Missing Microbes – by Dr. Martin Blaser
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably know that antibiotic resistance is a problem, but you might not realize just what a many-headed beast antibiotic overuse is.
From growing antibiotic superbugs, to killing the friendly bacteria that normally keep pathogens down to harmless numbers (resulting in death of the host, as the pathogens multiply unopposed), to multiple levels of dangers in antibiotic overuse in the farming of animals, this book is scary enough that you might want to save it for Halloween.
But, Dr. Blaser does not argue against antibiotic use when it’s necessary; many people are alive because of antibiotics—he himself recovered from typhoid because of such.
The style of the book is narrative, but information-dense. It does not succumb to undue sensationalization, but it’s also far from being a dry textbook.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand the real problems caused by antibiotics, and how we can combat that beyond merely “try not to take them unnecessarily”, this book is very worthy reading.
Click here to check out Missing Microbes, and learn more about yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Radical Remission – by Dr. Kelly Turner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not:an autobiographical account of the “I beat cancer and you can too” pep-talk style.
What it is: a very readable pop-science book based on the author’s own PhD research into radical remission.
She knew that a very small percentage of people experience spontaneous radical remission (or quasi-spontaneous, if the remission is attributed to lifestyle changes, and/or some alternative therapy), but a small percentage of people means a large number worldwide, so she travelled the world studying over 1,000 cases of people with late-stage cancer who had either not gone for conventional anticancer drugs, or had and then stopped, and lived to tell the tale.
While she doesn’t advocate for any particular alternative therapy, she does report on what things came to her attention. She does advocate for some lifestyle changes.
Perhaps the biggest value this book offers is in its promised “9 key factors that can make a real difference”, which are essentially her conclusions from her PhD dissertation.
There isn’t room to talk about them here in a way that wouldn’t be misleading/unhelpful for a paucity of space, so perhaps we’ll do a main feature one of these days.
Bottom line: if you have (or a loved one has) cancer, this is an incredibly sensible book to read. If you don’t, then it’s an interesting and thought-provoking book to read.
Click here to check out Radical Remission, and learn about the factors at hand!
Share This Post

Overcome Front-Of-Hip Pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Alyssa Kuhn, physiotherapist, demonstrates how:
One, two, three…
One kind of pain affects a lot of related things: hip pain has an impact on everything that’s connected to the pelvis, which is basically the rest of the body, but especially the spine itself. For this reason, it’s critical to keep it in as good condition as possible.
Two primary causes of hip stiffness and pain:
- Anterior pelvic tilt due to posture, weight distribution, or pain. This tightens the front muscles and weakens the back muscles.
- Prolonged sitting, which tightens the hip muscles due to inactivity.
Three exercises are recommended by Dr. Kuhn to relieve pain and stiffness:
- Bridge exercise:
- Lie on a firm surface with your knees bent.
- Push through your feet, engage your hamstrings, and flatten your lower back.
- Hold for 3–5 seconds, relax, and repeat (10–20 reps).
- Wall exercise with arms:
- Stand with your lower back against the wall, feet a step away.
- Tilt your hips backwards, keeping your lower back in contact with the wall.
- Alternate lifting one arm at a time while maintaining back contact with the wall (10–20 reps).
- Wall exercise with legs:
- Same stance as the previous exercise but wider now.
- Lift one heel at a time while keeping your hips stable and your back against the wall.
- Practice for 30–60 seconds, maintaining good form.
As ever, consistency is key for long-term relief. Dr. Kuhn recommends doing these regularly, especially before any expected periods of prolonged sitting (e.g. at desk, or driving, etc). And of course, do try to reduce, or at least break up, those sitting marathons if you can.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post

The Cluttered Mind – by Deborah McKenna
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coming from an eclectic psychotherapy background, Deborah McKenna outlines a wide array of techniques to “do what it says on the tin”, that is:
Organizing the junk drawer of your mind.
McKenna argues that it’s natural for something so gargantuan as our mind to get cluttered… but that it’s perfectly possible, with a good system, to tidy up considerably.
The benefit of this is much like the benefit of tidying a room:
Imagine a kitchen in which half the things have not been put away; there are dishes in the sink, something is growing behind the trash can… and you have a vague suspicion that if you open a certain cupboard, its contents are going to come falling out on your head. How are you going to cook a meal here?
Imagine a mind when many thoughts have been left untended; there are things you needed to process, and there’s a steady resentment of something growing in some dark part of your mind… and there’s some part of your memory that you’re afraid to even look at it, because of all it’ll cause to come surging back at you. How are you going to strategize your life here?
Fortunately, McKenna is here to guide you through doing for your mind what Marie Kondo would do for your home. And, even better, McKenna does it with a simple and clear writing style, assorted diagrams, and a step-by-step approach to getting everything in order.
Give Your Mind A Spring-Cleaning With This Book From Amazon Today
Share This Post
Related Posts

What Are Nootropics, Really?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What are nootropics, really?
A nootropic is anything that functions as a cognitive enhancer—in other words, improves our brainpower.
These can be sensationalized as “smart drugs”, misrepresented excitingly in science fiction, meme-ified in the mundane (“but first, coffee”), and reframed entirely, (“exercise is the best nootropic”).
So, clearly, “nootropics” can mean a lot of different things. Let’s look at some of the main categories…
The neurochemical modulators
These are what often get called “smart drugs”. They are literally drugs (have a chemical effect on the body that isn’t found in our diet), and they affect the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as by:
- Adding more of that neurotransmitter (simple enough)
- Decreasing the rate at which we lose that neurotransmitter (re-uptake inhibitors)
- Antagonizing an unhelpful neurotransmitter (doing the opposite thing to it)
- Blocking an unhelpful neurotransmitter (stopping the receptors from receiving it)
“Unhelpful” here is relative and subjective, of course. We need all the neurotransmitters that are in our brain, after all, we just don’t need all of them all the time.
Examples: modafinil, a dopamine re-uptake inhibitor (mostly prescribed for sleep disorders), reduces the rate at which our brains scrub dopamine, resulting in a gradual build-up of dopamine that we naturally produced, so we get to enjoy that dopamine for longer. This will tend to promote wakefulness, and may also help with problem-solving and language faculties—as well as giving a mood boost. In other words, all things that dopamine is used for. Mirtazaрine, an adrenoreceptor agonist (mostly prescribed as an antidepressant), increases noradrenergic neurotransmission, thus giving many other brain functions a boost.
Why it works: our brains need healthy levels of neurotransmitters, in order to function well. Those levels are normally self-regulating, but can become depleted in times of stress or fatigue, for example.
The metabolic brain boosters
These are the kind of things that get included in nootropic stacks (stack = a collection of supplements and/or drugs that complement each other and are taken together—for example, a multivitamin tablet could be described as a vitamin stack) even though they have nothing specifically relating them to brain function. Why are they included?
The brain needs so much fuel. Metabolically speaking, it’s a gas-guzzler. It’s the single most resource-intensive organ of our body, by far. So, metabolic brain boosters tend to:
- Increase blood flow
- Increase blood oxygenation
- Increase blood general health
- Improve blood pressure (this is relative and subjective, since very obviously there’s a sweet spot)
Examples: B-vitamins. Yep, it can be that simple. A less obvious example might be Co-enzyme Q10, which supports energy production on a cellular level, and good cardiovascular health.
Why it works: you can’t have a healthy brain without a healthy heart!
We are such stuff as brains are made of
Our brains are made of mostly fat, water, and protein. But, not just any old fat and protein—we’re at least a little bit special! So, brain-food foods tend to:
- Give the brain the fats and proteins it’s made of
- Give the brain the stuff to make the fats and proteins it’s made of (simpler fats, and amino acids)
- Give the brain hydration! Just having water, and electrolytes as appropriate, does this
Examples: healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and seafood; also, a lot of phytonutrients from greens and certain fruits. Long-time subscribers may remember our article “Brain Food: The Eyes Have It!” on the importance of dietary lutein in reducing Alzheimer’s risk, for example
Why it works: this is matter of structural upkeep and maintenance—our brains don’t work fabulously if deprived of the very stuff they’re made of! Especially hydration is seriously underrated as a nootropic factor, by the way. Most people are dehydrated most of the time, and the brain dehydrates quickly. Fortunately, it rehydrates quickly as well when we take hydrating liquids.
Weird things that sound like ingredients in a witch’s potion
These are too numerous and too varied in how they work to cover here, but they do appear a lot in nootropic stacks and in popular literature on the subject.
Often they work by one of the mechanisms described above; sometimes we’re not entirely sure how they work, and have only measured their effects sufficiently to know that, somehow, they do work.
Examples: panax ginseng is one of the best-studied examples that still remains quite mysterious in many aspects of its mechanism. Lion’s Mane (the mushroom, not the jellyfish or the big cat hairstyle), meanwhile, is known to contain specific compounds that stimulate healthy brain cell growth.
Why it works: as we say, it varies so much from on ingredient to another in this category, so… Watch out for our Research Review Monday features, as we’ll be covering some of these in the coming weeks!
(PS, if there’s any you’d like us to focus on, let us know! We always love to hear from you. You can hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Viruses aren’t always harmful. 6 ways they’re used in health care and pest control
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We tend to just think of viruses in terms of their damaging impacts on human health and lives. The 1918 flu pandemic killed around 50 million people. Smallpox claimed 30% of those who caught it, and survivors were often scarred and blinded. More recently, we’re all too familiar with the health and economic impacts of COVID.
But viruses can also be used to benefit human health, agriculture and the environment.
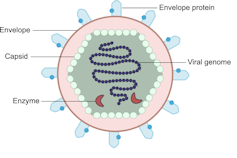
Viruses are comparatively simple in structure, consisting of a piece of genetic material (RNA or DNA) enclosed in a protein coat (the capsid). Some also have an outer envelope.
Viruses get into your cells and use your cell machinery to copy themselves.
Here are six ways we’ve harnessed this for health care and pest control.1. To correct genes
Viruses are used in some gene therapies to correct malfunctioning genes. Genes are DNA sequences that code for a particular protein required for cell function.
If we remove viral genetic material from the capsid (protein coat) we can use the space to transport a “cargo” into cells. These modified viruses are called “viral vectors”.

Viruses consist of a piece of RNA or DNA enclosed in a protein coat called the capsid.
DEXiViral vectors can deliver a functional gene into someone with a genetic disorder whose own gene is not working properly.
Some genetic diseases treated this way include haemophilia, sickle cell disease and beta thalassaemia.
2. Treat cancer
Viral vectors can be used to treat cancer.
Healthy people have p53, a tumour-suppressor gene. About half of cancers are associated with the loss of p53.
Replacing the damaged p53 gene using a viral vector stops the cancerous cell from replicating and tells it to suicide (apoptosis).
Viral vectors can also be used to deliver an inactive drug to a tumour, where it is then activated to kill the tumour cell.
This targeted therapy reduces the side effects otherwise seen with cytotoxic (cell-killing) drugs.
We can also use oncolytic (cancer cell-destroying) viruses to treat some types of cancer.
Tumour cells have often lost their antiviral defences. In the case of melanoma, a modified herpes simplex virus can kill rapidly dividing melanoma cells while largely leaving non-tumour cells alone.
3. Create immune responses
Viral vectors can create a protective immune response to a particular viral antigen.
One COVID vaccine uses a modified chimp adenovirus (adenoviruses cause the common cold in humans) to transport RNA coding for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein into human cells.
The RNA is then used to make spike protein copies, which stimulate our immune cells to replicate and “remember” the spike protein.
Then, when you are exposed to SARS-CoV-2 for real, your immune system can churn out lots of antibodies and virus-killing cells very quickly to prevent or reduce the severity of infection.
4. Act as vaccines
Viruses can be modified to act directly as vaccines themselves in several ways.
We can weaken a virus (for an attenuated virus vaccine) so it doesn’t cause infection in a healthy host but can still replicate to stimulate the immune response. The chickenpox vaccine works like this.
The Salk vaccine for polio uses a whole virus that has been inactivated (so it can’t cause disease).
Others use a small part of the virus such as a capsid protein to stimulate an immune response (subunit vaccines).
An mRNA vaccine packages up viral RNA for a specific protein that will stimulate an immune response.
5. Kill bacteria
Viruses can – in limited situations in Australia – be used to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
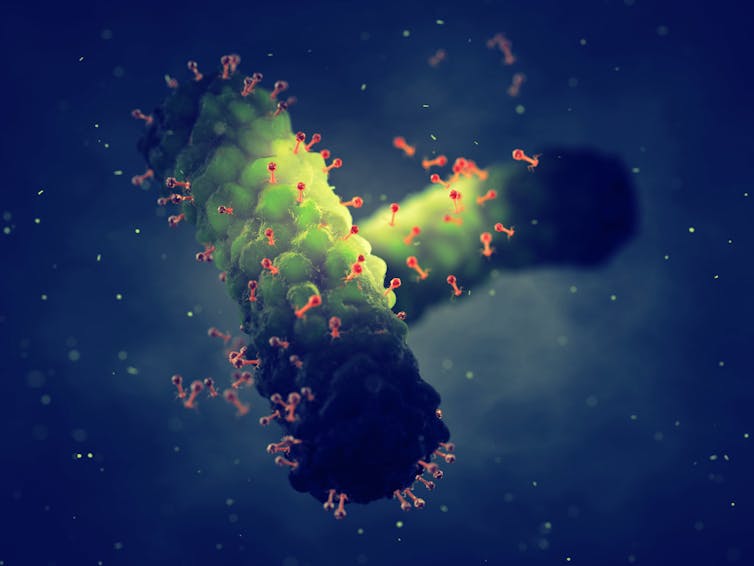
Bacteriophages are viruses that kill bacteria. Each type of phage usually infects a particular species of bacteria.
Unlike antibiotics – which often kill “good” bacteria along with the disease-causing ones – phage therapy leaves your normal flora (useful microbes) intact.

Bacteriophages (red) are viruses that kill bacteria (green).
Shutterstock6. Target plant, fungal or animal pests
Viruses can be species-specific (infecting one species only) and even cell-specific (infecting one type of cell only).
This occurs because the proteins viruses use to attach to cells have a shape that binds to a specific type of cell receptor or molecule, like a specific key fits a lock.
The virus can enter the cells of all species with this receptor/molecule. For example, rabies virus can infect all mammals because we share the right receptor, and mammals have other characteristics that allow infection to occur whereas other non-mammal species don’t.
When the receptor is only found on one cell type, then the virus will infect that cell type, which may only be found in one or a limited number of species. Hepatitis B virus successfully infects liver cells primarily in humans and chimps.
We can use that property of specificity to target invasive plant species (reducing the need for chemical herbicides) and pest insects (reducing the need for chemical insecticides). Baculoviruses, for example, are used to control caterpillars.
Similarly, bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial tomato and grapevine diseases.
Other viruses reduce plant damage from fungal pests.
Myxoma virus and calicivirus reduce rabbit populations and their environmental impacts and improve agricultural production.
Just like humans can be protected against by vaccination, plants can be “immunised” against a disease-causing virus by being exposed to a milder version.

Thea van de Mortel, Professor, Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Griffith University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: