Pulse – by Jenny Chandler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Beans, chickpeas, and lentils are well-established super-healthy foods, but they’re often not a lot of people’s favorite. And why? Usually because of unhappy associations with boring dishes that can barely be called dishes.
This book raises the bar for pulses of various kinds, and not only provides recipes (180 of them) but also guidelines on principles, tips and tricks, what works and what doesn’t, what makes things better or worse, perfect partners, sprouting, and more.
The recipes themselves are not all vegan, nor even all vegetarian, but the beans are the star throughout. For those who are vegan or vegetarian, it’s easy to make substitutions, not least of all because the author is generous with “try this instead of that” and “consider also” suggestions, to help us tailor each dish to our personal preferences, and even the desired vibe of a given meal.
The dishes are neither overly simplistic (it’s not a student survival cookbook, by any means) nor overly complicated; rather, enough is done to make each dish invitingly tasty, and nothing extraneous or pretentious is added for the sake of being fancy. This is about delicious home cooking, nothing more nor less.
If the book has a weakness, it’s that visual learners will feel the absence of pictures for many recipes. But, the text is clear, the instructions are easy to follow, and a photo for each dish would probably have doubled the cost of the book, at least, while halving the number of recipes.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get more beans and other pulses in your diet, but are unsure how to make it exciting, this is an excellent option.
Click here to check out Pulse, and expand your kitchen repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat to Beat Disease – by Dr. William Li
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. William Li asks the important question: is your diet feeding disease, or defeating it?
Because everything we put in our bodies makes our health just a little better—or just a little worse. Ok, sometimes a lot worse.
But for most people, when it comes to diet, it’s a death of a thousand cuts of unhealthy food. And that’s what he looks to fix with this book.
The good news: Dr. Li (while not advocating for unhealthy eating, of course), focuses less on what to restrict, and more on what to include. This book covers hundreds of such healthy foods, and ideas (practical, useful ones!) on incorporating them daily, including dozens of recipes.
He mainly looks at five ways our food can help us with…
- Angiogenesis (blood vessel replacement)
- Regeneration (of various bodily organs and systems)
- Microbiome health (and all of its knock-on effects)
- DNA protection (and thus slower cellular aging)
- Immunity (defending the body while also reducing autoimmune problems)
The style is simple and explanatory; Dr. Li is a great educator. Reading this isn’t a difficult read, but you’ll come out of it feeling like you just did a short course in health science.
Bottom line: if you’d like an easy way to improve your health in an ongoing and sustainable way, then this book can help you do just that.
Click here to check out Eat To Beat Disease, and eat to beat disease!
Share This Post
-
Quit Like a Woman – by Holly Whitaker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed “quit drinking” books before, so what makes this one different?
While others focus on the science of addiction and the tips and tricks of habit breaking/forming, this one is more about environmental factors, and that because of society being as it is, we as women often face different challenges when it comes to drinking (or not). Not necessarily easier or harder than men’s in this case, but different. And that sometimes calls for different methods to deal with them. This book explores those.
She also looks at such matters as how to quit alcohol when you’ve never stuck to a diet, and other such very down-to-earth topics, in a well-researched and non-preachy fashion.
Bottom line: if you’ve sometimes tried to quit drinking or even just to cut back, but found the deck stacked against you and things conspire to undermine your efforts, this book will give you a clearer path forward.
Click here to check out Quite Like A Woman, And Take Care Of Yourself!
Share This Post
-
Is Marine Collagen Worth Taking?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
I wanted to ask if you think marine collagen is decent to take. I’ve heard a lot of bad press about it
We don’t know what you’ve heard, but generally speaking it’s been found to be very beneficial to bones, joints, and skin! We wrote about it quite recently on a “Research Review Monday”:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
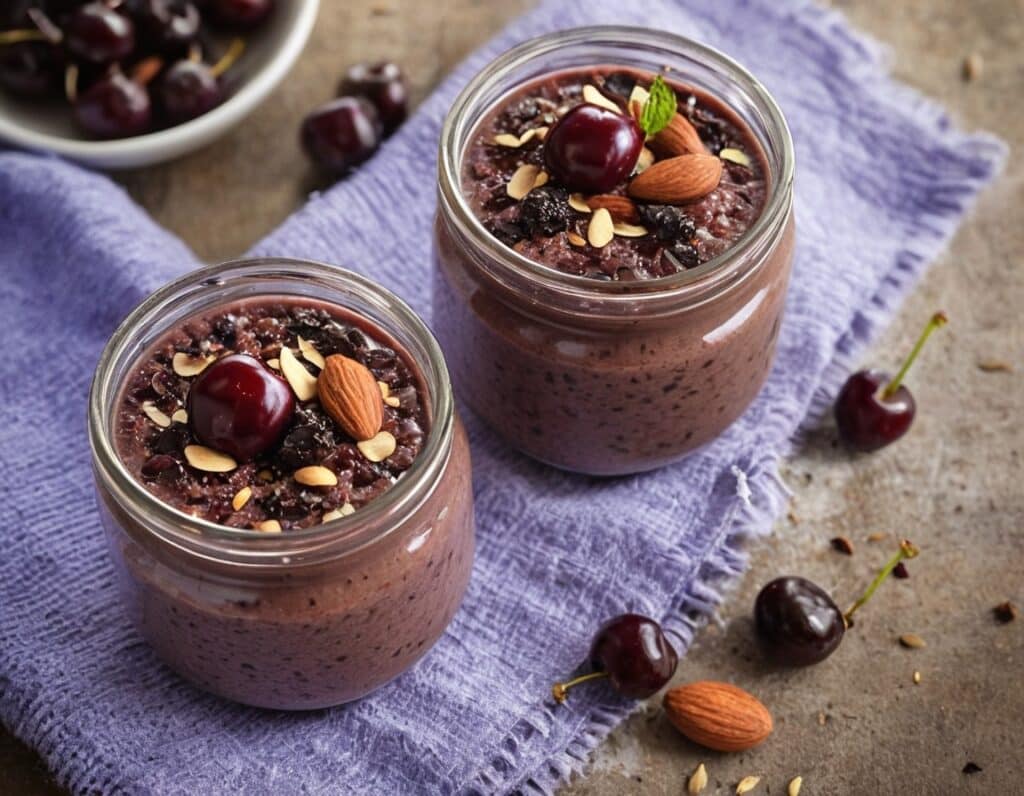
Black Forest Chia Pudding
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This pudding tastes so decadent, it’s hard to believe it’s so healthy, but it is! Not only is it delicious, it’s also packed with nutrients including protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats (including omega-3s), fiber, vitamins, minerals, and assorted antioxidant polyphenols. Perfect dessert or breakfast!
You will need
- 1½ cups pitted fresh or thawed-from-frozen cherries
- ½ cup mashed banana
- 3 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder
- 2 tbsp chia seeds, ground
- Optional: 2 pitted dates, soaked in hot water for 10 minutes and then drained (include these if you prefer a sweeter pudding)
- Garnish: a few almonds, and/or berries, and/or cherries and/or cacao nibs
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the ingredients except for the chia seeds and the garnish, with ½ cup of water, until completely smooth
2) Divide into two small bowls or glass jars
3) Add 1 tbsp ground chia seeds to each, and stir until evenly distributed
4) Add the garnish and refrigerate overnight or at least for some hours. There’s plenty of wiggle-room here, so make it at your convenience and serve at your leisure.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing honey to maple syrup, we picked the honey.
Why?
It was very close, as both have small advantages:
• Honey has some medicinal properties (and depending on type, may contain an antihistamine)
• Maple syrup is a good source of manganese, as well as low-but-present amounts of other mineralsHowever, you wouldn’t want to eat enough maple syrup to rely on it as a source of those minerals, and honey has the lower GI (average 46 vs 54; for comparison, refined sugar is 65), which works well as a tie-breaker.
(If GI’s very important to you, though, the easy winner here would be agave syrup if we let it compete, with its GI of 15)
Read more:
• Can Honey Relieve Allergies?
• From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose C’sDon’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Trout vs Haddock – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing trout to haddock, we picked the trout.
Why?
It wasn’t close.
In terms of macros, trout has more protein and more fat, although the fat is mostly healthy (some saturated though, and trout does have more cholesterol). This category could be a win for either, depending on your priorities. But…
When it comes to vitamins, trout has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, C, D, and E, while haddock is not higher in any vitamins.
In the category of minerals, trout has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, potassium, and zinc, while haddock has slightly more selenium. Given that a 10oz portion of trout already contains 153% of the RDA of selenium, however, the same size portion of haddock having 173% of the RDA isn’t really a plus for haddock (especially as selenium can cause problems if we get too much). Oh, and haddock is also higher in sodium, but in industrialized countries, most people most of the time need less of that, not more.
On balance, the overwhelming nutritional density of trout wins the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: It Makes Quite A Difference!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: