Healthy Kids, Happy Kids – by Dr. Elisa Song
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you have young children or perhaps grandchildren, you probably care deeply about those children and their wellbeing, but there can often be a lot more guesswork than would be ideal, when it comes to ensuring they be and remain healthy.
Nevertheless, a lot of common treatments for children are based (whether parents know it or not—and often they dont) on what is most convenient for the parent, not necessarily what is best for the child. Dr. Song looks to correct that.
Rather than dosing kids with acetaminophen or even antibiotics, assuming eczema can be best fixed with a topical cream (treating the symptom rather than the cause, much?), and that some things like asthma “just are”, and “that’s unfortunate”, Dr. Song takes us on a tour of pediatric health, centered around the gut.
Why the gut? Well, it’s pretty central to us as adults, and it’s the same for kids, except one difference: their gut microbiome is changing even more quickly than ours (along with the rest of their body), and as such, is even more susceptible to little nudges for better or for worse, having a big impact in either direction. So, might as well make it a good one!
After an explanatory overview, most of the book is given over to recognizing and correcting what things can go wrong, including the top 25 acute childhood conditions, and the most critical chronic ones, and how to keep things on-track as a team (the child is part of the team! An important part!).
The style of the book is very direct and instructional; easy to understand throughout. It’s a lot like being in a room with a very competent pediatrician who knows her stuff and explains it well, thus neither patronizing nor mystifying.
Bottom line: if there are kids in your life, be they yours or your grandkids or someone else, this is a fine book for giving them the best foundational health.
Click here to check out Healthy Kids, Happy Kids, and take care of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eye Exercises That Measurably Improve Your Vision
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our eyesight, like most of the rest of our body’s functions, will decline if not adequately maintained. Modern lifestyles see most of us indoors for most of the day (which means a reduced maximum focal length) and often looking at screens (even further reduced focal length), which means that part of our eyes responsible for focus will tend to atrophy and wither. And if we want to see something better, we adjust the settings instead of adjusting our eyes. However, it is perfectly possible to recover our clear youthful vision:
See the results for yourself (and see them clearly!)
The exercises that gave him the results he showed between the two tests, are:
- Blink for 30 seconds
- Focus on something in front and (keeping your focus on that stationary point) move your head left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
- Take a break and blink for 30 seconds
- Keep your head still while you move your eyes left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
- Focus on something in front while you move move your head left & right, upwards & downwards, and diagonally
This should temporarily improve your vision immediately, because of what has been going on in the capillaries in and around your eyes, but sustained results require sustained (i.e. daily) practice. This is because the vasculature is only part of the mechanism; it’s also a matter of improving the muscles responsible for focusing the eyes—and like any muscles, it’s not a case of “do it once and enjoy the results forever”. So, even just 2–3 minutes each day is recommended.
For more on all of this plus a visual demonstration, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Are Your Glasses Making Your Eyesight Worse?
or, if you are very serious about having excellent vision for life:
Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider ← this one’s a book, and a very good one at that
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Dopa-Bean
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mucuna pruriens, also called the “magic velvet bean”, is an established herbal drug used for the management of male infertility, nervous disorders, and also as an aphrodisiac:
The Magic Velvet Bean of Mucuna pruriens
How it works is more interesting than that, though.
It’s about the dopamine
M. pruriens contains levodopa (L-dopa). That’s right, the same as the dopaminergic medication most often prescribed for Parkinson’s disease. Furthermore, it might even be better than synthetic L-dopa, because:
❝M. pruriens seed extract demonstrated acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, while synthetic L-dopa enhanced the activity of the enzyme. It can be concluded that the administration of M. pruriens seed might be effective in protecting the brain against neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.
M. pruriens seed extract containing L-dopa has shown less acetylcholinesterase activity stimulation compared with L-dopa, suggesting that the extract might have a superior benefit for use in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.❞
~ Dr. Narisa Kamkaen et al.
Indeed, it has been tested specifically in (human!) Parkinson’s disease patients, which RCT found:
❝The rapid onset of action and longer on time without concomitant increase in dyskinesias on mucuna seed powder formulation suggest that this natural source of l-dopa might possess advantages over conventional l-dopa preparations in the long term management of Parkinson’s disease❞
~ Dr. Regina Katzenschlager et al.
Read more: Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind clinical and pharmacological study
Beyond Parkinson’s disease
M. pruriens has also been tested and found beneficial in cases of disease other than Parkinson’s, thus:
Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: recent advancement and future prospective
…but the science is less well-established for things not generally considered related to dopamine, such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiometabolic disorders.
Note, however, that the science for it being neuroprotective is rather stronger.
Against depression
Depression can have many causes, and (especially on a neurological level) diverse presentations. As such, sometimes what works for one person’s depression won’t touch another person’s, because the disease and treatment are about completely different neurotransmitter dysregulations. So, if a person’s depression is due to a shortage of serotonin, for example, then perking up the dopamine won’t help much, and vice versa. See also:
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
When it comes to M. pruriens and antidepressant activity, then predictably it will be more likely to help if your depression is due to too little dopamine. Note that this means that even if your depression is dopamine-based, but the problem is with your dopamine receptors and not the actual levels of dopamine, then this may not help so much, depending on what else you have going on in there.
The science for M. pruriens and depression is young, and we only found non-human animal studies so far, for example:
In summary
It’s good against Parkinson’s in particular and is good against neurodegeneration in general.
It may be good against depression, depending on the kind of depression you have.
Is it safe?
That’s a great question! And the answer is: it depends. For most people, in moderation, it should be fine (but, see our usual legal/medical disclaimer). Definitely don’t take it if you have bipolar disorder or any kind of schizoid/psychotic disorder; it is likely to trigger a manic/psychotic episode if you do.
For more on this, we discussed it (pertaining to L-dopa in general, not M. pruriens specifically) at greater length here:
An Accessible New Development Against Alzheimer’s ← scroll down to the heading that reads “Is there a catch?”
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What Your Doctor Wants You to Know to Crush Medical Debt – by Dr. Virgie Ellington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: this one’s really only of relevance to people living in the US. That’s most of our readership, but if it’s not you, then apologies, this one won’t be of interest.
For the US Americans, though, Dr. Ellington starts strong with “you got a bill—now get the right bill”, and then gives a step-by-step process for finding the mistakes in your medical bills, fixing them, dealing with insurers who do not want to live up to their part of the bargain, and how to minimize what you need to pay, when you actually arrive at your final bill.
The biggest strength of this book is the wealth of insider knowledge (the author has worked as a primary care physician as well as as a health insurance executive), and while this information won’t stay current forever, its relatively recent publication date (2022) means that little has changed since then, and once you’re up to speed with how things are now, it’ll be easy to roll with whatever changes may come in the future.
Bottom line: if you’re living in the US and would like to not be ripped off as badly as possible when it comes to healthcare costs, this book is a very small, very powerful, investment.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
7 things you can do if you think you sweat too much
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sweating is our body’s way of cooling down, a bit like an internal air conditioner.
When our core temperature rises (because it’s hot outside, or you’re exercising), sweat glands all over our skin release a watery fluid. As that fluid evaporates, it takes heat with it, keeping us from overheating.
But sweating can vary from person to person. Some people might just get a little dewy under the arms, others feel like they could fill a swimming pool (maybe not that dramatic, but you get the idea).
So what’s a normal amount of sweat? And what’s too much?
ERIK Miheyeu/Shutterstock Why do some people sweat more than others?
How much you sweat depends on a number of factors including:
- your age (young kids generally sweat less than adults)
- your sex (men tend to sweat more than women)
- how active you are.
The average person sweats at the rate of 300 millilitres per hour (at 30°C and about 40% humidity). But as you can’t go around measuring the volume of your own sweat (or weighing it), doctors use another measure to gauge the impact of sweating.
They ask whether sweating interferes with your daily life. Maybe you stop wearing certain clothes because of the sweat stains, or feel embarrassed so don’t go to social events or work.
If so, this is a medical condition called hyperhidrosis, which affects millions of people worldwide.
People with this condition most commonly report problematic armpit sweating, as you’d expect. But sweaty hands, feet, scalp and groin can also be an issue.
Hyperhidrosis can be a symptom of another medical condition, such as an overactive thyroid, fever or menopause.
But hyperhidrosis can have no obvious cause, and the reasons behind this so-called primary hyperhidrosis are a bit of a mystery. People have normal numbers of sweat glands but researchers think they simply over-produce sweat after triggers such as stress, heat, exercise, tobacco, alcohol and hot spices. There may also be a genetic link.
OK, I sweat a lot. What can I do?
1. Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants, particularly ones with aluminium, are your first line of defence and are formulated to reduce sweating. Deodorants only stop body odour.
Aluminum chloride hexahydrate, aluminium chloride or the weaker aluminum zirconium tetrachlorohydrex glycinate react with proteins in the sweat glands, forming a plug. This plug temporarily blocks the sweat ducts, reducing the amount of sweat reaching the skin’s surface.
These products can contain up to 25% aluminium. The higher the percentage the better these products work, but the more they irritate the skin.
Make sure you’re buying antiperspirant and not deodorant. Okrasiuk/Shutterstock 2. Beat the heat
This might seem obvious, but staying cool can make a big difference. That’s because you have less heat to lose, so the body makes less sweat.
Avoid super-hot, long showers (you will have more heat to loose), wear loose-fitting clothes made from breathable fabrics such as cotton (this allows any sweat you do produce to evaporate more readily), and carry a little hand fan to help your sweat evaporate.
When exercising try ice bandanas (ice wrapped in a scarf or cloth, then applied to the body) or wet towels. You can wear these around the neck, head, or wrists to reduce your body temperature.
Try also to modify the time or place you exercise; try to find cool shade or air-conditioned areas when possible.
If you have tried these first two steps and your sweating is still affecting your life, talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out the best way to manage it.
3. Medication
Some medications can help regulate your sweating. Unfortunately some can also give you side effects such as a dry mouth, blurred vision, stomach pain or constipation. So talk to your doctor about what’s best for you.
Your GP may also refer you to a dermatologist – a doctor like myself who specialises in skin conditions – who might recommend different treatments, including some of the following.
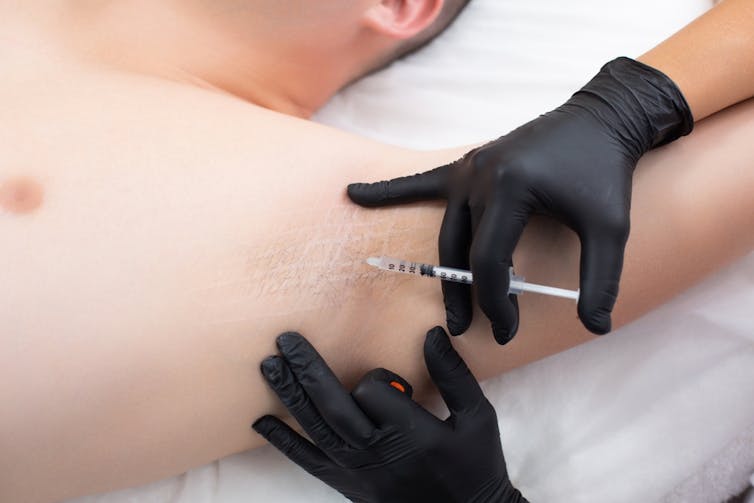
4. Botulinum toxin injections
Botulinum toxin injections are not just used for cosmetic reasons. They have many applications in medicine, including blocking the nerves that control the sweat glands. They do this for many months.
A dermatologist usually gives the injections. But they’re only subsidised by Medicare in Australia for the armpits and if you have primary hyperhidrosis that hasn’t been controlled by the strongest antiperspirants. These injections are given up to three times a year. It is not subsidised for other conditions, such as an overactive thyroid or for other areas such as the face or hands.
If you don’t qualify, you can have these injections privately, but it will cost you hundreds of dollars per treatment, which can last up to six months.
Injections are available on Medicare in some cases. Satyrenko/Shutterstock 5. Iontophoresis
This involves using a device that passes a weak electrical current through water to the skin to reducing sweating in the hands, feet or armpits. Scientists aren’t sure exactly how it works.
But this is the only way to control sweating of the hands and feet that does not require drugs, surgery or botulinum toxin injections.
This treatment is not subsidised by Medicare and not all dermatologists provide it. However, you can buy and use your own device, which tends to be cheaper than accessing it privately. You can ask your dermatologist if this is the right option for you.
6. Surgery
There is a procedure to cut certain nerves to the hands that stop them sweating. This is highly effective but can cause sweating to occur elsewhere.
There are also other surgical options, which you can discuss with your doctor.
7. Microwave therapy
This is a newer treatment that zaps your sweat glands to destroy them so they can’t work any more. It’s not super common yet, and it is quite painful. It’s available privately in a few centres.
Michael Freeman, Associate Professor of Dermatology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How the HHS impacts your community’s health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is responsible for programs that impact every community in the country. But most Americans aren’t aware of the department’s scope.
“Most of the power in the agency, most of the administrative authority comes from laws that Congress has passed,” former HHS Secretary Kathleen Sebelius told NPR. She added that the HHS secretary “could redefine terms that had a huge impact on people. And that could be done all administratively, not by going back to Congress.”
HHS is comprised of 13 agencies, all of which play an important role in promoting the health of all Americans. These are just some of the ways that HHS affects people’s lives and health.
Vaccines
One of HHS’s most salient roles is developing, approving, and monitoring vaccines after they are on the market. The National Institutes of Health funds and conducts research to develop new vaccines and improve existing ones. The NIH’s Vaccine Research Center spearheads research to develop vaccines against deadly diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis.
The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for overseeing clinical trials that test product safety and effectiveness, approving new vaccines, and monitoring the safety of all vaccines before and after approval. In conjunction with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA also manages the national surveillance systems that record and flag potential vaccine side effects.
In addition to safety monitoring, the CDC conducts research on vaccine safety and effectiveness and issues vaccination guidance. The agency’s recommended immunization schedule guides school and child care vaccination requirements and health care provider recommendations nationwide.
Although the CDC does not have the authority over school and childcare vaccination requirements at the state level, changes to the agency’s recommendations could have wide-ranging impacts.
“If this recommendation changes, there’s downstream effects, like insurance companies could stop covering them. And adding cost could easily deter uptake,” epidemiologist and creator of the Your Local Epidemiologist newsletter Katelyn Jetelina told PBS.
However, CDC vaccine recommendations are just that: recommendations. The agency cannot dictate, for example, vaccine requirements for school enrollment. Those standards are set at the state level, with the possible exception during a national public health emergency.
Drug safety
The FDA oversees all clinical trials in the United States. Every prescription drug and many medical products undergo a rigorous, closely regulated, multistep trial to test their safety and effectiveness. At the end of that process, the FDA determines whether a drug meets its standards for approval. Without FDA approval, a drug cannot be sold in the U.S.
Like with vaccines, the FDA monitors potential safety concerns related to over-the-counter and prescription medications, medical devices, and other products the agency regulates. Health care providers, FDA-regulated companies, and patients can report suspected safety issues to the agency, which evaluates each report for further investigation.
The FDA also alerts the public to safety concerns related to medical products by releasing safety notices, adding warning labels, and issuing drug recalls.
Pandemic and public health emergency response
Several HHS agencies are tasked with preventing, preparing for, and responding to disease outbreaks. This responsibility includes tracking potentially dangerous infectious diseases in the U.S. and globally, developing pandemic response strategies, and issuing guidance to contain ongoing outbreaks.
Both the CDC and FDA inform the public about public health concerns, including pandemics. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response works with communities, medical facilities, local and state governments, and industry partners to enhance responses to disasters and public health emergencies.
The CDC also tracks pathogens like the flu, norovirus, and sexually transmitted infections to better understand where diseases are spreading, how they are evolving, and how best to prepare for outbreaks.
In the event of a public health emergency, the CDC may issue guidance on how to stay safe and minimize health impacts. For example, in January, the agency released tips on how to protect against smoke during the wildfires affecting southern California and how to avoid frostbite and hypothermia, as extreme cold weather affected much of the country.
The FDA can issue emergency use authorizations, which allow the use of “unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical products … to diagnose, treat, or prevent serious or life-threatening diseases … when certain criteria are met” during public health emergencies. These authorizations help ensure that the standard FDA approval process is not a barrier to the public receiving lifesaving medical products, such as authorizing specific vaccines during a pandemic.
Food and water safety
The FDA, along with the U.S. Department of Agriculture, plays an important role in regulating food safety. The agency approves and monitors the safety of food additives, like sweeteners, dyes, and preservatives. It also regulates how food is prepared, packaged, and stored, including conducting inspections of food facilities and farms.
FDA food safety testing detects dangerous foodborne illnesses like salmonella and E. coli. For example, in late December 2024, the FDA began testing raw (unpasteurized) milk products for bird flu contamination. The CDC investigates outbreaks of foodborne illnesses and, along with the FDA and USDA, provides the public with information about food safety.
The FDA also regulates most food labels, including nutrition facts, ingredient lists, and health claims on food packaging. In January, the agency proposed new front-of-package nutrition labels that highlight sugar, fat, and sodium content in packaged food products.
HHS and the USDA are responsible for updating the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which are updated every five years. These guidelines are the basis of all federal food assistance programs for children, older adults, and low-income families.
HHS sets the guidelines for the maximum fluoride level in drinking water and periodically makes recommendations about fluoride levels. However, the department has no authority to require or ban fluoridation, which is regulated at the state and local level. U.S. cities began adding fluoride to drinking water in the 1940s to improve dental health and reduce cavities by 25 percent.
Health care access
The HHS secretary regulates the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, which provides health insurance to adults 65 and older, people with disabilities, low-income families, and eligible children through the Children’s Health Insurance Program. Together, Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP insure over 145 million Americans, or roughly 42 percent of the U.S. population. Changes to either of these programs could impact health care access and quality for millions of Americans.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Prevent Dementia – by Dr. Richard Restak
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written about this topic here, we know. But there’s a lot more we can do to be on guard against, and pre-emptively strengthen ourselves against, dementia.
The author, a neurologist, takes us on a detailed exploration of dementia in general, with a strong focus on Alzheimer’s in particular, as that accounts for more than half of all dementia cases.
But what if you can’t avoid it? It could be that with the wrong genes and some other factor(s) outside of your control, it will get you if something else doesn’t get you first.
Rather than scaremongering, Dr. Restak tackles this head-on too, and discusses how symptoms can be managed, to make the illness less anxiety-inducing, and look to maintain quality of life as much as possible.
The style of the book is… it reads a lot like an essay compilation. Good essays, then organized and arranged in a sensible order for reading, but distinct self-contained pieces. There are ten or eleven chapters (depending on how we count them), each divided into few or many sections. All this makes for:
- A very “read a bit now and a bit later and a bit the next day” book, if you like
- A feeling of a very quick pace, if you prefer to sit down and read it in one go
Either way, it’s a very informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand the many-headed beast that is dementia, this book gives a far more comprehensive overview than we could here, and also explains the prophylactic interventions available.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: