The 3 Phases Of Fat Loss (& How To Do It Right!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cori Lefkowith, of “Redefining Strength” and “Strength At Any Age” fame, has advice:
As easy as 1, 2, 3?
Any kind of fat loss plan will not work unless it takes into account that the body can and will adapt to a caloric deficit, meaning that constantly running a deficit will only ever yield short term results, followed by regaining weight (and feeling hungry the whole time). So, instead, if fat loss is your goal, you might want to consider doing it in these stages:
1. Lifestyle adjustments (main phase)
Focus on sustainable, gradual improvements in diet and workouts.
- Key strategies:
- Start with small, manageable changes, for example focusing on making your protein intake around 30–35% of your total calories.
- Track your current habits to identify realistic adjustments.
- Balance strength training and cardio, as maintaining your muscle is (and will remain) important.
- Signs of Progress:
- Slow changes in the numbers on the scale (up to 1 lb/week).
- Inches being lost (but probably not many), improved energy levels, and stable performance in workouts.
Caution: avoid feelings of extreme hunger or restriction. This is not supposed to be arduous.
2. Mini cut (short-term intensive)
Used for quick fat loss or breaking plateaus; lasts 7–14 days.
- Key strategies:
- Larger calorie deficit (e.g: 500 calories).
- High protein intake (40–50% of your total calories).
- Focus on strength training and reduce cardio, to avoid muscle loss.
- Signs of Progress:
- Rapid scale changes (up to 5 lbs/week).
- Reduced bloating, potential energy dips, and cravings.
- Temporary performance stagnation in workouts. Don’t worry about this; it’s expected and fine.
Caution: do not exceed 21 days, to avoid the metabolic adaptation that we talked about.
3. Diet break (rest & reset)
A maintenance period to recharge mentally and physically, typically lasting 7–21 days.
- Key strategies:
- Gradually increase calories (200–500) to maintenance level.
- Focus on performance goals and reintroducing foods you enjoy.
- Combine strength training with steady-state cardio.
- Signs of Progress:
- Increased energy, improved workout performance, and feeling fuller.
- Scale may fluctuate initially but stabilize or decrease by the end.
- Inches will be lost as muscle is built and fat is burned.
The purpose of this third stage is to prevent metabolic adaptation, regain motivation, and (importantly!) test maintenance.
For more on these and how best to implement them, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Retrain Your Brain – by Dr. Seth Gillihan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
15-Minute Arabic”, “Sharpen Your Chess Tactics in 24 Hours”, “Change Your Life in 7 Days”, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 weeks”—all real books from this reviewer’s shelves.
The thing with books with these sorts of time periods in the titles is that the time period in the title often bears little relation to how long it takes to get through the book. So what’s the case here?
You’ll probably get through it in more like 7 days, but the pacing is more important than the pace. By that we mean:
Dr. Gillihan starts by assuming the reader is at best “in a rut”, and needs to first pick a direction to head in (the first “week”) and then start getting one’s life on track (the second “week”).
He then gives us, one by one, an array of tools and power-ups to do increasingly better. These tools aren’t just CBT, though of course that features prominently. There’s also mindfulness exercises, and holistic / somatic therapy too, for a real “bringing it all together” feel.
And that’s where this book excels—at no point is the reader left adrift with potential stumbling-blocks left unexamined. It’s a “whole course”.
Bottom line: whether it takes you 7 hours or 7 months, “Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 Weeks” is a CBT-and-more course for people who like courses to work through. It’ll get you where you’re going… Wherever you want that to be for you!
Share This Post
-
Pear vs Peach – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pears to peaches, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But peaches are exceptional in some ways that pears just can’t match up to:
In terms of macros, pears have more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which results in an approximately equal glycemic index. Thus, we’ll say that pears win this round by virtue of being the nutritionally denser option.
Looking at the vitamins, pears have (slightly) more of vitamins B6, B9, and K, while peaches have (much) more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B7, C, E, and choline—thus sweeping this category easily for peaches.
In the category of minerals, pears have more calcium and copper, while peaches have more iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time, the margins of difference for each mineral are comparably low (i.e. pears are close behind peaches on all those minerals), but still, by strength of numbers, it’s a clear win for peaches.
When it comes to polyphenols, not only do peaches have more, but also, they have anticancer properties that pears don’t—see our link below for more about that!
Meanwhile, adding up the sections makes for an overall win for peaches, but as ever when it comes to fruits, by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← peaches in the #2 spot! They induce cell death in cancer cells while sparing healthy ones
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Lower Cholesterol Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Lower Cholesterol, Without Statins
We’ll start this off by saying that lowering cholesterol might not, in fact, be critical or even especially helpful for everyone, especially in the case of women. We covered this more in our article about statins:
…which was largely informed by the wealth of data in this book:
The Truth About Statins – by Dr. Barbara H. Roberts
…which in turn, may in fact put a lot of people off statins. We’re not here to tell you don’t use them—they may indeed be useful or even critical for some people, as Dr. Roberts herself also makes makes clear. But rather, we always recommend learning as much as possible about what’s going on, to be able to make the most informed choices when it comes to what often might be literally life-and-death decisions.
On which note, if anyone would like a quick refresher on cholesterol, what it actually is (in its various forms) and what it does, why we need it, the problems it can cause anyway, then here you go:
Now, with all that in mind, we’re going to assume that you, dear reader, would like to know:
- how to lower your LDL cholesterol, and/or
- how to maintain a safe LDL cholesterol level
Because, while the jury’s out on the dangers of high LDL levels for women in particular, it’s clear that for pretty much everyone, maintaining them within well-established safe zones won’t hurt.
Here’s how:
Relax
Or rather, manage your stress. This doesn’t just reduce your acute risk of a heart attack, it also improves your blood metrics along the way, and yes, that includes not just blood pressure and blood sugars, but even triglycerides! Here’s the science for that, complete with numbers:
What are the effects of psychological stress and physical work on blood lipid profiles?
With that in mind, here’s…
How To Manage Chronic Stress (Even While Chronically Stressed)
Not chemically “relaxed”, though
While relaxing is important, drinking alcohol and smoking are unequivocally bad for pretty much everything, and this includes cholesterol levels:
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← this also covers popular beliefs about red wine and heart health, and the answer is no, we cannot
As for smoking, it is good to quit as soon as possible, unless your doctor specifically advises you otherwise (there are occasional situations where something else needs to be dealt with first, but not as many some might like to believe):
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
If you’re wondering about cannabis (CBD and/or THC), then we’d love to tell you about the effect these things have on heart health in general and cholesterol levels in particular, but the science is far too young (mostly because of the historic, and in some places contemporary, illegality cramping the research), and we could only find small, dubious, mutually contradictory studies so far. So the honest answer is: science doesn’t know this one, yet.
Exercise… But don’t worry, you can still stay relaxed
When it comes to heart health, the most important thing is keeping moving, so getting in those famous 150 minutes per week of moderate exercise is critical, and getting more is ideal.
240 minutes per week is a neat 40 minutes per day, by the way and is very attainable (this writer lives a 20-minute walk away from where she does her daily grocery shopping, thus making for a daily 40-minute round trip, not counting the actual shopping).
See: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
If walking is for some reason not practical for you, here’s a whole list of fun options that don’t feel like exercise but are:
Manage your hormones
This one is mostly for menopausal women, though some people with atypical hormonal situations may find it applicable too.
Estrogen protects the heart… Until it doesn’t:
See also: World Menopause Day: Menopause & Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Here’s a great introduction to sorting it out, if necessary:
Dr. Jen Gunter: What You Should Have Been Told About Menopause Beforehand
Eat a heart-healthy diet
Shocking nobody, but it has to be said, for the sake of being methodical. So, what does that look like?
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
(it’s fiber in the #1 spot, but there’s a list of most important things there, that’s worth checking out and comparing it to what you habitually eat)
You can also check out the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) edition of the Mediterranean diet, here:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
As for saturated fat (and especially trans-fats), the basic answer is to keep them to minimal, but there is room for nuance with saturated fats at least:
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
And lastly, do make sure to get enough omega 3 fatty-acids:
What Omega-3s Really Do For Us
And enjoy plant sterols and stanols! This would need a whole list of their own, so here you go:
Take These To Lower Cholesterol! (Statin Alternatives)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Lost Connections – by Johann Hari
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Johann Hari had a long journey through (and out of!) depression, and shares his personal findings, including his disappointment with medical options, and a focus on the external factors that lead to depression.
And that’s key to this book—while he acknowledges later in the book that there are physiological factors involved in depression, he wants to look past things we can’t change (like genes accounting for 37% of depression) or things that there may be unwanted side-effects to changing (as in the case of antidepressants, for many people), to things we genuinely can choose.
And no, it’s not a “think yourself happy” book either; rather, it looks at nine key external factorsthat a) influence depression b) can mostly be changed.
If the book has a downside, it’s that the author does tend to extrapolate his own experience a lot more than might be ideal. If SSRIs didn’t help him, they are useless, and also the only kind of antidepressant. If getting into a green space helped him, a Londoner, someone who lives in the countryside will not be depressed in the first place. And so forth. It can also be argued that he cherry-picked data to arrive at some of his pre-decided conclusions. He also misinterprets data sometimes; which is understandable; he is after all a journalist, not a scientist.
Nevertheless, he offers a fresh perspective with a lot of ideas, and whether or not we agree with them all, new ideas tend to be worth reading. And if even one of his nine ideas helps you, that’s a win.
Bottom line: if you’d like to explore the treatment of depression from a direction other than medicalization or psychotherapy, then this is will be a good book for you.
Click here to check out Lost Connections, and reforge yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Does Eating Shellfish Contribute To Gout?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I have a question about seafood as healthy, doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to gout?❞
It can do! Gout (a kind of inflammatory arthritis characterized by the depositing of uric acid crystals in joints) has many risk factors, and diet is one component, albeit certainly the most talked-about one.
First, you may be wondering: isn’t all arthritis inflammatory? Since arthritis is by definition the inflammation of joints, this is a reasonable question, but when it comes to classifying the kinds, “inflammatory” arthritis is caused by inflammation, while “non-inflammatory” arthritis (a slightly confusing name) merely has inflammation as one of its symptoms (and is caused by physical wear-and-tear). For more information, see:
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis ←inflammatory
- Tips For Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis ← “non-inflammatory”
As for gout specifically, top risk factors include:
- Increasing age: risk increases with age
- Being male: women do get gout, but much less often
- Hypertension: all-cause hypertension is the biggest reasonably controllable factor
There’s not a lot we can do about age (but of course, looking after our general health will tend to slow biological aging, and after all, diseases only care about the state of our body, not what the date on the calendar is).
As for sex, this risk factor is hormones, and specifically has to do with estrogen and testosterone’s very different effects on the immune system (bearing in mind that chronic inflammation is a disorder of the immune system). However, few if any men would take up feminizing hormone therapy just to lower their gout risk!
That leaves hypertension, which happily is something that we can all (barring extreme personal circumstances) do quite a bit about. Here’s a good starting point:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
…and for further pointers:
How To Lower Your Blood Pressure (Cardiologists Explain)
As for diet specifically (and yes, shellfish):
The largest study into this (and thus, one of the top ones cited in a lot of other literature) looked at 47,150 men with no history of gout at the baseline.
So, with the caveat that their findings could have been different for women, they found:
- Eating meat in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific meats: beef, pork, and lamb were the worst offenders
- Eating seafood in general increased gout risk
- Narrowing down specific seafoods: all seafoods increased gout risk within a similar range
- As a specific quirk of seafoods: the risk was increased if the man had a BMI under 25
- Eating dairy in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down specific dairy foods: low-fat dairy products such as yogurt were associated with a decreased risk of gout
- Eating purine-rich vegetables in general was not associated with an increased risk of gout
- Narrowing down to specific purine-rich vegetables: no purine-rich vegetable was associated with an increase in the risk of gout
Dairy products were included in the study, as dairy products in general and non-fermented dairy products in particular are often associated with increased inflammation. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to gout risk.
Purine-rich vegetables were included in the study, as animal products highest in purines have typically been found to have the worst effect on gout. However, the association was simply not found to exist when it came to plants with purines.
You can read the full study here:
Purine-Rich Foods, Dairy and Protein Intake, and the Risk of Gout in Men
So, the short answer to your question of “doesn’t eating shellfish contribute to the risk of gout” is:
Yes, it can, but occasional consumption probably won’t result in gout unless you have other risk factors going against you.
If you’re a slim male 80-year-old alcoholic smoker with hypertension, then definitely do consider skipping the lobster, but honestly, there may be bigger issues to tackle there.
And similarly, obviously skip it if you have a shellfish allergy, and if you’re vegan or vegetarian or abstain from shellfish for religious reasons, then you can certainly live very healthily without ever having any.
See also: Do We Need Animal Products, To Be Healthy?
For most people most of the time, a moderate consumption of seafood, including shellfish if you so desire, is considered healthy.
As ever, do speak with your own doctor to know for sure, as your individual case may vary.
For reference, this question was surely prompted by the article:
Lobster vs Crab – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
From straight to curly, thick to thin: here’s how hormones and chemotherapy can change your hair
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Head hair comes in many colours, shapes and sizes, and hairstyles are often an expression of personal style or cultural identity.
Many different genes determine our hair texture, thickness and colour. But some people’s hair changes around the time of puberty, pregnancy or after chemotherapy.
So, what can cause hair to become curlier, thicker, thinner or grey?
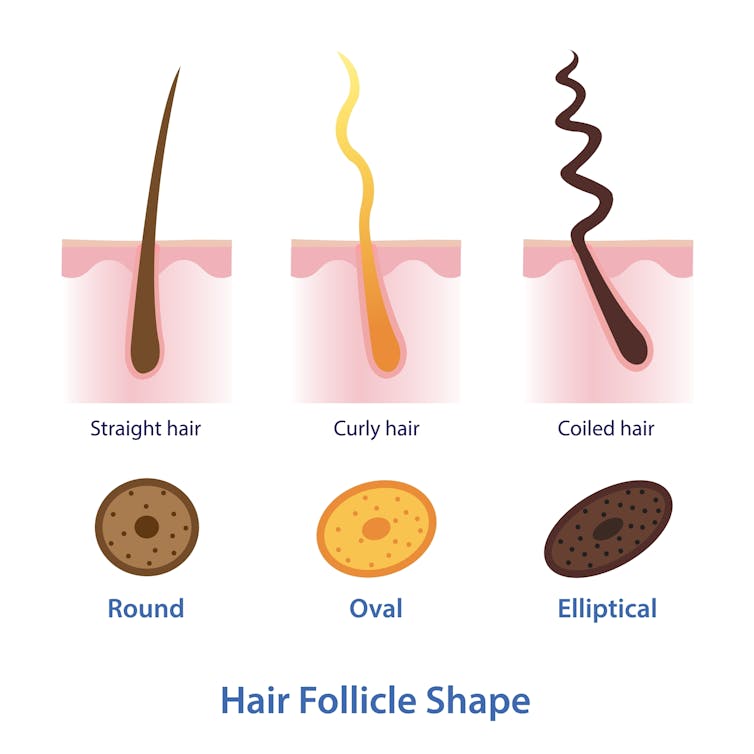
Curly or straight? How hair follicle shape plays a role
Hair is made of keratin, a strong and insoluble protein. Each hair strand grows from its own hair follicle that extends deep into the skin.
Curly hair forms due to asymmetry of both the hair follicle and the keratin in the hair.
Follicles that produce curly hair are asymmetrical and curved and lie at an angle to the surface of the skin. This kinks the hair as it first grows.
The asymmetry of the hair follicle also causes the keratin to bunch up on one side of the hair strand. This pulls parts of the hair strand closer together into a curl, which maintains the curl as the hair continues to grow.
Follicles that are symmetrical, round and perpendicular to the skin surface produce straight hair.
Each hair strand grows from its own hair follicle.
Mosterpiece/ShutterstockLife changes, hair changes
Our hair undergoes repeated cycles throughout life, with different stages of growth and loss.
Each hair follicle contains stem cells, which multiply and grow into a hair strand.
Head hairs spend most of their time in the growth phase, which can last for several years. This is why head hair can grow so long.
Let’s look at the life of a single hair strand. After the growth phase is a transitional phase of about two weeks, where the hair strand stops growing. This is followed by a resting phase where the hair remains in the follicle for a few months before it naturally falls out.
The hair follicle remains in the skin and the stems cells grow a new hair to repeat the cycle.
Each hair on the scalp is replaced every three to five years.
Each hair on the scalp is replaced every three to five years.
Just Life/ShutterstockHormone changes during and after pregnancy alter the usual hair cycle
Many women notice their hair is thicker during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, high levels of oestrogen, progesterone and prolactin prolong the resting phase of the hair cycle. This means the hair stays in the hair follicle for longer, with less hair loss.
A drop in hormones a few months after delivery causes increased hair loss. This is due to all the hairs that remained in the resting phase during pregnancy falling out in a fairly synchronised way.
Hair can change around puberty, pregnancy or after chemotherapy
This is related to the genetics of hair shape, which is an example of incomplete dominance.
Incomplete dominance is when there is a middle version of a trait. For hair, we have curly hair and straight hair genes. But when someone has one curly hair gene and one straight hair gene, they can have wavy hair.
Hormonal changes that occur around puberty and pregnancy can affect the function of genes. This can cause the curly hair gene of someone with wavy hair to become more active. This can change their hair from wavy to curly.
Researchers have identified that activating specific genes can change hair in pigs from straight to curly.
Chemotherapy has very visible effects on hair. Chemotherapy kills rapidly dividing cells, including hair follicles, which causes hair loss. Chemotherapy can also have genetic effects that influence hair follicle shape. This can cause hair to regrow with a different shape for the first few cycles of hair regrowth.
Your hair can change at different stages of your life.
Igor Ivakhno/ShutterstockHormonal changes as we age also affect our hair
Throughout life, thyroid hormones are essential for production of keratin. Low levels of thyroid hormones can cause dry and brittle hair.
Oestrogen and androgens also regulate hair growth and loss, particularly as we age.
Balding in males is due to higher levels of androgens. In particular, high dihydrotestosterone (sometimes shortened to DHT), which is produced in the body from testosterone, has a role in male pattern baldness.
Some women experience female pattern hair loss. This is caused by a combination of genetic factors plus lower levels of oestrogen and higher androgens after menopause. The hair follicles become smaller and smaller until they no longer produce hairs.
Reduced function of the cells that produce melanin (the pigment that gives our hair colour) is what causes greying.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: