Tasty Hot-Or-Cold Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Full of fiber as well as vitamins and minerals, this versatile “serve it hot or cold” soup is great whatever the weather—give it a try!
You will need
- 1 quart low-sodium vegetable stock—ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer until you had enough to boil in a big pan, but failing that, a large supermarket will generally be able to sell you low-sodium stock cubes.
- 2 medium potatoes, peeled and diced
- 2 leeks, chopped
- 2 stalks celery, chopped
- 1 large onion, diced
- 1 large carrot, diced, or equivalent small carrots, sliced
- 1 zucchini, diced
- 1 red bell pepper, diced
- 1 tsp rosemary
- 1 tsp thyme
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 small piece (equivalent of a teaspoon) ginger, minced
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp turmeric
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
- Optional: ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
About the MSG/salt: there should be enough sodium already from the stock and potatoes, but in case there’s not (since not all stock and potatoes are made equal), you might want to keep this on standby.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a sauté pan, and add the diced onion, frying until it begins to soften.
2) Add the ginger, potato, carrot, and leek, and stir for about 5 minutes. The hard vegetables won’t be fully cooked yet; that’s fine.
3) Add the zucchini, red pepper, celery, and garlic, and stir for another 2–3 minutes.
4) Add the remaining ingredients; seasonings first, then vegetable stock, and let it simmer for about 15 minutes.
5) Check the potatoes are fully softened, and if they are, it’s ready to serve if you want it hot. Alternatively, let it cool, chill it in the fridge, and enjoy it cold:
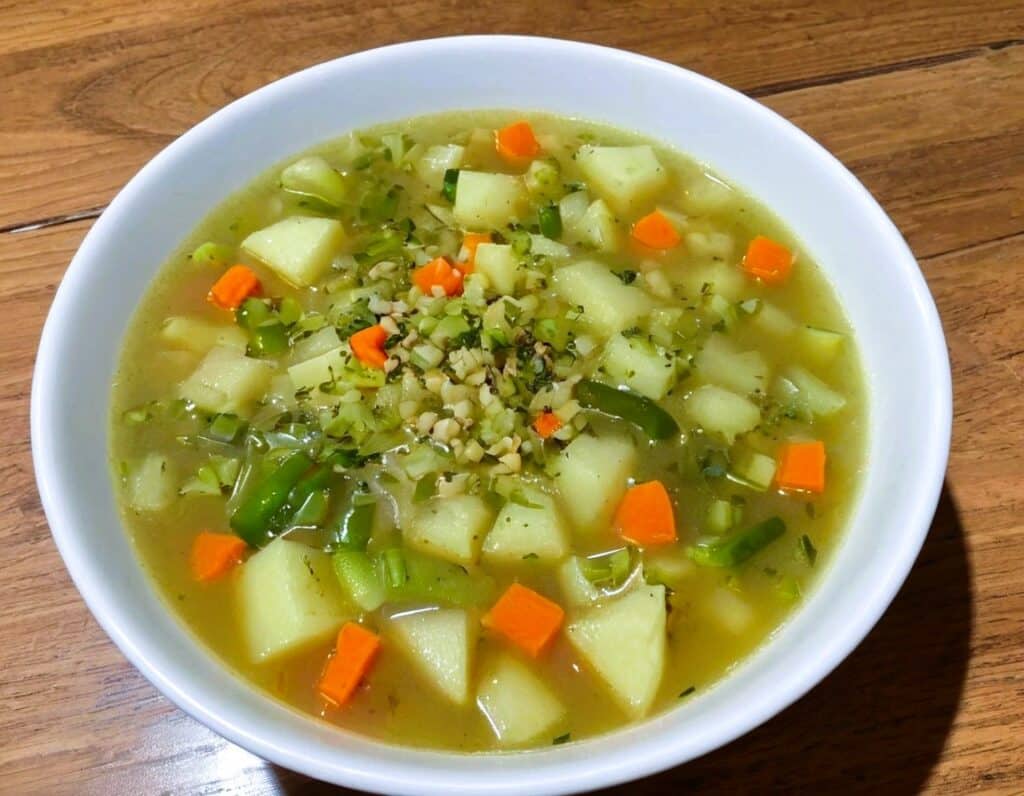

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← 5/5 in our recipe today!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Avoid Carer Burnout
Sometimes in life we find ourselves in a caregiving role.
Maybe we chose it. For example, by becoming a professional carer, or even just by being a parent.
Oftentimes we didn’t. Sometimes because our own parents now need care from us, or because a partner becomes disabled.
Philosophical note: an argument could be made for that latter also having been a pre-emptive choice; we probably at some point said words to the effect of “in sickness and in health”, hopefully with free will, and hopefully meant it. And of course, sometimes we enter into a relationship with someone who is already disabled.
But, we are not a philosophy publication, and will henceforth keep to the practicalities.
First: are you the right person?
Sometimes, a caregiving role might fall upon you unasked-for, and it’s worth considering whether you are really up for it. Are you in a position to be that caregiver? Do you want to be that caregiver?
It may be that you do, and would actively fight off anyone or anything that tried to stop you. If so, great, now you only need to make sure that you are actually in a position to provide the care in question.
It may be that you do want to, but your circumstances don’t allow you to do as good a job of it as you’d like, or it means you have to drop other responsibilities, or you need extra help. We’ll cover these things later.
It may be that you don’t want to, but you feel obliged, or “have to”. If that’s the case, it will be better for everyone if you acknowledge that, and find someone else to do it. Nobody wants to feel a burden, and nobody wants someone providing care to be resentful of that. The result of such is two people being miserable; that’s not good for anyone. Better to give the job to someone who actually wants to (a professional, if necessary).
So, be honest (first with yourself, then with whoever may be necessary) about your own preferences and situation, and take steps to ensure you’re only in a caregiving role that you have the means and the will to provide.
Second: are you out of your depth?
Some people have had a life that’s prepared them for being a carer. Maybe they worked in the caring profession, maybe they have always been the family caregiver for one reason or another.
Yet, even if that describes you… Sometimes someone’s care needs may be beyond your abilities. After all, not all care needs are equal, and someone’s condition can (and more often than not, will) deteriorate.
So, learn. Learn about the person’s condition(s), medications, medical equipment, etc. If you can, take courses and such. The more you invest in your own development in this regard, the more easily you will handle the care, and the less it will take out of you.
And, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Maybe the person knows their condition better than you, and certainly there’s a good chance they know their care needs best. And certainly, there are always professionals that can be contacted to ask for advice.
Sometimes, a team effort may be required, and there’s no shame in that either. Whether it means enlisting help from family/friends or professionals, sometimes “many hands make light work”.
Check out: Caregiver Action Network: Organizations Near Me
A very good resource-hub for help, advice, & community
Third: put your own oxygen mask on first
Like the advice to put on one’s own oxygen mask first before helping others (in the event of a cabin depressurization in an airplane), the rationale is the same here. You can’t help others if you are running on empty yourself.
As a carer, sometimes you may have to put someone else’s needs above yours, both in general and in the moment. But, you do have needs too, and cannot neglect them (for long).
One sleepless night looking after someone else is… a small sacrifice for a loved one, perhaps. But several in a row starts to become unsustainable.
Sometimes it will be necessary to do the best you can, and accept that you cannot do everything all the time.
There’s a saying amongst engineers that applies here too: “if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you”.
In other words: if you don’t give your body rest, your body will break down and oblige you to rest. Please be aware this goes for mental effort too; your brain is just another organ.
So, plan ahead, schedule breaks, find someone to take over, set up your cared-for-person with the resources to care for themself as well as possible (do this anyway, of course—independence is generally good so far as it’s possible), and make the time/effort to get you what you need for you. Sleep, distraction, a change of scenery, whatever it may be.
Lastly: what if it’s you?
If you’re reading this and you’re the person who has the higher care needs, then firstly:all strength to you. You have the hardest job here; let’s not forget that.
About that independence: well-intentioned people may forget that, so don’t be afraid to remind them when “I would prefer to do that myself”. Maintaining independence is generally good for the health, even if sometimes it is more work for all concerned than someone else doing it for you. The goal, after all, is your wellbeing, so this shouldn’t be cast aside lightly.
On the flipside: you don’t have to be strong all the time; nobody should.
Being disabled can also be quite isolating (this is probably not a revelation to you), so if you can find community with other people with the same or similar condition(s), even if it’s just online, that can go a very, very long way to making things easier. Both practically, in terms of sharing tips, and psychologically, in terms of just not feeling alone.
See also: How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Share This Post
-
5 Things You Can Change About Your Personality (But: Should You?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are many personality-typing systems that, with varying degrees of validity*, aim to describe a person’s personality.
*and often pseudoscience:
- sometimes obviously so like astrology
- sometimes dressed up in clinical words like the Meyers-Briggs
- sometimes openly, per “this is not science but you may find it useful to frame things this way”, like the Enneagram
There is currently one kind of personality-typing system (with some minor variations) that is used in the actual field of clinical psychology, specifically under the umbrella of “trait theory”, and that is…
The “Big Five” personality traits
Also called the OCEAN or CANOE model, based on its 5 components:
- openness to experience: inventive/curious rather than consistent/cautious
- conscientiousness: efficient/organized rather than extravagant/careless
- extroversion: outgoing/energetic rather than solitary/reserved
- agreeableness: friendly/compassionate rather than critical/judgmental
- neuroticism: sensitive/nervous rather than resilient/confident
The latter (neuroticism) is not to be confused with neurosis, which is very different and beyond the scope of today’s article.
Note that some of these seem more positive/negative than others at a glance, but really, any of these could be a virtue or a vice depending on specifics or extremity.
For scientific reference, here’s an example paper:
The Big Five Personality Factors and Personal Values
Quick self-assessment
There are of course many lengthy questionnaires for this, but in the interests of expediency:
Take a moment to rate yourself as honestly as you can, on a scale of 1–10, for each of those components, with 10 being highest for the named trait.
For example, this writer gives herself: O7, C6, E3, A8, N2 (in other words I’d say I’m fairly open, moderately conscientious, on the reserved side, quite agreeable, and quite resilient)
Now, put your rating aside (in your phone’s notes app is fine, if you hadn’t written it down already) and forget about it for the moment, because we want you to do the next exercise from scratch.
Who would you be, at your best?
Now imagine your perfect idealized self, the best you could ever be, with no constraints.
Take a moment to rate your idealized self’s personality, on a scale of 1–10, for each of those components, with 10 being highest for the named trait.
For example, this writer picks: O9, C10, E5, A8, N1.
Maybe this, or maybe your own idealized self’s personality, will surprise you. That some traits might already be perfect for you already; others might just be nudged a little here or there; maybe there’s some big change you’d like. Chances are you didn’t go for a string of 10s or 1s (though if you did, you do you; there are no wrong answers here as this one is about your preferences).
We become who we practice being
There are some aspects of personality that can naturally change with age. For example:
- confidence/resilience will usually gradually increase with age due to life experience (politely overlook teenagers’ bravado; they are usually a bundle of nerves inside, resulting in the overcompensatory displays of confidence)
- openness to experience may decrease with age, as we can get into a rut of thinking/acting a certain way, and/or simply consciously decide that our position on something is already complete and does not need revision.
But, we can decide for ourselves how to nudge our “Big Five” traits, for example:
- We can make a point of seeking out new experiences, and considering new ideas, or develop strategies for reining ourselves in
- We can use systems to improve our organization, or go out of our way to introduce a little well-placed chaos
- We can “put ourselves out there” socially, or make the decision to decline more social invitations because we simply don’t want to
- We can make a habit of thinking kindly of others and ourselves, or we can consciously detach ourselves and look on the cynical side more
- We can build on our strengths and eliminate our weaknesses, or lean into uncomfortable emotions
Some of those may provoke a “why would anyone want to…?” response, but the truth is we are all different. An artist and a police officer may have very different goals for who they want to be as a person, for example.
Interventions to change personality can and do work:
A systematic review of personality trait change through intervention
There are many ways to go about “being the change we want to see” in ourselves, and yes there can be a degree of “fake it until you make it” if that works for you, but it doesn’t have to be so. It can also simply be a matter of setting yourself reminders about the things that are most important to you.
Writer’s example: pinned above my digital workspace I have a note from my late beloved, written just under a week before death. The final line reads, “keep being the good person that you are” (on a human level, the whole note is uplifting and soothing to me and makes me smile and remember the love we shared; or to put it in clinical terms, it promotes high agreeableness, low neuroticism).
Other examples could be a daily practice of gratitude (promotes lower neuroticism), or going out of your way to speak to your neighbors (promotes higher extraversion), signing up for a new educational course (promotes higher openness) or downloading a budgeting app (promotes higher conscientiousness).
In short: be the person you want to be, and be that person deliberately, because you can.
Some resources that may help for each of the 5 traits:
- Curiosity Kills The Neurodegeneration
- How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex
- How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
- Optimism Seriously Increases Longevity!
- Building Psychological Resilience (Without Undue Hardship)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Most Anti Aging Exercise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve referenced this (excellent) video before, but never actually put it under the spotlight in one of these features, so here we go!
Deep squats
It’s about deep squats, also called Slav squats, Asian squats, sitting squats, resting squats, or various other names. However, fear not; you don’t need to be Slavic or Asian to do it; you just need to practice.
As for why this is called “anti-aging”, by the way, it’s because being able to get up off the ground is one of the main tests of age-related mobility decline, and if you can deep-squat comfortably, then you can do that easily. And so long as you continue being able to deep-squat comfortably, you’ll continue to be able to get up off the ground easily too, because you have the strength in the right muscles, as well as the suppleness, comfort with range of motion, and balance (those stabilizing muscles are used constantly in a deep squat, whereas Western lifestyle sitting leaves those muscles very neglected and thus atrophied).
Epidemiological note: chairs, couches, and assorted modern conveniences reduce the need for squatting in daily life, leading to stiffness in joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Many adults in developed countries struggle with deep squats due to lack of use, not aging. Which is a problem, because a lack of full range of motion in joints causes wear and tear, leading to chronic pain and degenerative joint diseases. People in countries where squatting is a common resting position have lower incidences of osteoarthritis, for example—contrary to what some might expect, squatting does not harm joints but rather protects them from arthritis and knee pain. Strengthening leg muscles through squatting can alleviate knee pain, whereas knee pain is often worsened by inactivity.
Notwithstanding the thumbnail, which is showing an interim position, one’s feet should be flat on the ground, by the way, and one’s butt should be nearby, just a few inches off the ground (in other words, the position that we see her in for most of this video).
Troubleshooting: if you’re accustomed to sitting in chairs a lot, then this may be uncomfortable at first. Zuzka advises us to go gently, and/but gradually increase our range of motion and (equally importantly) duration in the resting position.
You can use a wall or doorway to partially support you, at first, if you struggle with mobility or balance. Just try to gradually use it less, until you’re comfortable deep-squatting with no support.
Since this is not an intrinsically very exciting exercise, once you build up the duration for which you’re comfortable deep-squatting, it can be good to get in the habit of “sitting” this way (i.e. deep squatting, still butt-off-the-floor, but doing the job of sitting) while doing other things such as working (if you have an appropriate work set-up for that*), reading, or watching TV.
*this is probably easiest with a laptop placed on an object/surface of appropriate height, such as a coffee table or such. As a bonus, having your hands in front of you while working will also bring your center of gravity forwards a bit, making the position easier and more comfortable to maintain. This writer (hi, it’s me) prefers her standing desk for work in general, with a nice ergonomic keyboard and all that, but if using a laptop from time to time, then squatting is a very good option.
In terms of working up duration, if you can only manage seconds to start with, that’s fine. Just do a few more seconds each time, until it’s 30, 60, 120, and so on until it’s 5 minutes, 10, 15, and so on.
You can even start that habit-forming while you’re still in the “seconds at a time” stage! You can deep-squat just for some seconds while you:
- pick up something from the floor
- check on something in the oven
- get something out of the bottom of the fridge
…etc!
For more on all this, plus many visual demonstrations including interim exercises to get you there if it’s difficult for you at first, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Mobility For Now & For Later: Train For The Marathon That Is Your Life!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Feel Better In 5 – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Rangan Chatterjee before, and here’s a great book of his.
The premise is a realistic twist on a classic, the classic being “such-and-such, in just 5 minutes per day!”
In this case, Dr. Chatterjee offers many lifestyle interventions that each take just 5 minutes, with the idea that you implement 3 of them per day (your choice which and when), and thus gradually build up healthy habits. Of course, once things take as habits, you’ll start adding in more, and before you know it, half your lifestyle has changed for the better.
Which, you may be thinking “my lifestyle’s not that bad”, but if you improve the health outcomes of, say, 20 areas of your life by just a few percent each, you know much better health that adds up to? We’ll give you a clue: it doesn’t add up, it compounds, because each improves the other too, for no part of the body works entirely in isolation.
And Dr. Chatterjee does tackle the body systematically, by the way; interventions for the gut, heart, brain, and so on.
As for what these interventions look like; it is very varied. One might be a physical exercise; another, a mental exercise; another, a “make this health 5-minute thing in the kitchen”, etc, etc.
Bottom line: this is the most supremely easy of easy-ins to healthier living, whatever your starting point—because even if you’re doing half of these interventions, chances are you aren’t doing the other half, and the idea is to pick and choose how and when you adopt them in any case, just picking three 5-minute interventions each day with no restrictions. In short, a lot of value to had here when it comes to real changes to one’s serious measurable health.
Click here to check out Feel Better In 5, and indeed feel better in 5!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Deskbound – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve all heard that “sitting is the new smoking”, and whether or not that’s an exaggeration (the jury’s out), one thing that is clear is that sitting is very bad.
Popular advice is “here’s how to sit with good posture and stretch your neck sometimes”… but that advice tends to come from companies that pay people to sit for a long time. They might not be the a very unbiased source.
Starrett and Cordoza offer better. After one opening chapter covering the multifarious ways sitting ruins our health, the rest of the book is all advice, covering:
- The principles of how the body is supposed to be
- The most important movements that we should be doing
- A dynamic workstation setup
- This is great, because “get a standing desk” tends to present more questions than answers, and can cause as much harm as good if done wrong
- The authors also cover how to progressively cut down on sitting, rather than try to go cold-turkey.
- They also recognize that not everyone can stand at all, and…
- Optimizing the sitting position, for when we must sit
- Exercises to maintain our general mobility and compensate about as well as we can for the body-unfriendly nature of modern life.
The book is mostly explanations, so at 682 pages, you can imagine it’s not just “get up, lazybones!”. Rather, things are explained in such detail (and with many high-quality medical diagrams) so that we can truly understand them.
Most of us have gone through life knowing we should have “better posture” and “move more”… but without the details, that can be hard to execute correctly, and worse, we can even sabotage our bodies unknowingly with incorrect form.
This book straightens all that out very comprehensively, and we highly recommend it.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wise Old Fool
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
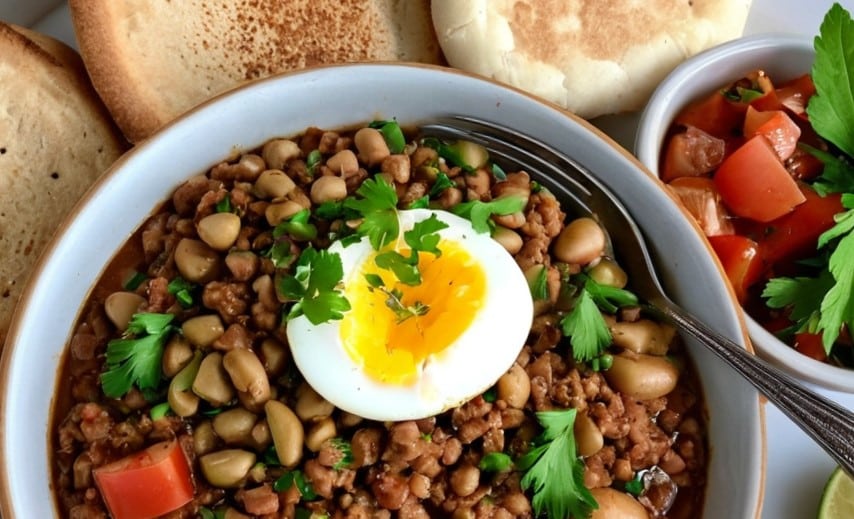
How old is this dish? Well, let’s put it this way, it used to be called “𓅮𓏏𓈖” and remnants of it have been found at neolithic burial sites in Egypt. Nowadays it’s called “فول مدمس”, which gets rendered a lot of different ways in the Latin alphabet, but “fūl mudammas” is one option. For short, it’s just called “fūl”, which is pronounced like the English word “fool”, and it’s about the beans.
From chana masala with poori to frijoles refritos to beans on toast, lots of cultures have some version of this breakfast food, and all can be great (yes, even the beans on toast). But today we’re about this particular kind of morning protein, fiber, fats, and healthful spices.
You will need
- 2x 14 oz cans fava beans (other kinds of beans work as substitute; kidney beans are common substitution, but this writer prefers black beans personally if she doesn’t have fava in), drained
- 4 garlic cloves, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 teaspoon sweet cinnamon (or ½ sweet cinnamon stick)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp paprika
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
- For the relish: 1 medium tomato, finely chopped; 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil; 2 tbsp parsley, finely chopped
- To serve: 4 pitta breads, 2 eggs (omit if vegan), and a selection of pickled vegetables, drained
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the olive oil to a saucepan over a medium heat; add the garlic, cumin seeds, and cinnamon. Keep these moving for a minute or two before moving to the next step.
2) Add the fava beans, as well as the other seasonings (chili flakes, paprika, black pepper), and mix thoroughly
3) Add 1 cup boiling water, and keep everything on a simmer for about 20 minutes, stirring often. Add the lemon juice while it’s simmering; when the beans start to break down and the mixture starts to thicken, it’s ready.
4) Mix the relish ingredients (finely chopped tomato, olive oil, parsley) thoroughly in a small bowl
5) Toast the pitta breads, and if using, soft-boil the eggs.
6) Serve! We suggest: fūl in a bowl, with one half of a soft-boiled egg per bowl, topped with the relish, and served with the pitta bread and pickled vegetables on the side.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Less Obvious Probiotic Benefits ← the pickled vegetables contain the probiotics here, while the beans are a great source of prebiotic fiber; this is why they work so well together
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
- Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: