It Didn’t Start with You – by Mark Wolynn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is a trend in psychology to “blame the parents” for “childhood trauma” that can result in problems later in life. Sometimes fairly, sometimes not. This book’s mostly not about that.
It does touch on our own childhood trauma, if applicable. But mostly, it’s about epigenetic trauma inheritance. In other words, not just trauma that’s passed on in terms of “the cycle of abuse”, but trauma that’s passed on in terms of “this generation experienced trauma x, developed trauma response y, encoded it epigenetically, and passed it on to their offspring”.
So, how does one heal from a trauma one never directly experienced, and just inherited the response to it? That’s what most of this book is about, after establishing how epigenetic trauma inheritance works.
The author, a therapist, provides practical advice for how to do the things that can be done to rewrite the epigenetic code we inherited. Better late than never!
Bottom line: it is well-established that trauma is inheritable. But unlike one’s eye color or the ability to smell asparagus metabolites in urine, we can rewrite epigenetic things, to a degree. This book explains how.
Click here to check out It Didn’t Start With You, and put things to rest!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why do some people’s hair and nails grow quicker than mine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Throughout recorded history, our hair and nails played an important role in signifying who we are and our social status. You could say, they separate the caveman from businessman.
It was no surprise then that many of us found a new level of appreciation for our hairdressers and nail artists during the COVID lockdowns. Even Taylor Swift reported she cut her own hair during lockdown.
So, what would happen if all this hair and nail grooming got too much for us and we decided to give it all up. Would our hair and nails just keep on growing?
The answer is yes. The hair on our head grows, on average, 1 centimeter per month, while our fingernails grow an average of just over 3 millimetres.
When left unchecked, our hair and nails can grow to impressive lengths. Aliia Nasyrova, known as the Ukrainian Rapunzel, holds the world record for the longest locks on a living woman, which measure an impressive 257.33 cm.
When it comes to record-breaking fingernails, Diana Armstrong from the United States holds that record at 1,306.58 cm.
Most of us, however, get regular haircuts and trim our nails – some with greater frequency than others. So why do some people’s hair and nails grow more quickly?
Jari Lobo/Pexels Remind me, what are they made out of?
Hair and nails are made mostly from keratin. Both grow from matrix cells below the skin and grow through different patterns of cell division.
Nails grow steadily from the matrix cells, which sit under the skin at the base of the nail. These cells divide, pushing the older cells forward. As they grow, the new cells slide along the nail bed – the flat area under the fingernail which looks pink because of its rich blood supply.
Nails, like hair, are made mostly of keratin. Scott Gruber/Unsplash A hair also starts growing from the matrix cells, eventually forming the visible part of the hair – the shaft. The hair shaft grows from a root that sits under the skin and is wrapped in a sac known as the hair follicle.
This sac has a nerve supply (which is why it hurts to pull out a hair), oil-producing glands that lubricate the hair and a tiny muscle that makes your hair stand up when it’s cold.
At the follicle’s base is the hair bulb, which contains the all-important hair papilla that supplies blood to the follicle.
Matrix cells near the papilla divide to produce new hair cells, which then harden and form the hair shaft. As the new hair cells are made, the hair is pushed up above the skin and the hair grows.
But the papilla also plays an integral part in regulating hair growth cycles, as it sends signals to the stem cells to move to the base of the follicle and form a hair matrix. Matrix cells then get signals to divide and start a new growth phase.
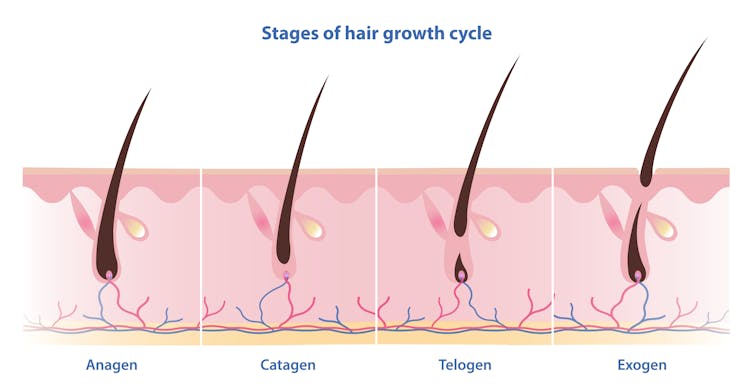
Unlike nails, our hair grows in cycles
Scientists have identified four phases of hair growth, the:
- anagen or growth phase, which lasts between two and eight years
- catagen or transition phase, when growth slows down, lasting around two weeks
- telogen or resting phase, when there is no growth at all. This usually lasts two to three months
- exogen or shedding phase, when the hair falls out and is replaced by the new hair growing from the same follicle. This starts the process all over again.
Hair follicles enter these phases at different times so we’re not left bald. Mosterpiece/Shutterstock Each follicle goes through this cycle 10–30 times in its lifespan.
If all of our hair follicles grew at the same rate and entered the same phases simultaneously, there would be times when we would all be bald. That doesn’t usually happen: at any given time, only one in ten hairs is in the resting phase.
While we lose about 100–150 hairs daily, the average person has 100,000 hairs on their head, so we barely notice this natural shedding.
So what affects the speed of growth?
Genetics is the most significant factor. While hair growth rates vary between individuals, they tend to be consistent among family members.
Nails are also influenced by genetics, as siblings, especially identical twins, tend to have similar nail growth rates.
Genetics have the biggest impact on growth speed. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels But there are also other influences.
Age makes a difference to hair and nail growth, even in healthy people. Younger people generally have faster growth rates because of the slowing metabolism and cell division that comes with ageing.
Hormonal changes can have an impact. Pregnancy often accelerates hair and nail growth rates, while menopause and high levels of the stress hormone cortisol can slow growth rates.
Nutrition also changes hair and nail strength and growth rate. While hair and nails are made mostly of keratin, they also contain water, fats and various minerals. As hair and nails keep growing, these minerals need to be replaced.
That’s why a balanced diet that includes sufficient nutrients to support your hair and nails is essential for maintaining their health.
Nutrition can impact hair and nail growth. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels Nutrient deficiencies may contribute to hair loss and nail breakage by disrupting their growth cycle or weakening their structure. Iron and zinc deficiencies, for example, have both been linked to hair loss and brittle nails.
This may explain why thick hair and strong, well-groomed nails have long been associated with perception of good health and high status.
However, not all perceptions are true.
No, hair and nails don’t grow after death
A persistent myth that may relate to the legends of vampires is that hair and nails continue to grow after we die.
In reality, they only appear to do so. As the body dehydrates after death, the skin shrinks, making hair and nails seem longer.
Morticians are well aware of this phenomenon and some inject tissue filler into the deceased’s fingertips to minimise this effect.
So, it seems that living or dead, there is no escape from the never-ending task of caring for our hair and nails.
Michelle Moscova, Adjunct Associate Professor, Anatomy, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
You can’t reverse the ageing process but these 5 things can help you live longer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At this time of year many of us resolve to prioritise our health. So it is no surprise there’s a roaring trade of products purporting to guarantee you live longer, be healthier and look more youthful.
While an estimated 25% of longevity is determined by our genes, the rest is determined by what we do, day to day.
There are no quick fixes or short cuts to living longer and healthier lives, but the science is clear on the key principles. Here are five things you can do to extend your lifespan and improve your health.
1. Eat a predominantly plant-based diet
What you eat has a huge impact on your health. The evidence overwhelmingly shows eating a diet high in plant-based foods is associated with health and longevity.
If you eat more plant-based foods and less meat, processed foods, sugar and salt, you reduce your risk of a range of illnesses that shorten our lives, including heart disease and cancer.
Plant-based foods are rich in nutrients, phytochemicals, antioxidants and fibre. They’re also anti-inflammatory. All of this protects against damage to our cells as we age, which helps prevent disease.
No particular diet is right for everyone but one of the most studied and healthiest is the Mediterranean diet. It’s based on the eating patterns of people who live in countries around the Mediterranean Sea and emphases vegetables, fruits, wholegrains, legumes, nuts and seeds, fish and seafood, and olive oil.
2. Aim for a healthy weight
Another important way you can be healthier is to try and achieve a healthy weight, as obesity increases the risk of a number of health problems that shorten our lives.
Obesity puts strain on all of our body systems and has a whole myriad of physiological effects including causing inflammation and hormonal disturbances. These increase your chances of a number of diseases, including heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, diabetes and a number of cancers.
In addition to affecting us physically, obesity is also associated with poorer psychological health. It’s linked to depression, low self-esteem and stress.
One of the biggest challenges we face in the developed world is that we live in an environment that promotes obesity. The ubiquitous marketing and the easy availability of high-calorie foods our bodies are hard-wired to crave mean it’s easy to consume too many calories.
3. Exercise regularly
We all know that exercise is good for us – the most common resolution we make this time of year is to do more exercise and to get fitter. Regular exercise protects against chronic illness, lowers your stress and improves your mental health.
While one of the ways exercising helps you is by supporting you to control your weight and lowering your body fat levels, the effects are broader and include improving your glucose (blood sugar) use, lowering your blood pressure, reducing inflammation and improving blood flow and heart function.
While it’s easy to get caught up in all of the hype about different exercise strategies, the evidence suggests that any way you can include physical activity in your day has health benefits. You don’t have to run marathons or go to the gym for hours every day. Build movement into your day in any way that you can and do things that you enjoy.
4. Don’t smoke
If you want to be healthier and live longer then don’t smoke or vape.
Smoking cigarettes affects almost every organ in the body and is associated with both a shorter and lower quality of life. There is no safe level of smoking – every cigarette increases your chances of developing a range of cancers, heart disease and diabetes.
Even if you have been smoking for years, by giving up smoking at any age you can experience health benefits almost immediately, and you can reverse many of the harmful effects of smoking.
If you’re thinking of switching to vapes as a healthy long term option, think again. The long term health effects of vaping are not fully understood and they come with their own health risks.
5. Prioritise social connection
When we talk about living healthier and longer, we tend to focus on what we do to our physical bodies. But one of the most important discoveries over the past decade has been the recognition of the importance of spiritual and psychological health.
People who are lonely and socially isolated have a much higher risk of dying early and are more likely to suffer from heart disease, stroke, dementia as well as anxiety and depression.
Although we don’t fully understand the mechanisms, it’s likely due to both behavioural and biological factors. While people who are more socially connected are more likely to engage in healthy behaviours, there also seems to be a more direct physiological effect of loneliness on the body.
So if you want to be healthier and live longer, build and maintain your connections to others.
Hassan Vally, Associate Professor, Epidemiology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To)
A subscriber recently requested:
❝Request: more people need to be aware of suicidal tendencies and what they can do to ward them off❞
…and we said we’d do that one of these Psychology Sundays, so here we are, doing it!
First of all, we’ll mention that we did previously do a main feature on managing depression (in oneself or a loved one); here it is:
The Mental Health First Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Now, not all depression leads to suicidality, and not all suicide is pre-empted by depression, but there’s a large enough crossover that it seems sensible to put that article here, for anyone who might find it of use, or even just of interest.
Now, onwards, to the specific, and very important, topic of suicide.
This should go without saying, but some of today’s content may be a little heavy.
We invite you to read it anyway if you’re able, because it’s important stuff that we all should know, and not talking about it is part of what allows it to kill people.
So, let’s take a deep breath, and read on…
The risk factors
Top risk factors for suicide include:
- Not talking about it
- Having access to a firearm
- Having a plan of specifically how to commit suicide
- A lack of social support
- Being male
- Being over 40
Now, some of these are interesting sociologically, but aren’t very useful practically; what a convenient world it’d be if we could all simply choose to be under 40, for instance.
Some serve as alarm bells, such as “having a plan of specifically how to commit suicide”.
If someone has a plan, that plan’s never going to disappear entirely, even if it’s set aside!
(this writer is deeply aware of the specifics of how she has wanted to end things before, and has used the advice she gives in this article herself numerous times. So far so good, still alive to write about it!)
Specific advices, therefore, include:
Talk about it / Listen
Depending on whether it’s you or someone else at risk:
- Talk about it, if it’s you
- Listen attentively, if it’s someone else
There are two main objections that you might have at this point, so let’s look at those:
“I have nobody to talk to”—it can certainly feel that way, sometimes, but you may be surprised who would listen if you gave them the chance. If you really can’t trust anyone around you, there are of course suicide hotlines (usually per area, so we’ll not try to list them here; a quick Internet search will get you what you need).
If you’re worried it’ll result in bad legal/social consequences, check their confidentiality policy first:
- Some hotlines can and will call the police, for instance.
- Others deliberately have a set-up whereby they couldn’t even trace the call if they wanted to.
- On the one hand, that means they can’t intervene
- On the other hand, that means they’re a resource for anyone who will only trust a listener who can’t intervene.
“But it is just a cry for help”—then that person deserves help. What some may call “attention-seeking” is, in effect, care-seeking. Listen, without judgement.
Remove access to firearms, if applicable and possible
Ideally, get rid of them (safely and responsibly, please).
If you can’t bring yourself to do that, make them as inconvenient to get at as possible. Stored securely at your local gun club is better than at home, for example.
If your/their plan isn’t firearm-related, but the thing in question can be similarly removed, remove it. You/they do not need that stockpile of pills, for instance.
And of course you/they could get more, but the point is to make it less frictionless. The more necessary stopping points between thinking “I should just kill myself” and being able to actually do it, the better.
Have/give social support
What do the following people have in common?
- A bullied teenager
- A divorced 40-something who just lost a job
- A lonely 70-something with no surviving family, and friends that are hard to visit
Often, at least, the answer is: the absence of a good social support network
So, it’s good to get one, and be part of some sort of community that’s meaningful to us. That could look different to a lot of people, for example:
- A church, or other religious community, if we be religious
- The LGBT+ community, or even just a part of it, if that fits for us
- Any mutual-support oriented, we-have-this-shared-experience community, could be anything from AA to the VA.
Some bonus ideas…
If you can’t live for love, living for spite might suffice. Outlive your enemies; don’t give them the satisfaction.
If you’re going to do it anyway, you might as well take the time to do some “bucket list” items first. After all, what do you have to lose? Feel free to add further bucket list items as they occur to you, of course. Because, why not? Before you know it, you’ve postponed your way into a rich and fulfilling life.
Finally, some gems from Matt Haig’s “The Comfort Book”:
- “The hardest question I have been asked is: “How do I stay alive for other people if I have no one?” The answer is that you stay alive for other versions of you. For the people you will meet, yes, but also the people you will be.”
- “Stay for the person you will become”
- “You are more than a bad day, or week, or month, or year, or even decade”
- “It is better to let people down than to blow yourself up”
- “Nothing is stronger than a small hope that doesn’t give up”
- “You are here. And that is enough.”
You can find Matt Haig’s excellent “The Comfort Book” on Amazon, as well as his more well-known book more specifically on the topic we’ve covered today, “Reasons To Stay Alive“.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
For tennis star Destanee Aiava, borderline personality disorder felt like ‘a death sentence’ – and a relief. What is it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Last week, Australian Open player Destanee Aiava revealed she had struggled with borderline personality disorder.
The tennis player said a formal diagnosis, after suicidal behaviour and severe panic attacks, “was a relief”. But “it also felt like a death sentence because it’s something that I have to live with my whole life”.
A diagnosis is often associated with therapeutic nihilism. This means it’s viewed as impossible to treat, and can leave clinicians and people with the condition in despair.
In fact, people with this disorder can and do recover with adequate support. Understanding it is caused by trauma is fundamental to effectively treat this complex and poorly understood mental illness.
A stigmatising diagnosis
The name “borderline personality disorder” is confusing and adds greatly to the stigma around it.
Doctors first used “borderline” to describe a condition they believed was in-between two others: neurosis and psychosis.
But this implies the condition is not real in itself, and can invalidate the suffering and distress the person and their loved ones experience.
“Personality disorder” is a judgemental term that describes the very essence of a person – their personality – as flawed.
What is borderline personality disorder?
People with the disorder can express a range of symptoms, but high levels of anxiety – including panic attacks – are usually constant.
Symptoms cluster around four main areas:
- high impulsivity (leading to suicidal thoughts and behaviour, self-harm and other risky behaviours)
- unstable or poor sense of self (including low self-esteem)
- mood disturbances (including intense, inappropriate anger, episodic depression or mania)
- problems in relationships.
People with the disorder greatly fear being abandoned and as a result, commonly have distressing difficulties in interpersonal relationships.
This creates a “push-pull” dynamic with loved ones, as people with borderline personality disorder seek closeness, but push away those they love to test the strength of the relationship.
For example, they may escalate a small issue into a major disagreement to see if the loved one will “stick with them” and reinforce their love.
Conversely, if a loved one appears distant or fed up – for example, is thinking about ending the relationship – the person with borderline personality disorder will make major efforts to “pull” them back. This might look like a flurry of messages, expressions of despair, or even suicidal behaviours.
People with borderline personality disorder greatly fear being abandoned, making relationship issues common. Drazen Zigic/Shutterstock Who does it affect?
The disorder affects one in 100 Australians, although this is likely a conservative estimate, as diagnosis is based on the most severe symptoms.
Women are much more likely to be diagnosed with it than men – but why this is so remains a major debate, with political and sociological factors playing a role in making psychiatric diagnoses. Symptoms usually begin in the mid to late teens.
While an initial response to receiving a diagnosis can be comforting for some, it is commonly seen as a chronic, relapsing condition, meaning symptoms can return after a period of improvement.
Borderline personality disorder can fluctuate in intensity and mimic other conditions such as major depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders and psychosis.
Estimates suggest 26% of presentations at emergency departments for mental health issues are by people diagnosed with personality disorders, particularly borderline personality disorder.
What causes it?
The main cause for borderline personality disorder appears to be trauma in early life, compounded by repeated traumas later.
Early life trauma can lead to biological changes in the brain that cause behavioural, emotional or cognitive shifts, leading to social and relationship issues. This is known as complex post-traumatic stress disorder.
Aiava has acknowledged the disorder is “mainly from childhood trauma”, although she has not given details about her specific experiences.
People with borderline personality disorder usually have complex post-traumatic stress disorder. But complex post-traumatic stress disorder doesn’t always result in a borderline personality disorder diagnosis.
Although the two disorders are not identical, they share many similarities, in particular that they are both caused by complex and repeated trauma.
However those with borderline personality disorder tend to experience more rage, emotional disturbances and have a greater fear of abandonment.
They also face greater stigma, whereas the term “complex post-traumatic stress disorder” doesn’t carry the same negative connotations and focuses on the cause of the condition – trauma – rather than “personality”, leading to better treatment options.
The recognition of the major role of trauma in borderline personality disorder is an important step forward in treating the disorder. But because of the stigma associated with it, using the diagnosis of complex post-traumatic stress disorder maybe a better step forward in the future.
Can it be treated?
There are many effective psychological therapies and other treatments for people with borderline personality disorder or complex post-traumatic stress disorder.
For example, dialectical behavioural therapy is a type of cognitive therapy that helps people learn skills such as tolerating distress, managing relationships, regulating emotions and practising mindfulness.
The treatment of people with post-traumatic stress disorder, including victims of war and rape, has taught us a lot about how to treat complex, underlying trauma. For example, with trauma-focused psychological therapies.
Other new treatments, such as eye movement desensitisation and reprogramming, have also shown to be effective.
Many people with borderline personality disorder who receive treatment and have supportive relationships are able to “outgrow” the condition. Others may need to continue to manage symptoms while pursuing a good quality of life.
Treating trauma, not personality
Rethinking borderline personality disorder as a trauma disorder enables a more effective and understanding approach for those with it.
Understanding what trauma does to the brain means newer, targeted medications can also be used.
For example, our research has shown how the brain’s glutamate system – the chemicals responsible for learning and making sense of one’s environment – is overactive in people with complex post-traumtic stress disorder. Medications that work on the glutumate system may therefore help alleviate borderline personality disorder symptoms.
Educating partners and families about borderline personality disorder, providing them support and co-designing crisis strategies are also important parts of total care. Preventing early life trauma is also critical.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14.
Jayashri Kulkarni, Professor of Psychiatry, Monash University and Eveline Mu, Research Fellow in Women’s Mental Health, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Older adults need another COVID-19 vaccine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- The CDC recommends people 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine.
- Updated COVID-19 vaccines are effective at protecting against severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
- The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19.
Last week, the CDC said people 65 and older should receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring. The recommendation also applies to immunocompromised people, who were already eligible for an additional dose.
Older adults made up two-thirds of COVID-19-related hospitalizations between October 2023 and January 2024, so enhancing protection for this group is critical.
The CDC also shortened the isolation period for people who are sick with COVID-19, although the contagiousness of COVID-19 has not changed.
Read on to learn more about the CDC’s updated vaccination and isolation recommendations.
Who is eligible for another COVID-19 vaccine this spring?
The CDC recommends that people ages 65 and older and immunocompromised people receive an additional dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccine this spring—if at least four months have passed since they received a COVID-19 vaccine. It’s safe to receive an updated COVID-19 vaccine from Pfizer, Moderna, or Novavax, regardless of which COVID-19 vaccines you received in the past.
Updated COVID-19 vaccines are available at pharmacies, local clinics, or doctor’s offices. Visit Vaccines.gov to find an appointment near you.
Under- and uninsured adults can get the updated COVID-19 vaccine for free through the CDC’s Bridge Access Program. If you’re over 60 and unable to leave your home, call the Aging Network at 1-800-677-1116 to learn about free at-home vaccination options.
What are the benefits of staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines?
Staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines prevents severe illness, hospitalization, death, and long COVID.
Additionally, the CDC says staying up to date on COVID-19 vaccines is a safer and more reliable way to build protection against COVID-19 than getting sick from COVID-19.
What are the new COVID-19 isolation guidelines?
According to the CDC’s general respiratory virus guidance, people who are sick with COVID-19 or another common respiratory illness, like the flu or RSV, should isolate until they’ve been fever-free for at least 24 hours without the use of fever-reducing medication and their symptoms improve.
After that, the CDC recommends taking additional precautions for the next five days: wearing a well-fitting mask, limiting close contact with others, and improving ventilation in your home if you live with others.
If you’re sick with COVID-19, you can infect others for five to 12 days, or longer. Moderately or severely immunocompromised patients may remain infectious beyond 20 days.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Redcurrants vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing redcurrants to cranberries, we picked the redcurrants.
Why?
First know: here we’re comparing raw redcurrants to raw cranberries, with no additives in either case. If you buy jelly made from either, or if you buy dried fruits but the ingredients list has a lot of added sugar and often some vegetable oil, then that’s going to be very different. But for now… Let’s look at just the fruits:
In terms of macros, redcurrants are higher in carbs, but also higher in fiber, and have the lower glycemic index as cranberries have nearly 2x the GI.
When it comes to vitamins, redcurrants have more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, C, K, and choline, while cranberries have more of vitamins A, B5, and E. In other words, a clear win for redcurrants.
In the category of minerals, redcurrants sweep even more convincingly with a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, cranberries boast a little more manganese; they also have about 2x the sodium.
Both berries have generous amounts of assorted phytochemicals (flavonoids and others), and/but nothing to set one ahead of the other.
As per any berries that aren’t poisonous, both of these are fine choices for most people most of the time, but redcurrants win with room to spare in most categories.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: