Building & Maintaining Mobility
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Building & Maintaining Mobility!

This is Juliet Starrett. She’s a CrossFit co-founder, and two-time white-water rafting world champion. Oh, and she won those after battling thyroid cancer. She’s now 50 years old, and still going strong, having put aside her career as a lawyer to focus on fitness. Specifically, mobility training.
The Ready State
Together with her husband Kelly, Starrett co-founded The Ready State, of which she’s CEO.
It used to be called “Mobility WOD” (the “WOD” stands for “workout of the day”) but they changed their name as other companies took up the use of the word “mobility”, something the fitness world hadn’t previously focussed on much, and “WOD”, which was also hardly copyrightable.
True to its origins, The Ready State continues to offer many resources for building and maintaining mobility.
Why the focus on mobility?
When was the last time you had to bench-press anything larger than a small child? Or squat more than your partner’s bodyweight? Or do a “farmer’s walk” with anything heavier than your groceries?
For most of us, unless our lifestyles are quite extreme, we don’t need ridiculous strength (fun as that may be).
You know what makes a huge difference to our quality of life though? Mobility.
Have you ever felt that moment of panic when you reach for something on a high shelf and your shoulder or back twinges (been there!)? Or worse, you actually hurt yourself and the next thing you know, you need help putting your socks on (been there, too!)?
And we say to ourselves “I’m not going to let that happen to me again”
But how? How do we keep our mobility strong?
First, know your weaknesses
Starrett is a big fan of mobility tests to pinpoint areas that need more work.
Most of her resources for this aren’t free, and we’re drawing heavily from her book here, so for your convenience, we’ll link to some third party sources for this:
- Timed Up and Go—start with this, before progressing to the next!
- Sit To Rise Test—not to be underestimated (this page also has excerpts from Starrett’s mobility book, by the way)
- Shoulders/Spine/Hips—7 quick tests; note any that you can’t do, or struggle with
Next, eliminate those weaknesses
Do mobility exercises in any weak areas, until they’re not weak:
Want to train the full body in one session?
Try out The Ready State’s 10-Minute Morning Mobility Routine
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy her book that we reviewed previously:
Built to Move: The Ten Essential Habits to Help You Move Freely and Live Fully
You might also enjoy The Ready State App, available for iOS and for Android:
The Ready State Virtual Mobility Coach
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Signs Of Low Estrogen In Women: What Your Skin, Hair, & Nails Are Trying To Tell You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Skin, hair, and nails are often thought of purely as a beauty thing, but in fact they can be indicative of a lot of other aspects of health. Dr. Andrea Suarez takes us through some of them in this video about the systemic (i.e., whole-body, not just related to sex things) effects of estrogen, and/or a deficiency thereof.
Beyond the cosmetic
Low estrogen levels are usual in women during and after untreated menopause, resulting in various changes in the skin, hair, and nails, that reflect deeper issues, down to bone health, heart health, brain health, and more. Since we can’t see our bones or hearts or brains without scans (or a serious accident/incident), we’re going to focus on the outward signs of estrogen deficiency.
Estrogen helps maintain healthy collagen production, skin elasticity, wound healing, and moisture retention, making it essential for youthful and resilient skin. Declining estrogen levels with menopause lead to a thinner epidermis, decreased collagen production, and more pronounced wrinkles. Skin elasticity also diminishes, which slows the skin’s ability to recover from stretching or deformation. Wound healing also becomes slower, increasing the risk of infections and extended recovery periods after injuries or surgeries—bearing in mind that collagen is needed in everything from our skin to our internal connective tissue (fascia) and joints and bones. So all those things are going to struggle to recover from injury (and surgery is also an injury) without it.
Other visible changes associated with declining estrogen include significant dryness as a result of reduced hyaluronic acid and glycosaminoglycan production, which are essential for moisture retention. The skin becomes more prone to irritation and increased water loss. Additionally, estrogen deficiency results in less resistance to oxidative stress, making the skin more susceptible to damage from environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution, as well as any from-the-inside pollution that some may have depending on diet and lifestyle.
Acne and enlarged pores are associated with increased testosterone, but testosterone and estrogen are antagonistic in most ways, and in this case a decrease in estrogen will do the same, due increased unopposed androgen signaling affecting the oil glands. The loss of supportive collagen also causes the skin around pores to lose structure, making them appear larger. The reduction in skin hydration further exacerbates the visibility of pores and can contribute to the development of blackheads due to abnormal cell turnover.
Blood vessel issues tend to arise as estrogen levels drop, leading to a reduction in angiogenesis, i.e. the formation and integrity of blood vessels. This results in more fragile and leaky blood vessels, making the skin more prone to bruising, especially on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the backs of the hands. This weakened vasculature also further contributes to the slower wound healing that we talked about, due to less efficient delivery of growth factors.
Hair and nail changes often accompany estrogen deficiency. Women may notice hair thinning, increased breakage, and a greater likelihood of androgenic alopecia. The texture of the hair can change, becoming more brittle. Similarly, nails can develop ridges, split more easily, and become more fragile due to reduced collagen and keratin production, which also affects the skin around the nails.
As for what to do about it? Management options for estrogen-deficient skin include:
- Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can improve skin elasticity, boost collagen production, and reduce dryness and fragility, as well as addressing the many more serious internal things that are caused by the same deficiency as these outward signs.
- Low-dose topical estrogen cream, which can help alleviate skin dryness and increase skin strength, won’t give the systemic benefits (incl. to bones, heart, brain, etc) that only systemic HRT can yield.
- Plant-based phytoestrogens, which are not well-evidenced, but may be better than nothing if nothing is your only other option. However, if you are taking anything other form of estrogen, don’t use phytoestrogens as well, or they will compete for estrogen receptors, and do the job not nearly so well while impeding the bioidentical estrogen from doing its much better job.
And for all at any age, sunscreen continues to be one of the best things to put on one’s skin for general skin health, and this is even more true if running low on estrogen.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What is Ryeqo, the recently approved medicine for endometriosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For women diagnosed with endometriosis it is often a long sentence of chronic pain and cramping that impacts their daily life. It is a condition that is both difficult to diagnose and treat, with many women needing either surgery or regular medication.
A medicine called Ryeqo has just been approved for marketing specifically for endometriosis, although it was already available in Australia to treat a different condition.
Women who want the drug will need to consult their local doctor and, as it is not yet on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, they will need to pay the full cost of the script.
What does Ryeqo do?
Endometriosis affects 14% of women of reproductive age. While we don’t have a full understanding of the cause, the evidence suggests it’s due to body tissue that is similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) growing outside the uterus. This causes pain and inflammation, which reduces quality of life and can also affect fertility.
Ryeqo is a tablet containing three different active ingredients: relugolix, estradiol and norethisterone.
Relugolix is a drug that blocks a particular peptide from releasing other hormones. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Estradiol is a naturally occurring oestrogen hormone in women that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Norethisterone is a synthetic hormone commonly used in birth control medications and to delay menstruation and help with heavy menstrual bleeding.
All three components work together to regulate the levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body that contribute to endometriosis, alleviating its symptoms.
Relugolix reduces the overall levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body. The estradiol compensates for the loss of oestrogen because low oestrogen levels can cause hot flushes (also called hot flashes) and bone density loss. And norethisterone blocks the effects of estradiol on the uterus (where too much tissue growth is unwanted).
Is it really new?
The maker of Ryeqo claims it is the first new drug for endometriosis in Australia in 13 years.
But individually, all three active ingredients in Ryeqo have been in use since 2019 or earlier.
Ryeqo has been available in Australia since 2022, but until now was not specifically indicated for endometriosis. It was originally approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids, which share some common symptoms with endometriosis and have related causes.
In addition to Ryeqo, current medical guidance lists other drugs that are suitable for endometriosis and some reformulations of these have also only been recently approved.
The oral medicine Dienogest was approved in 2021, and there have been a number of injectable drugs for endometriosis recently approved, such as Sayana Press which was approved in a smaller dose form for self-injection in 2023.
You can’t take the contraceptive pill with Ryeqo but the endometriosis drug could replace it.
ShutterstockHow to take it and what not to do
Ryeqo is a once-a-day tablet. You can take it with, or without food, but it should be taken about the same time each day.
It is recommended you start taking Ryeqo within the first five days after the start of your next period. If you start at another time during your period, you may experience initial irregular or heavier bleeding.
Because it contains both synthetic and natural hormones, you can’t use the contraceptive pill and Ryeqo together. However, because Ryeqo does contain norethisterone it can be used as your contraception, although it will take at least one month of use to be effective. So, if you are on Ryeqo, you should use a non-hormonal contraceptive – such as condoms – for a month when starting the medicine.
Ryeqo may be incompatible with other medicines. It might not be suitable for you if you take medicines for epilepsy, HIV and AIDS, hepatitis C, fungal or bacterial infections, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, angina (chest pain), or organ rejection. You should also not take Ryeqo if you have a liver tumour or liver disease.
The possible side effects of Ryeqo are similar to those of oral contraceptives. Blood clots are a risk with any medicine that contains an oestrogen or a progestogen, which Ryeqo does. Other potential side effects include bone loss, a reduction in menstrual blood loss or loss of your period.
It’s costly for now
Ryeqo can now be prescribed in Australia, so you should discuss whether Ryeqo is right for you with the doctor you usually consult for your endometriosis.
While the maker has made a submission to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, it is not yet subsidised by the Australian government. This means that rather than paying the normal PBS price of up to A$31.60, it has been reported it may cost as much as $135 for a one-month supply. The committee will make a decision on whether to subsidise Ryeqo at its meeting next month.
Correction: this article has been updated to clarify the recent approval of specific formulations of drugs for endometriosis.
Nial Wheate, Associate Professor of the School of Pharmacy, University of Sydney and Jasmine Lee, Pharmacist and PhD Candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eat These Greens!
Chlorella vulgaris, henceforth “chlorella”, is a simple green algae that has a lot of health benefits.
Note: most of the studies here are for Chlorella vulgaris specifically. However, some are for other species of the Chlorella genus, of which Chlorella vulgaris is by far the most common, hence the name (vulgaris = common). The relevant phytochemical properties appear to be the same regardless.
Superfood
While people generally take it as a supplement rather than a food item in any kind of bulk, it is more than 50% protein and contains all 9 essential amino acids.
As you might expect of a green superfood, it’s also full of many antioxidants, most of them carotenoids, and these pack a punch, for example against cancer:
It also has a lot of vitamins and minerals, and even omega-3.
Which latter also means it helps improve lipids and is thus particularly…
Heart healthy
❝Daily consumption of Chlorella supplements provided the potential of health benefits reducing serum lipid risk factors, mainly triglycerides and total cholesterol❞
Its heart-healthy benefits don’t stop at lipids though, and include blood pressure management, as in this study that found…
❝GABA-rich Chlorella significantly decreased high-normal blood pressure and borderline hypertension, and is a beneficial dietary supplement for prevention of the development of hypertension. ❞
About that GABA, if you’re curious about that, check out:
GABA Against Stress, Anxiety, & More
May remove heavy metals
We’re going with “may” for this one as we could only find animal studies so far (probably because most humans don’t have megadoses of heavy metals in them, which makes testing harder).
Here’s an example animal study, though:
Enhanced elimination of tissue methyl mercury in [Chlorella]-fed mice
Immunostimulant
This one’s clearer, for example in this 8-week study (with humans) that found…
❝Serum concentrations of interferon-γ (p<0.05) and interleukin-1β (p<0.001) significantly increased and that of interleukin-12 (p<0.1) tended to increase in the Chlorella group.
The increments of these cytokines after the intervention were significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than those in the placebo group. In addition, NK cell activities (%) were significantly increased in Chlorella group, but not in Placebo group.
The increments of NK cell activities (%) were also significantly bigger in the Chlorella group than the placebo group.
Additionally, changed levels of NK cell activity were positively correlated with those of serum interleukin-1β (r=0.280, p=0.047) and interferon-γ (r=0.271, p<0.005).❞
tl;dr = it boosts numerous different kinds of immune cells
PS, if you click though to the study, you may be momentarily alarmed by the first paragraph of the abstract that says “However, there were no direct evidences for the effect of Chlorella supplementation on immune/inflammation response in healthy humans“
this is from the “Background” section of the abstract, so what they are saying is “before we did this study, nobody had done this yet”.
So, be assured that the results are worthwhile and compelling.
Is it safe?
Based on the studies, it has a good safety profile. However, as it boosts the immune system, you may want to check with your doctor if you have an autoimmune disorder, and/or you are on immunosuppressants.
And in general, of course always check with your doctor/pharmacist if unsure about any potential drug interactions.
Want some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The 6 Pillars Of Nutritional Psychiatry
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Naidoo’s To-Dos
This is Dr. Uma Naidoo. She’s a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, professional chef graduating with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry.
She’s also the Director of Nutritional and Lifestyle Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) & Director of Nutritional Psychiatry at MGH Academy while serving on the faculty at Harvard Medical School.
What is nutritional psychiatry?
Nutritional psychiatry is the study of how food influences our mood (in the short term) and our more generalized mental health (in the longer term).
We recently reviewed a book of hers on this topic:
This Is Your Brain On Food – by Dr. Uma Naidoo
The “Six Pillars” of nutritional psychiatry
Per Dr. Naidoo, these are…
Be Whole; Eat Whole
Here Dr. Naidoo recommends an “80/20 rule”, and a focus on fiber, to keep the gut (“the second brain”) healthy.
See also: The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Eat The Rainbow
This one’s simple enough and speaks for itself. Very many brain-nutrients happen to be pigments, and “eating the rainbow” (plants, not Skittles!) is a way to ensure getting a lot of different kinds of brain-healthy flavonoids and other phytonutrients.
The Greener, The Better
As Dr. Naidoo writes:
❝Greens contain folate, an important vitamin that maintains the function of our neurotransmitters. Its consumption has been associated with a decrease in depressive symptoms and improved cognition.❞
Tap into Your Body Intelligence
This is about mindful eating, interoception, and keeping track of how we feel 30–60 minutes after eating different foods.
Basically, the same advice here as from: The Kitchen Doctor
(do check that out, as there’s more there than we have room to repeat here today!)
Consistency & Balance Are Key
Honestly, this one’s less a separate item and is more a reiteration of the 80/20 rule discussed in the first pillar, and an emphasis on creating sustainable change rather than loading up on brain-healthy superfoods for half a weekend and then going back to one’s previous dietary habits.
Avoid Anxiety-Triggering Foods
This is about avoiding sugar/HFCS, ultra-processed foods, and industrial seed oils such as canola and similar.
As for what to go for instead, she has a broad-palette menu of ingredients she recommends using as a base for one’s meals (remember she’s a celebrated chef as well as a psychiatrist and nutritionist), which you can check out here:
Dr. Naidoo’s “Food for Mood” project
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fascia Hopping: The Powerful Over-50 Exercise You’re Probably Not Doing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A 62-year-old man reported feeling 10 years younger after just 8 days of fascia hopping. Now, anecdote ≠ data, but it seems worth investigating:
Let’s hop straight to it
Fascia is the web-like layer of connective tissue that divides your muscles and organs from each other. It simultaneously holds some stuff in place, and allows other parts to glide over each other with minimal friction.
At least, that’s what it’s supposed to do.
Like any body part, it can go wrong. And like any body part, it needs maintenance. In fascia’s case, the maintenance is to keep it slippy where it should be slippy and grippy where it should be grippy.
Here’s an exercise series for that, as described/shown in the video:
Prepping the fascia:
- Align posture: head lifted, shoulders down.
- Stretch fascia in all directions (up-down, left-right).
- Maintain a “fascia wetsuit” concept—taut but not unduly tense.
Springboard feet setup:
- Stand on balls of feet, heels slightly raised.
- Bounce gently to engage fascia elasticity.
“Fascia Strength & Power” dance:
- Move hips in a figure-eight motion.
- Keep shoulders relaxed, allowing movement to flow from the center.
Fascia hopping:
- Keep heels fixed, bounce lightly.
- Progress to small hops if possible.
- Maintain a smooth rhythm to activate elasticity.
Do these for 2 minutes daily for 7 days. It doesn’t have to be a dedicated exercise session; you can do it while you’re waiting for the water to boil in the kitchen, or things like that.
For more on these exercises plus visual demonstrations (it’s very simple), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
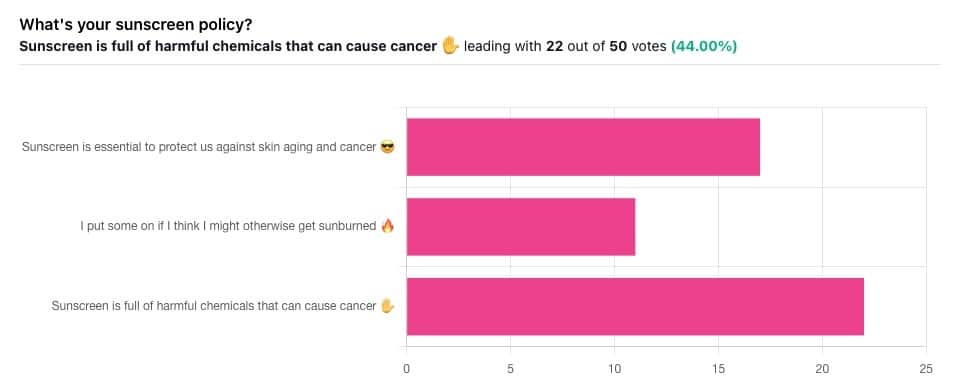
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: