A Deeper Dive Into Seaweed
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We wrote briefly about nori yesterday, when we compared it with well-known superfood spirulina. In nutritional terms, it blew spirulina out of the water:
Spirulina vs Nori – Which Is Healthier?
We also previously touched on it here:
21% Stronger Bones in a Year at 62? Yes, It’s Possible (No Calcium Supplements Needed!) ← nori was an important part of the diet enjoyed here
What is nori?
Nori is a seaweed, but that can mean lots of different things. In nori’s case, it’s an aggregate of several kinds of red algae that clump together in the sea.
When dried and/or toasted (which processes improve* the nutritional value rather than diminishing it, by the way), it looks dark green or dark purple to black in color.
*Effects of pan- and air fryer-roasting on volatile and umami compounds and antioxidant activity of dried laver (Porphyra dentata) ← this is nori, by another name
If you enjoy sushi, nori is the dark flat sheety stuff that other things are often wrapped in.
The plant that has animal nutrients
As established in the head-to-head we linked above, nori is a nutritional powerhouse. But not only is it very full of the perhaps-expected vitamins and minerals, it also contains:
Omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA, which plants do not normally have (plants usually have just ALA, which the body can convert into other forms including EPA). While ALA is versatile, having EPA in food saves the body the job of converting it, and thus makes it more readily bioavailable. For more on the benefits of this, see:
What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
Iodine, which land plants don’t generally have, but seaweed usually does. However, nori contains less iodine than other kinds of seaweed, which is (counterintuitively) good, since other kinds of seaweed often contain megadoses that go too far the other way and can cause different health problems.
- Recommended daily amount of iodine: 150µg ← note that’s micrograms, not milligrams
- One 10g serving of dried nori contains: 232µg ← this is good
- Tolerable daily upper limit of iodine: 1,100µg (i.e: 1.1mg)
- One 10g serving of dried kombu (kelp) contains: 13,270µg (i.e: 13.3mg) ← this is far too much; not good!
So: a portion of nori puts us into the healthiest spot of the range, whereas a portion of another example seaweed would put us nearly 13x over the tolerable upper limit.
For why this matters, see:
- 8 Signs Of Iodine Deficiency You Might Not Expect
- Foods For Managing Hypothyroidism (incl. Hashimoto’s)
- Eat To Beat Hyperthyroidism!
As you might note from the mentions of both hypo- and hyperthyroidism, (which are exacerbated by too little and too much iodine, respectively) hitting the iodine sweet spot is important, and nori is a great way to do that.
Vitamin B12, again not usually found in plants (most vegans supplement, often with nutritional yeast, which is technically neither an animal nor a plant). However, nori scores even higher:
Vitamin B12-Containing Plant Food Sources for Vegetarians
Beyond nutrients
Nori is also one of the few foods that actually live up the principle of a “detox diet”, as it can help remove toxins such as dioxins:
Detox diets for toxin elimination and weight management: a critical review of the evidence
It’s also been…
❝revealed to have anti-aging, anti-cancer, anti-coagulant, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-Alzheimer and anti-tuberculose activities.❞
~ Dr. Şükran Çakir Arica et al.
Read: A study on the rich compounds and potential benefits of algae: A review
(for this to make sense you will need to remember that nori is, as we mentioned, an aggregate of diverse red algae species; in that paper, you can scroll down to Table 1, and see which species has which qualities. Anything whose name starts with “Porphyra” or “Porphridum” is found in nori)
Is it safe?
Usually! There are two potential safety issues:
- Seaweed can, while it’s busy absorbing valuable minerals from the sea, also absorb heavy metals if there are such pollutants in the region. For this reason, it is good to buy a product with trusted certifications, such that it will have been tested for such along the way.
- Seaweed can, while it’s busy absorbing things plants don’t usually have from the sea, also absorb allergens from almost-equally-small crustaceans. So if you have a seafood allergy, seaweed could potentially trigger that.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What’s the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Changes in thinking and memory as we age can occur for a variety of reasons. These changes are not always cause for concern. But when they begin to disrupt daily life, it could indicate the first signs of dementia.
Another term that can crop up when we’re talking about dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, or Alzheimer’s for short.
So what’s the difference?
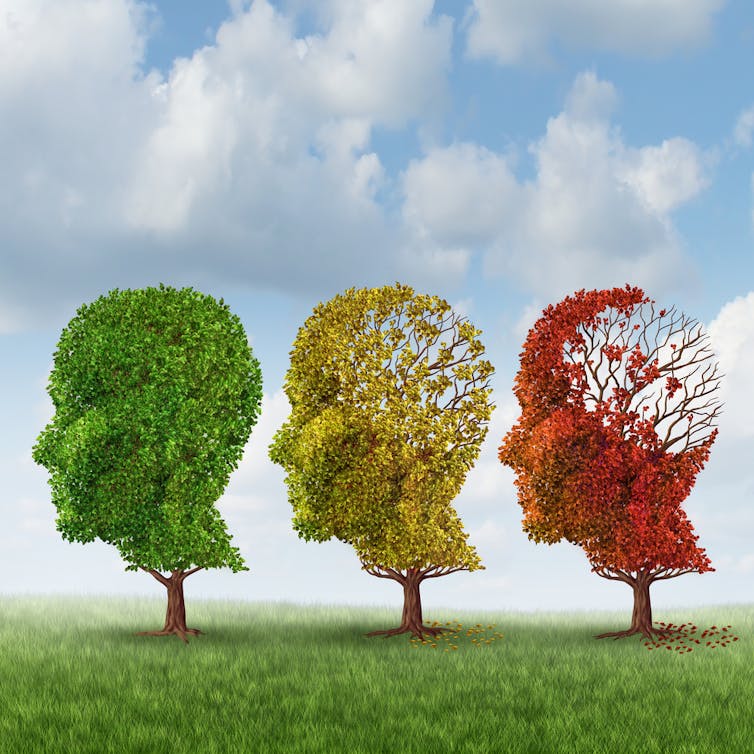
Lightspring/Shutterstock What is dementia?
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of syndromes that result in changes in memory, thinking and/or behaviour due to degeneration in the brain.
To meet the criteria for dementia these changes must be sufficiently pronounced to interfere with usual activities and are present in at least two different aspects of thinking or memory.
For example, someone might have trouble remembering to pay bills and become lost in previously familiar areas.
It’s less-well known that dementia can also occur in children. This is due to progressive brain damage associated with more than 100 rare genetic disorders. This can result in similar cognitive changes as we see in adults.
So what’s Alzheimer’s then?
Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases.
So it’s not surprising many people use the terms dementia and Alzheimer’s interchangeably.
Changes in memory are the most common sign of Alzheimer’s and it’s what the public most often associates with it. For instance, someone with Alzheimer’s may have trouble recalling recent events or keeping track of what day or month it is.
People with dementia may have trouble keeping track of dates. Daisy Daisy/Shutterstock We still don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s. However, we do know it is associated with a build-up in the brain of two types of protein called amyloid-β and tau.
While we all have some amyloid-β, when too much builds up in the brain it clumps together, forming plaques in the spaces between cells. These plaques cause damage (inflammation) to surrounding brain cells and leads to disruption in tau. Tau forms part of the structure of brain cells but in Alzheimer’s tau proteins become “tangled”. This is toxic to the cells, causing them to die. A feedback loop is then thought to occur, triggering production of more amyloid-β and more abnormal tau, perpetuating damage to brain cells.
Alzheimer’s can also occur with other forms of dementia, such as vascular dementia. This combination is the most common example of a mixed dementia.
Vascular dementia
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia. This results from disrupted blood flow to the brain.
Because the changes in blood flow can occur throughout the brain, signs of vascular dementia can be more varied than the memory changes typically seen in Alzheimer’s.
For example, vascular dementia may present as general confusion, slowed thinking, or difficulty organising thoughts and actions.
Your risk of vascular dementia is greater if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.
Frontotemporal dementia
Some people may not realise that dementia can also affect behaviour and/or language. We see this in different forms of frontotemporal dementia.
The behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia is the second most common form (after Alzheimer’s disease) of younger onset dementia (dementia in people under 65).
People living with this may have difficulties in interpreting and appropriately responding to social situations. For example, they may make uncharacteristically rude or offensive comments or invade people’s personal space.
Semantic dementia is also a type of frontotemporal dementia and results in difficulty with understanding the meaning of words and naming everyday objects.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies results from dysregulation of a different type of protein known as α-synuclein. We often see this in people with Parkinson’s disease.
So people with this type of dementia may have altered movement, such as a stooped posture, shuffling walk, and changes in handwriting. Other symptoms include changes in alertness, visual hallucinations and significant disruption to sleep.
Do I have dementia and if so, which type?
If you or someone close to you is concerned, the first thing to do is to speak to your GP. They will likely ask you some questions about your medical history and what changes you have noticed.
Sometimes it might not be clear if you have dementia when you first speak to your doctor. They may suggest you watch for changes or they may refer you to a specialist for further tests.
There is no single test to clearly show if you have dementia, or the type of dementia. A diagnosis comes after multiple tests, including brain scans, tests of memory and thinking, and consideration of how these changes impact your daily life.
Not knowing what is happening can be a challenging time so it is important to speak to someone about how you are feeling or to reach out to support services.
Dementia is diverse
As well as the different forms of dementia, everyone experiences dementia in different ways. For example, the speed dementia progresses varies a lot from person to person. Some people will continue to live well with dementia for some time while others may decline more quickly.
There is still significant stigma surrounding dementia. So by learning more about the various types of dementia and understanding differences in how dementia progresses we can all do our part to create a more dementia-friendly community.
The National Dementia Helpline (1800 100 500) provides information and support for people living with dementia and their carers. To learn more about dementia, you can take this free online course.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How To Ease Neck Pain At Home
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Bang is offering exercises to alleviate neck pain, which pain can be a real… Well, if only there were a good phrase for expressing how troublesome pain in that part of the body can be.
To be clear, he’s a doctor of chiropractic, not a medical doctor, but his advice has clearly been helping people alleviate pain, so without further ado, he advises the following things:
- Taking the head and neck slowly and carefully through the full range of motion available
- Contracting the neck muscles while repeating the above exercise, three times each way
- Backing off a little if it hurts at any point, but noting where the limits lie
- Repeating again the range of motion exercise, this time adding gentle resistance
- Holding each end of this for twenty seconds before releasing and doing the other side, three times each way
- Finally, stabilizing the head centrally and pushing into one’s hands, as an isometric strengthening exercise
He demonstrates each part clearly in this short (5:58) video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to know more about chiropractic?
You might like our previous main feature:
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One
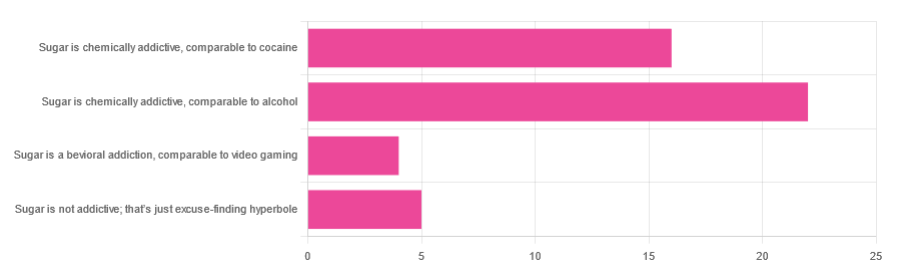
LumpMechanism Of Addiction Or Two?In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you to what extent, if any, you believe sugar is addictive; we got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “Sugar is chemically addictive, comparable to alcohol”
- About 34% said “Sugar is chemically addictive, comparable to cocaine”
- About 11% said “Sugar is not addictive; that’s just excuse-finding hyperbole”
- About 9% said “Sugar is a behavioral addiction, comparable to video gaming”
So what does the science say?
Sugar is not addictive; that’s just excuse-finding hyperbole: True or False?
False, by broad scientific consensus. As ever, the devil’s in the
detailsdefinitions, but while there is still discussion about how best to categorize the addiction, the scientific consensus as a whole is generally: sugar is addictive.That doesn’t mean scientists* are a hive mind, and so there will be some who disagree, but most papers these days are looking into the “hows” and “whys” and “whats” of sugar addiction, not the “whether”.
*who are also, let us remember, a diverse group including chemists, neurobiologists, psychologists, social psychologists, and others, often collaborating in multidisciplinary teams, each with their own focus of research.
Here’s what the Center of Alcohol and Substance Use Studies has to say, for example:
Sugar Addiction: More Serious Than You Think
Sugar is a chemical addiction, comparable to alcohol: True or False?
True, broadly, with caveats—for this one, the crux lies in “comparable to”, because the neurology of the addiction is similar, even if many aspects of it chemically are not.
In both cases, sugar triggers the release of dopamine while also (albeit for different chemical reasons) having a “downer” effect (sugar triggers the release of opioids as well as dopamine).
Notably, the sociology and psychology of alcohol and sugar addictions are also similar (both addictions are common throughout different socioeconomic strata as a coping mechanism seeking an escape from emotional pain).
See for example in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs:
On the other hand, withdrawal symptoms from heavy long-term alcohol abuse can kill, while withdrawal symptoms from sugar are very much milder. So there’s also room to argue that they’re not comparable on those grounds.
Sugar is a chemical addiction, comparable to cocaine: True or False?
False, broadly. There are overlaps! For example, sugar drives impulsivity to seek more of the substance, and leads to changes in neurobiological brain function which alter emotional states and subsequent behaviours:
The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors
However!
Cocaine triggers a release of dopamine (as does sugar), but cocaine also acts directly on our brain’s ability to remove dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine:
The Neurobiology of Cocaine Addiction
…meaning that in terms of comparability, they (to use a metaphor now, not meaning this literally) both give you a warm feeling, but sugar does it by turning up the heating a bit whereas cocaine does it by locking the doors and burning down the house. That’s quite a difference!
Sugar is a behavioral addiction, comparable to video gaming: True or False?
True, with the caveat that this a “yes and” situation.
There are behavioral aspects of sugar addiction that can reasonably be compared to those of video gaming, e.g. compulsion loops, always the promise of more (without limiting factors such as overdosing), anxiety when the addictive element is not accessible for some reason, reduction of dopaminergic sensitivity leading to a craving for more, etc. Note that the last is mentioning a chemical but the mechanism itself is still behavioral, not chemical per se.
So, yes, it’s a behavioral addiction [and also arguably chemical in the manners we’ve described earlier in this article].
For science for this, we refer you back to:
The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors
Want more?
You might want to check out:
Beating Food Addictions: When It’s More Than “Just” Cravings
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Guinness Is Good For You*
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Guinness Is Good For You*
*This is our myth-buster edition, so maybe best not take that at face value!
To this day, writing the words “Guinness is” into Google will autocomplete to “Guinness is good for you”. The ad campaign proclaiming such launched about a hundred years ago, and was based on Guinness as it was when it was launched another hundred years before that.
Needless to say, none of this was based on modern science.
Is there any grain of truth?
Perhaps its strongest health claim, in terms of what stands up to modern scrutiny, is that it does contain some B vitamins. Famously (as it was once given to pregnant women in Ireland on the strength of such) it contains folate (also known as Vitamin B9). How much?
A 15oz glass of Guinness contains 12.8µg of folate, which is 3.2% of the RDA. In other words, you could get all the folate your body needs by drinking just 32 glasses of Guinness per day.
With that in mind, you might want to get the non-alcoholic version!
“I heard you could live on just Guinness and oranges, because it contains everything but vitamin C?”
The real question is: how long could you live? Otherwise, a facetious answer here could be akin to the “fun fact” that you can drink lava… once.
Guinness is missing many essential amino acids and fatty acids, several vitamins, and many minerals. Exactly what it’s missing may vary slightly from region to region, as while the broad recipe is the same, some processes add or remove some extra micronutrients.
As to what you’d die of first, for obvious reasons there have been no studies done on this, but our money would be on liver failure.
It would also wreak absolute havoc with your kidneys, but kidneys are tricky beasts—you can be down to 10% functionality and unaware that anything’s wrong yet. So we think liver failure would get you first.
(Need that 0.0% alcohol Guinness link again? Here it is)
Fun fact: Top contender in the category of “whole food” is actually seaweed (make sure you don’t get too much iodine, though)!
Or, should we say, top natural contender. Because foods that have been designed by humans to contain everything we need and more for optimized health, such as Huel, do exactly what they say on the tin.
And in case you’re curious…
Read: what bare minimum nutrients do you really need, to survive?
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Important Steps For Good Health
This is Dr. Kelly Starrett. He’s a physiotherapist, author, speaker, trainer. He has been described as a “celebrity” and “founding father” of CrossFit. He mostly speaks and writes about mobility in general; today we’re going to be looking at what he has to say specifically about our feet.
A strong foundation
“An army marches on its stomach”, Napoleon famously wrote.
More prosaically: an army marches on its feet, and good foot-care is a top priority for soldiers—indeed, in some militaries, even so much as negligently getting blisters is a military offense.
Most of us are not soldiers, but there’s a lesson to be learned here:
Your feet are the foundation for much of the rest of your health and effectiveness.
KISS for feet
No, not like that.
Rather: “Keep It Simple, Stupid”
Dr. Starrett is not only a big fan of not overcomplicating things, but also, he tells us how overcomplicating things can actively cause problems. When it comes to footwear, for example, he advises:
❝When you wear shoes, wear the flat kind. If you’re walking the red carpet on Oscar night, fine, go ahead and wear a shoe with a heel. Once in a while is okay.
But most of the time, you should wear shoes that are flat and won’t throw your biological movement hardware into disarray.
When you have to wear shoes, whether it’s running shoes, work shoes, or combat boots, buy the flat kind, also known as “zero drop”—meaning that the heel is not raised above the forefoot (at all).
What you want to avoid, or wean yourself away from, are shoes with the heels raised higher off the ground than the forefeet.❞
Of course, going barefoot is great for this, but may not be an option for all of us when out and about. And in the home, going barefoot (or shod in just socks) will only confer health benefits if we’re actually on our feet! So… How much time do you spend on your feet at home?
Allow your feet to move like feet
By evolution, the human body is built for movement—especially walking and running. That came with moving away from hanging around in trees for fruit, to hunting and gathering between different areas of the savannah. Today, our hunting and gathering may be done at the local grocery store, but we still need to keep our mobility, especially when it comes to our feet.
Now comes the flat footwear you don’t want: flip-flops and similar
If we wear flip-flops, or other slippers or shoes that hold onto our feet only at the front, we’re no longer walking like we’re supposed to. Instead of being the elegant product of so much evolution, we’re now walking like those AT-AT walkers in Star Wars, you know, the ones that fell over so easily?
Our feet need to be able to tilt naturally while walking/running, without our footwear coming off.
Golden rule for this: if you can’t run in them, you shouldn’t be walking in them
Exception: if for example you need something on your feet for a minute or two in the shower at the gym/pool, flip-flops are fine. But anything more than that, and you want something better.
Watch your step
There’s a lot here that’s beyond the scope of what we can include in this short newsletter, but:
If we stand or walk or run incorrectly, we’re doing gradual continual damage to our feet and ankles (potentially also our knees and hips, which problems in turn have a knock-on effect for our spine, and you get the idea—this is Bad™)
Some general pointers for keeping things in good order include:
- Your weight should be mostly on the balls of your feet, not your heels
- Your feet should be pretty much parallel, not turned out or in
- When standing, your center of gravity should be balanced between heel and forefoot
Quick tip for accomplishing this last one: Stand comfortably, your feet parallel, shoulder-width apart. Now, go up on your tip-toes. When you’ve done so, note where your spine is, and keep it there (apart from in its up-down axis) when you slowly go back to having your feet flat on the ground, so it’s as though your spine is sliding down a pole that’s fixed in place.
If you do this right, your center of gravity will now be perfectly aligned with where it’s supposed to be. It might feel a bit weird at first, but you’ll get used to it, and can always reset it whenever you want/need, by repeating the exercise.
If you’d like to know more from Dr. Starrett, you can check out his website here 🙂
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How we can prepare for future public health emergencies
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. is experiencing an increasing number of disease outbreaks and extreme weather events. While state and national preparedness for public health emergencies has improved in some areas, dangerous gaps remain, says a recent report from Trust for America’s Health.
Titled, “Ready or Not 2024: Protecting the Public’s Health from Diseases, Disasters, and Bioterrorism,” the report identifies gaps in national and state preparedness for public health emergencies and provides recommendations for improvement.
Using nine key indicators, the report categorizes all U.S. states and the District of Columbia into three readiness levels: high, medium, and low. The writers hope the report will help policymakers in under-performing states improve public health infrastructure.
Read on to learn more about what the research found and how we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies.
There’s work to be done
The report highlights areas with strong performance as well as those that need improvement.
Some areas with strong performance:
- State public health funding: Most states and the District of Columbia either maintained or increased their public health funding during the 2023 fiscal year.
- Health care labor force preparedness: Most states have started expanding the health care labor force for improved emergency response. As of 2023, 39 states participated in the Nurse Licensure Compact, which allows nurses to work in multiple member states without the need for additional state licenses.
Some areas that need improvement:
- Hospital safety scores: Only 25 percent of acute care hospitals earned the highest patient safety grade in fall 2023. These scores measure health care-associated infection rates, intensive care unit capacity, and other metrics. More high-scoring hospitals would improve preparedness for future public health emergencies.
- Access to paid time off: From March 2018 to March 2023, only 55 percent of U.S. workers used paid time off. Access to paid time off is important for reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
We can all do our part by staying up to date on vaccines
While the report focuses on policy changes that would improve emergency preparedness, Trust for America’s Health’s research identifies one way that we can individually prepare for future public health emergencies: staying up to date on vaccines.
The report found that during the 2022-2023 flu season, only 49 percent of those eligible for the flu vaccine received it. Public health experts are concerned that false claims about COVID-19 vaccines have resulted in overall vaccine hesitancy.
A decline in vaccination rates has led to an uptick in life-threatening, vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles. Increasing vaccine uptake would prevent the spread of vaccine-preventable diseases and reduce strain on hospital systems during public health crises.
Make sure that you and your children have received all recommended vaccines to prevent severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Learn more about recommended vaccines for adults and children from the CDC.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: