Macadamias vs Hazelnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing macadamias to hazelnuts, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
In terms of macros first, hazelnuts have 2x the protein, and slightly more carbs and fiber. We call this a win for hazelnuts.
When it comes to vitamins, macadamias have more of vitamins B1, B2, and B3, while hazelnuts have more of vitamins A, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and E. Notably, 28x more vitamin E, so that’s not inconsiderable. Also 10x the vitamin B9, and 5x the vitamin C, and the rest, more modest wins. In any case, clearly a strong win for hazelnuts here.
In the category of minerals, macadamias have more selenium, while hazelnuts have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Another clear win for hazelnuts.
In short, hazelnuts win in all categories. However, by all means enjoy either or both (unless you have a nut allergy, in which case, obviously don’t).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Path To Revenue – by Theresa Marcroft
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So many books about start-ups skip right over the elephant in the room: survivorship bias. Not so for Marcroft! This book contains the most comprehensive and unapologetic treatment of it we’ve seen.
Less “here’s what Steve Jobs did right and here’s what Chocolate-Teapots-For-Dogs-R-Us did wrong; don’t mess up that badly and you’ll be fine”… and more realism. Marcroft gives us a many-angled critical analytic approach. In it, she examines why many things can seem similar in both content and presentation… but can cause growth or failure (and how and why), based on more than anecdotes and luck.
The book is information-dense (taking a marketing-centric approach) and/but well-presented in a very readable format.
If we can find any criticism of the book, it’s less about what’s in it and more about what’s not in it. This can never be a “your start-up bible!” book because it’s not comprehensive. It doesn’t cover assembling your team, for example. Nor does it give a lot of attention to management, preferring to focus on strategy.
But no single book can be all things, and we highly recommend this one—the marketing advice alone is more than worth the cost of the book!
Take Your First Step Along The Path To Revenue By Checking It Out On Amazon!
Share This Post
-
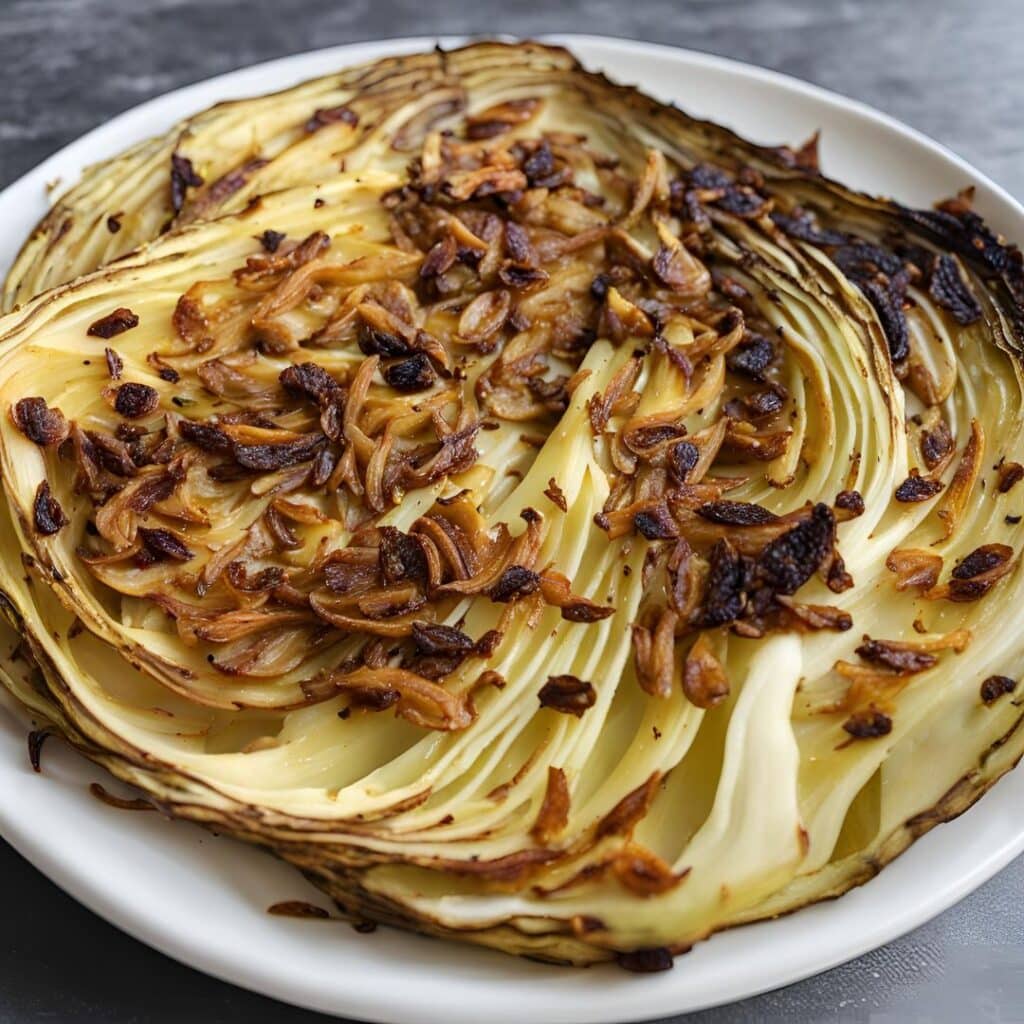
Caramelized Caraway Cabbage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cabbage is an underrated vegetable for its many nutrients and its culinary potential—here’s a great way to make it a delectable starter or respectable side.
You will need
- 1 medium white cabbage, sliced into 1″ thick slabs
- 1 tbsp extra-virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp caraway seeds
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp turmeric
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the non-cabbage ingredients in a small bowl, whisking to mix thoroughly—with a tiny whisk if you have one, but a fork will work if necessary.
3) Arrange the cabbage slices on a lined baking tray and brush the seasoning-and-oil mixture over both sides of each slice.
4) Roast for 20–25 minutes until the cabbage is tender and beginning to caramelize.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Curcumin (Turmeric) is worth its weight in gold
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Bell Peppers: A Spectrum Of Specialties
We were going to do this as part of our ongoing “This Or That?” challenge, but as there are four main types all with many different benefits, we thought this bunch of fruits deserved a main feature.
And yes, they’re botanically fruits, even if culinarily used as vegetables—much like tomatoes, famously!
They’re all the same (but also very much not)
A thing to know is that whether bell peppers be green, yellow, orange, or red, they’re all the same plant, Capiscum anuum. All that differs is how early or late they’re harvested.
Notwithstanding the “Capiscum” genus, they don’t contain capsaicin (as is found in hot peppers). Capsaicin’s a wonderful phytochemical:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
…but today we’re all about the bell peppers.
So, let’s see how they stack up!
💚 Green for lutein
Lutein is especially important for the eyes and [the rest of the] brain, to the point that there’s now an Alzheimer’s test that measures lutein concentration in the eye:
Green peppers have most of this important carotenoid, though the others all have some too. See also:
💛 Yellow for vitamin C
Yellow peppers are technically highest in vitamin C, but all of them contain far more than the daily dose per fruit already, so if there’s any color of pepper that’s nutritionally the most expendable, it’s yellow, since any other color pepper can take its place.
Watch out, though! Cooking destroys vitamin C, so if you want to get your Cs in, you’re going to want to do it raw.
🧡 Orange for zeaxanthin and cryptoxanthins
Similar in their benefits to lutein, these antioxidant carotenoids are found most generously in orange peppers (20x as much as in yellow, 10x as much as in red, and slightly more than in green).
❤️ Red for vitamins A & B6
Red peppers are richest by far in vitamin A, with one fruit giving the daily dose already. The others have about 10% of that, give or take.
Red peppers also have the most vitamin B6, though the others also have nearly as much.
❤️ Red for lycopene
We must do a main feature for lycopene sometime, as unlike a lot of antioxidant carotenoids, lycopene is found in comparatively very few foods (most famously it’s present in tomatoes).
Red is the only color of pepper to have lycopene.
10almonds tip: to get the most out of your lycopene, cook these ones!
Lycopene becomes 4x more bioavailable when cooked:
Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing ← this paper is about tomatoes but lycopene is lycopene and this applies to the lycopene in red peppers, too
And the overall winner is…
You! Because you get to eat all four of them
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Resistance Beyond Weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance, Your Way
We’ve talked before about the importance of resistance training:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And we’ve even talked about how to make resistance training more effective:
(High Intensity Interval Training, but make it High Intensity Resistance Training)
Which resistance training exercises are best?
There are two reasonable correct answers here:
- The resistance training exercises that you will actually do (because it’s no good knowing the best exercise ever if you’re not going to do it because it is in some way offputting to you)
- The resistance training exercises that will prevent you from getting a broken bone in the event of some accident or incident
This latter is interesting, because when people think resistance training, the usually immediate go-to exercises are often things like the bench press, or the chest machine in the gym.
But ask yourself: how often do we hear about some friend or relative who in their old age has broken their humerus?
It can happen, for sure, but it’s not as often as breaking a hip, a tarsal (ankle bones), or a carpal (wrist bones).
So, how can we train to make those bones strong?
Strong bones grow under strong muscles
When archaeologists dig up a skeleton from a thousand years ago, one of the occupations that’s easy to recognize is an archer. Why?
An archer has an unusual frequent exercise: pushing with their left arm while pulling with their right arm. This will strengthen different muscles on each side, and thus, increase bone density in different places on each arm. The left first metacarpal and right first and second metacarpals and phalanges are also a giveaway.
This is because: one cannot grow strong muscles on weak bones (or else the muscles would just break the bones), so training muscles will force the body to strengthen the relevant bones.
So: if you want strong bones, train the muscles attached to those bones
This answers the question of “how am I supposed to exercise my hips” etc.
Weights, bodyweight, resistance bands
If you go to the gym, there’s a machine for everything, and a member of gym staff will be able to advise which of their machines will strengthen which muscles.
If you train with free weights at home:
- Wrist curls (forearm supported and stationary, lifting a dumbbell in your hand, palm-upwards) will strengthen the wrist
- The farmer’s walk (carrying a heavy weight in each hand) will also strengthen your wrist
- A modified version of this involves holding the weight with just your fingertips, and then raising and lowering it by curling and uncurling your fingers)
- Lateral leg raises (you will need ankle-weights for this) will strengthen your ankles and your hips, as will hip abductions (as in today’s featured video), especially with a weight attached.
- Ankle raises (going up on your tip-toes and down again, repeat) while holding weights in your hands will strengthen your ankles
If you don’t like weights:
- Press-ups will strengthen your wrists
- Fingertip press-ups are even better: to do these, do your press-ups as normal, except that the only parts of your hands in contact with the ground are your fingertips
- This same exercise can be done the other way around, by doing pull-ups
- And that same “even better” works by doing pull-ups, but holding the bar only with one’s fingertips, and curling one’s fingers to raise oneself up
- Lateral leg raises and hip abductions can be done with a resistance band instead of with weights. The great thing about these is that whereas weights are a fixed weight, resistance bands will always provide the right amount of resistance (because if it’s too easy, you just raise your leg further until it becomes difficult again, since the resistance offered is proportional to how much tension the band is under).
Remember, resistance training is still resistance training even if “all” you’re resisting is gravity!
If it fells like work, then it’s working
As for the rest of preparing to get older?
Check out:
Training Mobility Ready For Later Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Physical Sunscreen or Chemical Sunscreen – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing physical sunscreens to chemical sunscreens, we picked the physical sunscreens.
Why?
It’s easy to vote against chemical sunscreens, because it has “chemical” in the name, which tends to be offputting PR-wise no matter how healthy something is.
But in this case, there’s actual science here too!
Physical sunscreens physically block the UV rays.
- On the simplest of levels, mud is a physical sunscreen, as you can see widely used by elephants, hippos, pigs, and other animals.
- On a more sophisticated level, modern physical sunscreens often use tiny zinc particles (or similar) to block the UV rays in a way that isn’t so obvious to the naked eye—so we can still see our skin, and it looks just like we applied an oil or other moisturizer.
Chemical sunscreens interact with the UV rays in a way that absorbs them.
- Specifically, they usually convert it into relatively harmless thermal energy (heat)
- However, this can cause problems if there’s too much heat!
- Additionally, chemical sunscreens can get “used up” in a way that physical sunscreens can’t* becoming effectively deactivated once the chemical reaction has run its course and there is no more reagent left unreacted.
- Worse, some of the reagents, when broken down by the UV rays, can potentially cause harm when absorbed by the skin.
*That said, physical sunscreens will still need “topping up” because we are a living organism and our body can’t resist redistributing and using stuff—plus, depending on the climate and our activities, we can lose some externally too.
Further reading
We wrote about sunscreens (of various kinds) here:
And you can also read specifically about today’s topic in more detail, here:
What’s The Difference Between Physical And Chemical Sunscreens?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Food Additive You Do Want
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Q: When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber?
A: when it’s a resistant starch. What’s it resistant to? Digestion. So, it functions as though a fiber, and by some systems, may get classified as such.
It’s a little like how sucralose is technically a sugar, but the body processes it like a fiber (but beware, because the sweetness of this disaccharide alone can trigger an insulin response anyway—dose dependent)
There may be other problems too:
But today’s not about sucralose, it’s about…
Guar gum’s surprising dietary role
You may have noticed “guar gum” on the list of ingredients of all kinds of things from baked goods to dairy products to condiments to confectionary and more.
It’s also used in cosmetics and explosives, but let’s not focus on that.
It’s used in food products as…
- a bulking agent
- a thickener
- a stabilizer
Our attention was caught by a new study, that found:
Resistant starch intake facilitates weight loss in humans by reshaping the gut microbiota
Often people think of “fiber helps weight loss” as “well yes, if you are bulking out your food with sawdust, you will eat less”, but it’s not that.
There’s an actual physiological process going on here!
We can’t digest it, but our gut microbiota can and will ferment it. See also:
Fiber against pounds: Resistant starch found to support weight loss
Beyond weight loss
Not everyone wants to lose weight, and even where weight loss is a goal, it’s usually not the only goal. As it turns out, adding guar gum into our diet does more things too:
Resistant starch supplement found to reduce liver triglycerides in people with fatty liver disease
(specifically, this was about NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
Digging a little, it seems the benefits don’t stop there either:
Diet high in guar gum fiber limits inflammation and delays multiple sclerosis symptoms
(this one was a rodent study, but still, it’s promising and it’s consistent with what one would expect based on what else we know about its function in diet)
Should we just eat foods with guar gum in as an additive?
That depends on what they are, but watch out for the other additives if you do!
You can just buy guar gum by itself, by the way (here’s an example product on Amazon).
It’s doubtlessly no fun to take as a supplement (we haven’t tried this one), but it can be baked into bread, if baking’s your thing, or just used as a thickener in recipes where ordinarily you might use cornstarch or something else.
Can I get similar benefits from other foods?
The relevant quality is also present in resistant starches in general, so you might want to check out these foods, for example:
9 Foods That Are High in Resistant Starch
You can also check out ways to increase your fiber intake in general:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: