Older adults need another COVID-19 vaccine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
- Updated COVID-19 vaccines are effective at protecting against severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
- The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19.
Last week, the CDC said people 65 and older should receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring. The recommendation also applies to immunocompromised people, who were already eligible for an additional dose.
Older adults made up two-thirds of COVID-19-related hospitalizations between October 2023 and January 2024, so enhancing protection for this group is critical.
The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19, although the contagiousness of COVID-19 has not changed.
Read on to learn more about the CDC’s updated vaccination and isolation recommendations.
Who is eligible for another COVID-19 vaccine this spring?
The CDC recommends that people ages 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine. It’s safe to receive an updated COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, Moderna, or Novavax, regardless of which COVID-19 vaccines you received in the past.
Updated COVID-19 vaccines are available at pharmacies, local clinics, or doctor’s offices. Visit Vaccines.gov to find an appointment near you.
Under- and uninsured adults can get the updated COVID-19 vaccine for free through the CDC’s Bridge Access Program. If you’re over 60 and unable to leave your home, call the Aging Network at 1-800-677-1116 to learn about free at-home vaccination options.
What are the benefits of staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines?
Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines prevents severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
Additionally, the CDC says staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines is a safer and more reliable way to build protection against COVID-19 than getting sick from COVID-19.
What are the new COVID-19 isolation guidelines?
According to the CDC’s general respiratory virus guidance, people who are sick with COVID-19 or another common respiratory illness, like the flu or RSV, should isolate until they’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medication and their symptoms improve.
After that, the CDC recommends taking additional precautions for the next five days: wearing a well-fitting mask, limiting close contact with others, and improving ventilation in your home if you live with others.
If you’re sick with COVID-19, you can infect others for five to 12 days, or longer. Moderately or severely immunocompromised patients may remain infectious beyond 20 days.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Guava vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing guava to pineapple, we picked the guava.
Why?
Pineapple is great, but guava just beats it in most ways:
In terms of macros, guava has nearly 4x the fiber and nearly 5x the protein, for the same carbs, giving it the notably lower glycemic index. An easy win for guava in this category.
In the category of vitamins, guava has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pineapple has marginally more vitamin B1. Another clear win for guava.
When it comes to minerals, guava has more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pineapple has more iron and manganese. One more win for guava.
One big thing in pineapple’s favor is that it contains bromelain, which is an enzyme* found in pineapple (and only in pineapple), that has many very healthful properties, some of them unique to bromelain (and thus: unique to pineapple)
*actually a combination of enzymes, but most often referred to collectively in the singular. But when you do see it referred to as “they”, that’s what that means.
However cool that is, we think it unfair to weight it against guava winning in every other category, so we still say guava gets the overall win.
Of course, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Let’s Get Fruity: Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Vaping: A Lot Of Hot Air?
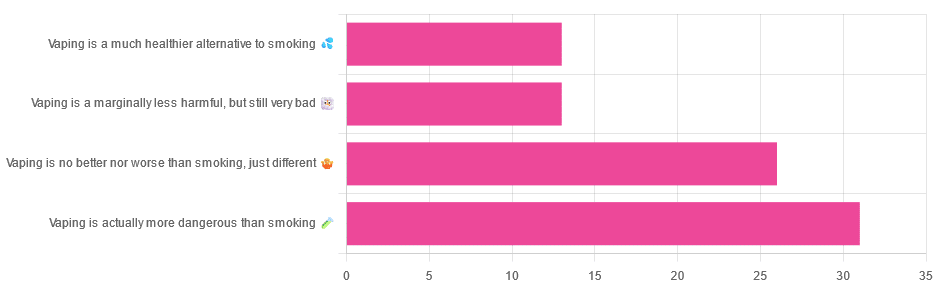
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) opinions on vaping, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over a third of respondents said it’s actually more dangerous than smoking
- A little under a third of respondents said it’s no better nor worse, just different
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s marginally less harmful, but still very bad
- A little over 10% of respondents said it’s a much healthier alternative to smoking
So what does the science say?
Vaping is basically just steam inhalation, plus the active ingredient of your choice (e.g. nicotine, CBD, THC, etc): True or False?
False! There really are a lot of other chemicals in there.
And “chemicals” per se does not necessarily mean evil green glowing substances that a comicbook villain would market, but there are some unpleasantries in there too:
- Potential harmful health effects of inhaling nicotine-free shisha-pen vapor: a chemical risk assessment of the main components propylene glycol and glycerol
- Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses Induced by Exposure to Commonly Used e-Cigarette Flavoring Chemicals and Flavored e-Liquids without Nicotine
So, the substrate itself can cause irritation, and flavorings (with cinnamaldehyde, the cinnamon flavoring, being one of the worst) can really mess with our body’s inflammatory and oxidative responses.
Vaping can cause “popcorn lung”: True or False?
True and False! Popcorn lung is so-called after it came to attention when workers at a popcorn factory came down with it, due to exposure to diacetyl, a chemical used there.
That chemical was at that time also found in most vapes, but has since been banned in many places, including the US, Canada, the EU and the UK.
Vaping is just as bad as smoking: True or False?
False, per se. In fact, it’s recommended as a means of quitting smoking, by the UK’s famously thrifty NHS, that absolutely does not want people to be sick because that costs money:
Of course, the active ingredients (e.g. nicotine, in the assumed case above) will still be the same, mg for mg, as they are for smoking.
Vaping is causing a health crisis amongst “kids nowadays”: True or False?
True—it just happens to be less serious on a case-by-case basis to the risks of smoking.
However, it is worth noting that the perceived harmlessness of vapes is surely a contributing factor in their widespread use amongst young people—decades after actual smoking (thankfully) went out of fashion.
On the other hand, there’s a flipside to this:
Flavored vape restrictions lead to higher cigarette sales
So, it may indeed be the case of “the lesser of two evils”.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth science-ful exploration than we have room for here…
BMJ | Impact of vaping on respiratory health
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Pine Nuts vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to peanuts, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
An argument could be made for either, honestly, as it depends on what we prioritize the most. These are both very high-calorie foods, and/but are far from empty calories, as they both contain main nutrients. Obviously, if you are allergic to nuts, this one is just not a comparison for you, sorry.
Looking at the macros first, peanuts are higher in protein, carbs, and fiber, while pine nuts are higher in fats—though the fats are healthy, being mostly polyunsaturated, with about a third of the total fats monounsaturated, and a low amount of saturated fat (peanuts have nearly 2x the saturated fat). On balance, we’ll call the macros category a moderate win for peanuts, though.
In terms of vitamins, peanuts have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, and B9, while pine nuts have more of vitamins A, B2, C, E, K, and choline. All in all, a marginal win for pine nuts.
In the category of minerals, peanuts have more calcium and selenium, while pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. An easy win for pine nuts, even before we take into account that peanuts have nearly 10x as much sodium. And yes, we are talking about the raw nuts, not nuts that have been roasted and salted.
Adding up the categories gives a win for pine nuts—but if you have certain particular priorities, you might still prefer peanuts for the areas in which peanuts are stronger.
Of course, the best solution is to enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Small Changes For A Healthier Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
I am interested in what I can substitute for ham in bean soup?
Well, that depends on what the ham was like! You can certainly buy ready-made vegan lardons (i.e. small bacon/ham bits, often in tiny cubes or similar) in any reasonably-sized supermarket. Being processed, they’re not amazing for the health, but are still an improvement on pork.
Alternatively, you can make your own seitan! Again, seitan is really not a health food, but again, it’s still relatively less bad than pork (unless you are allergic to gluten, in which case, definitely skip this one).
Alternatively alternatively, in a soup that already contains beans (so the protein element is already covered), you could just skip the ham as an added ingredient, and instead bring the extra flavor by means of a little salt, a little yeast extract (if you don’t like yeast extract, don’t worry, it won’t taste like it if you just use a teaspoon in a big pot, or half a teaspoon in a smaller pot), and a little smoked paprika. If you want to go healthier, you can swap out the salt for MSG, which enhances flavor in a similar fashion while containing less sodium.
Wondering about the health aspects of MSG? Check out our main feature on this, from last month:
I thoroughly enjoy your daily delivery. I’d love to see one for teens too!
That’s great to hear! The average age of our subscribers is generally rather older, but it’s good to know there’s an interest in topics for younger people. We’ll bear that in mind, and see what we can do to cater to that without alienating our older readers!
That said: it’s never too soon to be learning about stuff that affects us when we’re older—there are lifestyle factors at 20 that affect Alzheimer’s risk at 60, for example (e.g. drinking—excessive drinking at 20* is correlated to higher Alzheimer’s risk at 60).
*This one may be less of an issue for our US readers, since the US doesn’t have nearly as much of a culture of drinking under 21 as some places. Compare for example with general European practices of drinking moderately from the mid-teens, or the (happily, diminishing—but historically notable) British practice of drinking heavily from the mid-teens.
How much turmeric should I take each day?
Dr. Michael Greger’s research (of “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” and “How Not To Die” fame) recommends getting at least ¼ tsp turmeric per day
Remember to take it with black pepper though, for a 2000% absorption bonus!
A great way to get it, if you don’t want to take capsules and don’t want to eat spicy food every day, is to throw a teaspoon of turmeric in when making a pot of (we recommend wholegrain!) rice. Turmeric is very water-soluble, so it’ll be transferred into the rice easily during cooking. It’ll make the rice a nice golden yellow color, and/but won’t noticeably change the taste.
Again remember to throw in some black pepper, and if you really want to boost the nutritional content,some chia seeds are a great addition too (they’ll get cooked with the rice and so it won’t be like eating seeds later, but the nutrients will be there in the rice dish).
You can do the same with par-boiled potatoes or other root vegetables, but because cooking those has water to be thrown away at the end (unlike rice), you’ll lose some turmeric in the water.
Request: more people need to be aware of suicidal tendencies and what they can do to ward them off
That’s certainly a very important topic! We’ll cover that properly in one of our Psychology Sunday editions. In the meantime, we’ll mention a previous special that we did, that was mostly about handling depression (in oneself or a loved one), and obviously there’s a degree of crossover:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Unnoticed Environmental Mold Harming Your Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Environmental mold can be a lot more than just the famously toxic black mold that sometimes makes the headlines, and many kinds you might not notice, but it can colonizes your sinuses and gut just the same:
Breaking the mold
Around 25% of homes in North America are estimated to have mold, though the actual number is likely to be higher, affecting both older and new homes. For that matter, mold can grow in unexpected areas, like inside air conditioning units, even in dry regions.
If mold just sat where it is minding its own business, it might not be so bad, but instead they release their spores, which are de facto airborne mycotoxins, which can colonize places like the sinuses or gut, causing significant health issues.
Not everyone in the same household is affected the same way by mold due to genetic differences and varying pre-existing health conditions. But as a general rule of thumb, mold inflames the brain, nerves, gut, and skin, and can negatively impact the vagal nerve, which is linked to the gut-brain connection. Mycotoxins also damage mitochondria, leading to symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and cognitive issues. To complicate matters further, mold illness can mimic other conditions like anxiety, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, IBS, and more, making it difficult to diagnose.
Testing is possible, though they all have limitations, e.g:
- Home testing: testing the home for mold spores and mycotoxins is crucial for effective treatment; professional mold remediation companies are a good idea (to do a thorough job of cleaning, without also breathing in half the mold while cleaning it).
- Mold allergy testing: mold allergy testing (IgE testing or skin tests) is often used, but it doesn’t diagnose mold-related illnesses linked to severe symptoms like fatigue or neurodegeneration.
- Serum antibody testing: tests for immune reactions (IgG) to mycotoxins may not always show positive results if the immune system is weakened by long-term exposure.
- Urine mycotoxin testing: urine tests can detect mycotoxins in the body, though are likely to be more expensive, being probably not covered by public health in Canada or insurance in the US.
- Organic acid testing: this urine test can indicate mold colonization in areas like the sinuses or gut. Again, cost/availability may vary, though.
For more information on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Curcumin (Turmeric) is worth its weight in gold
Not financially! But, this inexpensive golden spice has an impressive list of well-studied health benefits, for something so freely available in any supermarket, and there’s a reason it gets a place in “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen”, right up there with things like “leafy greens” and “berries” when it comes to superfoods.
Let’s do a quick run-down:
- It fights inflammation, and thus helps fight many diseases where inflammation is a factor (ranging from atherosclerosis to arthritis to Alzheimer’s and more)
- It has powerful antioxidant effects too
- It boosts brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) and thus improves memory and attention
- It helps protect against heart disease…
- …and can give a 65% decreased risk of experiencing a heart attack
- It can help prevent cancer, and reduce cancerous lesions by 40%
- It’s also good against depression
- It even slows aging
In short, it’s—like we said—worth its weight in gold.
Quick advice though before we move on…
If you take curcumin with black pepper, it allows your body to use the curcumin around 2,000% better. This goes whether you’re cooking with both, or take them as a supplement (they’re commonly sold as a combo-capsule for this reason).
Want to get some?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: