How To Recover Quickly From A Stomach Bug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Recover Quickly From A Stomach Bug
Is it norovirus, or did you just eat something questionable? We’re not doctors, let alone your doctors, and certainly will not try to diagnose from afar. And as ever, if unsure and/or symptoms don’t go away or do get worse, seek professional medical advice.
That out of the way, we can give some very good general-purpose tips for this one…
Help your immune system to help you
So far as you can, you want a happy healthy immune system. For the most part, we’d recommend the following things:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
…but you probably don’t want to be exercising with a stomach bug, so perhaps sit that one out. Exercise is the preventative; what you need right now is rest.
Hydrate—but watch out
Hydration is critical for recovery especially if you have diarrhea, but drinking too much water too quickly will just make things worse. Great options for getting good hydration more slowly are:
- Peppermint tea
- (peppermint also has digestion-settling properties)
- Ginger tea
- See also: Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Broths
- These will also help replenish your sodium and other nutrients, gently. Chicken soup for your stomach, and all that. A great plant-based option is sweetcorn soup.
- By broths, we mean clear(ish) water-based soups. This is definitely not the time for creamier soups.
❝Milk and dairy products should be avoided for 24 to 48 hours as they can make diarrhea worse.
Initial dietary choices when refeeding should begin with soups and broth.❞
Source: American College of Gastroenterology
Other things to avoid
Caffeine stimulates the digestion in a way that can make things worse.
Fat is more difficult to digest, and should also be avoided until feeling better.
To medicate or not to medicate?
Loperamide (also known by the brand name Imodium) is generally safe when used as directed.
Click here to see its uses, dosage, side effects, and contraindications
Antibiotics may be necessary for certain microbial infections, but should not be anyone’s first-choice treatment unless advised otherwise by your doctor/pharmacist.
Note that if your stomach bug is not something that requires antibiotics, then taking antibiotics can actually make it worse as the antibiotics wipe out your gut bacteria that were busy helping fight whatever’s going wrong in there:
- Facing a new challenge: the adverse effects of antibiotics on gut microbiota and host immunity
- Antibiotics as major disruptors of gut microbiota
- Microbiotoxicity: antibiotic usage and its unintended harm to the microbiome
A gentler helper
If you want to give your “good bacteria” a hand while giving pathogens a harder time of it, then a much safer home remedy is a little (seriously, do not over do it; we are talking 1–2 tablespoons, or around 20ml) apple cider vinegar, taken diluted in a glass of water.
❝Several studies indicate apple cider vinegar (ACV)’s usefulness in lowering postprandial glycemic response, specifically by slowing of gastric motility❞
(Slowing gastric motility is usually exactly what you want in the case of a stomach bug, and apple cider vinegar)
See also:
- Antimicrobial activity of apple cider vinegar against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans
- Antibacterial apple cider vinegar eradicates methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and resistant Escherichia coli
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Over-50s Physio: What My 5 Oldest Patients (Average Age 92) Do Right
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Oftentimes, people of particularly advanced years will be asked their secret to longevity, and sometimes the answers aren’t that helpful because they don’t actually know, and ascribe it to some random thing. Will Harlow, the over-50s specialist physio, talks about the top 5 science-based things that his 5 oldest patients do, that enhances the healthy longevity that they are enjoying:
The Top 5’s Top 5
Here’s what they’re doing right:
Daily physical activity: all five patients maintain a consistent habit of daily exercise, which includes activities like exercise classes, home workouts, playing golf, or taking daily walks. They prioritize movement even when it’s difficult, rarely skipping a day unless something serious happened. A major motivator was the fear of losing mobility, as they had seen spouses, friends, or family members stop exercising and never start again.
Stay curious: a shared trait among the patients was their curiosity and eagerness to learn. They enjoy meeting new people, exploring new experiences, and taking on new challenges. Two of them attended the University of the Third Age to learn new skills, while another started playing bridge as a new hobby. The remaining two have recently made new friends. They all maintain a playful attitude, a good sense of humor, and aren’t afraid to fail or laugh at themselves.
Prioritize sleep (but not too much): the patients each average seven hours of sleep per night, aligning with research suggesting that 7–9 hours of sleep is ideal for health. They maintain consistent sleep and wake-up times, which contributes to their well-being. While they allow themselves short naps when needed, they avoid long afternoon naps to avoid disrupting their sleep patterns.
Spend time in nature: spending time outdoors is a priority for all five individuals. Whether through walking, gardening, or simply sitting on a park bench, they make it a habit to connect with nature. This aligns with studies showing that time spent in natural environments, especially near water, significantly reduces stress. When water isn’t accessible, green spaces still provide a beneficial boost to mental health.
Stick to a routine: the patients all value simple daily routines, such as enjoying an evening cup of tea, taking a daily walk, or committing to small gardening tasks. These routines offer mental and physical grounding, providing stability even when life becomes difficult sometimes. They emphasized the importance of keeping routines simple and manageable to ensure they could stick to them regardless of life’s challenges.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Top 8 Habits Of The Top 1% Healthiest Over-50s ← another approach to the same question, this time with a larger sample size, and/but many younger (than 90s) respondents.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Heal Your Stressed Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Rochelle Walsh, therapist, explains the problem and how to fix it:
Not all brain damage is from the outside
Long-term stress and burnout cause brain damage; it’s not just a mindset issue—it impacts the brain physiologically. To compound matters, it also increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. While the brain can indeed grow new neurons and regenerate itself, chronic stress damages specific regions, and inhibits that.
There are some effects of chronic stress that can seem positive—the amygdalae and hypothalamus are seen to grow larger and stronger, for instance—but this is, unfortunately, “all the better to stress you with”. In compensation for this, chronic stress deprioritizes the pre-frontal cortex and hippocampi, so there goes your reasoning and memory.
This often results in people not managing chronic stress well. Just like a weak heart and lungs might impede the exercise that could make them stronger, the stressed brain is not good at permitting you to do the things that would heal it—preferring to keep you on edge all day, worrying and twitchy, mind racing and body tense. It also tends to lead to autoimmune diseases, due to the increased inflammation (because the body’s threat-detection system as at “jumping at own shadow” levels so it’s deploying every defense it has, including completely inappropriate ones).
Notwithstanding the “Heal Your Stressed Brain” thumbnail, she doesn’t actually go into this in detail and bids us sign up for her masterclass. We at 10almonds however like to deliver, so you can find useful advice and free resources in our links-drop at the bottom of this article.
Meanwhile, if you’d like to hear more about the neurological woes described above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
- How To Manage/Reduce Chronic Stress
- Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
- How Healthy People Regulate Their Emotions
- Sleep: Yes, You Really Do Still Need It!
- Give Your Adrenal Glands A Chance
- The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Quick Healthy Recipe Ideas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
“It was superb !! Just loved that healthy recipe !!! I would love to see one of those every day, if possible !! Keep up the fabulous work !!! ”
We’re glad you enjoyed! We can’t promise a recipe every day, but here’s one just for you:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Kiwi vs Lime – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to lime, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, kiwi has more protein, more carbs, and more fiber. As with most fruits, the fiber is the number we’re most interested in for health purposes; in this case, kiwi is just slightly ahead of lime on all three of those.
In terms of vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while lime has a tiny bit more vitamin B5. As in, the vitamin that’s in pretty much anything and is practically impossible to be deficient in unless you are literally starving to death. You may be thinking: aren’t limes a famously good source of vitamin C? And yes, yes they are. But kiwis have >3x more. In other big differences, kiwis also have >6x more vitamin E and >67 times more vitamin K.
When it comes to minerals, kiwi has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while lime has more iron and selenium. Another easy win for kiwis.
In short: enjoy both; both are good. But kiwis are the more nutritionally dense option by almost every way of measuring it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← kiwi is top of the list; it promotes cancer cell death while sparing healthy cells
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
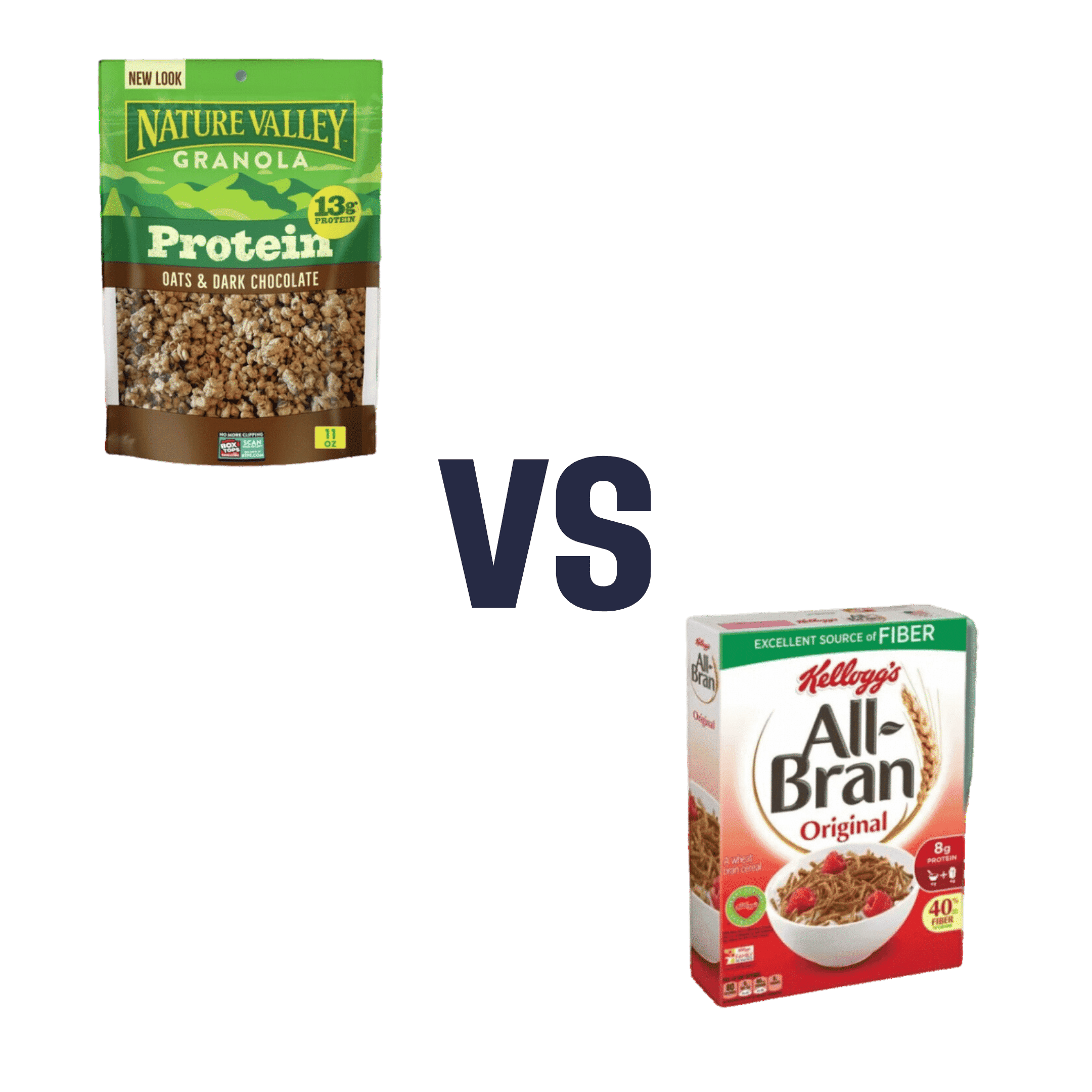
Nature Valley Protein Granola vs Kellog’s All-Bran – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Nature Valley Protein Granola to Kellog’s All-Bran, we picked the All-Bran.
Why?
While the Protein Granola indeed contains more protein (13g/cup, compared to 5g/cup), it also contains three times as much sugar (18g/cup, compared to 9g/cup) and only ⅓ as much fiber (4g/cup, compared to 12g/cup)
Given that fiber is what helps our bodies to absorb sugar more gently (resulting in fewer spikes), this is extremely important, especially since 18g of sugar in one cup of Protein Granola is already most of the recommended daily allowance, all at once!
For reference: the AHA recommends no more than 25g added sugar for women, or 32g for men
Hence, we went for the option with 3x as much fiber and ⅓ of the sugar, the All-Bran.
For more about keeping blood sugars stable, see:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Be Your Own Therapist – by Owen O’Kane
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Finding the right therapist can be hard. Sometimes, even just accessing a therapist, any therapist, can be hard, if circumstances are adverse. Sometimes we’d like therapy, but want to feel “better prepared for it” before we do.
Owen O’Kane, a highly qualified and well-respected psychotherapist, wants to put some tools in our hands. The premise of this book is that “in 10 minutes a day” one can give oneself an amount of therapy that will be beneficial.
Naturally, in 10 minutes a day, this isn’t going to be the kind of therapy that will work through major traumas, so what can it do?
Those 10 minutes are spread into three sessions:
- 4 minutes in the morning
- 3 minutes in the afternoon
- 3 minutes in the evening
The idea is:
- To do a quick mental health “check-in” before the day gets started, ascertain what one needs in that context, and make a simple plan to get/have it.
- To keep one’s mental health on track by taking a little pause to reassess and adjust if necessary
- To reflect on the day, amplify the positive, and let go of the negative to what extent is practical, in order to rest well ready for the next day
Where O’Kane excels is in explaining how to do those things in a way that is neither overly simplistic and wishy-washy, nor so arcane and convoluted as to create more work and render the day more difficult.
In short, this book is a great prelude to (or adjunct to) formal therapy, and for those for whom therapy isn’t accessible and/or desired, a great way to keep oneself on a mentally healthy track.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: