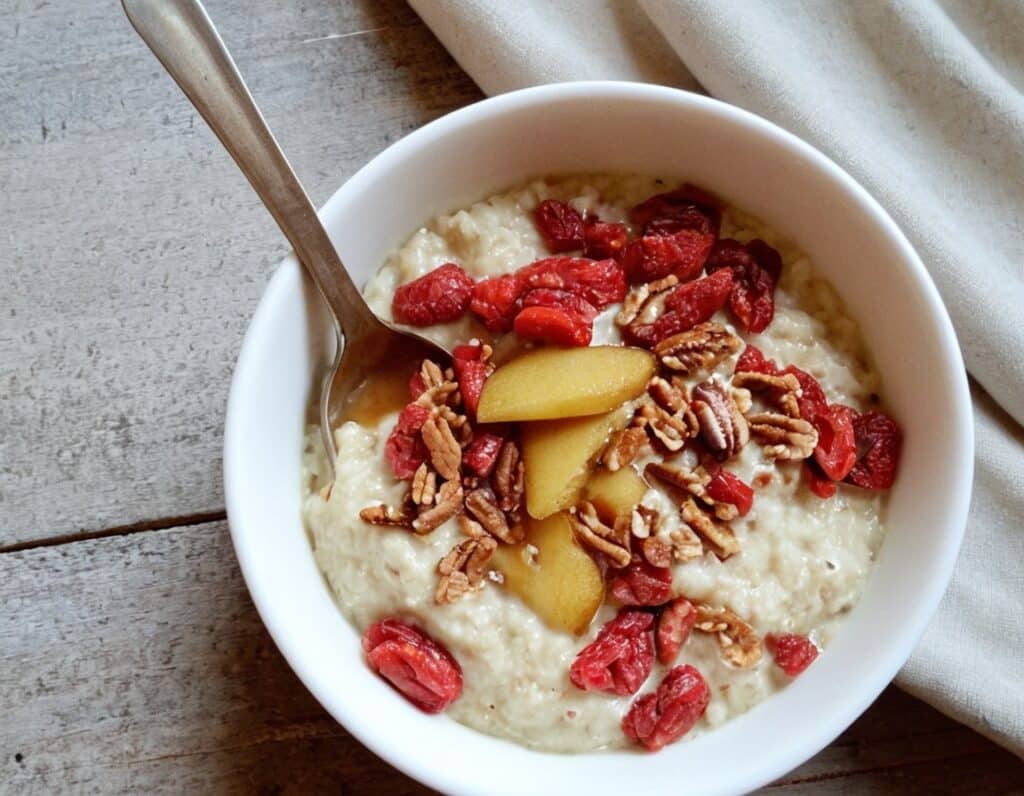
Spiced Pear & Pecan Polyphenol Porridge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Porridge doesn’t have to be boring; in fact, it can be a real treat. And while oats are healthy by default, this version has extra layers of benefits:
You will need
Per person:
- 1 cup milk (your choice what kind; we recommend almond for this)
- ½ cup oats
- 1 pear, peeled, cored, and sliced
- ¼ cup toasted pecans, chopped
- 2 tbsp goji berries
- 1 tsp sweet cinnamon
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the goji berries in a small amount of hot water. If you have an espresso cup or something of a similar size, that’s a great “bowl” for this task. A ramekin will suffice, otherwise, but use only as much water as is absolutely necessary to cover the goji berries (excess water will just leech polyphenols from the berries, reducing their nutritional value).
2) Combine the pear and cinnamon in a saucepan with a couple of tablespoons of water, and simmer for 5 minutes.
3) Combine the oats and milk in a separate saucepan (we imagine you know how to make porridge, but we’d be remiss to not include the step), and simmer for 5 minutes, stirring as necessary.
4) Drain the goji berries and the pear, if there is water remaining outside of the fruits.
5) Assemble: we recommend the order: goji berries, porridge, pear, pecans.
Alternative method: simply layer everything in a slow cooker, in the following order: goji berries (no need to pre-soak), oats, milk (stir it a little to ensure oats are all wet), pear-dusted-with-cinnamon (no need to pre-cook), pecans. Put it on the lowest heat with the lid on, and leave for a couple of hours.
Alternative alternative method: layer everything as we just said, but this time in portions of 1 jar per person, and leave it overnight, per overnight oats. Then, in the morning, gently warm it (if you like) by putting it in the microwave (lid removed!) for 2 minutes on medium power.
These latter methods are increasingly better nutritionally, as they won’t wash away some of the polyphenols from the goji berries and the lower temperatures keep the glycemic index of the oats lower, but we appreciate you won’t always have the time to do it this way.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats!
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier? ← this is a very important distinction
- Make Overnight Oats Shorter Or Longer For Different Benefits!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
White Bread vs White Pasta – Which Is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing a white bread to a white pasta, we picked the pasta.
Why?
Neither are great for the health! But like for like, the glycemic index of the bread is usually around 150% of the glycemic index for pasta.
All that said, we heartily recommend going for wholegrain in either case!
Bonus tip: cooking pasta “al dente”, so it is still at least a little firm to the bite, results in a lower GI compared to being boiled to death.
Bonus bonus tip: letting pasta cool increases resistant starches. You can then reheat the pasta without losing this benefit.
Please don’t put it in the microwave though; you will make an Italian cry. Instead, simply put it in a colander and pour boiling water over it, and then serve in your usual manner (a good approach if serving it separately is: put it in the serving bowl/dish/pan, drizzle a little extra virgin olive oil and a little cracked black pepper, stir to mix those in, and serve)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Air Purifiers & Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I’ve read that air pollution has a negative effect on sleep quality and duration. Since I live next to a busy road, I was wondering whether I should invest in an air purifier. What are 10Almonds’s views?❞
Going straight to the science, there are two questions here:
- Does air pollution negatively affect sleep quality and duration?
- Does the use of an air purify actually improve the air quality in the way(s) necessary to make a difference?
We thought we’d have to tackle these questions separately, but we did find one study that addressed your question directly. It was a small study (n=30 if you believe the abstract; n=29 if you read the paper itself—one person dropped out); the results were modest but clear:
❝The purifier filter was associated with increased total sleep time for an average of 12 min per night, and increased total time in bed for an average of 19 min per night relative to the placebo.
There were several sleep and mood outcomes for which no changes were observed, and time awake after sleep onset was higher for the purifier filter. Air quality was better during the high-efficiency particulate air filter condition.
These findings offer positive indications that environmental interventions that improve air quality can have benefits for sleep outcomes in healthy populations who are not exhibiting clinical sleep disturbances.❞
In the above-linked paper’s introduction, it does establish the deleterious effect of air pollution on a wide variety of health metrics, including sleep, this latter evidenced per Caddick et al. (2018): A review of the environmental parameters necessary for an optimal sleep environment
Now, you may be wondering: is an extra 12 minutes per night worth it?
That’s your choice to make, but we would argue that it is. We can make many choices in our lives that affect our health slightly for the better or the worse. If we make a stack of choices in a particular direction, the effects will also stack, if not outright compound.
So in the case of sleep, it might be (arbitrary numbers for the sake of illustration):
- Get good exercise earlier in the day (+3%)
- Get good food earlier in the day (+2.5%)
- Practice mindfulness/meditation before bed (+2.5%)
- Have a nice dark room (+5%)
- Have fresh bedding (+2.5%)
- Have an air purifier running (+3%)
Now, those numbers are, as we said, arbitrary*, but remember that percentages don’t add up; they compound. So that “+3%” starts being a lot more meaningful than if it were just by itself.
*Confession: the figure of 3% for the air purifier wasn’t entirely arbitrary; it was based on 100(12/405) = 80/27 ≈ 3, wherein the 405 figure was an approximation of the average total time (in minutes) spent sleeping with placebo, based on a peep at their results graph. There are several ways the average could be reasonably calculated, but 6h45 (i.e., 405 minutes) was an approximate average of those reasonable approximate averages.
So, 12 minutes is a 3% improvement on that.
Don’t have an air purifier and want one?
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example on Amazon, for your convenience
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Younger For Life – by Dr. Anthony Youn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed anti-aging books before, so what makes this one different? Mostly, it’s the very practical focus.
Which is not to say there’s not also good science in here; there is. But the focus is on what everything means for the reader, not what happened with a certain cohort of lab mice. Instead, he looks at the causes of aging, the process of aging, and what interventions to implement to address those, and reverse many of them.
Some parts are more general lifestyle interventions that 10almonds readers will know well already, but other parts are very specific advices, protocols, and regimes; in particular his skincare section is well worth reading. As for nutrition, there’s even a respectable recipes section, so this book does have it all!
The final section of the book is dedicated to plastic surgeries (the author is a plastic surgeon who believes that most people should not need those, and would do well to stick to the advices in the rest of the book). We suspect this last part of the book will be of least interest to 10almonds readers.
Bottom line: if you’re of the view that getting older should come with as little as possible physical deterioration along the way, then this book can help a lot with that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Top 5 Foods Seniors Should Eat To Sleep Better Tonight (And 5 To Avoid)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Breus, a sleep specialist, advises:
A prescription for rest
Dr. Breus’s top 5 foods to eat for a good night’s sleep are:
1) Chia seeds: high in fiber, protein, omega-3s, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, and tryptophan, they help raise melatonin levels for better sleep. The high fiber content also reduces late-night snacking, and in any case, it’s recommended to eat them 2–3 hours before bed. As for how, they can be added to smoothies, baked goods, salads, or made into chia seed pudding.
2) Nuts (especially pistachios & almonds): both of these nuts are rich in B vitamins and melatonin, so take your pick! He does recommend, however, no more than ¼ cup about 1.5 hours before bed. Either can be eaten as-is or with an unsweetened Greek yogurt.
3) Bananas (especially banana tea): contain magnesium, especially in the peel. Boil an organic banana (with peel) in water and drink the water, which provides magnesium and helps improve sleep. It’s recommended to drink it about an hour before bed.
10almonds tip: he doesn’t mention this, but if you prefer, you can also simply eat it—banana peel is perfectly edible, and is not tough when cooked. If you’ve ever had plantains, you’ll know how they are, and bananas (and their peel) are much softer than plantains. Boiling is fine, or alternatively you can wrap them in foil and bake them. The traditional way is to cook them in the leaves, but chances are you live somewhere that doesn’t grow bananas locally and so they didn’t come with leaves, so foil is fine.
4) Tart cherries: are rich in melatonin, antioxidants, and other anti-inflammatory compounds, which all help with falling asleep faster and reducing night awakenings. Can be consumed as juice, dried fruit, or tart cherry extract capsules. Suggested intake: once in the morning and once an hour before bed.
5) Kiwis: are high in serotonin, which aids melatonin production and sleep. This also helps regulate cortisol levels (lower cortisol promotes sleep). He recommends eating kiwi fruit about 2 hours before bed.
Also, in the category of foods (or rather: food types) to avoid before bed…
- High quantities of red meat: can disrupt sleep-related amino acid balance.
- Acidic foods: can cause acid reflux.
- High sugar foods: can slow melatonin production when consumed in the evening.
- Caffeine-rich foods & drinks: includes chocolate and coffee; avoid in the evening.
- Large meals before bed: digestion is less efficient when lying down, causing sleep disruption.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep ← Our “Expert Insights” main feature on Dr. Breus
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
All In Your Head (Which Is Where It’s Supposed To Be)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today’s news is all about things above the neck, and mostly in the brain. From beating depression to beating cognitive decline, from mindfulness against pain to dentistry nightmares to avoid:
Transcranial ultrasound stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation is one of those treatments that sounds like it’s out of a 1950s sci-fi novel, and yet, it actually works (it’s very well-evidenced against treatment-resistant depression, amongst other things). However, a weakness of it is that it’s difficult to target precisely, making modulation of most neurological disorders impossible. Using ultrasound instead of a magnetic field allows for much more finesse, with very promising initial results across a range of neurological disorders
Read in full: Transcranial ultrasound stimulation: a new frontier in non-invasive brain therapy
Related: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
This may cause more pain and damage, but at least it’s more expensive too…
While socialized healthcare systems sometimes run into the problem of not wanting to spend money where it actually is needed, private healthcare systems have the opposite problem: there’s a profit incentive to upsell to more expensive treatments. Here’s how that’s played out in dentistry:
Read in full: Dentists are pulling healthy and treatable teeth to profit from implants, experts warn
Related: Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
Mindfulness vs placebo, for pain
It can be difficult with some “alternative therapies” to test against placebo, for example “and control group B will merely believe that they are being pierced with needles”, etc. However, in this case, mindfulness meditation was tested as an analgesic vs sham meditation (just deep breathing) and also vs placebo analgesic cream, vs distraction (listening to an audiobook). Mindfulness meditation beat all of the other things:
Read in full: Mindfulness meditation outperforms placebo in reducing pain
Related: No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
Getting personal with AI doctors
One of the common reasons that people reject AI doctors is the “lack of a human touch”. However, human and AI doctors may be meeting in the middle nowadays, as humans are pressed to see more patients in less time, and AI is trained to be more personal—not just a friendlier affect, but also, such things as remembering the patient’s previous encounters (again, something with which overworked human doctors sometimes struggle). This makes a big difference to patient satisfaction:
Read in full: Personalization key to patient satisfaction with AI doctors
Related: AI: The Doctor That Never Tires?
Combination brain therapy against cognitive decline
This study found that out of various combinations trialled, the best intervention against cognitive decline was a combination of 1) cognitive remediation (therapeutic interventions designed to improve cognitive functioning, like puzzles and logic problems), and 2) transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a form of non-invasive direct brain stimulation, similar to the magnetic or ultrasound methods we mentioned earlier today. Here’s how it worked:
Read in full: Study reveals effective combination therapy to slow cognitive decline in older adults
Related: How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: