Scattered Minds – by Dr. Gabor Maté
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This was not the first book that Dr. Maté sat down to write, by far. But it was the first that he actually completed. Guess why.
Writing from a position of both personal and professional experience and understanding, Dr. Maté explores the inaptly-named Attention Deficit Disorder (if anything, there’s often a surplus of attention, just, to anything and everything rather than necessarily what would be most productive in the moment), its etiology, its presentation, and its management.
This is a more enjoyable book than some others by the same author, as while this condition certainly isn’t without its share of woes (often, for example, a cycle of frustration and shame re “why can’t I just do the things; this is ruining my life and it would be so easy if I could just do the things!”), it’s not nearly so bleak as entire books about trauma, addiction, and so forth (worthy as those books also are).
Dr. Maté frames it specifically as a development disorder, and one whereby with work, we can do the development later that (story of an ADHDer’s life) we should have done earlier but didn’t. In terms of practical advice, he includes a program for effecting this change, including as an adult.
The style is easy-reading, in small chapters, with ADHD’d-up readers in mind, giving a strong sense of speeding pleasantly through the book.
Bottom line: when it’s a book by Dr. Gabor Maté, you know it’s going to be good, and this is no exception. Certainly read it if you, anyone you care about, or even anyone you just spend a lot of time around, has ADHD or similar.
Click here to check out Scattered Minds, and unscatter yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Little-Known Truth…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Myth-Buster, Myth-Buster, Bust Us A Myth (or three!)
Let’s can this myth for good
People think of “canned foods” as meaning “processed foods” and therefore bad. But the reality is it’s all dependent on what’s in the can (check the ingredients!). And as for nutrients?
Many canned fruits and vegetables contain more nutrients than fresh ones! This is because the way they’ve been stored preserves them better. For example:
- Canned tomatoes contain more bioavailable lycopene than fresh
- Canned spinach contains more bioavailable carotene than fresh
- Canned corn contains more bioavailable lutein than fresh
- The list goes on, but you get the idea!
Don’t Want To Take Our Word For It? Read The Scientific Paper Here!
Gaslight, Gymkeep, Girl-loss?
Many women and girls avoid doing weight-training as part of their exercise—or use only the smallest weights—to avoid “bulking up” and “looking like a man”.
Many men, meanwhile, wish it were that easy to bulk up!
The reality is that nobody, unless you have very rare genes, packs on a lot of muscle by accident. Even with the genes for it, it won’t happen unless you’re also eating for it!
Resistance-based strength training (such as lifting weights), is a great way for most people to look after an important part of their long-term health: bone density!
You can’t have strong muscles on weak bones, so strengthening the muscles cues the body to strengthen the bones. In short, your strength-training at age 45 or 55 (or earlier) could be what helps you avoid a broken hip at 65 or 75.
We’re Not Kidding, It Really Is That Important (Read The Study Here)!
Something doesn’t smell right about this
There’s been a big backlash against anti-perspirants and deodorants. The popular argument is that the aluminium in them causes cancer.
This led to many people buying “deodo-rocks”, crystal rocks that can be run under water and then rubbed on the armpits to deodorize “naturally”. But, those crystal rocks are actually alum crystals (guess what they contain…).
The belief that deodorants cause cancer came from studies done by applying deodorant to cells (like the canine kidney cells in this study) in petri dishes. So, assuming you don’t cut out your kidney and then spray it directly with the deodorant, the jury is still out!
A more recent systematic review sorted out quite clearly the ways in which aluminium was, or was not, harmful, and said:
❝Neither is there clear evidence to show use of Al-containing underarm antiperspirants or cosmetics increases the risk of Alzheimer’s Disease or breast cancer. Metallic Al, its oxides, and common Al salts have not been shown to be either genotoxic or carcinogenic.❞
Critical Reviews in Toxicology
…but also says that you should avoid eating aluminium while pregnant or breastfeeding. We hope you can resist the urge.
See The Summary For Yourself Here!
(actually the whole article is there, but we know you value condensed knowledge, so: the abstract at the top will probably tell you all you want to know!)
Share This Post
-
From Strength to Strength – by Dr. Arthur Brooks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For most professions, there are ways in which performance can be measured, and the average professional peak varies by profession, but averages are usually somewhere in the 30–45 range, with a pressure to peak between 25–35.
With a peak by age 45 or perhaps 50 at the latest (aside from some statistical outliers, of course), what then to expect at age 50+? Not long after that, there’s a reason for mandatory retirement ages in some professions.
Dr. Brooks examines the case for accepting that rather than fighting it, and/but making our weaknesses into our strengths as we go. If our fluid intelligence slows, our accumulated crystal intelligence (some might call it “wisdom“) can make up for it, for example.
But he also champions the idea of looking outside of ourselves; of the importance of growing and fostering connections; giving to those around us and receiving support in turn; not transactionally, but just as a matter of mutualism of the kind found in many other species besides our own. Indeed, Dr. Brooks gives the example of a grove of aspen trees (hence the cover art of this book) that do exactly that.
The style is very accessible in terms of language but with frequent scientific references, so very much a “best of both worlds” in terms of readability and information-density.
Bottom line: if ever you’ve wondered at what age you might outlive your usefulness, this book will do as the subtitle suggests, and help you carve out your new place.
Click here to check out From Strength To Strength, and find yours!
Share This Post
-
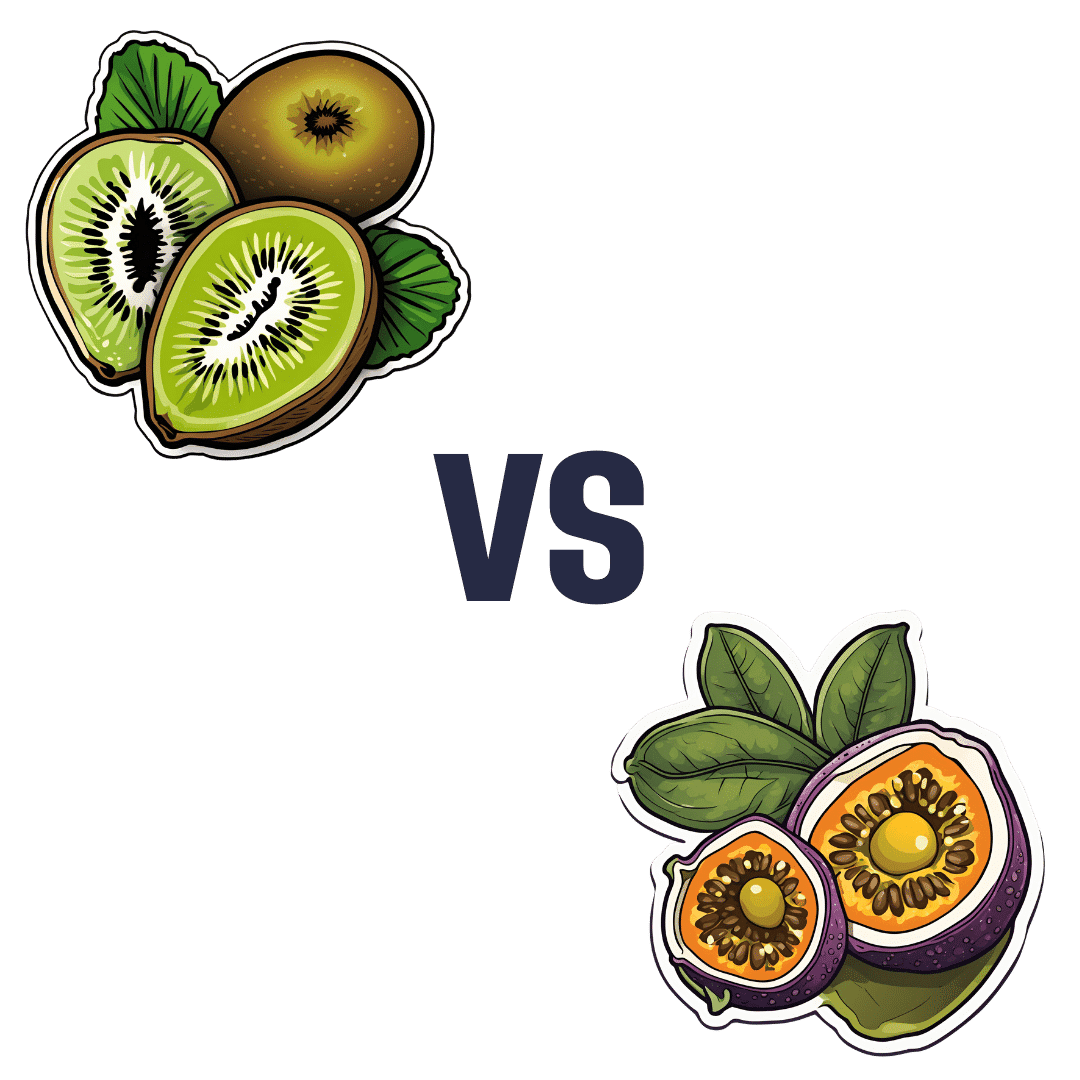
Kiwi vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to passion fruit, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
This fruit is so passionate about delivery nutrient-dense goodness, that at time of writing, nothing has beaten it yet!
In terms of macros, passion fruit has a little more protein, as well as 50% more carbs, and/but more than 3x the fiber. That last stat is particularly impressive, and also results in passion fruit having a much lower glycemic index, too. In short, a clear win for passion fruit in the macros category.
In the category of vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins B9, C, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and B6, making for a tie this time.
As for minerals, kiwi has more calcium, copper, manganese, and zinc, while passion fruit has more iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, resulting in a modest, marginal win for passion fruit in this category.
Adding up the categories gives a convincing win for passion fruit, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good! And kiwi has its merits too (for example, it’s particularly high in vitamin K, appropriately enough).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Intermittent Fasting, Intermittently?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Have you come across any research on alternate-day intermittent fasting—specifically switching between one day of 16:8 fasting and the next day of regular eating patterns? I’m curious if there are any benefits or drawbacks to this alternating approach, or if the benefits mainly come from consistent intermittent fasting?❞
Short and unhelpful answer: no
Longer and hopefully more helpful answer:
As you probably know, usually people going for approaches based on the above terms either
- practise 16:8 fasting (fast for 16 hours each day, eat during an 8-hour window) or
- practise alternate-day fasting (fast for 24 hours, eat whenever for 24 hours, repeat)
…which latter scored the best results in this large meta-analysis of studies:
There is also the (popular) less extreme version of alternate-day fasting, sometimes called “eat stop eat”, which is not a very helpful description because that describes almost any kind of eating/fasting, but it usually refers to “once per week, take a day off from eating”.
You can read more about each of these (and some other variants), here:
Intermittent Fasting: What’s The Truth?
What you are describing (doing 16:8 fasting on alternate days, eating whenever on the other days) is essentially: intermittent fasting, just with one 16-hour fast per 48 hours instead of per the usual 24 hours.
See also: International consensus on fasting terminology ← the section on the terms “STF & PF” covers why this gets nudged back under the regular IF umbrella
Good news: this means there is a lot of literature into the acute (i.e., occurring the same day, not long-term)* benefits of 16:8 IF, and that means that you will be getting those benefits, every second day.
You remember that meta-analysis we posted above? While it isn’t mentioned in the conclusion (which only praised complete alternate-day fasting producing the best outcomes overall), sifting through the results data discovers that time-restricted eating (which is what you are doing, by these classifications) was the only fasting method to significantly reduce fasting blood glucose levels.
(However, no significant differences were observed between any IF form and the reference (continuous energy restriction, CER, i.e. calorie-controlled) diets in fasting insulin and HbA1c levels)
*This is still good news in the long-term though, because getting those benefits every second day is better than getting those benefits on no days, and this will have a long-term impact on your healthy longevity, just like how it is better to exercise every second day than it is to exercise no days, or better to abstain from alcohol every second day than it is to abstain on no days, etc.
In short, by doing IF every second day, you are still giving your organs a break sometimes, and that’s good.
All the same, if it would be convenient and practical for you, we would encourage you to consider either the complete alternate-day fasting (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best results overall),or time-restricted eating (TRE) every day (which, according to a lot of data, gives the best fasting blood sugar levels).
You could also improve the TRE days by shifting to 20:4 (i.e., 20 hours fasting and 4 hours eating), this giving your organs a longer break on those days.
Want to learn more?
For a much more comprehensive discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to intermitted fasting, check out:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Stop Binge-Eating: Flip This Switch!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“The Big Eating Therapist” Sarah Dosanjh has insights from both personal and professional experience:
No “Tough Love” Necessary
Eating certain foods is often socially shamed, and it’s easy to internalize that, and feel guilty. While often guilt is considered a pro-social emotion that helps people to avoid erring in a way that will get us excluded from the tribe (bearing in mind that for most of our evolutionary history, exile would mean near-certain death), it is not good at behavior modification when it comes to addictions or anything similar to addictions.
The reason for this is that if we indulge in a pleasure we feel we “shouldn’t” and expect we’d be shamed for, we then feel bad, and we immediately want something to make us feel better. Guess what that something will be. That’s right: the very same thing we literally just felt ashamed about.
So guilt is not helpful when it comes to (for example) avoiding binge-eating.
Instead, Dosanjh points us to a study whereby dieters ate a donut and drank water, before being given candy for taste testing. The control group proceeded without intervention, while the experimental group had a self-compassion intervention between the donut and the candy. This meant that researchers told the participants not to feel bad about eating the donut, emphasizing self-kindness, mindfulness, and common humanity. The study found that those who received the intervention, ate significantly less candy.
What we can learn from this is: we must be kind to ourselves. Allowing ourselves, consciously and mindfully, “a little treat”, secures its status as being “little”, and “a treat”. Then we smile, thinking “yes, that was a nice little thing to do for myself”, and proceed with our day.
This kind of self-compassion helps avoid the “meta-binge” process, where guilt from one thing leads to immediately reaching for another.
For more on this, plus a link to the study she mentioned, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
LGBTQ+ People Relive Old Traumas as They Age on Their Own
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bill Hall, 71, has been fighting for his life for 38 years. These days, he’s feeling worn out.
Hall contracted HIV, the virus that can cause AIDS, in 1986. Since then, he’s battled depression, heart disease, diabetes, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, kidney cancer, and prostate cancer. This past year, Hall has been hospitalized five times with dangerous infections and life-threatening internal bleeding.
But that’s only part of what Hall, a gay man, has dealt with. Hall was born into the Tlingit tribe in a small fishing village in Alaska. He was separated from his family at age 9 and sent to a government boarding school. There, he told me, he endured years of bullying and sexual abuse that “killed my spirit.”
Because of the trauma, Hall said, he’s never been able to form an intimate relationship. He contracted HIV from anonymous sex at bath houses he used to visit. He lives alone in Seattle and has been on his own throughout his adult life.
“It’s really difficult to maintain a positive attitude when you’re going through so much,” said Hall, who works with Native American community organizations. “You become mentally exhausted.”
It’s a sentiment shared by many older LGBTQ+ adults — most of whom, like Hall, are trying to manage on their own.
Of the 3 million Americans over age 50 who identify as gay, bisexual, or transgender, about twice as many are single and living alone when compared with their heterosexual counterparts, according to the National Resource Center on LGBTQ+ Aging.
This slice of the older population is expanding rapidly. By 2030, the number of LGBTQ+ seniors is expected to double. Many won’t have partners and most won’t have children or grandchildren to help care for them, AARP research indicates.
They face a daunting array of problems, including higher-than-usual rates of anxiety and depression, chronic stress, disability, and chronic illnesses such as heart disease, according to numerous research studies. High rates of smoking, alcohol use, and drug use — all ways people try to cope with stress — contribute to poor health.
Keep in mind, this generation grew up at a time when every state outlawed same-sex relations and when the American Psychiatric Association identified homosexuality as a psychiatric disorder. Many were rejected by their families and their churches when they came out. Then, they endured the horrifying impact of the AIDS crisis.
“Dozens of people were dying every day,” Hall said. “Your life becomes going to support groups, going to visit friends in the hospital, going to funerals.”
It’s no wonder that LGBTQ+ seniors often withdraw socially and experience isolation more commonly than other older adults. “There was too much grief, too much anger, too much trauma — too many people were dying,” said Vincent Crisostomo, director of aging services for the San Francisco AIDS Foundation. “It was just too much to bear.”
In an AARP survey of 2,200 LGBTQ+ adults 45 or older this year, 48% said they felt isolated from others and 45% reported lacking companionship. Almost 80% reported being concerned about having adequate social support as they grow older.
Embracing aging isn’t easy for anyone, but it can be especially difficult for LGBTQ+ seniors who are long-term HIV survivors like Hall.
Related Links
- Americans With HIV Are Living Longer. Federal Spending Isn’t Keeping Up. Jun 17, 2024
- ‘Stonewall Generation’ Confronts Old Age, Sickness — And Discrimination May 22, 2019
- Staying Out Of The Closet In Old Age Oct 17, 2016
Of 1.2 million people living with HIV in the United States, about half are over age 50. By 2030, that’s estimated to rise to 70%.
Christopher Christensen, 72, of Palm Springs, California, has been HIV-positive since May 1981 and is deeply involved with local organizations serving HIV survivors. “A lot of people living with HIV never thought they’d grow old — or planned for it — because they thought they would die quickly,” Christensen said.
Jeff Berry is executive director of the Reunion Project, an alliance of long-term HIV survivors. “Here people are who survived the AIDS epidemic, and all these years later their health issues are getting worse and they’re losing their peers again,” Berry said. “And it’s triggering this post-traumatic stress that’s been underlying for many, many years. Yes, it’s part of getting older. But it’s very, very hard.”
Being on their own, without people who understand how the past is informing current challenges, can magnify those difficulties.
“Not having access to supports and services that are both LGBTQ-friendly and age-friendly is a real hardship for many,” said Christina DaCosta, chief experience officer at SAGE, the nation’s largest and oldest organization for older LGBTQ+ adults.
Diedra Nottingham, a 74-year-old gay woman, lives alone in a one-bedroom apartment in Stonewall House, an LGBTQ+-friendly elder housing complex in New York City. “I just don’t trust people,“ she said. “And I don’t want to get hurt, either, by the way people attack gay people.”
When I first spoke to Nottingham in 2022, she described a post-traumatic-stress-type reaction to so many people dying of covid-19 and the fear of becoming infected. This was a common reaction among older people who are gay, bisexual, or transgender and who bear psychological scars from the AIDS epidemic.
Nottingham was kicked out of her house by her mother at age 14 and spent the next four years on the streets. The only sibling she talks with regularly lives across the country in Seattle. Four partners whom she’d remained close with died in short order in 1999 and 2000, and her last partner passed away in 2003.
When I talked to her in September, Nottingham said she was benefiting from weekly therapy sessions and time spent with a volunteer “friendly visitor” arranged by SAGE. Yet she acknowledged: “I don’t like being by myself all the time the way I am. I’m lonely.”
Donald Bell, a 74-year-old gay Black man who is co-chair of the Illinois Commission on LGBTQ Aging, lives alone in a studio apartment in subsidized LGBTQ+-friendly senior housing in Chicago. He spent 30 years caring for two elderly parents who had serious health issues, while he was also a single father, raising two sons he adopted from a niece.
Bell has very little money, he said, because he left work as a higher-education administrator to care for his parents. “The cost of health care bankrupted us,” he said. (According to SAGE, one-third of older LGBTQ+ adults live at or below 200% of the federal poverty level.) He has hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage in his feet. These days, he walks with a cane.
To his great regret, Bell told me, he’s never had a long-term relationship. But he has several good friends in his building and in the city.
“Of course I experience loneliness,” Bell said when we spoke in June. “But the fact that I am a Black man who has lived to 74, that I have not been destroyed, that I have the sanctity of my own life and my own person is a victory and something for which I am grateful.”
Now he wants to be a model to younger gay men and accept aging rather than feeling stuck in the past. “My past is over,” Bell said, “and I must move on.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: