Mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem. What should we call mental distress?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We talk about mental health more than ever, but the language we should use remains a vexed issue.
Should we call people who seek help patients, clients or consumers? Should we use “person-first” expressions such as person with autism or “identity-first” expressions like autistic person? Should we apply or avoid diagnostic labels?
These questions often stir up strong feelings. Some people feel that patient implies being passive and subordinate. Others think consumer is too transactional, as if seeking help is like buying a new refrigerator.
Advocates of person-first language argue people shouldn’t be defined by their conditions. Proponents of identity-first language counter that these conditions can be sources of meaning and belonging.
Avid users of diagnostic terms see them as useful descriptors. Critics worry that diagnostic labels can box people in and misrepresent their problems as pathologies.
Underlying many of these disagreements are concerns about stigma and the medicalisation of suffering. Ideally the language we use should not cast people who experience distress as defective or shameful, or frame everyday problems of living in psychiatric terms.
Our new research, published in the journal PLOS Mental Health, examines how the language of distress has evolved over nearly 80 years. Here’s what we found.

Generic terms for the class of conditions
Generic terms – such as mental illness, psychiatric disorder or psychological problem – have largely escaped attention in debates about the language of mental ill health. These terms refer to mental health conditions as a class.
Many terms are currently in circulation, each an adjective followed by a noun. Popular adjectives include mental, mental health, psychiatric and psychological, and common nouns include condition, disease, disorder, disturbance, illness, and problem. Readers can encounter every combination.
These terms and their components differ in their connotations. Disease and illness sound the most medical, whereas condition, disturbance and problem need not relate to health. Mental implies a direct contrast with physical, whereas psychiatric implicates a medical specialty.
Mental health problem, a recently emerging term, is arguably the least pathologising. It implies that something is to be solved rather than treated, makes no direct reference to medicine, and carries the positive connotations of health rather than the negative connotation of illness or disease.

Arguably, this development points to what cognitive scientist Steven Pinker calls the “euphemism treadmill”, the tendency for language to evolve new terms to escape (at least temporarily) the offensive connotations of those they replace.
English linguist Hazel Price argues that mental health has increasingly come to replace mental illness to avoid the stigma associated with that term.
How has usage changed over time?
In the PLOS Mental Health paper, we examine historical changes in the popularity of 24 generic terms: every combination of the nouns and adjectives listed above.
We explore the frequency with which each term appears from 1940 to 2019 in two massive text data sets representing books in English and diverse American English sources, respectively. The findings are very similar in both data sets.
The figure presents the relative popularity of the top ten terms in the larger data set (Google Books). The 14 least popular terms are combined into the remainder.
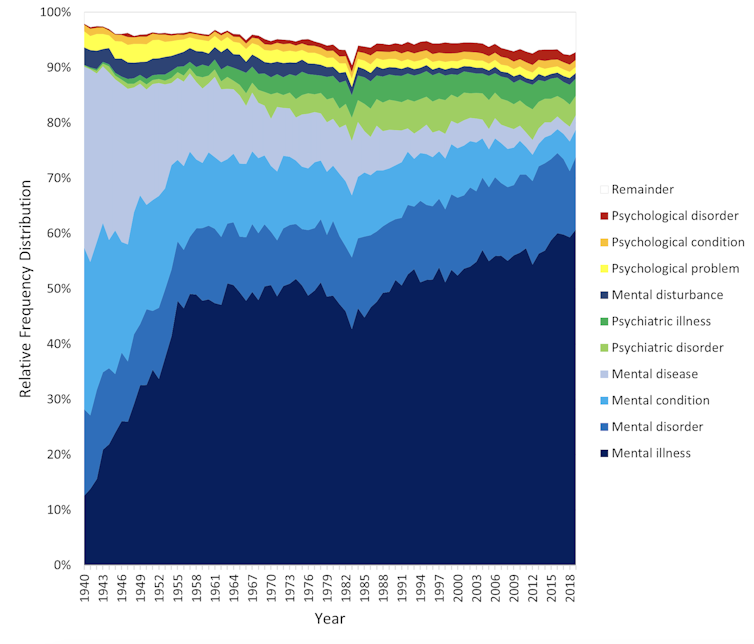
Several trends appear. Mental has consistently been the most popular adjective component of the generic terms. Mental health has become more popular in recent years but is still rarely used.
Among nouns, disease has become less widely used while illness has become dominant. Although disorder is the official term in psychiatric classifications, it has not been broadly adopted in public discourse.
Since 1940, mental illness has clearly become the preferred generic term. Although an assortment of alternatives have emerged, it has steadily risen in popularity.
Does it matter?
Our study documents striking shifts in the popularity of generic terms, but do these changes matter? The answer may be: not much.
One study found people think mental disorder, mental illness and mental health problem refer to essentially identical phenomena.
Other studies indicate that labelling a person as having a mental disease, mental disorder, mental health problem, mental illness or psychological disorder makes no difference to people’s attitudes toward them.
We don’t yet know if there are other implications of using different generic terms, but the evidence to date suggests they are minimal.

Is ‘distress’ any better?
Recently, some writers have promoted distress as an alternative to traditional generic terms. It lacks medical connotations and emphasises the person’s subjective experience rather than whether they fit an official diagnosis.
Distress appears 65 times in the 2022 Victorian Mental Health and Wellbeing Act, usually in the expression “mental illness or psychological distress”. By implication, distress is a broad concept akin to but not synonymous with mental ill health.
But is distress destigmatising, as it was intended to be? Apparently not. According to one study, it was more stigmatising than its alternatives. The term may turn us away from other people’s suffering by amplifying it.
So what should we call it?
Mental illness is easily the most popular generic term and its popularity has been rising. Research indicates different terms have little or no effect on stigma and some terms intended to destigmatise may backfire.
We suggest that mental illness should be embraced and the proliferation of alternative terms such as mental health problem, which breed confusion, should end.
Critics might argue mental illness imposes a medical frame. Philosopher Zsuzsanna Chappell disagrees. Illness, she argues, refers to subjective first-person experience, not to an objective, third-person pathology, like disease.
Properly understood, the concept of illness centres the individual and their connections. “When I identify my suffering as illness-like,” Chappell writes, “I wish to lay claim to a caring interpersonal relationship.”
As generic terms go, mental illness is a healthy option.
Nick Haslam, Professor of Psychology, The University of Melbourne and Naomi Baes, Researcher – Social Psychology/ Natural Language Processing, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rethinking Exercise: The Workout Paradox
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The notion of running a caloric deficit (i.e., expending more calories than we consume) to reduce bodyfat is appealing in its simplicity, but… we’d say “it doesn’t actually work outside of a lab”, but honestly, it doesn’t actually work outside of a calculator.
Why?
For a start, exercise calorie costs are quite small numbers compared to metabolic base rate. Our brain alone uses a huge portion of our daily calories, and the rest of our body literally never stops doing stuff. Even if we’re lounging in bed and ostensibly not moving, on a cellular level we stay incredibly busy, and all that costs (and the currency is: calories).
Since that cost is reflected in the body’s budget per kg of bodyweight, a larger body (regardless of its composition) will require more calories than a smaller one. We say “regardless of its composition” because this is true regardless—but for what it’s worth, muscle is more “costly” to maintain than fat, which is one of several reasons why the average man requires more daily calories than the average woman, since on average men will tend to have more muscle.
And if you do exercise because you want to run out the budget so the body has to “spend” from fat stores?
Good luck, because while it may work in the very short term, the body will quickly adapt, like an accountant seeing your reckless spending and cutting back somewhere else. That’s why in all kinds of exercise except high-intensity interval training, a period of exercise will be followed by a metabolic slump, the body’s “austerity measures”, to balance the books.
You may be wondering: why is it different for HIIT? It’s because it changes things up frequently enough that the body doesn’t get a chance to adapt. To labor the financial metaphor, it involves lying to your accountant, so that the compensation is not made. Congratulations: you’re committing calorie fraud (but it’s good for the body, so hey).
That doesn’t mean other kinds of exercise are useless (or worse, necessarily counterproductive), though! Just, that we must acknowledge that other forms of exercise are great for various aspects of physical health (strengthening the body, mobilizing blood and lymph, preventing disease, enjoying mental health benefits, etc) that don’t really affect fat levels much (which are decided more in the kitchen than the gym—and even in the category of diet, it’s more about what and how and when you eat, rather than how much).
For more information on metabolic balance in the context of exercise, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
- Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
- How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
- Lose Weight, But Healthily
- Build Muscle (Healthily!)
- How To Gain Weight (Healthily!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
“The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Magic of Mushrooms
“The Longevity Vitamin that’s not a vitamin” is a great tagline for what’s actually an antioxidant amino acid nutraceutical, but in this case, we’re not the ones spearheading its PR, but rather, the Journal of Nutritional Science:
Is ergothioneine a “longevity vitamin” limited in the American diet?
It can be found in all foods, to some extent, but usually in much tinier amounts than would be useful. The reason for this is that it’s synthesized by a variety of microbes (mostly fungi and actinobacteria), and enters the food chain via vegetables that are grown in soil that contain such (which is basically all soil, unless you were to go out of your way to sterilize it, or something really unusually happened).
About those fungi? That includes common popular edible fungi, where it is found quite generously. An 85g (3oz) portion of (most) mushrooms contains about 5mg of ergothioneine, the consumption of which is associated with a 16% reduced all-cause mortality:
However… Most Americans don’t eat that many mushrooms, and those polled averaged 1.1mg/day ergothioneine (in contrast with, for example, Italians’ 4.6mg/day average).
Antioxidant properties
While its antioxidant properties aren’t the most exciting quality, they are worth a mention, on account of their potency:
The biology of ergothioneine, an antioxidant nutraceutical
This is also part of its potential bid to get classified as a vitamin, because…
❝Decreased blood and/or plasma levels of ergothioneine have been observed in some diseases, suggesting that a deficiency could be relevant to the disease onset or progression❞
Source: Ergothioneine: a diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential
Healthy aging
Building on from the above, ergothioneine has been specifically identified as being associated with healthy aging and the prevention of cardiometabolic diseases:
❝An increasing body of evidence suggests ergothioneine may be an important dietary nutrient for the prevention of a variety of inflammatory and cardiometabolic diseases and ergothioneine has alternately been suggested as a vitamin, “longevity vitamin”, and nutraceutical❞
~ Dr. Bernadette Moore et al., citing more references every few words there
Source: Ergothioneine: an underrecognised dietary micronutrient required for healthy ageing?
Good for the heart = good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, “what’s good for the heart is good for the brain” is almost always true, and it appears to be so in this case, too:
❝Ergothioneine crosses the blood–brain barrier and has been reported to have beneficial effects in the brain. In this study, we discuss the cytoprotective and neuroprotective properties of ergotheioneine, which may be harnessed for combating neurodegeneration and decline during aging.❞
Source: Ergothioneine: A Stress Vitamin with Antiaging, Vascular, and Neuroprotective Roles?
Want to get some?
You can just eat a portion of mushrooms per day! But if you don’t fancy that, it is available as a supplement in convenient 1/day capsule form too.
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Antihistamines’ Generation Gap
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are You Ready For Allergy Season?
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, fall will be upon us soon, and we have a few weeks to be ready for it. A common seasonal ailment is of course seasonal allergies—it’s not serious for most of us, but it can be very annoying, and can disrupt a lot of our normal activities.
Suddenly, a thing that notionally does us no real harm, is making driving dangerous, cooking take three times as long, sex laughable if not off-the-table (so to speak), and the lightest tasks exhausting.
So, what to do about it?
Antihistamines: first generation
Ye olde antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine are probably not what to do about it.
They are small molecules that cross the blood-brain barrier and affect histamine receptors in the central nervous system. This will generally get the job done, but there’s a fair bit of neurological friendly-fire going on, and while they will produce drowsiness, the sleep will usually be of poor quality. They also tax the liver rather.
If you are using them and not experiencing unwanted side effects, then don’t let us stop you, but do be aware of the risks.
See also: Long-term use of diphenhydramine ← this is the active ingredient in Benadryl in the US and Canada, but safety regulations in many other countries mean that Benadryl has different, safer active ingredients elsewhere.
Antihistamines: later generations
We’re going to aggregate 2nd gen, 3rd gen, and 4th gen antihistamines here, because otherwise we’ll be writing a history article and we don’t have room for that. But suffice it to say, later generations of antihistamines do not come with the same problems.
Instead of going in all-guns-blazing to the CNS like first-gens, they are more specific in their receptor-targetting, resulting in negligible collateral damage:
Special shout-out to cetirizine and loratadine, which are the drugs behind half the brand names you’ll see on pharmacy shelves around most of the world these days (including many in the US and Canada).
Note that these two are very often discussed in the same sentence, sit next to each other on the shelf, and often have identical price and near-identical packaging. Their effectiveness (usually: moderate) and side effects (usually: low) are similar and comparable, but they are genuinely different drugs that just happen to do more or less the same thing.
This is relevant because if one of them isn’t working for you (and/or is creating an unwanted side effect), you might want to try the other one.
Another honorable mention goes to fexofenadine, for which pretty much all the same as the above goes, though it gets talked about less (and when it does get mentioned, it’s usually by its most popular brand name, Allegra).
Finally, one that’s a little different and also deserving of a special mention is azelastine. It was recently (ish, 2021) moved from being prescription-only to being non-prescription (OTC), and it’s a nasal spray.
It can cause drowsiness, but it’s considered safe and effective for most people. Its main benefit is not really the difference in drug, so much as the difference in the route of administration (nasal rather than oral). Because the drug is in liquid spray form, it can be absorbed through the mucus lining of the nose and get straight to work on blocking the symptoms—in contrast, oral antihistamines usually have to go into your stomach and take their chances there (we say “usually”, because there are some sublingual antihistamines that dissolve under the tongue, but they are less common.)
Better than antihistamines?
Writer’s note: at this point, I was given to wonder: “wait, what was I squirting up my nose last time anyway?”—because, dear readers, at the time I got it I just bought one of every different drug on the shelf, desperate to find something that worked. What worked for me, like magic, when nothing else had, was beclometasone dipropionate, which a) smelled delightfully of flowers, which might just be the brand I got, b) needs replacing now because I got it in March 2023 and it expired July 2024, and c) is not an antihistamine at all.
But, that brings us to the final chapter for today: systemic corticosteroids
They’re not ok for everyone (check with your doctor if unsure), and definitely should not be taken if immunocompromised and/or currently suffering from an infection (including colds, flu, COVID, etc) unless your doctor tells you otherwise (and even then, honestly, double-check).
But! They can work like magic when other things don’t. Unlike antihistamines, which only block the symptoms, systemic corticosteroids tackle the underlying inflammation, which can stop the whole thing in its tracks.
Here’s how they measure up against antihistamines:
❝The results of this systematic review, together with data on safety and cost effectiveness, support the use of intranasal corticosteroids over oral antihistamines as first line treatment for allergic rhinitis.❞
~ Dr. Robert Puy et al.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
We’ve talked before about how waist circumference is a much more useful indicator of metabolic health than BMI.
So, let’s say you’ve a bit more around the middle than you’d like, but it stubbornly stays there. What’s going on underneath what you can see, why is it going on, and how can you get it to change?
What is visceral fat?
First, let’s talk about subcutaneous fat. That’s the fat directly under your skin. Women usually have more than men, and that’s perfectly healthy (up to a point); it’s supposed to be that way. We (women) will tend to accumulate this mostly in places such as our breasts, hips, and butt, and work outwards from there. Men will tend to put it on more to the belly and face.
Side-note: if you’re undergoing (untreated) menopause, the changes in your hormone levels will tend to result in more subcutaneous fat to the belly and face too. That’s normal, and/but normal is not always good, and treatment options are great (with hormone replacement therapy, HRT, topping the list).
Visceral fat (also called visceral adipose tissue), on the other hand, is the fat of the viscera—the internal organs of the abdomen.
So, this is fat that goes under your abdominal muscles—you can’t squeeze this (directly).
So what can we do?
Famously “you can’t do spot reduction” (lose fat from a particular part of your body by focusing exercises on that area), but that’s about subcutaneous fat. There are things you can do that will reduce your visceral fat in particular.
Some of these advices you may think “that’s just good advice for losing fat in general” and it is, yes. But these are things that have the biggest impact on visceral fat.
Cut alcohol use
This is the biggie. By numerous mechanisms, some of which we’ve talked about before, alcohol causes weight gain in general yes, but especially for visceral fat.
Get better sleep
You might think that hitting the gym is most important, but this one ranks higher. Yes, you can trim visceral fat without leaving your bed (and even without getting athletic in bed, for that matter). Not convinced?
- Here’s a study of 101 people looking at sleep quality and abdominal adiposity
- Oh, and here’s a meta-analysis with 56,000 people (finding the same thing), in case that one study didn’t convince you.
So, the verdict is clear: you snooze, you lose (visceral fat)!
Tweak your diet
You don’t have to do a complete overhaul (unless you want to), but a few changes can make a big difference, especially:
- Getting more fiber (this is the biggie when it comes to diet)
- Eating less sugar (not really a surprise, but relevant to mention)
- Eat whole foods (skip the highly processed stuff)
If you’d like to learn more and enjoy videos, here’s an informative one to get you going!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tranquility by Tuesday?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
I Know How She Does It: How Successful Women Make The Most of Their Time
This is Laura Vanderkam, author of “Tranquility By Tuesday” (amongst other books). Her “thing” is spending more time on what’s important, and less on what isn’t. Sounds simple, but she’s made a career out of it, so condensed here for you are…
Laura’s 7 Keys To Productivity
Key One: Plan your weeks on Fridays
You don’t want your Monday morning to be a “James Bond intro” (where everything is already in action and you’re just along for the ride, trying to figure out what’s going on). So, take some time last thing each Friday, to plan ahead for the following week!
Key Two: Measure what matters
Whatever that means to you. Laura tracks her use of time in half-hour blocks, and likes keeping track of streaks. For her, that means running daily and keeping a log of it. She also keeps track of the books she reads. For someone else it could be music practice, or a Duolingo streak, or eating fruit each day.
On which note…
“Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen” is simpler than most nutrition trackers (where you must search for everything you eat, or scan barcodes for all ingredients).
Instead, it keeps track of whether you are having certain key health-giving foods often enough to maintain good health.
We might feature his method in a future edition of 10almonds, but for now, check the app out for yourself here:
Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on iOS / Get Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen on Android
Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen @ Nutrition Facts
Key Three: Figure out 2–3 “anchor” events for the weekend
Otherwise, it can become a bit of a haze and on Monday you find yourself thinking “where did the weekend go?”. So, plan some stuff! It doesn’t have to be anything out-of-this-world, just something that you can look forward to in advance and remember afterwards. It could be a meal out with your family, or a session doing some gardening, or a romantic night in with your partner. Whatever makes your life “living” and not passing you by!
Key Four: Tackle the toughest work first
You’ve probably heard about “swallowing frogs”. If not, there are various versions, usually attributed to Mark Twain.
Here’s one:
“If it’s your job to eat a frog, it’s best to do it first thing in the morning. And if it’s your job to eat two frogs, it’s best to eat the biggest one first.”
Top Productivity App “ToDoist” has an option for this, by the way!
Laura’s key advice here is: get the hard stuff done now! Before you get distracted or tired and postpone it to tomorrow (and then lather rinse repeat, so it never gets done)
10almonds Tip:
“But what if something’s really important but not as pressing as some less important, but more urgent tasks?”
Simple!
Set a timer (we love the Pomodoro method, by the way) and do one burst of the important-but-not-urgent task first. Then you can get to the more urgent stuff.
Repeat each day until the important-but-not-urgent task is done!
The 10almonds Team
Key Five: Use bits of time well
If, like many of us, you’ve a neverending “to read” list, use the 5–10 minute breaks that get enforced upon us periodically through the day!
- Use those few minutes before a meeting/phonecall!
- Use the time you spend waiting for public transport or riding on it!
- Use the time you spent waiting for a family member to finish doing a thing!
All those 5–10 minute bits soon add up… You might as well spend that time reading something you know will add value to your life, rather than browsing social media, for example.
Key Six: Make very short daily to-do lists
By “short”, Laura considers this “under 10 items”. Do this as the last part of your working day, ready for tomorrow. Not at bedtime! Bedtime is for winding down, not winding up
Key Seven: Have a bedtime
Laura shoots for 10:30pm, but whatever works for you and your morning responsibilities. Your morning responsibilities aren’t tied to a specific time? Lucky you, but try to keep a bedtime anyway. Otherwise, your daily rhythm can end up sliding around the clock, especially if you work from home!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
‘Naked carbs’ and ‘net carbs’ – what are they and should you count them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
According to social media, carbs come in various guises: naked carbs, net carbs, complex carbs and more.
You might be wondering what these terms mean or if all carbs are really the same. If you are into “carb counting” or “cutting carbs”, it’s important to make informed decisions about what you eat.
What are carbs?
Carbohydrates, or “carbs” for short, are one of the main sources of energy we need for brain function, muscle movement, digestion and pretty much everything our bodies do.
There are two classifications of carbs, simple and complex. Simple carbs have one or two sugar molecules, while complex carbs are three or more sugar molecules joined together. For example, table sugar is a simple carb, but starch in potatoes is a complex carb.
All carbs need to be broken down into individual molecules by our digestive enzymes to be absorbed. Digestion of complex carbs is a much slower process than simple carbs, leading to a more gradual blood sugar increase.
Fibre is also considered a complex carb, but it has a structure our body is not capable of digesting. This means we don’t absorb it, but it helps with the movement of our stool and prevents constipation. Our good gut bacteria also love fibre as they can digest it and use it for energy – important for a healthy gut.
What about ‘naked carbs’?
“Naked carbs” is a popular term usually used to refer to foods that are mostly simple carbs, without fibre or accompanying protein or fat. White bread, sugary drinks, jams, sweets, white rice, white flour, crackers and fruit juice are examples of these foods. Ultra-processed foods, where the grains are stripped of their outer layers (including fibre and most nutrients) leaving “refined carbs”, also fall into this category.
One of the problems with naked carbs or refined carbs is they digest and absorb quickly, causing an immediate rise in blood sugar. This is followed by a rapid spike in insulin (a hormone that signals cells to remove sugar from blood) and then a drop in blood sugar. This can lead to hunger and cravings – a vicious cycle that only gets worse with eating more of the same foods.
Naked carbs can make blood sugars spike then crash.
Pexels/Alexander GreyWhat about ‘net carbs’?
This is another popular term tossed around in dieting discussions. Net carbs refer to the part of the carb food that we actually absorb.
Again, fibre is not easily digestible. And some carb-rich foods contain sugar alcohols, such as sweeteners (like xylitol and sorbitol) that have limited absorption and little to no effect on blood sugar. Deducting the value of fibre and sugar alcohols from the total carbohydrate content of a food gives what’s considered its net carb value.
For example, canned pear in juice has around 12.3g of “total carbohydrates” per 100g, including 1.7g carb + 1.7g fibre + 1.9g sugar alcohol. So its net carb is 12.3g – 1.7g – 1.9g = 8.7g. This means 8.7g of the 12.3g total carbs impacts blood sugar.
The nutrition labels on packaged foods in Australia and New Zealand usually list fibre separately to carbohydrates, so the net carbs have already been calculated. This is not the case in other countries, where “total carbohydrates” are listed.
Does it matter though?
Whether or not you should care about net or naked carbs depends on your dietary preferences, health goals, food accessibility and overall nutritional needs. Generally speaking, we should try to limit our consumption of simple and refined carbs.
The latest World Health Organization guidelines recommend our carbohydrate intake should ideally come primarily from whole grains, vegetables, fruits and pulses, which are rich in complex carbs and fibre. This can have significant health benefits (to regulate hunger, improve cholesterol or help with weight management) and reduce the risk of conditions such as heart disease, obesity and colon cancer.
In moderation, naked carbs aren’t necessarily bad. But pairing them with fats, protein or fibre can slow down the digestion and absorption of sugar. This can help to stabilise blood sugar levels, prevent spikes and crashes and support personal weight management goals. If you’re managing diabetes or insulin resistance, paying attention to the composition of your meals, and the quality of your carbohydrate sources is essential.
A ketogenic (high fat, low carb) diet typically restricts carb intake to between 20 and 50g each day. But this carb amount refers to net carbs – so it is possible to eat more carbs from high-fibre sources.
Choose complex carbohydrates with lots of fibre.
ShutterstockSome tips to try
Some simple strategies can help you get the most out of your carb intake:
reduce your intake of naked carbs and foods high in sugar and white flour, such as white bread, table sugar, honey, lollies, maple syrup, jam, and fruit juice
opt for protein- and fibre-rich carbs. These include oats, sweet potatoes, nuts, avocados, beans, whole grains and broccoli
if you are eating naked carbs, dress them up with some protein, fat and fibre. For example, top white bread with a nut butter rather than jam
if you are trying to reduce the carb content in your diet, be wary of any symptoms of low blood glucose, including headaches, nausea, and dizziness
- working with a health-care professional such as an accredited practising dietitian or your GP can help develop an individualised diet plan that meets your specific needs and goals.
Correction: this article has been updated to indicate how carbohydrates are listed on food nutrition labels in Australia and New Zealand.
Saman Khalesi, Senior Lecturer and Discipline Lead in Nutrition, School of Health, Medical and Applied Sciences, CQUniversity Australia; Anna Balzer, Lecturer, Medical Science School of Health, Medical and Applied Sciences, CQUniversity Australia; Charlotte Gupta, Postdoctoral research fellow, CQUniversity Australia; Chris Irwin, Senior Lecturer in Nutrition and Dietetics, School of Health Sciences & Social Work, Griffith University, and Grace Vincent, Senior Lecturer, Appleton Institute, CQUniversity Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: