Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cancer is increasingly survivable – but it shouldn’t depend on your ability to ‘wrangle’ the health system
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One in three of us will develop cancer at some point in our lives. But survival rates have improved to the point that two-thirds of those diagnosed live more than five years.
This extraordinary shift over the past few decades introduces new challenges. A large and growing proportion of people diagnosed with cancer are living with it, rather than dying of it.
In our recently published research we examined the cancer experiences of 81 New Zealanders (23 Māori and 58 non-Māori).
We found survivorship not only entailed managing the disease, but also “wrangling” a complex health system.
Surviving disease or surviving the system
Our research focused on those who had lived longer than expected (four to 32 years since first diagnosis) with a life-limiting or terminal diagnosis of cancer.
Common to many survivors’ stories was the effort it took to wrangle the system or find others to advocate on their behalf, even to get a formal diagnosis and treatment.
By wrangling we refer to the practices required to traverse complex and sometimes unwelcoming systems. This is an often unnoticed but very real struggle that comes on top of managing the disease itself.
The common focus of the healthcare system is on symptoms, side effects of treatment and other biological aspects of cancer. But formal and informal care often falls by the wayside, despite being key to people’s everyday experiences.
Survival is often linked to someone’s social connections and capacity to access funds. Getty Images The inequities of cancer survivorship are well known. Analyses show postcodes and socioeconomic status play a strong role in the prevalence of cancer and survival.
Less well known, but illustrated in our research, is that survival is also linked to people’s capacity to manage the entire healthcare system. That includes accessing a diagnosis or treatment, or identifying and accessing alternative treatments.
Survivorship is strongly related to material resources, social connections, and understandings of how the health system works and what is available. For instance, one participant who was contemplating travelling overseas to get surgery not available in New Zealand said:
We don’t trust the public system. So thankfully we had private health insurance […] But if we went overseas, health insurance only paid out to $30,000 and I think the surgery was going to be a couple of hundred thousand. I remember Dad saying and crying and just being like, I’ll sell my business […] we’ll all put in money. It was really amazing.
Assets of survivorship
In New Zealand, the government agency Pharmac determines which medications are subsidised. Yet many participants were advised by oncologists or others to “find ways” of taking costly, unsubsidised medicines.
This often meant finding tens of thousands of dollars with no guarantees. Some had the means, but for others it meant drawing on family savings, retirement funds or extending mortgages. This disproportionately favours those with access to assets and influences who survives.
But access to economic capital is only one advantage. People also have cultural resources – often described as cultural capital.
In one case, a participant realised a drug company was likely to apply to have a medicine approved. They asked their private oncologist to lobby on their behalf to obtain the drug through a compassionate access scheme, without having to pay for it.
Others gained community support through fundraising from clubs they belonged to. But some worried about where they would find the money, or did not want to burden their community.
I had my doctor friend and some others that wanted to do some public fundraising. But at the time I said, “Look, most of the people that will be contributing are people from my community who are poor already, so I’m not going to do that option”.
Accessing alternative therapies, almost exclusively self-funded, was another layer of inequity. Some felt forced to negotiate the black market to access substances such as marijuana to treat their cancer or alleviate the side effects of orthodox cancer treatment.
Cultural capital is not a replacement for access to assets, however. Māori survivorship was greatly assisted by accessing cultural resources, but often limited by lack of material assets.
Persistence pays
The last thing we need when faced with the possibility of cancer is to have to push for formal diagnosis and care. Yet this was a common experience.
One participant was told nothing could be found to explain their abdominal pain – only to find later they had pancreatic cancer. Another was told their concerns about breathing problems were a result of anxiety related to a prior mental health history, only to learn later their earlier breast cancer had spread to their lungs.
Persistence is another layer of wrangling and it often causes distress.
Once a diagnosis was given, for many people the public health system kicked in and delivered appropriate treatment. However, experiences were patchy and variable across New Zealand.
Issues included proximity to hospitals, varying degrees of specialisation available, and the requirement of extensive periods away from home and whānau. This reflects an ongoing unevenness and lack of fairness in the current system.
When facing a terminal or life-limiting diagnosis, the capacity to wrangle the system makes a difference. We shouldn’t have to wrangle, but facing this reality is an important first step.
We must ensure it doesn’t become a continuing form of inequity, whereby people with access to material resources and social and cultural connections can survive longer.
Kevin Dew, Professor of Sociology, Te Herenga Waka — Victoria University of Wellington; Alex Broom, Professor of Sociology & Director, Sydney Centre for Healthy Societies, University of Sydney; Chris Cunningham, Professor of Maori & Public Health, Massey University; Elizabeth Dennett, Associate Professor in Surgery, University of Otago; Kerry Chamberlain, Professor of Social and Health Psychology, Massey University, and Richard Egan, Associate Professor in Health Promotion, University of Otago
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
It’s On Me – by Dr. Sara Kuburic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This isn’t about bootstrapping and nor is it a motivational pep talk. What it is, however, is a wake-up call for the wayward, and that doesn’t mean “disaffected youth” or such. Rather, therapist Dr. Sara Kuburic tackles the problem of self-loss.
It’s about when we get so caught up in what we need to do, should do, are expected to do, are in a rut of doing… That we forget to also live. After all, we only get one shot at life so far as we know, so we might as well live it in whatever way is right for us.
That probably doesn’t mean a life of going through the motions.
The writing style here is personal and direct, and it makes for quite compelling reading from start to finish.
Bottom line: if ever you find yourself errantly sleepwalking through life and would like to change that, this is a book for you.
Click here to check out It’s On Me, and take control of what’s yours!
Share This Post
-
Mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem. What should we call mental distress?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talk about mental health more than ever, but the language we should use remains a vexed issue.
Should we call people who seek help patients, clients or consumers? Should we use “person-first” expressions such as person with autism or “identity-first” expressions like autistic person? Should we apply or avoid diagnostic labels?
These questions often stir up strong feelings. Some people feel that patient implies being passive and subordinate. Others think consumer is too transactional, as if seeking help is like buying a new refrigerator.
Advocates of person-first language argue people shouldn’t be defined by their conditions. Proponents of identity-first language counter that these conditions can be sources of meaning and belonging.
Avid users of diagnostic terms see them as useful descriptors. Critics worry that diagnostic labels can box people in and misrepresent their problems as pathologies.
Underlying many of these disagreements are concerns about stigma and the medicalisation of suffering. Ideally the language we use should not cast people who experience distress as defective or shameful, or frame everyday problems of living in psychiatric terms.
Our new research, published in the journal PLOS Mental Health, examines how the language of distress has evolved over nearly 80 years. Here’s what we found.
Engin Akyurt/Pexels Generic terms for the class of conditions
Generic terms – such as mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem – have largely escaped attention in debates about the language of mental ill health. These terms refer to mental health conditions as a class.
Many terms are currently in circulation, each an adjective followed by a noun. Popular adjectives include mental, mental health, psychiatric and psychological, and common nouns include condition, disease, disorder, disturbance, illness, and problem. Readers can encounter every combination.
These terms and their components differ in their connotations. Disease and illness sound the most medical, whereas condition, disturbance and problem need not relate to health. Mental implies a direct contrast with physical, whereas psychiatric implicates a medical specialty.
Mental health problem, a recently emerging term, is arguably the least pathologising. It implies that something is to be solved rather than treated, makes no direct reference to medicine, and carries the positive connotations of health rather than the negative connotation of illness or disease.
Is ‘mental health problem’ actually less pathologising? Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Arguably, this development points to what cognitive scientist Steven Pinker calls the “euphemism treadmill”, the tendency for language to evolve new terms to escape (at least temporarily) the offensive connotations of those they replace.
English linguist Hazel Price argues that mental health has increasingly come to replace mental illness to avoid the stigma associated with that term.
How has usage changed over time?
In the PLOS Mental Health paper, we examine historical changes in the popularity of 24 generic terms: every combination of the nouns and adjectives listed above.
We explore the frequency with which each term appears from 1940 to 2019 in two massive text data sets representing books in English and diverse American English sources, respectively. The findings are very similar in both data sets.
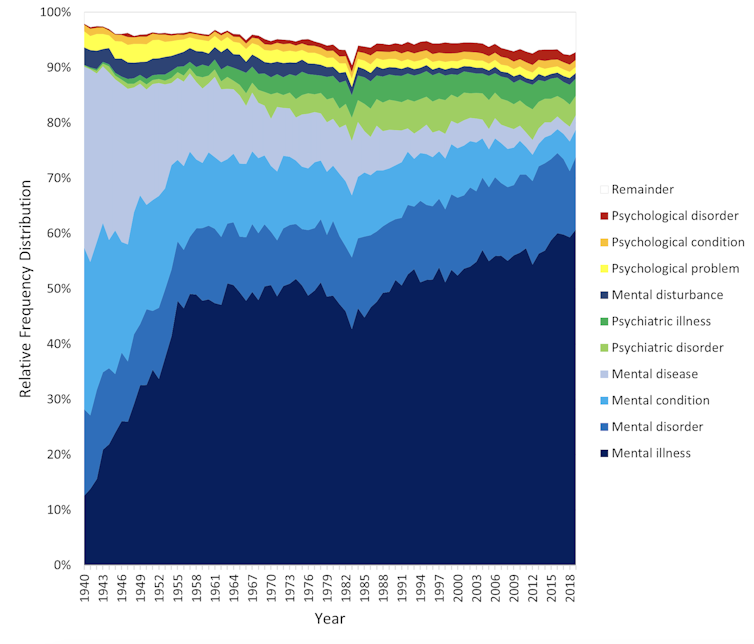
The figure presents the relative popularity of the top ten terms in the larger data set (Google Books). The 14 least popular terms are combined into the remainder.
Relative popularity of alternative generic terms in the Google Books corpus. Haslam et al., 2024, PLOS Mental Health. Several trends appear. Mental has consistently been the most popular adjective component of the generic terms. Mental health has become more popular in recent years but is still rarely used.
Among nouns, disease has become less widely used while illness has become dominant. Although disorder is the official term in psychiatric classifications, it has not been broadly adopted in public discourse.
Since 1940, mental illness has clearly become the preferred generic term. Although an assortment of alternatives have emerged, it has steadily risen in popularity.
Does it matter?
Our study documents striking shifts in the popularity of generic terms, but do these changes matter? The answer may be: not much.
One study found people think mental disorder, mental illness and mental health problem refer to essentially identical phenomena.
Other studies indicate that labelling a person as having a mental disease, mental disorder, mental health problem, mental illness or psychological disorder makes no difference to people’s attitudes toward them.
We don’t yet know if there are other implications of using different generic terms, but the evidence to date suggests they are minimal.
The labels we use may not have a big impact on levels of stigma. Pixabay/Pexels Is ‘distress’ any better?
Recently, some writers have promoted distress as an alternative to traditional generic terms. It lacks medical connotations and emphasises the person’s subjective experience rather than whether they fit an official diagnosis.
Distress appears 65 times in the 2022 Victorian Mental Health and Wellbeing Act, usually in the expression “mental illness or psychological distress”. By implication, distress is a broad concept akin to but not synonymous with mental ill health.
But is distress destigmatising, as it was intended to be? Apparently not. According to one study, it was more stigmatising than its alternatives. The term may turn us away from other people’s suffering by amplifying it.
So what should we call it?
Mental illness is easily the most popular generic term and its popularity has been rising. Research indicates different terms have little or no effect on stigma and some terms intended to destigmatise may backfire.
We suggest that mental illness should be embraced and the proliferation of alternative terms such as mental health problem, which breed confusion, should end.
Critics might argue mental illness imposes a medical frame. Philosopher Zsuzsanna Chappell disagrees. Illness, she argues, refers to subjective first-person experience, not to an objective, third-person pathology, like disease.
Properly understood, the concept of illness centres the individual and their connections. “When I identify my suffering as illness-like,” Chappell writes, “I wish to lay claim to a caring interpersonal relationship.”
As generic terms go, mental illness is a healthy option.
Nick Haslam, Professor of Psychology, The University of Melbourne and Naomi Baes, Researcher – Social Psychology/ Natural Language Processing, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Which Diet? Top Diets Ranked By Experts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A panel of 69 doctors and nutritionists examined the evidence for 38 diets, and scored them in 21 categories (e.g. best for weight loss, best for heart, best against diabetes, etc).
We’ll not keep it a mystery: the Mediterranean diet has been ranked as “best overall” for the 8th year in a row.
The Mediterranean (And Its Close Friends & Relations)
We’ve written before about the Mediterranean diet, here:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← What isn’t it good for?
👆 the above article also delineates what does and doesn’t go in a Mediterranean diet—hint, it’s not just any food from the Mediterranean region!
The Mediterranean diet’s strengths come from various factors including its good plant:animal ratio (leaning heavily on the plants), colorful fruit and veg minimally processed, and the fact that olive oil is the main source of fat:
All About Olive Oil ← pretty much one of the healthiest fats we can consume, if not healthiest all-rounder fat
The Mediterranean diet also won 1st place in various more specific categories, including:
- Best against arthritis (followed by Dr. Weil’s Anti-inflammatory, MIND, DASH)
- Best for mental health (followed by MIND, Flexitarian, DASH)
- Best against diabetes (followed by Flexitarian, DASH, MIND)
- best for liver regeneration (followed by Flexitarian, Vegan, DASH, MIND)
- Best for gut heath (followed by Vegan, DASH, Flexitarian, MIND)
If you’re not familiar with DASH and MIND, there are clues in their full names: Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension and Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay, and as you might well suspect, they are simply tweaked variations of the Mediterranean diet:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean ← DASH and MIND are the heart-healthiest and brain-healthiest versions of the Mediterranean; this article also includes a gut-healthiest version and a most anti-inflammatory version
What aren’t those best for?
The Mediterranean diet scored 1st or 2nd in most of the 21 categories, and usually had the other above-named diets keeping it company in the top few.
When it comes to weight loss, the Mediterranean scored 2nd place and wasn’t flanked by its usual friends and relations; instead in first place was commercial diet WeightWatchers (likely helped a lot by being also a peer support group), and in third place was the Volumetrics diet, which we wrote about here:
Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
And when it comes to rapid weight loss specifically, the Mediterranean didn’t even feature in the top spots at all, because it’s simply not an extreme diet and it prioritizes health over shedding the pounds at any cost. The top in that category were mostly commercial diets:
- Jenny Craig
- Slimfast
- Keto
- Nutrisystem
- WeightWatchers
We’ve not as yet written about any of those commercial diets, but we have written about keto here:
Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat Or Burning Out?
Want to know more?
You can click around, exploring by diet or by health category, here 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Learning to Love Midlife – by Chip Conley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While the book is titled about midlife, it could have said: midlife and beyond.
Some of the benefits discussed in this book really only kick in during one’s 50s, 60s, or 70s, usually. Which, for all but the most optimistic, is generally considered to be stretching beyond what is usually called “midlife”.
However! Chip Conley makes the argument for midlife being anywhere from one’s early 30s to mid-70s, depending on what (and how) we’re doing in life.
He talks about (as the subtitle promises) 12 reasons life gets better with age, and those reasons are grouped into 5 categories, thus:
- Physical life
- Emotional life
- Mental life
- Vocational life
- Spiritual life
It may surprise some readers that there are physical benefits that come with aging, but we do get two chapters in that category.
The writing style is very casual, yet with references to science throughout, and a bibliography for such.
Bottom line: if you’d like to make sure you’re making the most of your midlife and beyond, this a book that offers a lot of guidance on doing so!
Click here to check out Learning to Love Midlife, and age in style!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop Tinnitus, & Improve Your Hearing By 130%
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caveat: this will depend on the cause of your tinnitus, but there’s a quick diagnostic test first, and it’s for the most common kind 🙂
Step by step
To address noise in the ears (tinnitus) and improve hearing, start by identifying whether the issue is treatable. The diagnostic tests are:
- First, turn your head to the side, tilt it forward and backward, and observe changes in the noise. If the intensity changes, then the noise can be managed.
- Additionally, open and close your mouth, clenching and unclenching your teeth, and note any variations; this is about muscular tension affecting hearing.
- Finally, tilt your head downward—if the noise increases, it may mean it is a venous outflow disorder—there’s a fix for this, too.
Effective exercises focus on releasing tension and improving blood flow:
- Begin with the neck’s scalene muscles, located behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- Massage these areas by moving your hands up and down and varying head positions slightly forward and backward.
- Repeat on both sides to enhance blood circulation and reduce auditory interference. Next, target the chewing muscles.
- Massage painful areas of the jaw and temporalis muscle in circular motions, working along and across the muscle fibers.
- Divide the temporalis muscle into sections and address each thoroughly to relieve tension and improve hearing.
- Mobilize the outer auditory passage by gently pulling the ear in all directions—starting with the earlobe, middle part, and upper ear.
- Focus on the cartilage above the lobe, moving it up and down to restore mobility and improve blood flow.
These exercises should fix the most common kind of tinnitus, and improve hearing—you’ll know quickly whether it works for you or not. Regular practice is required for sustained results, though.
For more on all this, plus visual demonstrations (e.g. how to find that temporalis muscle, etc), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Tinnitus: Quieting The Unwanted Orchestra In Your Ears ← our main feature on this topic, with more things to try if this didn’t help!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: