Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat Or Burning Out?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
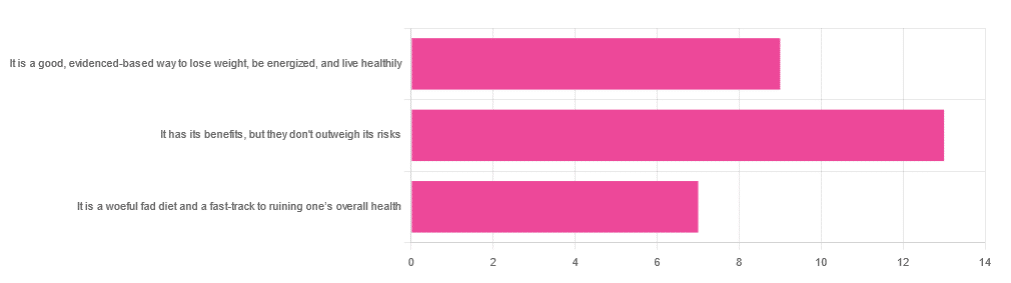
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the keto diet, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 45% said “It has its benefits, but they don’t outweigh the risks”
- About 31% said “It is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily”
- About 24% said “It is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health”
So what does the science say?
First, what is the ketogenic diet?
There are two different stories here:
- Per science, it’s a medical diet designed to help treat refractory epilepsy in children.
- Per popular lore, it’s an energizing weight loss diet for Instagrammers and YouTubers.
Can it be both? The answer is: yes, but with some serious caveats, which we’ll cover over the course of today’s feature.
The ketogenic diet works by forcing the body to burn fat for energy: True or False?
True! This is why it helps for children with refractory epilepsy. By starving the body (including the brain) of glucose, the liver must convert fat into fatty acids and ketones, which latter the brain (and indeed the rest of the body) can now use for energy instead of glucose, thus avoiding one of the the main triggers of refractory epilepsy in children.
See: The Ketogenic Diet: One Decade Later | Pediatrics
Even the pediatric epilepsy studies, however, conclude it does have unwanted side effects, such as kidney stones, constipation, high cholesterol, and acidosis:
Source: Dietary Therapies for Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet is good for weight loss: True or False?
True! Insofar as it does cause weight loss, often rapidly. Of course, so do diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not usually held to be healthy methods of weight loss. As for keto, a team of researchers recently concluded:
❝As obesity rates in the populace keep rising, dietary fads such as the ketogenic diet are gaining traction.
Although they could help with weight loss, this study had a notable observation of severe hypercholesterolemia and increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among the ketogenic diet participants.❞
~ Dr. Shadan Khdher et al.
On which note…
The ketogenic diet is bad for the heart: True or False?
True! As Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz concluded recently:
❝In terms of cardiovascular mortality, the low-carb pattern is more beneficial than very low-carbohydrate (including the ketogenic diet). There is still scarce evidence comparing ketogenic to the Mediterranean diet.
Other safety concerns in cardiovascular patients such as adverse events related to ketosis, fat-free mass loss, or potential pharmacological interactions should be also taken into consideration in future research.❞
~ Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz
Read in full: Ketogenic diet and cardiovascular risk: state of the art review
The ketogenic diet is good for short-term weight loss, but not long-term maintenance: True or False?
True! Again, insofar as it works in the short term. It’s not the healthiest way to lose weight and we don’t recommend it, but it did does indeed precipitate short-term weight loss. Those benefits are not typically observed for longer than a short time, though, as the above-linked paper mentions:
❝The ketogenic diet does not fulfill the criteria of a healthy diet. It presents the potential for rapid short-term reduction of body mass, triglycerides level, Hb1Ac, and blood pressure.
Its efficacy for weight loss and the above-mentioned metabolic changes is not significant in long-term observations.❞
~ Ibid.
The ketogenic diet is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily: True or False?
False, simply, as you may have gathered from the above, but we’ve barely scratched the surface in terms of the risks.
That said, as mentioned, it will induce short-term weight loss, and as for being energized, typically there is a slump-spike-slump in energy:
- At first, the body is running out of glucose, and so naturally feels weak and tired.
- Next, the body enters ketosis, and so feels energized and enlivened ← this is the part where the popular enthusiastic reviews come from
- Then, the body starts experiencing all the longer-term problems associated with lacking carbohydrates and having an overabundance of fat, so becomes gradually more sick and tired.
Because of this, the signs of symptoms of being in ketosis (aside from: measurably increased ketones in blood, breath, and urine) are listed as:
- Bad breath
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Increased focus and energy
- Increased fatigue and irritability
- Digestive issues
- Insomnia
The slump-spike-slump we mentioned is the reason for the seemingly contradictory symptoms of increased energy and increased fatigue—you get one and then the other.
Here’s a small but illustrative study, made clearer by its participants being a demographic whose energy levels are most strongly affected by dietary factors:
The ketogenic diet is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health: True or False?
True, subjectively in the first part, as it’s a little harsher than we usually go for in tone, though it has been called a fad diet in scientific literature. The latter part (ruining one’s overall health) is observably true.
One major problem is incidental-but-serious, which is that a low-carb diet is typically a de facto low-fiber diet, which is naturally bad for the gut and heart.
Other things are more specific to the keto diet, such as the problems with the kidneys:
However, kidney stones aren’t the worst of the problems:
Is Losing Weight Worth Losing Your Kidney: Keto Diet Resulting in Renal Failure
We’re running out of space and the risks associated with the keto diet are many, but for example even in the short term, it already increases osteoporosis risk:
❝Markers of bone modeling/remodeling were impaired after short-term low-carbohydrate high-fat diet, and only one marker of resorption recovered after acute carbohydrate restoration❞
~ Dr. Ida Heikura et al.
A Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Impairs Markers of Bone Health in Response to Exercise
Want a healthier diet?
We recommend the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
(the above is about keeping to the Mediterranean diet, while tweaking one’s choices within it for a specific extra health focus such as an anti-inflammatory upgrade, a heart-healthy upgrade, a gut-healthy upgrade, and a brain-healthy upgrade)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Millet vs Couscous – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing millet to couscous, we picked the millet.
Why?
In terms of macros, they’re pretty much equal, and are both moderately high glycemic index foods so to abate that, it’s good to have them with some fibrous foods (e.g. some vegetables) and fats (e.g. perhaps sauté the vegetables with a little olive oil), to slow down the carbs a little. But, as there’s nothing meaningful between them in this regard, we declare this category a tie.
In the category of vitamins, millet has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, K, and choline, while millet has more of vitmains B5 and E. An easy win for millet here.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story: millet has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while couscous has more calcium and selenium. Another clear win for millet.
For those avoiding gluten, you want to be aware that millet is naturally gluten-free, while couscous is usually made of durum wheat and thus contains gluten.
For those avoiding oxalates (shouldn’t make any difference for most people, but if you have certain kidney problems, then it can matter), millet is low in oxalates and couscous is high in oxalates.
All in all, it’s a clear overall win for millet!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Evidence-Based Skincare That Beats Product-Specific Hype
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A million videos on YouTube will try to sell you a 17-step skincare routine, or a 1-ingredient magical fix that’s messy and inconvenient enough you’ll do it once and then discard it. This one takes a simple, scientific approach instead.
The Basics That Count
Ali Abdaal, known for his productivity hacks channel, enlisted the help of his friend, dermatologist Dr. Usama Syed, who recommends the following 3–4 things:
- Moisturize twice per day. Skin acts as a barrier, locking in moisture and protecting against irritants. Moisturizers replenish fats and proteins, maintaining this barrier and preventing dry, inflamed, and itchy skin. He uses CeraVe, but if you have one you know works well with your skin, stick with that, because skin comes in many varieties and yours might not be like his.
- Use sunscreen every day. Your phone’s weather app should comment on your local UV index. If it’s “moderate” or above, then sunscreen is a must—even if you aren’t someone who burns easily at all, the critical thing here is avoiding UV radiation causing DNA mutations in skin cells, leading to wrinkles, dark spots, and potentially skin cancer. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen, ideally SPF 50.
- Use a retinoid. Retinoids are vitamin A-based and offer anti-aging benefits by promoting collagen growth, reducing pigmentation, and accelerating skin cell regeneration. Retinols are weaker, over-the-counter options, while stronger retinoids may require a prescription. Start gently with low dosage, whatever you choose, as initially they can cause dryness or sensitivity, before making everything better. He recommends adapalene as a starter retinoid (such as Differen gel, to give an example brand name).
- Optional: use a cleanser. Cleansers remove oils and dirt that water alone can’t. He recommends using a hydrating cleanser, to avoid stripping natural healthy oils as well as unwanted ones. That said, a cleanser is probably only beneficial if your skin tends towards the oily end of the dry-to-oily spectrum.
For more on all of these, plus an example routine, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Coffee & Your Gut
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee, in moderation, is generally considered a healthful drink—speaking for the drink itself, at least! Because the same cannot be said for added sugar, various sorts of creamers, or iced caramelatte mocha frappucino dessert-style drinks:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Caffeine, too, broadly has more pros than cons (again, in moderation):
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
Some people will be concerned about coffee and the heart. Assuming you don’t have a caffeine sensitivity (or you do but you drink decaf), it is heart-neutral in moderation, though there are some ways of preparing it that are better than others:
Make Your Coffee Heart-Healthier!
So, what about coffee and the gut?
The bacteria who enjoy a good coffee
Amongst our trillions of tiny friends, allies, associates, and enemies-on-the-inside, which ones like coffee, and what kind of coffee do they prefer?
A big (n=35,214) international multicohort analysis examined the associations between coffee consumption and very many different gut microbial species, and found:
115 species were positively associated with coffee consumption, mostly of the kind considered “friendly”, including ones often included in probiotic supplements, such as various Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species.
The kind that was most strongly associated with coffee consumption, however, was Lawsonibacter asaccharolyticus, a helpful little beast who converts chlorogenic acid (one of the main polyphenols in coffee) into caffeic acid, quinic acid, and various other metabolites that we can use.
More specifically: moderate coffee-drinkers, defined as drinking 1–3 cups per day, enjoyed a 300–400% increase in L. asaccharolyticus, while high coffee-drinkers (no, not that kind of high), defined as drinking 4 or more cups of coffee per day, enjoyed a 400–800% increase, compared to “never/rarely” coffee-drinkers (defined as drinking 2 or fewer cups per month).
Click here to see more data from the study, in a helpful infographic
Things that did not affect the outcome:
- The coffee-making method—it seems the bacteria are not fussy in this regard, as espresso or brewed, and even instant, yielded the same gut microbiome benefits
- The caffeine content—as both caffeinated and decaffeinated yielded the same gut microbiome benefits
You can read the paper itself in full for here:
Want to enjoy coffee, but not keen on the effects of caffeine or the taste of decaffeinated?
Taking l-theanine alongside coffee flattens the curve of caffeine metabolism, and means one can get the benefits without unwanted jitteriness:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
10 “Healthy” Foods That Are Often Worse Than You Think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“This is healthy, it’s a…” is an easy mistake to make if one doesn’t read the labels. Here are 10 tricksters to watch out for in particular!
Don’t be fooled by healthy aesthetics on the packaging…
Notwithstanding appearances and in many cases reputations, these all merit extra attention:
- Yogurt: sweetened yogurts, especially “fruit at the bottom / in the corner” types, often have 15–30g of sugar per serving. Plain Greek yogurt is a better choice, offering 15–20g of protein with no added sugar. You can always add fresh fruits or spices like sweet cinnamon for flavor without added sugar.
- Oatmeal: prepackaged oatmeal can contain 12–15 grams of added sugar per serving, similar to a glazed donut. Additionally, finely milled oats (as in “instant” oatmeal) can cause blood sugar spikes by itself, due to the loss of fiber. Better is plain oats, and if you like, you can sweeten them naturally with sweet cinnamon and/or fresh fruit for a healthier breakfast.
- Sushi: while sushi contains nutritious fish, it often has too much white rice (and in the US, sushi rice is also often cooked with sugar to “improve” the taste and help cohesion) and sugary sauces. This makes many rolls much less healthy. So if fish (the sashimi component of sushi) is your thing, then focus on that, and minimize sugar intake for a more balanced meal.
- Baked beans: store-bought baked beans can have up to 25g of added sugar per cup, similar to soda. Better to opt for plain beans and prepare them at home so that nothing is in them except what you personally put there.
- Deli meats: deli meats are convenient but often are more processed than they look, containing preservatives linked to health risks. Fresh, unprocessed meats like chicken or turkey breast are healthier and can still be cost-effective when bought in bulk.
- Fruit juices: fruit juices lack fiber (meaning their own natural sugars also become harmful, with no fiber to slow them down) and often contain added sugars too. Eating whole fruits is a much better way to get fiber, nutrients, and controlled healthy sugar intake.
- Hazelnut spread: hazelnut spreads are usually 50% added sugar and contain unhealthy oils like palm oil. So, skip those, and enjoy natural nut butters for healthier fats and proteins.
- Granola: granola is often loaded with added sugars and preservatives, so watch out for those.
- Sports drinks: sports drinks, with 20–25g of added sugar per serving, are unnecessary and unhelpful (except, perhaps, in case of emergency for correcting diabetic hypoglycemia). Stick to water or electrolyte drinks—and even in the latter case, check the labels for added sugar and excessive sodium!
- Dark chocolate: dark chocolate with 80% or more cocoa has health benefits but still typically contains a lot of added sugar. Check labels carefully!
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You’ve Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Cucumbers To Kindles
Q: Where do I get cucumber extract?
A: You can buy it from BulkSupplements.com (who, despite their name, start at 100g packs)
Alternatively: you want it as a topical ointment (for skin health) rather than as a dietary supplement (for bone and joint health), you can extract it yourself! No, it’s not “just juice cucumbers”, but it’s also not too tricky.
Click Here For A Quick How-To Guide!
Q: Tips for reading more and managing time for it?
A: We talked about this a little bit in yesterday’s edition, so you may have seen that, but aside from that:
- If you don’t already have one, consider getting a Kindle or similar e-reader. They’re very convenient, and also very light and ergonomic—no more wrist strain as can occur with physical books. No more eye-strain, either!
- Consider making reading a specific part of your daily routine. A chapter before bed can be a nice wind-down, for instance! What’s important is it’s a part of your day that’ll always, or at least almost always, allow you to do a little reading.
- If you drive, walk, run, or similar each day, a lot of people find that’s a great time to listen to an audiobook. Please be safe, though!
- If your lifestyle permits such, a “reading retreat” can be a wonderful vacation! Even if you only “retreat” to your bedroom, the point is that it’s a weekend (or more!) that you block off from all other commitments, and curl up with the book(s) of your choice.
Q: Any study tips as we approach exam season? A lot of the productivity stuff is based on working life, but I can’t be the only student!
A: We’ve got you covered:
- Be passionate about your subject! We know of no greater study tip than that.
- Find a willing person and lecture them on your subject. When one teaches, two learn!
- Your mileage may vary depending on your subject, but, find a way of studying that’s fun to you!
- If you can get past papers, get as many as you can, and use those as your “last minute” studying in the week before your exam(s). This will prime you for answering exam-style questions (and leverage state-dependent memory). As a bonus, it’ll also help ease any anxiety, because by the time of your exam it’ll be “same old, same old”!
Q: Energy drinks for biohacking, yea or nay?
A: This is definitely one of those “the dose makes the poison” things!
- Caffeine, in and of itself, can be healthy in moderation for most people.
- Taurine has assorted benefits at safe dosages:
- Other ingredients often have health benefits too.
But… The generally agreed safe dose of taurine is around 3g/day for most people; a standard Red Bull contains 1g.
That math would be simple, but… if you eat meat (including poultry or fish), that can also contain 10–950mg per 100g. For example, tuna is at the high end of that scale, with a standard 12oz (340g) tin already containing up to 3.23g of taurine!
And sweetened carbonated beverages in general have so many health issues that it’d take us a full article to cover them.
Short version? Enjoy in moderation if you must, but there are definitely better ways of getting the benefits they may offer.
Q: Best morning routine?
A: The best morning routine is whatever makes you feel most ready to take on your day!
This one’s going to vary a lot—one person’s morning run could be another person’s morning coffee and newspaper, for example.
In a nutshell, though, ask yourself these questions:
- How long does it take me to fully wake up in the morning, and what helps or hinders that?
- When I get out of bed, what do I really need before I can take on my day?
- If I could have the perfect morning, what would it look like?
- What can evening me do, to look after morning me’s best interests? (Semi-prepare breakfast ready? Lay out clothes ready? Running shoes? To-Do list?)
Q: I’m curious how much of these things you actually use yourselves, and are there any disagreements in the team? In a lot of places things can get pretty heated when it’s paleo vs vegan / health benefits of tea/coffee vs caffeine-abstainers / you need this much sleep vs rise and grinders, etc?
A: We are indeed genuinely enthusiastic about health and productivity, and that definitely includes our own! We may or may not all do everything, but between us, we probably have it all covered. As for disagreements, we’ve not done a survey, but if you take an evidence-based approach, any conflict will tend to be minimized. Plus, sometimes you can have the best of both!
- You could have a vegan paleo diet (you’d better love coconut if you do, though!
- There is decaffeinated coffee and tea (your taste may vary)
- You can get plenty of sleep and rise early (so long as an “early to bed, early to rise” schedule suits you!)
Interesting note: humans are social creatures on an evolutionary level. Evolution has resulted in half of us being “night owls” and the other half “morning larks”, the better to keep each other safe while sleeping. Alas, modern life doesn’t always allow us to have the sleep schedule that’d suit each of us best individually!
Have a question you’d like answered? Reply to this email, or use the feedback widget at the bottom! We always love to hear from you
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Language Fluency Beats General Intelligence & Memory For Longevity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
And no, it doesn’t have to be a second language, although that helps a lot:
An Underrated Tool Against Alzheimer’s ← you don’t even have to learn the second language to a high level, to benefit
Rather, what we’re talking about today is your first language fluency. So, for most of our readers, English. For the study participants it was German, because this was a German research team using data from the German population.
The Berlin Aging Study
Previous research has linked intelligence to longevity, but intelligence comprises multiple traits. So, what’s most important? Memory? General intelligence? Nope. Language fluency!
Let’s clarify something before we continue: “fluency” does not, in linguistics, mean what most people use it to mean. It’s not about the size of one’s overall knowledge of the language (e.g. vocabulary size), but rather, it is about one’s ability to speak and/or write fluently—literally, fluently means “flowingly”, i.e. without undue hesitation or difficulty.
The study used data from the Berlin Aging Study, which tracked 516 people aged 70–105 from 1989 onwards.
Researchers assessed four cognitive abilities, with two kinds of tests for each of:
- Verbal fluency (detailed description below)
- Perceptual speed (pattern-recognition speed)
- Verbal knowledge (vocabulary size)
- Episodic memory (personal memory recall)
General intelligence, meanwhile, was assessed as “the average of those 8 scores”.
The two tests for the cognitive ability of “verbal fluency” were:
Categories
Participants had to name as many different animals as possible within 90 seconds. Their answers were subsequently rated for correctness by two independent research assistants, to assure that noticed or unnoticed repetitions, wrong categories, and morphological variants were not coded as correct.
Word beginnings
Participants were asked to name as many different real words starting with the letter s as possible within 90 seconds. The named words were rated for correctness by two independent research assistants to avoid considering repetitions, morphological variants, and wrong words as correct.
You can read about these and the other tests for the other cognitive abilities, in the paper itself:
Verbal Fluency Selectively Predicts Survival in Old and Very Old Age ← if you’re looking for the test descriptions, scroll to “Method” and then scroll past the table, and you’ll see the test descriptions
They found that of all these metrics, only the two verbal fluency tests (and none of the other tests) showed a significant link to longevity.
Why this is important
Although the study does not prove causality (it could be that people who are predisposed to live longer for other reasons are more verbally fluent because of some common factor that influences both language fluency and longevity), it seems as good a reason as any to develop and maintain language fluency.
This builds on what was found in “The Nun Study“, that followed a convent of nuns (because they are a very homogenous sample in terms of occupation, location, diet, routine, etc, so a lot of confounding factors were already controlled-for) and made numerous major discoveries about things that impact aging (including the relevance of the APOE4 gene! That was The Nun Study).
When it came to nuns and language…
Based on the autobiographies written by the nuns in their youth upon taking their vows, there were two factors that were later correlated with not getting dementia:
- Longer sentences
- Positive outlook
- “Idea density”
That latter item means the relative linguistic density of ideas and complexity thereof, and the fluency and vivacity with which they were expressed (this was not a wishy-washy assessment; there was a hard-science analysis to determine numbers).
Want to spruce up yours? You might like to check out:
Reading, Better: Reading As A Cognitive Exercise
…for specific, evidence-based ways to tweak your reading to fight cognitive decline.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: