Move – by Caroline Williams
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
- Get 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, says the American Heart Association
- There are over 10,000 minutes per week, says the pocket calculator
Is 150/10,000 really the goal here? Really?
For Caroline Williams, the answer is no.
In this book that’s practically a manifesto, she outlines the case that:
- Humans evolved to move
- Industrialization and capitalism scuppered that
- We now spend far too long each day without movement
Furthermore, for Williams this isn’t just an anthropological observation, it’s a problem to be solved, because:
- Our lack of movement is crippling us—literally
- Our stagnation affects not just our bodies, but also our minds
- (again literally—there’s a direct correlation with mental health)
- We urgently need to fix this
So, what now, do we need to move in to the gym and become full-time athletes to clock up enough hours of movement? No.
Williams convincingly argues the case (using data from supercentenarian “blue zones” around the world) that even non-exertive movement is sufficient. In other words, you don’t have to be running; walking is great. You don’t have to be lifting weights; doing the housework or gardening will suffice.
From that foundational axiom, she calls on us to find ways to build our life around movement… rather than production-efficiency and/or convenience. She gives plenty of tips for such too!
Bottom line: some books are “I couldn’t put it down!” books. This one’s more of a “I got the urge to get up and get moving!” book.
Get your get-up-and-go up and going with “Move”—order yours from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fat’s Real Barriers To Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fat Justice In Healthcare
This is Aubrey Gordon, an author, podcaster, and fat justice activist. What does that mean?
When it comes to healthcare, we previously covered some ideas very similar to her work, such as how…
There’s a lot of discrimination in healthcare settings
In this case, it often happens that a thin person goes in with a medical problem and gets treated for that, while a fat person can go in with the same medical problem and be told “you should try losing some weight”.
Top tip if this happens to you… Ask: “what would you advise/prescribe to a thin person with my same symptoms?”
Other things may be more systemic, for example:
When a thin person goes to get their blood pressure taken, and that goes smoothly, while a fat person goes to get their blood pressure taken, and there’s not a blood pressure cuff to fit them, is the problem the size of the person or the size of the cuff? It all depends on perspective, in a world built around thin people.
That’s a trivial-seeming example, but the same principle has far-reaching (and harmful) implications in healthcare in general, e.g:
- Surgeons being untrained (and/or unwilling) to operate on fat people
- Getting a one-size-fits-all dose that was calculated using average weight, and now doesn’t work
- MRI machines are famously claustrophobia-inducing for thin people; now try not fitting in it in the first place
…and so forth. So oftentimes, obesity will be correlated with a poor healthcare outcome, where the problem is not actually the obesity itself, but rather the system having been set up with thin people in mind.
It would be like saying “Having O- blood type results in higher risks when receiving blood transfusions”, while omitting to add “…because we didn’t stock O- blood”.
Read more on this topic: Shedding Some Obesity Myths
Does she have practical advice about this?
If she could have you understand one thing, it would be:
You deserve better.
Or if you are not fat: your fat friends deserve better.
How this becomes useful is: do not accept being treated as the problem!
Demand better!
If you meekly accept that you “just need to lose weight” and that thus you are the problem, you take away any responsibility from your healthcare provider(s) to actually do their jobs and provide healthcare.
See also Gordon’s book, which we’ve not reviewed yet but probably will one of these days:
“You Just Need to Lose Weight”: And 19 Other Myths About Fat People – by Aubrey Gordon
Are you saying fat people don’t need to lose weight?
That’s a little like asking “would you say office workers don’t need to exercise more?”; there are implicit assumptions built into the question that are going unaddressed.
Rather: some people might benefit healthwise from losing weight, some might not.
In fact, over the age of 65, being what is nominally considered “overweight” reduces all-cause mortality risk.
For details of that and more, see: When BMI Doesn’t Measure Up
But what if I do want/need to lose weight?
Gordon’s not interested in helping with that, but we at 10almonds are, so…
Check out: Lose Weight, But Healthily
Where can I find more from Aubrey Gordon?
You might enjoy her blog:
Aubrey Gordon | Your Fat Friend
Or her other book, which we reviewed previously:
What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat – by Aubrey Gordon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Oh She Glows Cookbook – by Angela Liddon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s get the criticism out of the way first: notwithstanding the subtitle promising over 100 recipes, there are about 80-odd here, if we discount recipes that are no-brainer things like smoothies, sides such as for example “roasted garlic”, or meta-ingredients such as oat flour (instructions: blend the oats and you get oat flour).
The other criticism is more subjective: if you are like this reviewer, you will want to add more seasonings than recommended to most of the recipes. But that’s easy enough to do.
As for the rest: this is a very healthy cookbook, and quite wide-ranging and versatile, with recipes that are homely, with a lot of emphasis on comfort foods (but still, healthy), though certainly some are perfectly worthy of entertaining too.
A nice bonus of this book is that it offers a lot of available substitutions (much like we do at 10almonds), and also ways of turning the recipe into something else entirely with just a small change. This trait more than makes up for the slight swindle in terms of number of recipes, since some of the recipes have bonus recipes snuck in.
Bottom line: if you’d like to broaden your plant-based cooking range, this book is a fine option for expanding your repertoire.
Click here to check out The Oh She Glows Cookbook, and indeed glow!
Share This Post
-
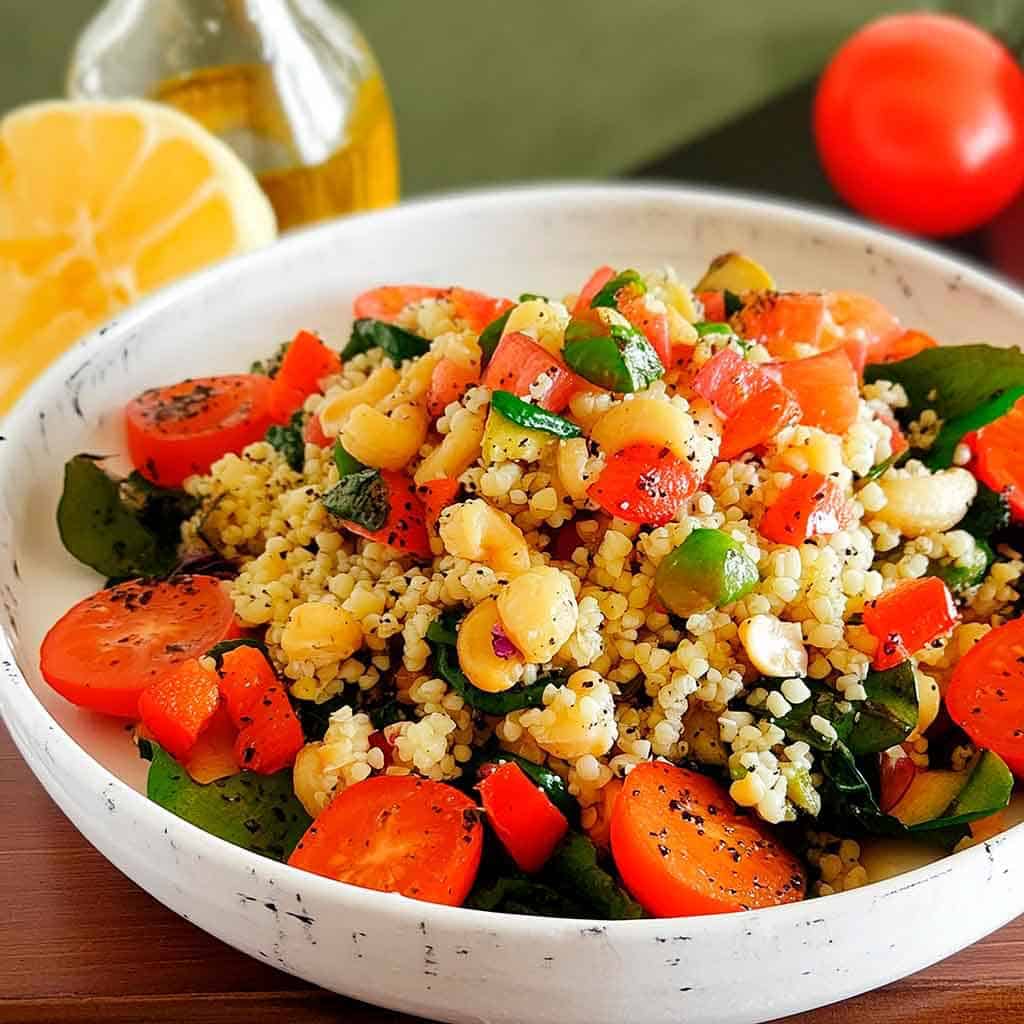
Tasty Tabbouleh with Tahini
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tabbouleh is a salad, but it’s not “just a salad”. It’s a special kind of salad that’s as exciting for the tastebuds as it is healthy for the body and brain. Its core ingredients have been traditional for about a dozen generations, and seasonings are always a personal matter (not to mention that Lebanese tabbouleh-makers centuries ago might not have used miso and nooch, as we will today), but the overall feel of the Gestalt of tabbouleh seasonings remains the same, and this recipe is true to that.
You will need
For the tabbouleh:
- 1 cup bulgur wheat
- 1 cup plum tomatoes, chopped
- 1 cucumber, peeled and chopped (add the peel to a jug of water and put it in the fridge; this will be refreshing cucumber water later!)
- 1 cup chickpeas, cooked without salt
- 1/2 cup parsley, chopped
- 1/2 cup mint, chopped
- 2 spring onions, finely chopped
- 2oz fresh lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp garlic powder
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground celery seeds
- 1 tsp ground nigella seeds
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- 1 tsp MSG, or 1/2 tsp low sodium salt (you can find it in supermarkets, the sodium chloride is cut with potassium chloride to make it have less sodium and more potassium)
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (nooch), ground (it comes in flakes; you will have to grind it in a spice grinder or with a pestle and mortar)
For the tahini sauce:
- 3 garlic cloves, crushed
- 3 tbsp tahini
- 1 tbsp fresh lemon juice
- 1 tbsp white miso paste
- 1 tsp ground cumin
To serve:
- A generous helping of leafy greens; we recommend collard greens, but whatever works for you is good; just remember that dark green is best. Consider cavolo nero, or even kale if that’s your thing, but to be honest this writer doesn’t love kale
- 1 tsp coarsely ground nigella seeds
- Balsamic vinegar, ideally aged balsamic vinegar (this is thicker and sweeter, but unlike most balsamic vinegar reductions, doesn’t have added sugar).
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Rinse the bulgur wheat and then soak it in warm water. There is no need to boil it; the warm water is enough to soften it and you don’t need to cook it (bulgur wheat has already been parboiled before it got to you).
2) While you wait, take a small bowl and mix the rest of the ingredients from the tabbouleh section (so, the lemon juice, miso paste, and all those ground spices and MSG/salt and ground nutritional yeast); you’re making a dressing out of all the ingredients here.
3) When the bulgur wheat is soft (expect it to take under 15 minutes), drain it and put it in a big bowl. Add the tomatoes, cucumber, chickpeas, parsley, mint, and spring onions. This now technically qualifies as tabbouleh already, but we’re not done.
4) Add the dressing to the tabbouleh and mix thoroughly but gently (you don’t want to squash the tomatoes, cucumber, etc). Leave it be for at least 15 minutes while the flavors blend.
5) Take the “For the tahini sauce” ingredients (all of them) and blend them with 4 oz water, until smooth. You’re going to want to drizzle this sauce, so if the consistency is too thick for drizzling, add a little more water and/or lemon juice (per your preference), 1 tbsp at a time.
6) Roughly chop the leafy greens and put them in a bowl big enough for the tabbouleh to join them there. The greens will serve as a bed for the tabbouleh itself.
7) Drizzle the tahini over the tabbouleh, and drizzle a little of the aged balsamic vinegar too.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Elon Musk says ketamine can get you out of a ‘negative frame of mind’. What does the research say?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
X owner Elon Musk recently described using small amounts of ketamine “once every other week” to manage the “chemical tides” that cause his depression. He says it’s helpful to get out of a “negative frame of mind”.
This has caused a range of reactions in the media, including on X (formerly Twitter), from strong support for Musk’s choice of treatment, to allegations he has a drug problem.
But what exactly is ketamine? And what is its role in the treatment of depression?
It was first used as an anaesthetic
Ketamine is a dissociative anaesthetic used in surgery and to relieve pain.
At certain doses, people are awake but are disconnected from their bodies. This makes it useful for paramedics, for example, who can continue to talk to injured patients while the drug blocks pain but without affecting the person’s breathing or blood flow.
Ketamine is also used to sedate animals in veterinary practice.
Ketamine is a mixture of two molecules, usually referred to a S-Ketamine and R-Ketamine.
S-Ketamine, or esketamine, is stronger than R-Ketamine and was approved in 2019 in the United States under the drug name Spravato for serious and long-term depression that has not responded to at least two other types of treatments.
Ketamine is thought to change chemicals in the brain that affect mood.
While the exact way ketamine works on the brain is not known, scientists think it changes the amount of the neurotransmitter glutamate and therefore changes symptoms of depression.How was it developed?
Ketamine was first synthesised by chemists at the Parke Davis pharmaceutical company in Michigan in the United States as an anaesthetic. It was tested on a group of prisoners at Jackson Prison in Michigan in 1964 and found to be fast acting with few side effects.
The US Food and Drug Administration approved ketamine as a general anaesthetic in 1970. It is now on the World Health Organization’s core list of essential medicines for health systems worldwide as an anaesthetic drug.
In 1994, following patient reports of improved depression symptoms after surgery where ketamine was used as the anaesthetic, researchers began studying the effects of low doses of ketamine on depression.
Researchers have been investigating ketamine for depression for 30 years.
SB Arts Media/ShutterstockThe first clinical trial results were published in 2000. In the trial, seven people were given either intravenous ketamine or a salt solution over two days. Like the earlier case studies, ketamine was found to reduce symptoms of depression quickly, often within hours and the effects lasted up to seven days.
Over the past 20 years, researchers have studied the effects of ketamine on treatment resistant depression, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic sress disorder obsessive-compulsive disorder, eating disorders and for reducing substance use, with generally positive results.
One study in a community clinic providing ketamine intravenous therapy for depression and anxiety found the majority of patients reported improved depression symptoms eight weeks after starting regular treatment.
While this might sound like a lot of research, it’s not. A recent review of randomised controlled trials conducted up to April 2023 looking at the effects of ketamine for treating depression found only 49 studies involving a total of 3,299 patients worldwide. In comparison, in 2021 alone, there were 1,489 studies being conducted on cancer drugs.
Is ketamine prescribed in Australia?
Even though the research results on ketamine’s effectiveness are encouraging, scientists still don’t really know how it works. That’s why it’s not readily available from GPs in Australia as a standard depression treatment. Instead, ketamine is mostly used in specialised clinics and research centres.
However, the clinical use of ketamine is increasing. Spravato nasal spray was approved by the Australian Therapuetic Goods Administration (TGA) in 2021. It must be administered under the direct supervision of a health-care professional, usually a psychiatrist.
Spravato dosage and frequency varies for each person. People usually start with three to six doses over several weeks to see how it works, moving to fortnightly treatment as a maintenance dose. The nasal spray costs between A$600 and $900 per dose, which will significantly limit many people’s access to the drug.
Ketamine can be prescribed “off-label” by GPs in Australia who can prescribe schedule 8 drugs. This means it is up to the GP to assess the person and their medication needs. But experts in the drug recommend caution because of the lack of research into negative side-effects and longer-term effects.
What about its illicit use?
Concern about use and misuse of ketamine is heightened by highly publicised deaths connected to the drug.
Ketamine has been used as a recreational drug since the 1970s. People report it makes them feel euphoric, trance-like, floating and dreamy. However, the amounts used recreationally are typically higher than those used to treat depression.
Information about deaths due to ketamine is limited. Those that are reported are due to accidents or ketamine combined with other drugs. No deaths have been reported in treatment settings.
Reducing stigma
Depression is the third leading cause of disability worldwide and effective treatments are needed.
Seeking medical advice about treatment for depression is wiser than taking Musk’s advice on which drugs to use.
However, Musk’s public discussion of his mental health challenges and experiences of treatment has the potential to reduce stigma around depression and help-seeking for mental health conditions.
Clarification: this article previously referred to a systematic review looking at oral ketamine to treat depression. The article has been updated to instead cite a review that encompasses other routes of administration as well, such as intravenous and intranasal ketamine.
Julaine Allan, Associate Professor, Mental Health and Addiction, Rural Health Research Institute, Charles Sturt University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Eat to Change How You Drink – by Dr. Brooke Scheller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether you want to stop drinking or just cut down, this book can help. But what makes it different from the other reduce/stop drinking books we’ve reviewed?
Mostly, it’s about nutrition. This book focuses on the way that alcohol changes our relationship to food, our gut, our blood sugars, and more. The author also explains how reducing/stopping drinking, without bearing these things in mind, can be unnecessarily extra hard.
The remedy? To bear them in mind, of course, but that requires knowing them. So what she does is explain the physiology of what’s going on in terms of each of the above things (and more), and how to adjust your diet to make up for what alcohol has been doing to you, so that you can reduce/quit without feeling constantly terrible.
The style is very pop-science, light in tone, readable. She makes reference to a lot of hard science, but doesn’t discuss it in more depth than is necessary to convey the useful information. So, this is a practical book, aimed at all people who want to reduce/quit drinking.
Bottom line: if you feel like it’s hard to drink less because it feels like something is missing, it’s probably because indeed something is missing, and this book can help you bridge that gap!
Click here to check out How To Eat To Change How You Drink, and do just that!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tranquility by Tuesday?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
I Know How She Does It: How Successful Women Make The Most of Their Time
This is Laura Vanderkam, author of “Tranquility By Tuesday” (amongst other books). Her “thing” is spending more time on what’s important, and less on what isn’t. Sounds simple, but she’s made a career out of it, so condensed here for you are…
Laura’s 7 Keys To Productivity
Key One: Plan your weeks on Fridays
You don’t want your Monday morning to be a “James Bond intro” (where everything is already in action and you’re just along for the ride, trying to figure out what’s going on). So, take some time last thing each Friday, to plan ahead for the following week!
Key Two: Measure what matters
Whatever that means to you. Laura tracks her use of time in half-hour blocks, and likes keeping track of streaks. For her, that means running daily and keeping a log of it. She also keeps track of the books she reads. For someone else it could be music practice, or a Duolingo streak, or eating fruit each day.
On which note…
“Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” is simpler than most nutrition trackers (where you must search for everything you eat, or scan barcodes for all ingredients).
Instead, it keeps track of whether you are having certain key health-giving foods often enough to maintain good health.
We might feature his method in a future edition of 10almonds, but for now, check the app out for yourself here:
Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on iOS / Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on Android
Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen @ Nutrition Facts
Key Three: Figure out 2–3 “anchor” events for the weekend
Otherwise, it can become a bit of a haze and on Monday you find yourself thinking “where did the weekend go?”. So, plan some stuff! It doesn’t have to be anything out-of-this-world, just something that you can look forward to in advance and remember afterwards. It could be a meal out with your family, or a session doing some gardening, or a romantic night in with your partner. Whatever makes your life “living” and not passing you by!
Key Four: Tackle the toughest work first
You’ve probably heard about “swallowing frogs”. If not, there are various versions, usually attributed to Mark Twain.
Here’s one:
“If it’s your job to eat a frog, it’s best to do it first thing in the morning. And if it’s your job to eat two frogs, it’s best to eat the biggest one first.”
Top Productivity App “ToDoist” has an option for this, by the way!
Laura’s key advice here is: get the hard stuff done now! Before you get distracted or tired and postpone it to tomorrow (and then lather rinse repeat, so it never gets done)
10almonds Tip:
“But what if something’s really important but not as pressing as some less important, but more urgent tasks?”
Simple!
Set a timer (we love the Pomodoro method, by the way) and do one burst of the important-but-not-urgent task first. Then you can get to the more urgent stuff.
Repeat each day until the important-but-not-urgent task is done!
The 10almonds Team
Key Five: Use bits of time well
If, like many of us, you’ve a neverending “to read” list, use the 5–10 minute breaks that get enforced upon us periodically through the day!
- Use those few minutes before a meeting/phonecall!
- Use the time you spend waiting for public transport or riding on it!
- Use the time you spent waiting for a family member to finish doing a thing!
All those 5–10 minute bits soon add up… You might as well spend that time reading something you know will add value to your life, rather than browsing social media, for example.
Key Six: Make very short daily to-do lists
By “short”, Laura considers this “under 10 items”. Do this as the last part of your working day, ready for tomorrow. Not at bedtime! Bedtime is for winding down, not winding up
Key Seven: Have a bedtime
Laura shoots for 10:30pm, but whatever works for you and your morning responsibilities. Your morning responsibilities aren’t tied to a specific time? Lucky you, but try to keep a bedtime anyway. Otherwise, your daily rhythm can end up sliding around the clock, especially if you work from home!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: