The Herbal Supplement That Rivals Prozac
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Flower Power: St. John’s Wort’s Drug-Level Effectiveness
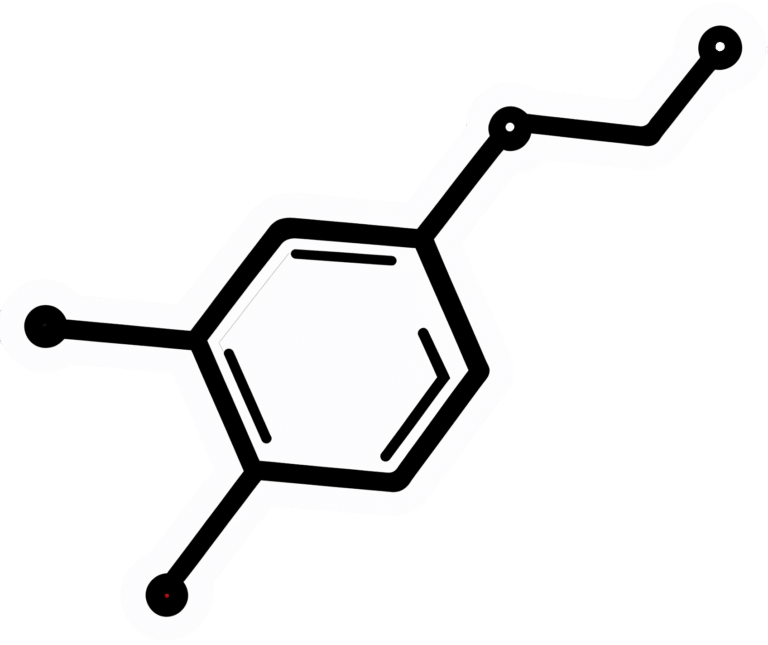
St. John’s wort is a small yellow flower, extract of which can be bought inexpensively off-the-shelf in pretty much any pharmacy in most places.
It’s sold and used as a herbal mood-brightener.
Does it work?
Yes! It’s actually very effective. This is really uncontroversial, so we’ll keep it brief.
The main findings of studies are that St. John’s wort not only gives significant benefits over placebo, but also works about as well as prescription anti-depressants:
A systematic review of St. John’s wort for major depressive disorder
They also found that fewer people stop taking it, compared to how many stop taking antidepressants. It’s not known how much of this is because of its inexpensive, freely-accessible nature, and how much might be because it gave them fewer adverse side effects:
Clinical use of Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) in depression: A meta-analysis
How does it work?
First and foremost, it’s an SSRI—a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Basically, it doesn’t add serotonin, but it makes whatever serotonin you have, last longer. Same as most prescription antidepressants. It also affects adenosine and GABA pathways, which in lay terms, means it promotes feelings of relaxation, in a similar way to many prescription antianxiety medications.
Mechanism of action of St John’s wort in depression: what is known?
Any problems we should know about?
Yes, definitely. To quote directly from the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health:
St. John’s wort can weaken the effects of many medicines, including crucially important medicines such as:
- Antidepressants
- Birth control pills
- Cyclosporine, which prevents the body from rejecting transplanted organs
- Some heart medications, including digoxin and ivabradine
- Some HIV drugs, including indinavir and nevirapine
- Some cancer medications, including irinotecan and imatinib
- Warfarin, an anticoagulant (blood thinner)
- Certain statins, including simvastatin
I’ve read all that, and want to try it!
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but here’s an example product on Amazon.
Please be safe and do check with your doctor and/or pharmacist, though!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Problem With Active Listening
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The problem with active listening
Listening is an important skill to keep well-trained at any age. It’s important in romantic relationships, parent-child relationships, friendships, and more.
First, for any unfamiliar or hazy-of-memory: active listening is the practice of listening, actively. The “active” side of this comes in several parts:
- Asking helpful questions
- Giving feedback to indicate that the answer has been understood
- Prompting further information-giving
This can look like:
- A: How did you feel when that happened?
- B: My heart was racing and I felt panicked, it really shocked me
- A: It really shocked you?
- B: Yes, because it was so unexpected; I’d never imagined something like this happening
- A: You’d never expect something like that
- B: No, I mean, I had no reason to
And… As a superficial listening technique, it’s not terrible, and it has its place
But unfortunately, if it’s one’s only listening technique, one will very quickly start sounding like a Furby—that children’s toy from the 90s that allegedly randomly parroted fragments of things that had been said to it. In fact this was a trick of programming, but that’s beyond the scope of this article.
The point is: the above technique, if used indiscriminately and/or too often, starts to feel like talking to a very basic simulacrum.
Which is the opposite of feeling like being listened to!
A better way to listen
Start off similarly, but better.
Ask open questions, or otherwise invite sharing of information.
People can be resistant to stock phrases like “How did that make you feel?”, but this can be got around by simply changing it up, e.g.:
- “What was your reaction?” ← oblique but often elicits the same information
- “I’m not sure how I’d feel about that, in your shoes” ← not even a question, but shows active attention much better than the “mmhmm” noises of traditional active listening, and again prompts the same information
Express understanding… But better
People have been told “I understand” a lot, and often it’s code for “Stop talking”. So, avoid “I understand”. Instead, try:
- “I can understand that”
- “Understandable”
- “That makes sense”
Ask clarifying questions… Better
Sometimes, a clarifying question doesn’t have to have its own point, beyond prompting more sharing, and sometimes, an “open question” can be truly wide open, meaning that vaguer is better, such as:
- “Oh?”
- “How so?” ← this is the heavy artillery that can open up a lot
Know when to STFU
Something that good therapists (and also military interrogators) know: when to STFU
If someone is talking, don’t interrupt them. If you do, they might not start again, or might skip what they were going to say.
Interruption says “I think you’ve said all that needs to be said there”, or else, if the interruption was to ask one of the above questions, it says “you’re not doing a good enough job of talking”, and neither of those sentiments encourage people to share, nor do they make someone feel listened-to!
Instead, just listen. Passive listening has its place too! When there’s a break, then you can go to one of the above questions/prompts/expressions of understanding, as appropriate.
Judge not, lest they feel judged
Reserve judgement until the conversation is over, at the earliest. If asked for your judgement of some aspect, be as reassuring as you can. People feel listened-to when they don’t feel judged.
If they feel judged, conversely, they can often feel you didn’t listen properly, or else you’d be in agreement with them. So instead, just sit on it for as long as you can.
Note: that goes for positive judgements too! Sit on it. Expressing a positive judgement too soon can seem that you were simply eager to please, and can suggest insincerity.
If this seems simple, that’s because it is. But, try it, and see the difference.
Share This Post
-
10 “Healthy” Foods That Are Often Worse Than You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“This is healthy, it’s a…” is an easy mistake to make if one doesn’t read the labels. Here are 10 tricksters to watch out for in particular!
Don’t be fooled by healthy aesthetics on the packaging…
Notwithstanding appearances and in many cases reputations, these all merit extra attention:
- Yogurt: sweetened yogurts, especially “fruit at the bottom / in the corner” types, often have 15–30g of sugar per serving. Plain Greek yogurt is a better choice, offering 15–20g of protein with no added sugar. You can always add fresh fruits or spices like sweet cinnamon for flavor without added sugar.
- Oatmeal: prepackaged oatmeal can contain 12–15 grams of added sugar per serving, similar to a glazed donut. Additionally, finely milled oats (as in “instant” oatmeal) can cause blood sugar spikes by itself, due to the loss of fiber. Better is plain oats, and if you like, you can sweeten them naturally with sweet cinnamon and/or fresh fruit for a healthier breakfast.
- Sushi: while sushi contains nutritious fish, it often has too much white rice (and in the US, sushi rice is also often cooked with sugar to “improve” the taste and help cohesion) and sugary sauces. This makes many rolls much less healthy. So if fish (the sashimi component of sushi) is your thing, then focus on that, and minimize sugar intake for a more balanced meal.
- Baked beans: store-bought baked beans can have up to 25g of added sugar per cup, similar to soda. Better to opt for plain beans and prepare them at home so that nothing is in them except what you personally put there.
- Deli meats: deli meats are convenient but often are more processed than they look, containing preservatives linked to health risks. Fresh, unprocessed meats like chicken or turkey breast are healthier and can still be cost-effective when bought in bulk.
- Fruit juices: fruit juices lack fiber (meaning their own natural sugars also become harmful, with no fiber to slow them down) and often contain added sugars too. Eating whole fruits is a much better way to get fiber, nutrients, and controlled healthy sugar intake.
- Hazelnut spread: hazelnut spreads are usually 50% added sugar and contain unhealthy oils like palm oil. So, skip those, and enjoy natural nut butters for healthier fats and proteins.
- Granola: granola is often loaded with added sugars and preservatives, so watch out for those.
- Sports drinks: sports drinks, with 20–25g of added sugar per serving, are unnecessary and unhelpful (except, perhaps, in case of emergency for correcting diabetic hypoglycemia). Stick to water or electrolyte drinks—and even in the latter case, check the labels for added sugar and excessive sodium!
- Dark chocolate: dark chocolate with 80% or more cocoa has health benefits but still typically contains a lot of added sugar. Check labels carefully!
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is Unnoticed Environmental Mold Harming Your Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Environmental mold can be a lot more than just the famously toxic black mold that sometimes makes the headlines, and many kinds you might not notice, but it can colonizes your sinuses and gut just the same:
Breaking the mold
Around 25% of homes in North America are estimated to have mold, though the actual number is likely to be higher, affecting both older and new homes. For that matter, mold can grow in unexpected areas, like inside air conditioning units, even in dry regions.
If mold just sat where it is minding its own business, it might not be so bad, but instead they release their spores, which are de facto airborne mycotoxins, which can colonize places like the sinuses or gut, causing significant health issues.
Not everyone in the same household is affected the same way by mold due to genetic differences and varying pre-existing health conditions. But as a general rule of thumb, mold inflames the brain, nerves, gut, and skin, and can negatively impact the vagal nerve, which is linked to the gut-brain connection. Mycotoxins also damage mitochondria, leading to symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and cognitive issues. To complicate matters further, mold illness can mimic other conditions like anxiety, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, IBS, and more, making it difficult to diagnose.
Testing is possible, though they all have limitations, e.g:
- Home testing: testing the home for mold spores and mycotoxins is crucial for effective treatment; professional mold remediation companies are a good idea (to do a thorough job of cleaning, without also breathing in half the mold while cleaning it).
- Mold allergy testing: mold allergy testing (IgE testing or skin tests) is often used, but it doesn’t diagnose mold-related illnesses linked to severe symptoms like fatigue or neurodegeneration.
- Serum antibody testing: tests for immune reactions (IgG) to mycotoxins may not always show positive results if the immune system is weakened by long-term exposure.
- Urine mycotoxin testing: urine tests can detect mycotoxins in the body, though are likely to be more expensive, being probably not covered by public health in Canada or insurance in the US.
- Organic acid testing: this urine test can indicate mold colonization in areas like the sinuses or gut. Again, cost/availability may vary, though.
For more information on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Well Plated Cookbook – by Erin Clarke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Clarke’s focus here is on what she calls “stealthy healthy”, with the idea of dishes that feel indulgent while being great for the health.
The recipes, of which there are well over 100, are indeed delicious and easy to make without being oversimplified, and since she encourages the use of in-season ingredients, many recipes come with a “market swaps” substitution guide, to make each recipe seasonal.
The book is largely not vegetarian, let alone vegan, but the required substitutions will be second-nature to any seasoned vegetarian or vegan. Indeed, “skip the meat sometimes” is one of the advices she offers near the beginning of the book, in the category of tips to make things even healthier.
Bottom line: if you want to add dishes to your repertoire that are great for entertaining and still super-healthy, this book will be a fine addition to your collection.
Click here to check out The Well Plated Cookbook, and get cooking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Set Anxiety Aside
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Set Anxiety Aside
We’ve talked previously about how to use the “release” method to stop your racing mind.
That’s a powerful technique, but sometimes we need to be calm enough to use it. So first…
Breathe
Obviously. But, don’t underestimate the immediate power of focusing on your breath, even just for a moment.
There are many popular breathing exercises, but here’s one of the simplest and most effective, “4–4 breathing”:
- Breathe in for a count of four
- Hold for a count four
- Breathe out for a count of four
- Hold for a count of four
- Repeat
Depending on your lung capacity and what you’re used to, it may be that you need to count more quickly or slowly to make it feel right. Experiment with what feels comfortable for you, but the general goal should breathing deeply and slowly.
Identify the thing that’s causing you anxiety
We’ve also talked previously about how to use the RAIN technique to manage difficult emotions, and that’s good for handling anxiety too.
Another powerful tool is journaling.
Read: How To Use Journaling to Challenge Anxious Thoughts
If you don’t want to use any of those (very effective!) methods, that’s fine too—journaling isn’t for everyone.
You can leverage some of the same benefits by simply voicing your worries, even to yourself:
There’s an old folk tradition of “worry dolls”; these are tiny little dolls so small they can be kept in a pocket-size drawstring purse. Last thing at night, the user whispers their worries to the dolls and puts them back in their bag, where they will work on the person’s problem overnight.
We’re a health and productivity newsletter, not a dealer of magic and spells, but you can see how it works, right? It gets the worries out of one’s head, and brings about a helpful placebo effect too.
Focus on what you can control
- Most of what you worry about will not happen.
- Some of what you worry about may happen.
- Worrying about it will not help.
In fact, in some cases it may bring about what you fear, by means of the nocebo effect (like the placebo effect, but bad). Additionally, worrying drains your body and makes you less able to deal with whatever life does throw at you.
So while “don’t worry; be happy” may seem a flippant attitude, sometimes it can be best. However, don’t forget the other important part, which is actually focusing on what you can control.
- You can’t control whether your car will need expensive maintenance…
- …but you can control whether you budget for it.
- You can’t control whether your social event will go well or ill…
- …but you can control how you carry yourself.
- You can’t control whether your loved one’s health will get better or worse…
- …but you can control how you’re there for them, and you can help them take what sensible precautions they may.
…and so forth.
Look after your body as well!
Your body and mind are deeply reliant on each other. In this case, just as anxiety can drain your body’s resources, keeping your body well-nourished, well-exercised, and well-rested and can help fortify you against anxiety. For example, when it comes to diet, exercise, and sleep:
- Read: Fruit and vegetable intake is inversely associated with perceived stress across the adult lifespan
- Read: Exercise and anxiety: physical activity appears to be protective against anxiety disorders in clinical and non-clinical populations
- Read: Sleep problems predict and are predicted by generalized anxiety/depression
Don’t know where to start? How about the scientifically well-researched, evidence-based, 7-minute workout?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Your Brain On (And Off) Estrogen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Lisa Mosconi. She’s a professor of Neuroscience in Neurology and Radiology, and is one of the 1% most influential scientists of the 21st century. That’s not a random number or an exaggeration; it has to do with citation metrics collated over 20 years:
A standardized citation metrics author database annotated for scientific field
What does she want us to know?
Women’s brains age differently from men’s
This is largely, of course, due to menopause, and as such is a generalization, but it’s a statistically safe generalization, because:
- Most women go through menopause—and most women who don’t, avoid it by dying pre-menopause, so the aging also does not occur in those cases
- Menopause is very rarely treated immediately—not least of all because menopause is diagnosed officially when it has been one year since one’s last period, so there’s almost always a year of “probably” first, and often numerous years, in the case of periods slowing down before stopping
- Menopausal HRT is great, but doesn’t completely negate that menopause occurred—because of the delay in starting HRT, some damage can be done already and can take years to reverse.
Medicated and unmedicated menopause proceed very differently from each other, and this fact has historically caused obfuscation of a lot of research into age-related neurodegeneration.
For example, it is well-established that women get Alzheimer’s at nearly twice the rate than men do, and deteriorate more rapidly after onset, too.
Superficially, one might conclude “estrogen is to blame” or maybe “the xx-chromosomal karyotype is to blame”.
The opposite, however, is true with regard to estrogen—estrogen appears to be a protective factor in women’s neurological health, which is why increased neurodegeneration occurs when estrogen levels decline (for example, in menopause).
For a full rundown on this, see:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
It’s not about the extra X
Dr. Mosconi examines this in detail in her book “The XX Brain”. To summarize and oversimplify a little: the XX karyotype by itself makes no difference, or more accurately, the XY karyotype by itself makes no difference (because biologically speaking, female physiological attributes are more “default” than male ones; it is only 12,000ish* years of culture that has flipped the social script on this).
*Why 12,000ish years? It’s because patriarchalism largely began with settled agriculture, for reasons that are fascinating but beyond the scope of this article, which is about health science, not archeology.
The topic of “which is biologically default” is relevant, because the XY karyotype (usually) informs the body “ignore previous instructions about ovaries, and adjust slightly to make them into testes instead”, which in turn (usually) results in a testosterone-driven system instead of an estrogen-driven system. And that is what makes the difference to the brain.
One way we can see that it’s about the hormones not the chromosomes, is in cases of androgen insensitivity syndrome, in which the natal “congratulations, it’s a girl” pronouncement may later be in conflict with the fact it turns out she had XY chromosomes all along, but the androgenic instructions never got delivered successfully, so she popped out with fairly typical female organs. And, relevantly for Dr. Mosconi, a typically female brain that will age in a typically female fashion, because it’s driven by estrogen, regardless of the Y-chromosome.
The good news
The good news from all of this is that while we can’t (with current science, anyway) do much about our chromosomes, we can do plenty about our hormones, and also, the results of changes in same.
Remember, Dr. Mosconi is not an endocrinologist, nor a gynecologist, but a neurologist. As such, she makes the case for how a true interdisciplinary team for treating menopause should not confined to the narrow fields usually associated with “bikini medicine”, but should take into account that a lot of menopause-related changes are neurological in nature.
We recently reviewed another book by Dr. Mosconi:
The Menopause Brain – by Dr. Lisa Mosconi
…and as we noted there, many sources will mention “brain fog” as a symptom of menopause, Dr. Mosconi can (and will) point to a shadowy patch on a brain scan and say “that’s the brain fog, there”.
And so on, for other symptoms that are often dismissed as “all in your head”, as though that’s a perfectly acceptable place for problems to be.
This is critical, because it’s treating real neurological things as the real things they are.
Dr. Mosconi’s advice, beyond HRT
Dr. Mosconi notes that brain health tends to dip during perimenopause but often recovers, showing the brain’s resilience to hormonal shifts. As such, all is not lost if for whatever reason, hormone replacement therapy isn’t a viable option for you.
Estrogen plays a crucial role in brain energy, and women’s declining estrogen levels during menopause increase the need for antioxidants to protect brain health—something not often talked about.
Specifically, Dr. Mosconi tells us, women need more antioxidants and have different metabolic responses to diets compared to men.*
*Yes, even though men usually have negligible estrogen, because their body (and thus brain, being also part of their body) is running on testosterone instead, which is something that will only happen if either you are producing normal male amounts of testosterone (requires normal male testes) or you are taking normal male amounts of testosterone (requires big bottles of testosterone; this isn’t the kind of thing you can get from a low dose of testogel as sometimes prescribed as part of menopausal HRT to perk your metabolism up).
Note: despite women being a slight majority on Earth, and despite an aging population in wealthy nations, meaning “a perimenopausal woman” is thus the statistically average person in, for example, the US, and despite the biological primacy of femaleness… Medicine still mostly looks to men as the “default person”, which in this case can result in seriously low-balled estimates of what antioxidants are needed.
In terms of supplements, therefore, she recommends:
- Antioxidants: key for brain health, especially in women. Rich sources include fruits (especially berries) and vegetables. Then there’s the world’s most-consumed antioxidant, which is…
- Coffee: Italian-style espresso has the highest antioxidant power. Adding a bit of fat (e.g. oat milk) helps release caffeine more slowly, reducing jitters. Taking it alongside l-theanine also “flattens the curve” and thus improves its overall benefits.
- Flavonoids: important for both men and women but particularly essential for women. Found in many fruits and vegetables.
- Chocolate: dark chocolate is an excellent source of antioxidants and flavonoids!
- Turmeric: a natural neuroprotectant with anti-inflammatory properties, best boosted by taking with black pepper, which improves absorption as well as having many great qualities of its own.
- B Vitamins: B6, B9, and B12 are essential for anti-aging and brain health; deficiency in B6 is rare, while deficiency in B9 (folate) and especially B12 is very common later in life.
- Vitamins C & E: important antioxidants, but caution is needed with fat-soluble vitamins to avoid toxicity.
- Omega-3s: important for brain health; can be consumed in the diet, but supplements may be necessary.
- Caution with zinc: zinc can support immunity and endocrine health (and thus, indirectly, brain health) but may be harmful in excess, particularly for brain health.
- Probiotics & Prebiotics: beneficial for gut health, and in Dr. Mosconi’s opinion, hard to get sufficient amounts from diet alone.
For more pointers, you might want to check out the MIND diet, that is to say, the “Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay” upgrade to make the Mediterranean diet even brain-healthier than it is by default:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Want to know more from Dr. Mosconi?
Here’s her TED talk:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: