I Will Make You Passionate About Exercise – by Bevan Eyles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this isn’t: a “just do it!” motivational pep-talk.
What this is:a compassionate and thoughtful approach to help non-exercisers become regular exercisers, by looking at the real life factors of what holds people back (learning from his own early failures as a coach, by paying attention now to things he inadvertently neglected back then), both in the material/practical and in the psychological/emotional.
Further, he gives a 10-step method, for those who would like to be walked through it by the hand, making the transition to exercising regularly (and as a leisure habit, rather than as a chore) as frictionless as possible.
The style is friendly and energetic, and very easy-reading throughout.
Bottom line: if you are someone who finds exercising to be a chore, this book can definitely help you “get from here to there” in terms of finding joy in it, and finding exercise even easier than not exercising. Yes, really.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make, Really?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How Much Difference Do Probiotic Supplements Make?
There are three main things that get talked about with regard to gut health:
- Prebiotics (fibrous foods)
- Probiotics (things containing live “good” bacteria)
- Postbiotics (things to help them thrive)
Today we’ll be talking about probiotics, but if you’d like a refresher on general gut health, here’s our previous main feature:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
What bacteria are in probiotics?
There are many kinds, but the most common by far are Lactobacillus sp. and Bifidobacteria sp.
Taxonomical note: “sp.” just stands for “species”. The first name is the genus, which contains a plurality of (sometimes, many) species.
Lactobacillus acidophilus, also written L. acidophilus, is a common species of Lactobacillus sp. in probiotics.
Bifidobacterium bifidum, also written B. bifidum, is a common species of Bifidobacterium sp. in probiotics.
What difference do they make?
First, and perhaps counterintuitively, putting more bacteria into your gut has a settling effect on the digestion. In particular, probiotics have been found effective against symptoms of IBS and ulcerative colitis, (but not Crohn’s):
- Probiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review
- The role of probiotics in the prevention and treatment of IBS and other related diseases: a systematic review of randomized human clinical trials
- Safety and Potential Role of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Administration as Monotherapy in Ulcerative Colitis Patients
- Probiotics for induction of remission in Crohn’s disease
Probiotics are also helpful against diarrhea, including that caused by infections and/or antibiotics, as well as to reduce antibiotic resistance:
- Probiotics for the prevention of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults and children
- Probiotic approach to prevent antibiotic resistance
Probiotics also boost the immune system outside of the gut, too, for example reducing the duration of respiratory infections:
You may recallthe link between gut health and brain health, thanks in large part to the vagus nerve connecting the two:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
No surprises, then, that probiotics benefit mental health. See:
- The effects of probiotics on mental health and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood
- Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
There are so many kinds; which should I get?
Diversity is good, so more kinds is better. However, if you have specific benefits you’d like to enjoy, you may want to go stronger on particular strains:
Choosing an appropriate probiotic product for your patient: An evidence-based practical guide
Where can I get them?
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience.
Alternatively, you can check out today’s sponsor, who also sell such; we recommend comparing products and deciding which will be best for you
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How To Keep Warm (Without Sweat Patches!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I saw an advert on the subway for a pillow spray that guarantees a perfect night’s sleep. What does the science say about smells/sleep?❞
That is certainly a bold claim! Unless it’s contingent, e.g. “…or your money back”. Because otherwise, it absolutely cannot guarantee that.
There is some merit:
❝Odors can modulate the latency to sleep onset, as well as the quality and duration of sleep. Olfactory modulation of sleep may be mediated by direct synaptic interaction between the olfactory system and sleep control nuclei, and/or indirectly through odor modulation of arousal and respiration.
Such modulation appears most heavily influenced by past associations and expectations about the odor, beyond any potential direct physicochemical effect❞
Source: Reciprocal relationships between sleep and smell
Translating that from sciencese:
Sometimes we find pleasant smells relaxing, and placebo effect also helps.
That “any potential direct physiochemical effect”, though, when it does occur, is things like this…
Read: Odor blocking of stress hormone responses
…but that’s a mouse study, and those odors may only work to block three specific mouse stress responses to three specific stressors: physical restraint, predator odor, and male–male confrontation.
In other words: if, perchance, those three things are not what’s stressing you in bed at night (we won’t make assumptions), and/or you are not a mouse, it may not help.
(and this, dear readers, is why we must read articles, and not just headlines!)
But! If you are going to go for a pillow fragrance, something well-associated with being relaxing and soporific, such as lavender, is the way to go:
- Effects of aromatherapy on sleep quality and anxiety of patients
- Effects of Aromatherapy on the Anxiety, Vital Signs, and Sleep Quality of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Patients in Intensive Care Units
- Effect of lavender aromatherapy on vital signs and perceived quality of sleep in the intermediate care unit: a pilot study
tl;dr = patients found lavender fragrances relaxing, experienced less anxiety, got better sleep (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study) and enjoyed lower blood pressure (significantly or insignificantly, depending on the study).
PS: this writer uses a pillow spray like this one
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Water Water Everywhere, But Which Is Best To Drink?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Well Well Well…
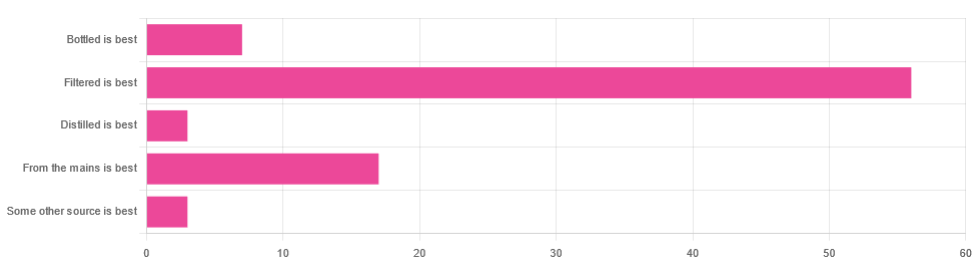
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on drinking water—with the understanding that this may vary from place to place. We got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 65% said “Filtered is best”
- About 20% said “From the mains is best”
- About 8% said “Bottled is best”
- About 3% said “Distilled is best”
- About 3% said “Some other source is best”
Of those who said “some other source is best”, one clarified that their preferred source was well water.
So what does the science say?
Fluoridated water is bad for you: True or False?
False, assuming a normal level of consumption. Rather than take up more space today though, we’ll link to what we previously wrote on this topic:
You may be wondering: but what if my level of consumption is higher than normal?
Let’s quickly look at some stats:
- The maximum permitted safety level varies from place to place, but is (for example) 2mg/l in the US, 1.5mg/l in Canada & the UK.
- The minimum recommended amount also varies from place to place, but is (for example) 0.7mg/l in Canada and the US, and 1mg/l in the UK.
It doesn’t take grabbing a calculator to realize that if you drink twice as much water as someone else, then depending on where you are, water fluoridated to the minimum may give you more than the recommended maximum.
However… Those safety margins are set so much lower than the actual toxicity levels of fluoride, that it doesn’t make a difference.
For example: your writer here takes a medication that has the side effect of causing dryness of the mouth, and consequently she drinks at least 3l of water per day in a climate that could not be described as hot (except perhaps for about 2 weeks of the year). She weighs 72kg (that’s about 158 pounds), and the toxicity of fluoride (for ill symptoms, not death) is 0.2mg/kg. So, she’d need 14.4mg of fluoride, which even if the water fluoridation here were 2mg/l (it’s not; it’s lower here, but let’s go with the highest figure to make a point), would require drinking more than 7l of water faster than the body can process it.
For more about the numbers, check out:
Acute Fluoride Poisoning from a Public Water System
Bottled water is the best: True or False?
False, if we consider “best” to be “healthiest”, which in turn we consider to be “most nutrients, with highest safety”.
Bottled water generally does have higher levels of minerals than most local mains supply water does. That’s good!
But you know what else is generally has? Microplastics and nanoplastics. That’s bad!
We don’t like to be alarmist in tone; it’s not what we’re about here, but the stats on bottled water are simply not good; see:
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
You may be wondering: “but what about bottled water that comes in glass bottles?”
Indeed, water that comes in glass bottles can be expected to have lower levels of plastic than water that comes in plastic bottles, for obvious reasons.
However, we invite you to consider how likely you believe it to be that the water wasn’t stored in plastic while being processed, shipped and stored, before being portioned into its final store-ready glass bottles for end-consumer use.
Distilled water is the best: True or False?
False, generally, with caveats:
Distilled water is surely the safest water anywhere, because you know that you’ve removed any nasties.
However, it’s also devoid of nutrients, because you also removed any minerals it contained. Indeed, if you use a still, you’ll be accustomed to the build-up of these minerals (generally simplified and referenced as “limescale”, but it’s a whole collection of minerals).
Furthermore, that loss of nutrients can be more than just a “something good is missing”, because having removed certain ions, that water could now potentially strip minerals from your teeth. In practice, however, you’d probably have to swill it excessively to cause this damage.
Nevertheless, if you have the misfortune of living somewhere like Flint, Michigan, then a water still may be a fair necessity of life. In other places, it can simply be useful to have in case of emergency, of course.
Here’s an example product on Amazon if you’d like to invest in a water still for such cases.
PS: distilled water is also tasteless, and is generally considered bad, tastewise, for making tea and coffee. So we really don’t recommend distilling your water unless you have a good reason to do so.
Filtered water is the best: True or False?
True for most people in most places.
Let’s put it this way: it can’t logically be worse than whatever source of water you put into it…
Provided you change the filter regularly, of course.
Otherwise, after overusing a filter, at best it won’t be working, and at worst it’ll be adding in bacteria that have multiplied in the filter over however long you left it there.
You may be wondering: can water filters remove microplastics, and can they remove minerals?
The answer in both cases is: sometimes.
- For microplastics it depends on the filter size and the microplastic size (see our previous article for details on that).
- For minerals, it depends on the filter type. Check out:
The H2O Chronicles | 5 Water Filters That Remove Minerals
One other thing to think about: while most water filtration jugs are made of PFAS-free BPA-free plastics for obvious reasons, for greater peace of mind, you might consider investing in a glass filtration jug, like this one ← this is just one example product on Amazon; by all means shop around and find one you like
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Accidental falls in the older adult population: What academic research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Accidental falls are among the leading causes of injury and death among adults 65 years and older worldwide. As the aging population grows, researchers expect to see an increase in the number of fall injuries and related health spending.
Falls aren’t unique to older adults. Nealy 684,000 people die from falls each year globally. Another 37.3 million people each year require medical attention after a fall, according to the World Health Organization. But adults 65 and older account for the greatest number of falls.
In the United States, more than 1 in 4 older adults fall each year, according to the National Institute on Aging. One in 10 report a fall injury. And the risk of falling increases with age.
In 2022, health care spending for nonfatal falls among older adults was $80 billion, according to a 2024 study published in the journal Injury Prevention.
Meanwhile, the fall death rate in this population increased by 41% between 2012 and 2021, according to the latest CDC data.
“Unfortunately, fall-related deaths are increasing and we’re not sure why that is,” says Dr. Jennifer L. Vincenzo, an associate professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the department of physical therapy and the Center for Implementation Research. “So, we’re trying to work more on prevention.”
Vincenzo advises journalists to write about how accidental falls can be prevented. Remind your audiences that accidental falls are not an inevitable consequence of aging, and that while we do decline in many areas with age, there are things we can do to minimize the risk of falls, she says. And expand your coverage beyond the national Falls Prevention Awareness Week, which is always during the first week of fall — Sept. 23 to 27 this year.
Below, we explore falls among older people from different angles, including injury costs, prevention strategies and various disparities. We have paired each angle with data and research studies to inform your reporting.
Falls in older adults
In 2020, 14 million older adults in the U.S. reported falling during the previous year. In 2021, more than 38,700 older adults died due to unintentional falls, according to the CDC.
A fall could be immediately fatal for an older adult, but many times it’s the complications from a fall that lead to death.
The majority of hip fractures in older adults are caused by falls, Vincenzo says, and “it could be that people aren’t able to recover [from the injury], losing function, maybe getting pneumonia because they’re not moving around, or getting pressure injuries,” she says.
In addition, “sometimes people restrict their movement and activities after a fall, which they think is protective, but leads to further functional declines and increases in fall risk,” she adds.
Factors that can cause a fall include:
- Poor eyesight, reflexes and hearing. “If you cannot hear as well, anytime you’re doing something in your environment and there’s a noise, it will be really hard for you to focus on hearing what that noise is and what it means and also moving at the same time,” Vincenzo says.
- Loss of strength, balance, and mobility with age, which can lessen one’s ability to prevent a fall when slipping or tripping.
- Fear of falling, which usually indicates decreased balance.
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or problems with nerves or feet that can affect balance.
- Conditions like incontinence that cause rushed movement to the bathroom.
- Cognitive impairment or certain types of dementia.
- Unsafe footwear such as backless shoes or high heels.
- Medications or medication interactions that can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Safety hazards in the home or outdoors, such as poor lighting, steps and slippery surfaces.
Related Research
Nonfatal and Fatal Falls Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2020–2021
Ramakrishna Kakara, Gwen Bergen, Elizabeth Burns and Mark Stevens. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, September 2023.Summary: Researchers analyzed data from the 2020 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System — a landline and mobile phone survey conducted each year in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia — and data from the 2021 National Vital Statistics System to identify patterns of injury and death due to falls in the U.S. by sex and state for adults 65 years and older. Among the findings:
- The percentage of women who reported falling was 28.9%, compared with 26.1% of men.
- Death rates from falls were higher among white and American Indian or Alaska Native older adults than among older adults from other racial and ethnic groups.
- In 2020, the percentage of older adults who reported falling during the past year ranged from 19.9% in Illinois to 38.0% in Alaska. The national estimate for 18 states was 27.6%.
- In 2021, the unintentional fall-related death rate among older adults ranged from 30.7 per 100,000 older adults in Alabama to 176.5 in Wisconsin. The national estimate for 26 states was 78.
“Although common, falls among older adults are preventable,” the authors write. “Health care providers can talk with patients about their fall risk and how falls can be prevented.”
Trends in Nonfatal Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2012-2018
Briana Moreland, Ramakrishna Kakara and Ankita Henry. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, July 2020.Summary: Researchers compared data from the 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Among the findings:
- The percentage of older adults reporting a fall increased from 2012 to 2016, then slightly decreased from 2016 to 2018.
- Even with this decrease in 2018, older adults reported 35.6 million falls. Among those falls, 8.4 million resulted in an injury that limited regular activities for at least one day or resulted in a medical visit.
“Despite no significant changes in the rate of fall-related injuries from 2012 to 2018, the number of fall-related injuries and health care costs can be expected to increase as the proportion of older adults in the United States grows,” the authors write.
Understanding Modifiable and Unmodifiable Older Adult Fall Risk Factors to Create Effective Prevention Strategies
Gwen Bergen, et al. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, October 2019.Summary: Researchers used data from the 2016 U.S. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System to better understand the association between falls and fall injuries in older adults and factors such as health, state and demographic characteristics. Among the findings:
- Depression had the strongest association with falls and fall injuries. About 40% of older adults who reported depression also reported at least one fall; 15% reported at least one fall injury.
- Falls and depression have several factors in common, including cognitive impairment, slow walking speed, poor balance, slow reaction time, weakness, low energy and low levels of activity.
- Other factors associated with an increased risk of falling include diabetes, vision problems and arthritis.
“The multiple characteristics associated with falls suggest that a comprehensive approach to reducing fall risk, which includes screening and assessing older adult patients to determine their unique, modifiable risk factors and then prescribing tailored care plans that include evidence-based interventions, is needed,” the authors write.
Health care use and cost
In addition to being the leading cause of injury, falls are the leading cause of hospitalization in older adults. Each year, about 3 million older adults visit the emergency department due to falls. More than 1 million get hospitalized.
In 2021, falls led to more than 38,000 deaths in adults 65 and older, according to the CDC.
The annual financial medical toll of falls among adults 65 years and older is expected to be more than $101 billion by 2030, according to the National Council on Aging, an organization advocating for older Americans.
Related research
Healthcare Spending for Non-Fatal Falls Among Older Adults, USA
Yara K. Haddad, et al. Injury Prevention, July 2024.Summary: In 2015, health care spending related to falls among older adults was roughly $50 billion. This study aims to update the estimate, using the 2017, 2019 and 2021 Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey, the most comprehensive and complete survey available on the Medicare population. Among the findings:
- In 2020, health care spending for non-fatal falls among older adults was $80 billion.
- Medicare paid $53.3 billion of the $80 billion, followed by $23.2 billion paid by private insurance or patients and $3.5 billion by Medicaid.
“The burden of falls on healthcare systems and healthcare spending will continue to rise if the risk of falls among the aging population is not properly addressed,” the authors write. “Many older adult falls can be prevented by addressing modifiable fall risk factors, including health and functional characteristics.”
Cost of Emergency Department and Inpatient Visits for Fall Injuries in Older Adults Lisa Reider, et al. Injury, February 2024.
Summary: The researchers analyzed data from the 2016-2018 National Inpatient Sample and National Emergency Department Sample, which are large, publicly available patient databases in the U.S. that include all insurance payers such as Medicare and private insurance. Among the findings:
- During 2016-2018, more than 920,000 older adults were admitted to the hospital and 2.3 million visited the emergency department due to falls. The combined annual cost was $19.2 billion.
- More than half of hospital admissions were due to bone fractures. About 14% of these admissions were due to multiple fractures and cost $2.5 billion.
“The $20 billion in annual acute treatment costs attributed to fall injury indicate an urgent need to implement evidence-based fall prevention interventions and underscores the importance of newly launched [emergency department]-based fall prevention efforts and investments in geriatric emergency departments,” the authors write.
Hip Fracture-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths by Mechanism of Injury Among Adults Aged 65 and Older, United States 2019
Briana L. Moreland, Jaswinder K. Legha, Karen E. Thomas and Elizabeth R. Burns. Journal of Aging and Health, June 2024.Summary: The researchers calculated hip fracture-related U.S. emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths among older adults, using data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project and the National Vital Statistics System. Among the findings:
- In 2019, there were 318,797 emergency department visits, 290,130 hospitalizations and 7,731 deaths related to hip fractures among older adults.
- Nearly 88% of emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 83% of deaths related to hip fractures were caused by falls.
- These rates were highest among those living in rural areas and among adults 85 and older. More specifically, among adults 85 and older, the rate of hip fracture-related emergency department visits was nine times higher than among adults between 65 and 74 years old.
“Falls are common among older adults, but many are preventable,” the authors write. “Primary care providers can prevent falls among their older patients by screening for fall risk annually or after a fall, assessing modifiable risk factors such as strength and balance issues, and offering evidence-based interventions to reduce older adults’ risk of falls.”
Fall prevention
Several factors, including exercising, managing medication, checking vision and making homes safer can help prevent falls among older adults.
“Exercise is one of the best interventions we know of to prevent falls,” Vincenzo says. But “walking in and of itself will not help people to prevent falls and may even increase their risk of falling if they are at high risk of falls.”
The National Council on Aging also has a list of evidence-based fall prevention programs, including activities and exercises that are shown to be effective.
The National Institute on Aging has a room-by-room guide on preventing falls at home. Some examples include installing grab bars near toilets and on the inside and outside of the tub and shower, sitting down while preparing food to prevent fatigue, and keeping electrical cords near walls and away from walking paths.
There are also national and international initiatives to help prevent falls.
Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries, or STEADI, is an initiative by the CDC’s Injury Center to help health care providers who treat older adults. It helps providers screen patients for fall risk, assess their fall risk factors and reduce their risk by using strategies that research has shown to be effective. STEADI’s guidelines are in line with the American and British Geriatric Societies’ Clinical Practice Guidelines for fall prevention.
“We’re making some iterations right now to STEADI that will come out in the next couple of years based on the World Falls Guidelines, as well as based on clinical providers’ feedback on how to make [STEADI] more feasible,” Vincenzo says.
The World Falls Guidelines is an international initiative to prevent falls in older adults. The guidelines are the result of the work of 14 international experts who came together in 2019 to consider whether new guidelines on fall prevention were needed. The task force then brought together 96 experts from 39 countries across five continents to create the guidelines.
The CDC’s STEADI initiative has a screening questionnaire for consumers to check their risk of falls, as does the National Council on Aging.
On the policy side, U.S. Rep. Carol Miller, R-W.V., and Melanie Stansbury, D-N.M., introduced the Stopping Addiction and Falls for the Elderly (SAFE) Act in March 2024. The bill would allow occupational and physical therapists to assess fall risks in older adults as part of the Medicare Annual Wellness Benefit. The bill was sent to the House Subcommittee on Health in the same month.
Meanwhile, older adults’ attitudes toward falls and fall prevention are also pivotal. For many, coming to terms with being at risk of falls and making changes such as using a cane, installing railings at home or changing medications isn’t easy for all older adults, studies show.
“Fall is a four-letter F-word in a way to older adults,” says Vincenzo, who started her career as a physical therapist. “It makes them feel ‘old.’ So, it’s a challenge on multiple fronts: U.S. health care infrastructure, clinical and community resources and facilitating health behavior change.”
Related research
Environmental Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community
Lindy Clemson, et al. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, March 2023.Summary: This review includes 22 studies from 10 countries involving a total of 8,463 older adults who live in the community, which includes their own home, a retirement facility or an assisted living facility, but not a hospital or nursing home. Among the findings:
- Removing fall hazards at home reduced the number of falls by 38% among older adults at a high risk of having a fall, including those who have had a fall in the past year, have been hospitalized or need support with daily activities. Examples of fall hazards at home include a stairway without railings, a slippery pathway or poor lighting.
- It’s unclear whether checking prescriptions for eyeglasses, wearing special footwear or installing bed alarm systems reduces the rate of falls.
- It’s also not clear whether educating older adults about fall risks reduces their fall risk.
The Influence of Older Adults’ Beliefs and Attitudes on Adopting Fall Prevention Behaviors
Judy A. Stevens, David A. Sleet and Laurence Z. Rubenstein. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. January 2017.Summary: Persuading older adults to adopt interventions that reduce their fall risk is challenging. Their attitudes and beliefs about falls play a large role in how well they accept and adopt fall prevention strategies, the authors write. Among the common attitudes and beliefs:
- Many older adults believe that falls “just happen,” are a normal result of aging or are simply due to bad luck.
- Many don’t acknowledge or recognize their fall risk.
- For many, falls are considered to be relevant only for frail or very old people.
- Many believe that their home environment or daily activities can be a risk for fall, but do not consider biological factors such as dizziness or muscle weakness.
- For many, fall prevention simply consists of “being careful” or holding on to things when moving about the house.
“To reduce falls, health care practitioners have to help patients understand and acknowledge their fall risk while emphasizing the positive benefits of fall prevention,” the authors write. “They should offer patients individualized fall prevention interventions as well as provide ongoing support to help patients adopt and maintain fall prevention strategies and behaviors to reduce their fall risk. Implementing prevention programs such as CDC’s STEADI can help providers discuss the importance of falls and fall prevention with their older patients.”
Reframing Fall Prevention and Risk Management as a Chronic Condition Through the Lens of the Expanded Chronic Care Model: Will Integrating Clinical Care and Public Health Improve Outcomes?
Jennifer L. Vincenzo, Gwen Bergen, Colleen M. Casey and Elizabeth Eckstrom. The Gerontologist, June 2024.Summary: The authors recommend approaching fall prevention from the lens of chronic disease management programs because falls and fall risk are chronic issues for many older adults.
“Policymakers, health systems, and community partners can consider aligning fall risk management with the [Expanded Chronic Care Model], as has been done for diabetes,” the authors write. “This can help translate high-quality research on the effectiveness of fall prevention interventions into daily practice for older adults to alter the trajectory of older adult falls and fall-related injuries.”
Disparities
Older adults face several barriers to reducing their fall risk. Accessing health care services and paying for services such as physical therapy is not feasible for everyone. Some may lack transportation resources to go to and from medical appointments. Social isolation can increase the risk of death from falls. In addition, physicians may not have the time to fit in a fall risk screening while treating older patients for other health concerns.
Moreover, implementing fall risk screening, assessment and intervention in the current U.S. health care structure remains a challenge, Vincenzo says.
Related research
Mortality Due to Falls by County, Age Group, Race, and Ethnicity in the USA, 2000-19: A Systematic Analysis of Health Disparities
Parkes Kendrick, et al. The Lancet Public Health, August 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed death registration data from the U.S. National Vital Statistics System and population data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics to estimate annual fall-related mortality. The data spanned from 2000 to 2019 and includes all age groups. Among the findings:
- The disparities between racial and ethnic populations varied widely by age group. Deaths from falls among younger adults were highest for the American Indian/Alaska Native population, while among older adults it was highest for the white population.
- For older adults, deaths from falls were particularly high in the white population within clusters of counties across states including Florida, Minnesota and Wisconsin.
- One factor that could contribute to higher death rates among white older adults is social isolation, the authors write. “Studies suggest that older Black and Latino adults are more likely to have close social support compared with older white adults, while AIAN and Asian individuals might be more likely to live in multigenerational households,” they write.
“Among older adults, current prevention techniques might need to be restructured to reduce frailty by implementing early prevention and emphasizing particularly successful interventions. Improving social isolation and evaluating the effectiveness of prevention programs among minoritized populations are also key,” the authors write.
Demographic Comparisons of Self-Reported Fall Risk Factors Among Older Adults Attending Outpatient Rehabilitation
Mariana Wingood, et al. Clinical Interventions in Aging, February 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed the electronic health record data of 108,751 older adults attending outpatient rehabilitation within a large U.S. health care system across seven states, between 2018 and 2022. Among the findings:
- More than 44% of the older adults were at risk of falls; nearly 35% had a history of falls.
- The most common risk factors for falls were diminished strength, gait and balance.
- Compared to white older adults, Native American/Alaska Natives had the highest prevalence of fall history (43.8%) and Hispanics had the highest prevalence of falls with injury (56.1%).
“Findings indicate that rehabilitation providers should perform screenings for these impairments, including incontinence and medication among females, loss of feeling in the feet among males, and all Stay Independent Questionnaire-related fall risk factors among Native American/Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and Blacks,” the authors write.
Resources and articles
- National Institute on Aging
- National Council on Aging
- Gerontological Society of America
- Home Health Agencies Failed To Report Over Half of Falls With Major Injury and Hospitalization Among Their Medicare Patients, a 2023 report from the U.S Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General.
- 6 tips for improving new coverage of older people, a tip sheet from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Crosswalk and pedestrian safety: What you need to know from recent research, from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Aging-in-place technology challenges and trends, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
- Successful aging at home: what reporters should know, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Almonds vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almonds to cashews, we picked the almonds.
Why?
Both are great! But here’s why we picked the almonds:
In terms of macros, almonds have a little more protein and more than 4x the fiber. Given how critical fiber is to good health, and how most people in industrialized countries in general (and N. America in particular) aren’t getting enough, we consider this a major win for almonds.
Things are closer to even for vitamins, but almonds have a slight edge. Almonds are higher in vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, and especially 27x higher in vitamin E, while cashews are higher in vitamins B1, B5, B6, C & K. So, a moderate win for almonds.
In the category of minerals, cashews do a bit better on average. Cashews have moderately more copper, iron, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while almonds boast 6x more calcium, and slightly more manganese and potassium. We say this one’s a slight win for cashews.
Adding the categories up, however, makes it clear that almonds win the day.
However, of course, enjoy both! Diversity is healthy. Just, if you’re going to choose between them, we recommend almonds.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
- Pistachios vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Over-50s Physio: What My 5 Oldest Patients (Average Age 92) Do Right
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Oftentimes, people of particularly advanced years will be asked their secret to longevity, and sometimes the answers aren’t that helpful because they don’t actually know, and ascribe it to some random thing. Will Harlow, the over-50s specialist physio, talks about the top 5 science-based things that his 5 oldest patients do, that enhances the healthy longevity that they are enjoying:
The Top 5’s Top 5
Here’s what they’re doing right:
Daily physical activity: all five patients maintain a consistent habit of daily exercise, which includes activities like exercise classes, home workouts, playing golf, or taking daily walks. They prioritize movement even when it’s difficult, rarely skipping a day unless something serious happened. A major motivator was the fear of losing mobility, as they had seen spouses, friends, or family members stop exercising and never start again.
Stay curious: a shared trait among the patients was their curiosity and eagerness to learn. They enjoy meeting new people, exploring new experiences, and taking on new challenges. Two of them attended the University of the Third Age to learn new skills, while another started playing bridge as a new hobby. The remaining two have recently made new friends. They all maintain a playful attitude, a good sense of humor, and aren’t afraid to fail or laugh at themselves.
Prioritize sleep (but not too much): the patients each average seven hours of sleep per night, aligning with research suggesting that 7–9 hours of sleep is ideal for health. They maintain consistent sleep and wake-up times, which contributes to their well-being. While they allow themselves short naps when needed, they avoid long afternoon naps to avoid disrupting their sleep patterns.
Spend time in nature: spending time outdoors is a priority for all five individuals. Whether through walking, gardening, or simply sitting on a park bench, they make it a habit to connect with nature. This aligns with studies showing that time spent in natural environments, especially near water, significantly reduces stress. When water isn’t accessible, green spaces still provide a beneficial boost to mental health.
Stick to a routine: the patients all value simple daily routines, such as enjoying an evening cup of tea, taking a daily walk, or committing to small gardening tasks. These routines offer mental and physical grounding, providing stability even when life becomes difficult sometimes. They emphasized the importance of keeping routines simple and manageable to ensure they could stick to them regardless of life’s challenges.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Top 8 Habits Of The Top 1% Healthiest Over-50s ← another approach to the same question, this time with a larger sample size, and/but many younger (than 90s) respondents.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: