any meds I should be taking?
Note: If the answer is “no”, then maybe there’s something you can do to fix that first. If the answer is “no” and also you can’t fix the thing for some reason, then that’s unfortunate, but just recognize it anyway for now. It doesn’t mean the thing in question is necessarily responsible for how you feel, but it’s good to check off this list as a matter of good practice.
Bonus question: it’s cliché, but if applicable… What time of the month is it? Because while hormonal mood swings won’t create moods out of nothing, they sure aren’t irrelevant either and should be listened to too.
Bodyscanning next
What do you feel in each part of your body? Are you clenching your jaw? Are your shoulders tense? Do you have a knot in your stomach? What are your hands doing? How’s your posture? What’s your breathing like? How about your heart? What are your eyes doing?
Your observations at this point should be neutral, by the way. Not “my posture is terrible”, but “my posture is stooped”, etc. Much like in mindfulness meditation, this is a time for observing, not for judging.
Narrowing it down
Now, like a good scientist, you have assembled data. But what does the data mean for your emotions? You may have to conduct some experiments to find out.
Thought experiments: what calls to you? What do you feel like doing? Do you feel like curling up in a ball? Breaking something? Taking a bath? Crying?
Maybe what calls to you, or what you feel like doing, isn’t something that’s possible for you to do. This is often the case with anxiety, for example, and perhaps also guilt. But whatever calls to you, notice it, reflect on it, and if it’s something that your conscious mind considers reasonable and safe for you to do, you can even try doing it.
Your body is trying to help you here, by the way! It will try (and usually succeed) to give you a little dopamine spike when you anticipate doing the thing it wants you to do. Warning: it won’t always be right about what’s best for you, so do still make your own decisions about whether it is a good idea to safely do it.
Practical experiments: whether you have a theory or just a hypothesis (if you have neither make up a hypothesis; that is also what scientists do), you can also test it:
If in the previous step you identified something you’d like to do and are able to safely do it, now is the time to try it. If not…
- Find something that is likely to (safely) tip you into emotional expression, ideally, in a cathartic way. But, whatever you can get is good.
- Music is great for this. What songs (or even non-lyrical musical works) make you sad, happy, angry, energized? Try them.
- Literature and film can be good too, albeit they take more time. Grab that tear-jerker or angsty rage-fest, and see if it feels right.
- Other media, again, can be completely unrelated to the situation at hand, but if it evokes the same emotion, it’ll help you figure out “yes, this is it”.
- It could be a love letter or a tax letter, it could be an outrage-provoking news piece or some nostalgic thing you own.
Ride it out, wherever it takes you (safely)
Feelings feel better felt. It doesn’t always seem that way! But, really, they are.
Emotions, just like physical sensations, are messengers. And when a feeling/sensation is troublesome, one of the best ways to get past it is to first fully listen to it and respond accordingly.
- If your body tells you something, then it’s good to acknowledge that and give it some reassurance by taking some action to appease it.
- If your emotions are telling you something, then it’s good to acknowledge that and similarly take some action to appease it.
There is a reason people feel better after “having a good cry”, or “pounding it out” against a punchbag. Even stress can be dealt with by physically deliberately tensing up and then relaxing that tension, so the body thinks that you had a fight and won and can relax now.
And when someone is in a certain (not happy) mood and takes (sometimes baffling!) actions to stay in that mood rather than “snap out of it”, it’s probably because there’s more feeling to be done before the body feels heard. Hence the “ride it out if you safely can” idea.
How much feeling is too much?
While this is in large part a subjective matter, clinically speaking the key question is generally: is it adversely affecting daily life to the point of being a problem?
For example, if you have to spend half an hour every day actively managing a certain emotion, that’s probably indicative of something unusual, but “unusual” is not inherently pathological. If you’re managing it safely and in a way that doesn’t negatively affect the rest of your life, then that is generally considered fine, unless you feel otherwise about it.
If you do think “I would like to not think/feel this anymore”, then there are tools at your disposal too:
- How To Manage Chronic Stress
- How To Set Anxiety Aside
- How To Stop Revisiting Those Memories
- How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vit D + Calcium: Too Much Of A Good Thing?
- Myth: you can’t get too much calcium!
- Myth: you must get as much vitamin D as possible!
Let’s tackle calcium first:
❝Calcium is good for you! You need more calcium for your bones! Be careful you don’t get calcium-deficient!❞
Contingently, those comments seem reasonable. Contingently on you not already having the right amount of calcium. Most people know what happens in the case of too little calcium: brittle bones, osteoporosis, and so forth.
But what about too much?
Hypercalcemia
Having too much calcium—or “hypercalcemia”— can lead to problems with…
- Groans: gastrointestinal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Peptic ulcer disease and pancreatitis.
- Bones: bone-related pains. Osteoporosis, osteomalacia, arthritis and pathological fractures.
- Stones: kidney stones causing pain.
- Moans: refers to fatigue and malaise.
- Thrones: polyuria, polydipsia, and constipation
- Psychic overtones: lethargy, confusion, depression, and memory loss.
(mnemonic courtesy of Sadiq et al, 2022)
What causes this, and how do we avoid it? Is it just dietary?
It’s mostly not dietary!
Overconsumption of calcium is certainly possible, but not common unless one has an extreme diet and/or over-supplementation. However…
Too much vitamin D
Again with “too much of a good thing”! While keeping good levels of vitamin D is, obviously, good, overdoing it (including commonly prescribed super-therapeutic doses of vitamin D) can lead to hypercalcemia.
This happens because vitamin D triggers calcium absorption into the gut, and acts as gatekeeper to the bloodstream.
Normally, the body only absorbs 10–20% of the calcium we consume, and that’s all well and good. But with overly high vitamin D levels, the other 80–90% can be waved on through, and that is very much Not Good™.
See for yourself:
- Hypercalcemia of Malignancy: An Update on Pathogenesis and Management
- Vitamin D-Mediated Hypercalcemia: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
How much is too much?
The United States’ Office of Dietary Supplements defines 4000 IU (100μg) as a high daily dose of vitamin D, and recommends 600 IU (15μg) as a daily dose, or 800 IU (20μg) if aged over 70.
See for yourself: Vitamin D Fact Sheet for Health Professionals ← there’s quite a bit of extra info there too
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
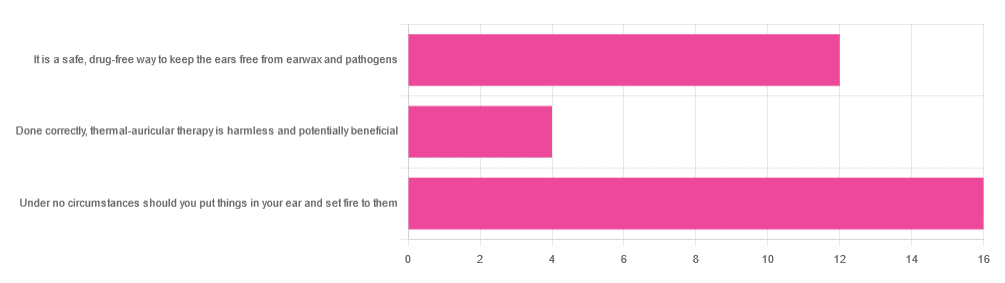
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
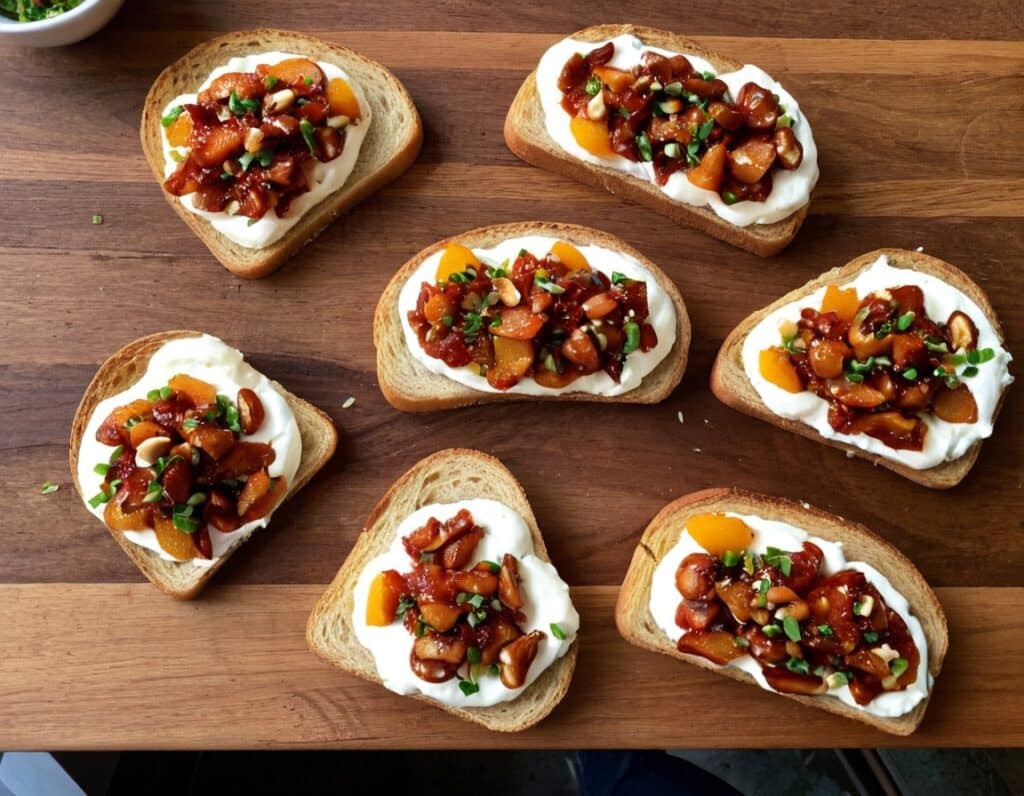
Chili Chestnut, Sweet Apricot, & Whipped Feta Toasts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a delightful breakfast or light lunch option, full of gut-healthy ingredients and a fair list of healthy polyphenols too.
You will need
- ½ baguette, sliced into ½” slices; if making your own, feel free to use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe. If buying shop-bought, a sourdough baguette will likely be the healthiest option, and tasty too.
- 4 oz feta cheese; if you are vegan, a plant-based version will work in culinary terms, but will have a different (less gut-healthy) nutritional profile, as plant-based cheeses generally use a lot of coconut oil and potato starch, and are not actually fermented.
- 1 tbsp yogurt; your preference what kind; live-cultured with minimal additives is of course best—and this time, plant-based is also just as good, healthwise, since they are fermented and contain more or less the same beneficial bacteria, and have a good macro profile too.
- 4 oz precooked chestnuts, finely chopped
- 6 dried apricots, finely chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- 2 tsp harissa paste
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- Optional garnish: finely chopped chives
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the feta and yogurt in a small, high-speed blender and process into a smooth purée. If it isn’t working, add 1 tbsp kettle-hot water and try again.
2) Heat the oil in a skillet over a medium heat; add the garlic and when it starts to turn golden, add the chestnuts and harissa, as well as the black pepper and MSG/salt. Stir for about 2 minutes, and then stir in the apricots and take it off the heat.
3) Toast the baguette slices under the grill. If you’re feeling bold about the multitasking, you can start this while still doing the previous step, for optimal timing. If not, simply doing it in the order presented is fine.
4) Assemble: spread the whipped feta over the toast; add the apricot-chestnut mixture, followed by the finely chopped chives if using, and serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: