Cost of living: if you can’t afford as much fresh produce, are canned veggies or frozen fruit just as good?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The cost of living crisis is affecting how we spend our money. For many people, this means tightening the budget on the weekly supermarket shop.
One victim may be fresh fruit and vegetables. Data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) suggests Australians were consuming fewer fruit and vegetables in 2022–23 than the year before.
The cost of living is likely compounding a problem that exists already – on the whole, Australians don’t eat enough fruit and vegetables. Australian dietary guidelines recommend people aged nine and older should consume two serves of fruit and five serves of vegetables each day for optimal health. But in 2022 the ABS reported only 4% of Australians met the recommendations for both fruit and vegetable consumption.
Fruit and vegetables are crucial for a healthy, balanced diet, providing a range of vitamins and minerals as well as fibre.
If you can’t afford as much fresh produce at the moment, there are other ways to ensure you still get the benefits of these food groups. You might even be able to increase your intake of fruit and vegetables.

Frozen
Fresh produce is often touted as being the most nutritious (think of the old adage “fresh is best”). But this is not necessarily true.
Nutrients can decline in transit from the paddock to your kitchen, and while the produce is stored in your fridge. Frozen vegetables may actually be higher in some nutrients such as vitamin C and E as they are snap frozen very close to the time of harvest. Variations in transport and storage can affect this slightly.
Minerals such as calcium, iron and magnesium stay at similar levels in frozen produce compared to fresh.
Another advantage to frozen vegetables and fruit is the potential to reduce food waste, as you can use only what you need at the time.

As well as buying frozen fruit and vegetables from the supermarket, you can freeze produce yourself at home if you have an oversupply from the garden, or when produce may be cheaper.
A quick blanching prior to freezing can improve the safety and quality of the produce. This is when food is briefly submerged in boiling water or steamed for a short time.
Frozen vegetables won’t be suitable for salads but can be eaten roasted or steamed and used for soups, stews, casseroles, curries, pies and quiches. Frozen fruits can be added to breakfast dishes (with cereal or youghurt) or used in cooking for fruit pies and cakes, for example.
Canned
Canned vegetables and fruit similarly often offer a cheaper alternative to fresh produce. They’re also very convenient to have on hand. The canning process is the preservation technique, so there’s no need to add any additional preservatives, including salt.
Due to the cooking process, levels of heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C will decline a little compared to fresh produce. When you’re using canned vegetables in a hot dish, you can add them later in the cooking process to reduce the amount of nutrient loss.
To minimise waste, you can freeze the portion you don’t need.
Fermented

Fermentation has recently come into fashion, but it’s actually one of the oldest food processing and preservation techniques.
Fermentation largely retains the vitamins and minerals in fresh vegetables. But fermentation may also enhance the food’s nutritional profile by creating new nutrients and allowing existing ones to be absorbed more easily.
Further, fermented foods contain probiotics, which are beneficial for our gut microbiome.
5 other tips to get your fresh fix
Although alternatives to fresh such as canned or frozen fruit and vegetables are good substitutes, if you’re looking to get more fresh produce into your diet on a tight budget, here are some things you can do.
1. Buy in season
Based on supply and demand principles, buying local seasonal vegetables and fruit will always be cheaper than those that are imported out of season from other countries.
2. Don’t shun the ugly fruit and vegetables
Most supermarkets now sell “ugly” fruit and vegetables, that are not physically perfect in some way. This does not affect the levels of nutrients in them at all, or their taste.

3. Reduce waste
On average, an Australian household throws out A$2,000–$2,500 worth of food every year. Fruit, vegetables and bagged salad are the three of the top five foods thrown out in our homes. So properly managing fresh produce could help you save money (and benefit the environment).
To minimise waste, plan your meals and shopping ahead of time. And if you don’t think you’re going to get to eat the fruit and vegetables you have before they go off, freeze them.
4. Swap and share
There are many websites and apps which offer the opportunity to swap or even pick up free fresh produce if people have more than they need. Some local councils are also encouraging swaps on their websites, so dig around and see what you can find in your local area.
5. Gardening
Regardless of how small your garden is you can always plant produce in pots. Herbs, rocket, cherry tomatoes, chillies and strawberries all grow well. In the long run, these will offset some of your cost on fresh produce.
Plus, when you have put the effort in to grow your own produce, you are less likely to waste it.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & Neuroprotectant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Think Pink For Brain Health!
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid that’s found in:
- certain marine microalgae
- tiny crustaceans that eat the algae
- fish (and flamingos!) that eat the crustaceans
Yes, it’s the one that makes things pink.
But it does a lot more than that…
Super-antioxidant
Move over, green tea! Astaxanthin has higher antioxidant activity than most carotenoids. For example, it is 2–5 times more effective than alpha-carotene, lutein, beta-carotene, and lycopene:
Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids
We can’t claim credit for naming it a super-antioxidant though, because:
Astaxanthin: A super antioxidant from microalgae and its therapeutic potential
Grow new brain cells
Axtaxanthin is a neuroprotectant, but that’s to be expected from something with such a powerful antioxidant ability.
What’s more special to astaxanthin is that it assists continued adult neurogenesis (creation of new brain cells):
❝The unique chemical structure of astaxanthin enables it to cross the blood-brain barrier and easily reach the brain, where it may positively influence adult neurogenesis.
Furthermore, astaxanthin appears to modulate neuroinflammation by suppressing the NF-κB pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and limiting neuroinflammation associated with aging and chronic microglial activation.
By modulating these pathways, along with its potent antioxidant properties, astaxanthin may contribute to the restoration of a healthy neurogenic microenvironment, thereby preserving the activity of neurogenic niches during both normal and pathological aging. ❞
That first part is very important, by the way! There are so many things that our brain needs, and we can eat, but the molecules are unable to pass the blood-brain barrier, meaning they either get wasted, or used elsewhere, or dismantled for their constituent parts. In this case, it zips straight into the brain instead.
See also:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
(Probably) good for the joints, too
First, astaxanthin got a glowing report in a study we knew not to trust blindly:
…and breathe. What a title that was! But, did you catch why it’s not to be trusted blindly? It was down at the bottom…
❝Conflict of interest statement
NOVAREX Co., Ltd. funded the study. Valensa International provided the FlexPro MD® ingredients, and NOVAREX Co., Ltd. encapsulated the test products (e.g., both FlexPro MD® and placebo)❞
Studies where a supplement company funded the study are not necessarily corrupt, but they can certainly sway publication bias, i.e. the company funds a bunch of studies and then pulls funding from the ones that aren’t going the way it wants.
So instead let’s look at:
Astaxanthin attenuates joint inflammation induced by monosodium urate crystals
and
Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis
…which had no such conflicts of interest.
They agree that astaxanthin indeed does the things (attenuates joint inflammation & ameliorates cartilage damage).
However, they are animal studies (rats), so we’d like to see studies with humans to be able to say for sure how much it helps these things.
Summary of benefits
Based on the available research, astaxanthin…
- is indeed a super-antioxidant
- is a neuroprotective agent
- also assists adult neurogenesis
- is probablygood for joints too
How much do I take, and is it safe?
A 2019 safety review concluded:
❝Recommended or approved doses varied in different countries and ranged between 2 and 24 mg.
We reviewed 87 human studies, none of which found safety concerns with natural astaxanthin supplementation, 35 with doses ≥12 mg/day.❞
Source: Astaxanthin: How much is too much? A safety review
In short: for most people, it’s very safe and well-tolerated. If you consume it to an extreme, you will likely turn pink, much as you would turn orange if you did the same thing with carrots. But aside from that, the risks appear to be minimal.
However! If you have a seafood allergy, please take care to get a supplement that’s made from microalgae, not one that’s made from krill or other crustaceans, or from other creatures that eat those.
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What Is “75 Hard”?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Andy Frisella. He’s not a doctor, scientist, nutritionist, personal trainer, or professional athlete, but he has kicked off a viral fitness challenge, so let’s take a look at it:
What it is
Firstly, Frisella asserts that it’s not a fitness challenge, but rather, he describes it as a “transformative mental toughness program”.
Here’s what it consists of:
- Follow a healthy diet plan with no deviations from it (i.e. no “cheat days”)
- Abstain from alcohol
- Exercise 2x per day, 45 minutes each
- One of the exercise sessions each day must be outside
- No rest days
- Drink 3.5 liters of water per day
And the duration? 75 days, hence the name of the
fitness challengetransformative mental toughness program.Why it is
Frisella’s rationale is:
- we must cultivate mental toughness by doing hard things
- allowing ourselves any deviation would be a sign of mental weakness
- if we allow ourselves to deviate, it becomes a habit
For this reason, he does not “allow” any substitutions, for example if somebody wants to do such-and-such a thing slightly differently instead. We put “allow” in quotation marks because of course, he’s not the boss of you, but per the rules of his challenge, at least.
These reasonings are in and of themselves somewhat sound, however, we at 10almonds would argue:
- before doing hard things, it is good to first consider “is it a good idea?” (amputating your leg using only a spork is a “hard thing”, and demonstrates incredible mental toughness, but that doesn’t make it a good idea)
- while being able to decide to do a thing and then do it is great characteristic to have, it’s good to first consider science; for example, restrictive diets with no flexibility simply do not work, and our bodies do require adequate rest, especially if being pushed through hard things, or problems will happen (injuries, illnesses, etc).
- while it’s true that allowing ourselves to deviate can become a habit, it’s good to first consider what habits we want to make, and make those habits, instead of potentially unsustainable or even simply unpleasant ones.
See also: What Flexible Dieting Really Means: When Flexibility Is The Dish Of The Day
And for that matter: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Want a “75 Gentle” instead?
If you like the idea of making new habits, but are not sure if extreme (and perhaps arbitrary) standards are the ones you want to hold, check out:
Cori Lefkowith’s 25 Healthy Habits That Will Change Your Life
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Eggs: Nutritional Powerhouse or Heart-Health Timebomb?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
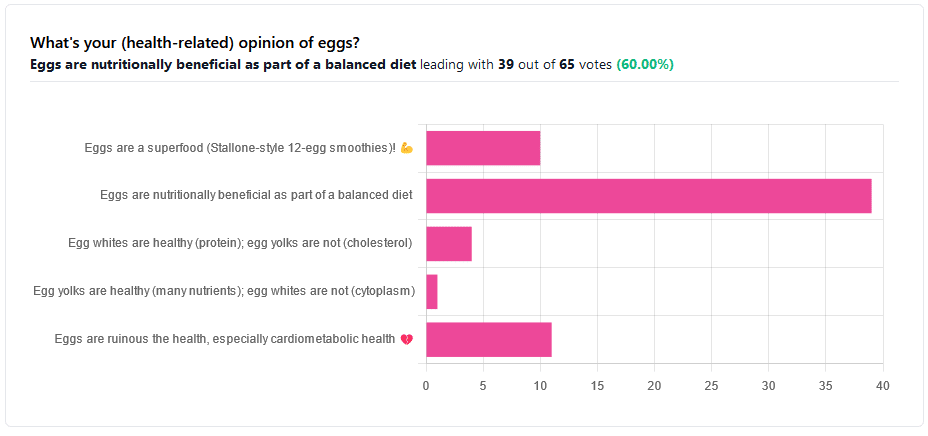
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on eggs. We specified that, for the sake of simplicity, let’s say that they are from happy healthy backyard hens who enjoy a good diet.
Apparently this one wasn’t as controversial as it might have been! We (for myth-busting purposes) try to pick something polarizing and sometimes even contentious for our Friday editions, and pick apart what science lies underneath public perceptions.
However, more than half (in fact, 60%) of the subscribers who voted in the poll voted for “Eggs are nutritionally beneficial as part of a balanced diet”, which very moderate statement is indeed pretty much the global scientific consensus.
Still, we’ve a main feature to write, so let’s look at the science, and what the other 40% had in mind:
Eggs are ruinous to health, especially cardiometabolic health: True or False?
False, per best current science, anyway!
Scientific consensus has changed over the years. We learned about cholesterol, then we learned about different types of cholesterol, and now we’ve even learned about in some instances even elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol aren’t necessarily a cause of cardiometabolic disorders so much as a symptom—especially in women.
Not to derail this main feature about eggs (rather than just cholesterol), but for those who missed it, this is actually really interesting: basically, research (pertaining to the use of statins) has found that in women, higher LDL levels aren’t anywhere near the same kind of risk factor as they are for men, and thus may mean that statins (whose main job is reducing LDL) may be much less helpful for women than for men, and more likely to cause unwanted serious side effects in women.
Check out our previous main feature about this: Statins: His & Hers?
But, for back on topic, several large studies (totalling 177,000 people in long-term studies in 50 countries) found:
❝Results from the three cohorts and from the updated meta-analysis show that moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) is not associated with cardiovascular disease risk overall, and is associated with potentially lower cardiovascular disease risk in Asian populations.❞
Egg whites are healthy (protein); egg yolks are not (cholesterol): True or False?
True and False, respectively. That is to say, egg whites are healthy (protein), and egg yolks are also healthy (many nutrients).
We talked a bit already about cholesterol, so we’ll not rehash that here. As to the rest:
Eggs are one of the most nutritionally dense foods around. After all, they have everything required to allow a cluster of cells to become a whole baby chick. That’s a lot of body-building!
They’re even more nutritionally heavy-hitters if you get omega-3 enriched eggs, which means the hens were fed extra omega-3, usually in the form of flax seeds.
Also, free-range is better healthwise than others. Do bear in mind that unless they really are from your backyard, or a neighbor’s, chances are that the reality is not what the advertising depicts, though. There are industry minimum standards to be able to advertise as “free-range”, and those standards are a) quite low b) often ignored, because an occasional fine is cheaper than maintaining good conditions.
So if you can look after your own hens, or get them from somewhere that you can see for yourself how they are looked after, so much the better!
Check out the differences side-by-side, though:
Pastured vs Omega-3 vs “Conventional” Eggs: What’s the Difference?
Stallone-style 12-egg smoothies are healthy: True or False?
False, at least if taken with any regularity. One can indeed have too much of a good thing.
So, what’s the “right amount” to eat?
It may vary depending on individual factors (including age and ethnicity), but a good average, according to science, is to keep it to 3 eggs or fewer per day. There are a lot of studies, but we only have so much room here, so we’ll pick one. Its findings are representative of (and in keeping with) the many other studies we looked at, so this seems uncontroversial scientifically:
❝Intake of 1 egg/d was sufficient to increase HDL function and large-LDL particle concentration; however, intake of 2-3 eggs/d supported greater improvements in HDL function as well as increased plasma carotenoids. Overall, intake of ≤3 eggs/d favored a less atherogenic LDL particle profile, improved HDL function, and increased plasma antioxidants in young, healthy adults.❞
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
8 Signs Of Hypothyroidism Beyond Tiredness & Weight Gain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to hypothyroidism, most people know to look out for tiredness and weight gain, and possibly menstrual disturbances in those who menstruate. But those symptoms could be caused by very many things, so what more specific signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism should we look out for?
Dr. James O’Donovan shows us in this short video:
The lesser-known signs
Dr. O’Donovan discusses:
- Asteatotic eczema (also called: eczema craquelé): dry, cracked skin with a “crazy paving” appearance, leading to fissures. It’s common on the lower legs, back, torso, and arms, especially in older patients and especially in winter.
- Cold peripheries with pale, dry, coarse skin: cold hands and feet, along with dryness due to decreased sweating; these invariably come together, though the exact link is unclear.
- Yellowish hue to the skin (carotenoderma): yellow-orange discoloration from elevated beta-carotene levels. This can easily be mistaken for jaundice and also occurs in diabetes, liver, and kidney diseases.
- Thin, brittle hair: the hair on one’s head may become dry, coarse, and fall out in handfuls.
- Loss of hair on the outer third of eyebrows: thinning or disappearance of hair in this very specific area.
- Slow-growing, rigid, brittle nails: slowed nail growth due to decreased cell turnover rate. Ridges may form as keratin cells accumulate.
- Myxedema: puffy face, eyelids, legs, and feet caused by tissue swelling from cutaneous deposition.
- Delayed wound healing: is what it sounds like; a slower healing process.
10almonds note: this video, like much of medical literature as well, does focus on what things are like for white people. Black people with hypothyroidism are more likely to see a lightening of hair pigmentation, and, in contrast, hyperpigmentation of the skin, usually in patches. We couldn’t find data for other ethnicities or skintones, but it does seem that most of the signs and symptoms (unrelated to pigmentation) should be the same for most people.
Meanwhile, for more on the above 8 signs, with visuals, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Three Rs To Boost Thyroid-Related Energy Levels
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Grapefruit vs Lemon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing grapefruit to lemon, we picked the lemon.
Why?
Grapefruit has its merits, but in the battle of the citrus fruits, lemons come out on top nutritionally:
In terms of macros, grapefruit has more carbs while lemons have more fiber. So, while both have a low glycemic index, lemon is still the winner by the numbers.
Looking at the vitamins, here we say grapefruit’s strengths: grapefruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and choline, while lemon has more of vitamins B6 and C. So, a 4:2 win for grapefruit here.
In the category of minerals, lemons retake the lead: grapefruit has more zinc, while lemon has more calcium, copper, iron, manganese, and selenium.
One final consideration that’s not shown in the nutritional values, is that grapefruit contains high levels of furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
PS: the same substance is quite available in pummelos and sour oranges (but not meaningfully in sweet oranges); you can see a chart here showing the relative furanocoumarin contents of many citrus fruits, or lack thereof as the case may be, as it is for lemons and most limes)
Adding up the sections gives us a clear win for lemons, but by all means enjoy either or both; just watch out for that furanocoumarin content of grapefruit if you’re on any meds affected by such (again, do check with your pharmacist, as our list was far from exhaustive—and yes, this question is one that a pharmacist will answer more easily and accurately than a doctor will).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← citrus fruits in general make the list; they inhibit tumor growth and kill cancer cells; regular consumption is also associated with a lower cancer risk 🙂
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Distracted Mind – by Dr. Adam Gazzaley and Dr. Larry Rosen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yes, yes, we know, unplug once in a while. But what else do this highly-qualified pair of neuroscientists have to offer?
Rather than being a book for the sake of being a book, with lots of fluff and the usual advice about single-tasking, the authors start with a reframe:
Neurologically speaking, the hit of dopamine we get when looking for information is the exact same as the hit of dopamine that we, a couple of hundred thousand years ago, got when looking for nuts and berries.
- When we don’t find them, we become stressed, and search more.
- When we do find them, we are encouraged and search more nearby, and to the other side of nearby, and near around, to find more.
But in the case of information (be it useful information or celebrity gossip or anything in between), the Internet means that’s always available now.
So, we jitter around like squirrels, hopping from one to the next to the next.
A strength of this book is where it goes from there. Specifically, what evidence-based practices will actually keep our squirrel-brain focused… and which are wishful thinking for anyone who lives in this century.
Bringing original research from their own labs, as well as studies taken from elsewhere, the authors present a science-based toolkit of genuinely useful resources for actual focus.
Bottom line: if you think you could really optimize your life if you could just get on track and stay on track, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Distracted Mind, and get yours to focus!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: