Smart Sex – by Dr. Emily Morse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this isn’t: this isn’t a mere book of sex positions and party tricks, nor is it a book of Cosmo-style “drive your man wild by using hot sauce as lube” advice.
What it offers instead, is a refreshingly mature take on sex, free from the “teehee” titillations and blushes that many books of the genre go for.
Dr. Emily Morse outlines five pillars of sex:
- Embodiment
- Health
- Collaboration
- Self-knowledge
- Self-acceptance
…and talks about each of them in detail, and how we can bring them together. And, of course, how we or our partner(s) could accidentally sabotage ourselves or each other, and the conversations we can (and should!) have, to work past that.
She also, critically, and this is a big source of value in the book, looks at “pleasure thieves”: stress, trauma, and shame. The advice for overcoming these is not “don’t worry; be happy” but rather is actual practical steps one can take.
The style throughout is direct and unpatronizing. Since the advice within pertains to everyone who has and/or wants an active sex life, very little is divided by gender etc.
There is some attention given to anatomy and physiology, complete with clear diagrams. Honestly, most people could benefit from these, because most people’s knowledge of the relevant anatomy stopped with a very basic high school text book diagram that missed a lot out.
Bottom line: this book spends more time on what’s between your ears than what’s between your legs, and yet is very comprehensive in all areas. Everyone has something to gain from this one.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mindfulness: An Eight-Week Plan – by Dr. Mark Williams & Dr. Danny Penman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The authors, with their PhDs in psychology and biochemistry, respectively, bring the science that you might expect (and some that you might not!) to this book about mindfulness meditation and mindfulness in everyday life.
The book’s realism comes not just from studies, though, but also from a realistic perspective on modern life, in which many of us have sufficient responsibilities to afford us only limited downtime, and we certainly cannot all take time off for a mountaintop retreat.
What we can do, however, is enjoy this eight-week program for finding peace in a frantic world, while still going about our necessary business in that frantic world on a daily basis.
The eight weeks go as follows:
- Waking up to the autopilot
- Keeping the body in mind
- The mouse in the maze
- Moving beyond the rumor mill
- Turning toward difficulties
- Trapped in the past or living in the present?
- When did you stop dancing?
- Your wild and precious life
…with meditations, as well as reframes and other tools, for each.
The style is very easy-reading, with neither scientific jargon nor spiritual arcana, just clear explanations, instructions, and guidance.
Bottom line: if you’re the sort of person who tries to take each day as it comes, but sometimes several days gang up on you at once, then this book can help get things into order.
Share This Post
-
Fully Present – by Dr. Susan Smalley and Diana Winston
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“The Science and the Art of…” tends to be a bit of a fuzzy obfuscation, but in this case, it’s accurate, especially in this presentation. The authors are, indeed, a scientist and an artist—and both practitioners, meeting in the middle.
As such, we get the clinical insights of a researcher and professor of psychiatry, and the grounded-yet-spiritual insights of an erstwhile Buddhist nun.
While the book is pop psychology in essence, the format is much more that of a textbook than a self-help book. Will it be useful for helping yourself anyway, though? Yes, absolutely, if you apply the information contained within.
Don’t be fooled into thinking that a textbook format makes it dry, though—the writing is very compelling, and you’ll find yourself turning pages eagerly. There’s no time like the present, after all!
Bottom line: if you find the scientific evidence-base for the usefulness of mindfulness appealing, but find a lot of guides a little fluffy, this one is perfectly balanced—and very well written, too.
Click here to check out Fully Present, bring yourself into the moment, always!
Share This Post
-
Why 7 Hours Sleep Is Not Enough
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Sleep-Deprived Are You, Really?
This is Dr. Matthew Walker. He’s a neuroscientist and sleep specialist, and is the Director of the Center for Human Sleep Science at UC Berkeley’s Department of Psychology. He’s also the author of the international bestseller “Why We Sleep”.
What does he want us to know?
Sleep deprivation is more serious than many people think it is. After about 16 hours without sleep, the brain begins to fail, and needs more than 7 hours of sleep to “reset” cognitive performance.
Note: note “seven or more”, but “more than seven”.
After ten days with only 7 hours sleep (per day), Dr. Walker points out, the brain is as dysfunctional as it would be after going without sleep for 24 hours.
Here’s the study that sparked a lot of Dr. Walker’s work:
Importantly, in Dr. Walker’s own words:
❝Three full nights of recovery sleep (i.e., more nights than a weekend) are insufficient to restore performance back to normal levels after a week of short sleeping❞
~ Dr. Matthew Walker
See also: Why You Probably Need More Sleep
Furthermore: the sleep-deprived mind is unaware of how sleep-deprived it is.
You know how a drunk person thinks they can drive safely? It’s like that.
You do not know how sleep-deprived you are, when you are sleep-deprived!
For example:
❝(60.7%) did not signal sleepiness before a sleep fragment occurred in at least one of the four MWT trials❞
Source: Sleepiness is not always perceived before falling asleep in healthy, sleep-deprived subjects
Sleep efficiency matters
With regard to the 7–9 hours band for optimal health, Dr. Walker points out that the sleep we’re getting is not always the sleep we think we’re getting:
❝Assuming you have a healthy sleep efficiency (85%), to sleep 9 hours in terms of duration (i.e. to be a long-sleeper), you would need to be consistently in bed for 10 hours and 36 minutes a night. ❞
~ Dr. Matthew Walker
At the bottom end of that, by the way, doing the same math: to get only the insufficient 7 hours sleep discussed earlier, a with a healthy 85% sleep efficiency, you’d need to be in bed for 8 hours and 14 minutes per night.
The unfortunate implication of this: if you are consistently in bed for 8 hours and 14 minutes (or under) per night, you are not getting enough sleep.
“But what if my sleep efficiency is higher than 85%?”
It shouldn’t be.If your sleep efficiency is higher than 85%, you are sleep-deprived and your body is having to enforce things.
Want to know what your sleep efficiency is?
We recommend knowing this, by the way, so you might want to check out:
Head-To-Head Comparison of Google and Apple’s Top Sleep-Monitoring Apps
(they will monitor your sleep and tell you your sleep efficiency, amongst other things)
Want to know more?
You might like his book:
Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and Dreams
…and/or his podcast:
…and for those who like videos, here’s his (very informative) TED talk:
Prefer text? Click here to read the transcript
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Recipe For Empowered Leadership – by Doug Meyer-Cuno
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not a “here’s how to become a leader, you young would-be Machiavelli”; it’s more a “so you’re in a leadership role; now what?” book. The book’s subtitle describes well its contents: “25 Ingredients For Creating Value & Empowering Others”
The book is written with the voice of experience, but without the ego-driven padding that accompanies many such books. Especially: any anecdotal illustrations are short and to-the-point, no chapter-long diversions here.
Which we love!
Equally helpful is where the author does spend a little more time and energy: on the “down to brass tacks” of how exactly to do various things.
In short: if instead of a lofty-minded book of vague idealized notions selling a pipedream, you’d rather have a manual of how to actually be a good leader when it comes down to it, this is the book for you.
Pick Up The Recipe For Empowered Leadership On Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
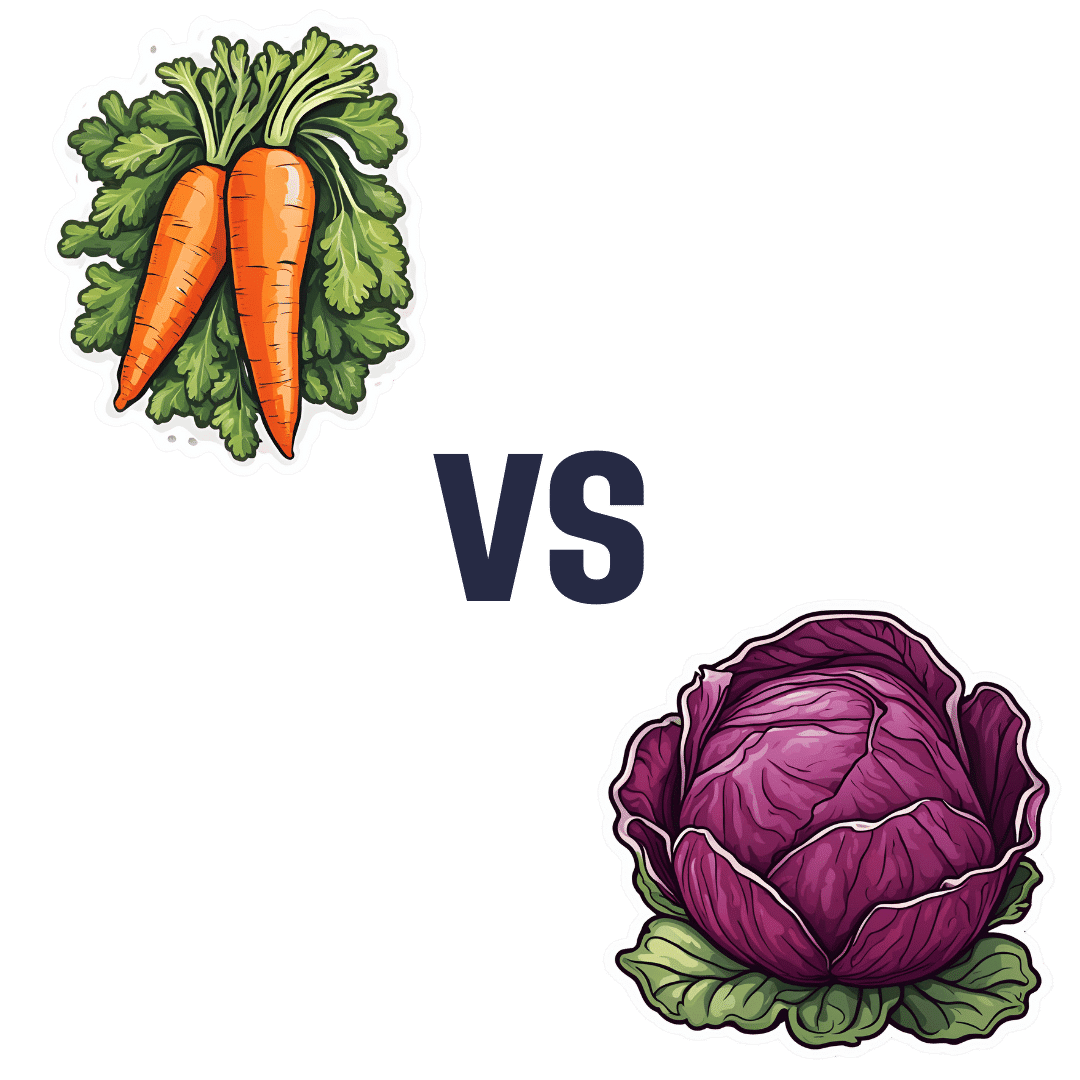
Carrots vs Red Cabbage – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrots to red cabbage, we picked the red cabbage.
Why?
It’s very close!
In terms of macros, these two vegetables are pretty much equal on all metrics. By official numbers, carrots have a tiny bit more fiber and red cabbage has a tiny bit more protein, but realistically, the difference are so small that they’re within the margin of variation (i.e. while we look at official average values, in reality one plant’s figures will differ very slightly from another’s; it could depend on what the soil was like or which plant got more sun, etc). So, a tie here.
In the category of vitamins, carrots have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, and E, while red cabbage has more of vitamins B2, B6, C, K, and choline. So, both have their merits, but red cabbage enjoys a measurable marginal victory here.
Looking at minerals, carrots have more copper, phosphorus, and potassium, while red cabbage has more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, and selenium. So, another marginal win for red cabbage here.
When it comes to phytochemicals, they’re about equal on polyphenols and other relevant phytonutrients not otherwise mentioned above.
Adding up the sections makes for a win for red cabbage, but it was close, and carrots are certainly great too. Enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
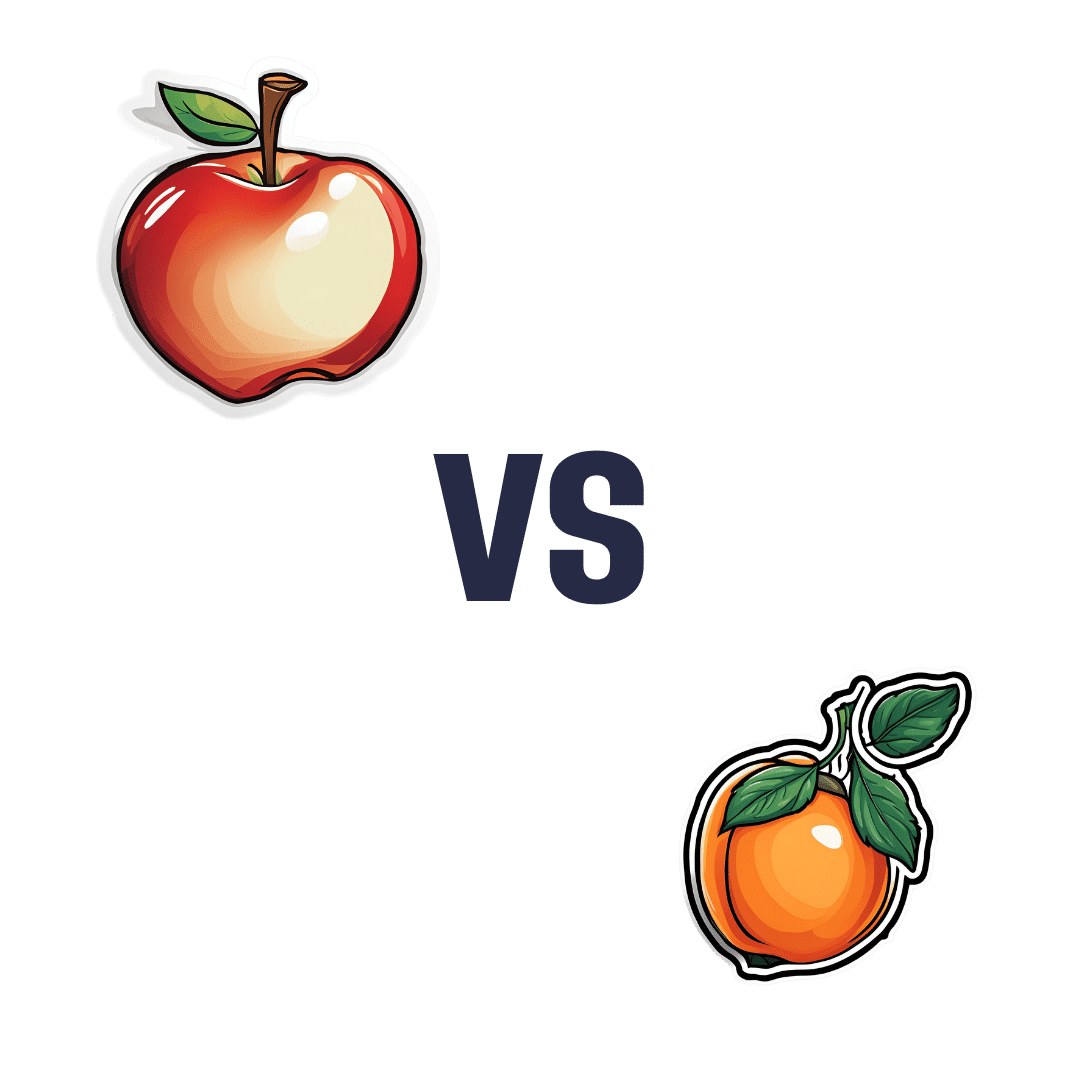
Apple vs Apricot – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to apricot, we picked the apricot.
Why?
In terms of macros, there’s not too much between them; apples are higher in carbs and only a little higher in fiber, which disparity makes for a slightly higher glycemic index, but it’s not a big difference and they are both low GI foods.
Micronutrients, however, set these two fruits apart:
In the category of vitamins, apple is a tiny bit higher in choline, while apricots are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and K—in most cases, by quite large margins, too. All in all, a clear and easy win for apricots.
When it comes to minerals, apples are not higher in any minerals, while apricots are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. There’s simply no contest here.
In short, if an apple a day keeps the doctor away, then an apricot will give the doctor a nice weekend break somewhere.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: