With Medical Debt Burdening Millions, a Financial Regulator Steps In to Help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When President Barack Obama signed legislation in 2010 to create the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, he said the new agency had one priority: “looking out for people, not big banks, not lenders, not investment houses.”
Since then, the CFPB has done its share of policing mortgage brokers, student loan companies, and banks. But as the U.S. health care system turns tens of millions of Americans into debtors, this financial watchdog is increasingly working to protect beleaguered patients, adding hospitals, nursing homes, and patient financing companies to the list of institutions that regulators are probing.
In the past two years, the CFPB has penalized medical debt collectors, issued stern warnings to health care providers and lenders that target patients, and published reams of reports on how the health care system is undermining the financial security of Americans.
In its most ambitious move to date, the agency is developing rules to bar medical debt from consumer credit reports, a sweeping change that could make it easier for Americans burdened by medical debt to rent a home, buy a car, even get a job. Those rules are expected to be unveiled later this year.
“Everywhere we travel, we hear about individuals who are just trying to get by when it comes to medical bills,” said Rohit Chopra, the director of the CFPB whom President Joe Biden tapped to head the watchdog agency in 2021.
“American families should not have their financial lives ruined by medical bills,” Chopra continued.
The CFPB’s turn toward medical debt has stirred opposition from collection industry officials, who say the agency’s efforts are misguided. “There’s some concern with a financial regulator coming in and saying, ‘Oh, we’re going to sweep this problem under the rug so that people can’t see that there’s this medical debt out there,’” said Jack Brown III, a longtime collector and member of the industry trade group ACA International.
Brown and others question whether the agency has gone too far on medical billing. ACA International has suggested collectors could go to court to fight any rules barring medical debt from credit reports.
At the same time, the U.S. Supreme Court is considering a broader legal challenge to the agency’s funding that some conservative critics and financial industry officials hope will lead to the dissolution of the agency.
But CFPB’s defenders say its move to address medical debt simply reflects the scale of a crisis that now touches some 100 million Americans and that a divided Congress seems unlikely to address soon.
“The fact that the CFPB is involved in what seems like a health care issue is because our system is so dysfunctional that when people get sick and they can’t afford all their medical bills, even with insurance, it ends up affecting every aspect of their financial lives,” said Chi Chi Wu, a senior attorney at the National Consumer Law Center.
CFPB researchers documented that unpaid medical bills were historically the most common form of debt on consumers’ credit reports, representing more than half of all debts on these reports. But the agency found that medical debt is typically a poor predictor of whether someone is likely to pay off other bills and loans.
Medical debts on credit reports are also frequently riddled with errors, according to CFPB analyses of consumer complaints, which the agency found most often cite issues with bills that are the wrong amount, have already been paid, or should be billed to someone else.
“There really is such high levels of inaccuracy,” Chopra said in an interview with KFF Health News. “We do not want to see the credit reporting system being weaponized to get people to pay bills they may not even owe.”
The aggressive posture reflects Chopra, who cut his teeth helping to stand up the CFPB almost 15 years ago and made a name for himself going after the student loan industry.
Targeting for-profit colleges and lenders, Chopra said he was troubled by an increasingly corporate higher-education system that was turning millions of students into debtors. Now, he said, he sees the health care system doing the same thing, shuttling patients into loans and credit cards and reporting them to credit bureaus. “If we were to rewind decades ago,” Chopra said, “we saw a lot less reliance on tools that banks used to get people to pay.”
The push to remove medical bills from consumer credit reports culminates two years of intensive work by the CFPB on the medical debt issue.
The agency warned nursing homes against forcing residents’ friends and family to assume responsibility for residents’ debts. An investigation by KFF Health News and NPR documented widespread use of lawsuits by nursing homes in communities to pursue friends and relatives of nursing home residents.
The CFPB also has highlighted problems with how hospitals provide financial assistance to low-income patients. Regulators last year flagged the dangers of loans and credit cards that health care providers push on patients, often saddling them with more debt.
And regulators have gone after medical debt collectors. In December, the CFPB shut down a Pennsylvania company for pursuing patients without ensuring the debts were accurate.
A few months before that, the agency fined an Indiana company working with medical debt for violating collection laws. Regulators said the company had “risked harming consumers by pressuring or inducing them to pay debts they did not owe.”
With their business in the crosshairs, debt collectors are warning that cracking down on credit reporting and other collection tools may prompt more hospitals and doctors to demand patients pay upfront for care.
There are some indications this is happening already, as hospitals and clinics push patients to enroll in loans or credit cards to pay their medical bills.
Scott Purcell, CEO of ACA International, said it would be wiser for the federal government to focus on making medical care more affordable. “Here we’re coming up with a solution that only takes money away from providers,” Purcell said. “If Congress was involved, there could be more robust solutions.”
Chopra doesn’t dispute the need for bigger efforts to tackle health care costs.
“Of course, there are broader things that we would probably want to fix about our health care system,” he said, “but this is having a direct financial impact on so many Americans.”
The CFPB can’t do much about the price of a prescription or a hospital bill, Chopra continued. What the federal agency can do, he said, is protect patients if they can’t pay their bills.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Daily Stoic – by Ryan Holiday & Stephen Hanselman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s this, a philosophy book in a health and productivity newsletter? Well, look at it this way: Aristotle basically wrote the “How To Win Friends And Influence People” of his day, and Plato before him wrote a book about management.
In this (chiefly modern!) book, we see what the later Stoic philosophers had to say about getting the most out of life—which is also what we’re about, here at 10almonds!
We tend to use the word “stoic” in modern English to refer to a person who is resolute in the face of hardship. The traditional meaning does encompass that, but also means a lot more: a whole, rounded, philosophy of life.
Philosophy in general is not an easy thing into which to “dip one’s toe”. No matter where we try to start, it seems, it turns out there were a thousand other things we needed to read first!
This book really gets around that. The format is:
- There’s a theme for each month
- Each month has one lesson per day
- Each daily lesson starts with some words from a renowned stoic philosopher, and then provides commentary on such
- The commentary provides a jumping-off point and serves as a prompt to actually, genuinely, reflect and apply the ideas.
Unlike a lot of “a year of…” day-by-day books, this is not light reading, by the way, and you are getting a weighty tome for your money.
But, the page-length daily lessons are indeed digestible—which, again, is what we like at 10almonds!
Share This Post
-
Mindsight – by Dr. Daniel Siegel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of books these days bear the subtitle “The New Science Of…”, but usually it’s not new, and often it’s not even science. So how does this one measure up?
- Is it new? The core ideas are mostly very old, but some of the interventions are new in presentation—and backed by relatively recent research—so we can give him this one on a technicality at least
- It is science? Yes! The author is a clinician (a psychatric clinician, specifically) and there’s nothing here that doesn’t have its foundations in robust science.
So, what’s this “mindsight”, then? Dr. Siegel wants to express to us a concept “for which no word currently exists”, so he had to make one up, to convey the idea of having a conscious awareness of what is going on in our brain, on an experiential basis. In other words: “mindfulness”. There was totally already a word for this, which he goes on to lampshade not very far into the book.
Nevertheless, we’ll forgive him a little copywriting swizzle with the title, because the content here is genuinely top-tier.
In the book, many ideas from many other pop-psychology books are covered, in useful, practical, no-nonsense fashion, laying out tools and interventions to strengthen various parts of our brain and our relationship with same.
Bottom line: this is the most comprehensive, science-centric, book on mindfulness that this reviewer has read.
Share This Post
-
Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burn, Calorie, Burn
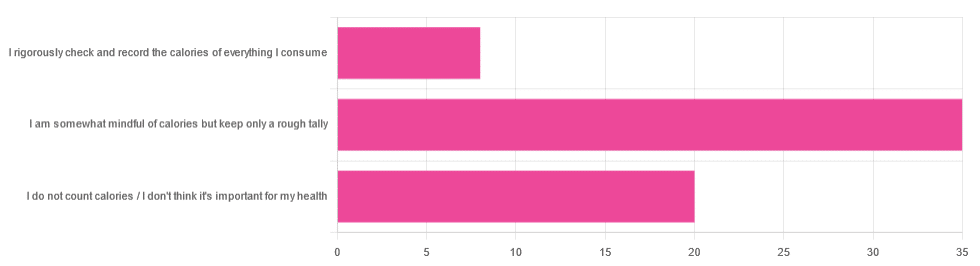
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you whether you count calories, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of answers:
- About 56% said “I am somewhat mindful of calories but keep only a rough tally”
- About 32% said “I do not count calories / I don’t think it’s important for my health”
- About 13% said “I rigorously check and record the calories of everything I consume”
So what does the science say, about the merits of all these positions?
A food’s calorie count is a good measure of how much energy we will, upon consuming the food, have to use or store: True or False?
False, broadly. It can be, at best, a rough guideline. Do you know what a calorie actually is, by the way? Most people don’t.
One thing to know before we get to that: there’s “cal” vs “kcal”. The latter is generally used when it comes to foodstuffs, and it’s what we’ll be meaning whenever we say “calorie” here. 1cal is 1/1000th of a kcal, that’s all.
Now, for what a calorie actually is:
A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃
Question: so, how to we measure how much food is needed to do that?
Answer: by using a bomb calorimeter! Which is the exciting name for the apparatus used to literally burn food and capture the heat produced to indeed raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃.
If you’re having trouble imagining such equipment, here it is:
Bomb Calorimeter: Definition, Construction, & Operation (with diagram and FAQs)
The unfortunate implication of the above information
A kilogram of sawdust contains about a 1000 kcal, give or take what wood was used and various other conditions.
However, that does not mean you can usefully eat the sawdust. In other words:
Calorie count tells us only how good something is at raising the temperature of water if physically burned.
Now do you see why oils and sugars have such comparably high calorie counts?
And while we may talk about “burning calories” as a metaphor, we do not, in fact, have a little wood stove inside us burning the food we eat.
A calorie is a calorie: True or False?
Definitely False! Building on from the above… We will get very little energy from sawdust; it’s not just that we can’t use it; we can’t store it either; it’ll mostly pass through as fiber.
(however, please do not use sawdust to get your daily dose of fiber either, as it is not safe for human consumption and may give you diseases, depending on what is lurking in it)
But let’s look at oil and sugar, two very high-calorie categories of food, because they’re really easy to physically burn and they give off a good flame.
A bomb calorimeter may treat them quite equally, but to our body, they are metabolically very different indeed.
For a start, most sugars will get absorbed and processed much more quickly than most oils, and that can overwhelm the liver (responsible for glycogen management), and lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and more. Metabolic syndrome in general, and if you keep it up too much and you may find it’s now a lottery between dying of NAFLD, diabetes, or heart disease (it’ll usually be the heart disease that kills).
See also:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Meanwhile, we know all about the different kinds of nutritional profiles that oils can have, and some can promote having high energy without putting on fat, while others can strain the heart. Not even “a fat is a fat”, so “a calorie is a calorie” doesn’t get much mileage outside of a bomb calorimeter!
See also:
A calorie-controlled / calorie-restricted diet is an effective weight loss strategy: True or False?
True, usually! Surprise!
- On the one hand: calories are a wildly imprecise way to reckon the value of food, and using them as a guide to health can be dangerously misleading
- On the other hand: the very activity of calorie-counting itself promotes mindful eating, which is very good for the health
There is a strong difference between the mind of somebody who is carefully logging their pre-bedtime piece of chocolate and reflecting on its nutritional value, vs someone who isn’t sure whether this is their second or third glass of wine, nor how much the glass contained.
So if you want to get most of the benefits of a calorie-controlled diet without counting calories, you may try taking a “mindful eating” approach to diet.
However! If you want to do this for weight loss, be aware, that you will have to practice it all the time, not just for one meal here and there.
You can read more on how to do “mindful eating” here:
Dr. Rupy Aujla: The Kitchen Doctor | Mindful Eating & Interoception
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Smart Woman’s Guide to Breast Cancer – by Dr. Jenn Simmons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s a lot more to breast cancer care than “check your breasts regularly”. Because… And then what? “Go see a doctor” obviously, but it’s a scary prospect with a lot of unknowns.
Dr. Simmons demystifies these unknowns, from both her position as an oncologist (and breast surgeon) and also her position as a breast cancer survivor herself.
What she found, upon getting to experience the patient side of things, was that the system is broken in ways she’d never considered before as a doctor.
This book is the product of the things she’s learned both within her field, and elsewhere because of realizing the former’s areas of shortcoming.
She gives a step-by-step guide, from diagnosis onwards, advising taking as much as possible into one’s own hands—especially in the categories of information and action. She also explains the things that make the biggest difference to cancer outcomes when it comes to eating, sleeping, and so forth, the best attitude to have to be neither despairing and giving up, nor overconfident and complacent.
She does also talk complementary therapies, be they supplements or more out-of-the-box approaches and the evidence for them where applicable, as well as doing some high-quality mythbusting about more prescription-based considerations such as HRT.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one have a breast cancer diagnosis, or you just prefer knowing this sort of thing than not, then this book is a top-tier “insider’s guide”.
Click here to check out the Smart Woman’s Guide To Breast Cancer, and take control!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
California Becomes Latest State To Try Capping Health Care Spending
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
California’s Office of Health Care Affordability faces a herculean task in its plan to slow runaway health care spending.
The goal of the agency, established in 2022, is to make care more affordable and accessible while improving health outcomes, especially for the most disadvantaged state residents. That will require a sustained wrestling match with a sprawling, often dysfunctional health system and powerful industry players who have lots of experience fighting one another and the state.
Can the new agency get insurers, hospitals, and medical groups to collaborate on containing costs even as they jockey for position in the state’s $405 billion health care economy? Can the system be transformed so that financial rewards are tied more to providing quality care than to charging, often exorbitantly, for a seemingly limitless number of services and procedures?
The jury is out, and it could be for many years.
California is the ninth state — after Connecticut, Delaware, Massachusetts, Nevada, New Jersey, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Washington — to set annual health spending targets.
Massachusetts, which started annual spending targets in 2013, was the first state to do so. It’s the only one old enough to have a substantial pre-pandemic track record, and its results are mixed: The annual health spending increases were below the target in three of the first five years and dropped beneath the national average. But more recently, health spending has greatly increased.
In 2022, growth in health care expenditures exceeded Massachusetts’ target by a wide margin. The Health Policy Commission, the state agency established to oversee the spending control efforts, warned that “there are many alarming trends which, if unaddressed, will result in a health care system that is unaffordable.”
Neighboring Rhode Island, despite a preexisting policy of limiting hospital price increases, exceeded its overall health care spending growth target in 2019, the year it took effect. In 2020 and 2021, spending was largely skewed by the pandemic. In 2022, the spending increase came in at half the state’s target rate. Connecticut and Delaware, by contrast, both overshot their 2022 targets.
It’s all a work in progress, and California’s agency will, to some extent, be playing it by ear in the face of state policies and demographic realities that require more spending on health care.
And it will inevitably face pushback from the industry as it confronts unreasonably high prices, unnecessary medical treatments, overuse of high-cost care, administrative waste, and the inflationary concentration of a growing number of hospitals in a small number of hands.
“If you’re telling an industry we need to slow down spending growth, you’re telling them we need to slow down your revenue growth,” says Michael Bailit, president of Bailit Health, a Massachusetts-based consulting group, who has consulted for various states, including California. “And maybe that’s going to be heard as ‘we have to restrain your margins.’ These are very difficult conversations.”
Some of California’s most significant health care sectors have voiced disagreement with the fledgling affordability agency, even as they avoid overtly opposing its goals.
In April, when the affordability office was considering an annual per capita spending growth target of 3%, the California Hospital Association sent it a letter saying hospitals “stand ready to work with” the agency. But the proposed number was far too low, the association argued, because it failed to account for California’s aging population, new investments in Medi-Cal, and other cost pressures.
The hospital group suggested a spending increase target averaging 5.3% over five years, 2025-29. That’s slightly higher than the 5.2% average annual increase in per capita health spending over the five years from 2015 to 2020.
Five days after the hospital association sent its letter, the affordability board approved a slightly less aggressive target that starts at 3.5% in 2025 and drops to 3% by 2029. Carmela Coyle, the association’s chief executive, said in a statement that the board’s decision still failed to account for an aging population, the growing need for mental health and addiction treatment, and a labor shortage.
The California Medical Association, which represents the state’s doctors, expressed similar concerns. The new phased-in target, it said, was “less unreasonable” than the original plan, but the group would “continue to advocate against an artificially low spending target that will have real-life negative impacts on patient access and quality of care.”
But let’s give the state some credit here. The mission on which it is embarking is very ambitious, and it’s hard to argue with the motivation behind it: to interject some financial reason and provide relief for millions of Californians who forgo needed medical care or nix other important household expenses to afford it.
Sushmita Morris, a 38-year-old Pasadena resident, was shocked by a bill she received for an outpatient procedure last July at the University of Southern California’s Keck Hospital, following a miscarriage. The procedure lasted all of 30 minutes, Morris says, and when she received a bill from the doctor for slightly over $700, she paid it. But then a bill from the hospital arrived, totaling nearly $9,000, and her share was over $4,600.
Morris called the Keck billing office multiple times asking for an itemization of the charges but got nowhere. “I got a robotic answer, ‘You have a high-deductible plan,’” she says. “But I should still receive a bill within reason for what was done.” She has refused to pay that bill and expects to hear soon from a collection agency.
The road to more affordable health care will be long and chock-full of big challenges and unforeseen events that could alter the landscape and require considerable flexibility.
Some flexibility is built in. For one thing, the state cap on spending increases may not apply to health care institutions, industry segments, or geographic regions that can show their circumstances justify higher spending — for example, older, sicker patients or sharp increases in the cost of labor.
For those that exceed the limit without such justification, the first step will be a performance improvement plan. If that doesn’t work, at some point — yet to be determined — the affordability office can levy financial penalties up to the full amount by which an organization exceeds the target. But that is unlikely to happen until at least 2030, given the time lag of data collection, followed by conversations with those who exceed the target, and potential improvement plans.
In California, officials, consumer advocates, and health care experts say engagement among all the players, informed by robust and institution-specific data on cost trends, will yield greater transparency and, ultimately, accountability.
Richard Kronick, a public health professor at the University of California-San Diego and a member of the affordability board, notes there is scant public data about cost trends at specific health care institutions. However, “we will know that in the future,” he says, “and I think that knowing it and having that information in the public will put some pressure on those organizations.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
USE OUR CONTENT
This story can be republished for free (details).
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vegan Eager for Milk Alternatives
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Q: Thanks for the info about dairy. As a vegan, I look forward to a future comment about milk alternatives
Thanks for bringing it up! What we research and write about is heavily driven by subscriber feedback, so notes like this really help us know there’s an audience for a given topic!
We’ll do a main feature on it, to do it justice. Watch out for Research Review Monday!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: