How to Read a Book – by Mortimer J. Adler and Charles Van Doren
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you a cover-to-cover person, or a dip-in-and-out person?
Mortimer Adler and Charles van Doren have made a science out of getting the most from reading books.
They help you find what you’re looking for (Maybe you want to find a better understanding of PCOS… maybe you want to find the definition of “heuristics”… maybe you want to find a new business strategy… maybe you want to find a romantic escape… maybe you want to find a deeper appreciation of 19th century poetry, maybe you want to find… etc).
They then help you retain what you read, and make sure that you don’t miss a trick.
Whether you read books so often that optimizing this is of huge value for you, or so rarely that when you do, you want to make it count, this book could make a real difference to your reading experience forever after.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Strong At Every Age: 15 Habits To Level Up Your Health & Fitness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not every increase in health and fitness needs to look like a training montage from the “Rocky” movies!
Making progress every day
We’ll not keep the 15 habits a secret; they are:
- Follow the one-minute rule: commit to just one minute of action—this makes starting easier, and often you’ll end up doing more once you’ve got started.
- Make the habit exciting: add fun elements to make the habit more enjoyable, like using new gear or accessories.
- Do it first: prioritize new habits by doing them early in the day to ensure they get done.
- Share the love: pair new habits with activities you already enjoy, where practical, to do “temptation bundling”.
- Embrace the uncomfortable: get used to discomfort daily to grow and build resilience for bigger changes.
- Do as little as possible: start small with habits, to minimize resistance and focus on consistency.
- Think how to be lazy: simplify processes and use shortcuts; there are no extra prizes for it having been difficult!
- Make the appointment: schedule habits with set dates and times, to increase accountability.
- Let habits evolve: adapt habits to fit current circumstances; that way you can still stay consistent over time.
- Plan ahead: prepare in advance to avoid setbacks—what could stop you from succeeding, and how can you pre-empt that?
- Pause to reflect: regularly evaluate what works and what doesn’t, to adjust and improve.
- Shut off your brain: avoid overthinking and start taking action now, not later, to build momentum.
- Question and learn: stay curious and open to learning, or else you will plateau quickly!
- Ask why: understand the deeper reasons behind any resistance, and make clear for yourself the value of the habit.
- Love your failures: embrace any setbacks as learning opportunities and, as such, stepping stones to success.
For more on all of each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How to keep your teeth young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to keep your teeth young
The association between aging and teeth is so well-established that it’s entered popular idiom, “too long in the tooth”, and when it comes to visual representations, false teeth are well-associated with old age.
And yet, avoiding such outcomes does not get anywhere near so much attention as, say, avoiding wrinkles or hair loss.
At 10almonds, we’ve covered general dental health before, in a three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing, Better (And Easier!)
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
Today, we’re going to be looking specifically at keeping our teeth young. What if you have lost your teeth already? Well, gum health remains important, and it’s foundational for everyone, so…
Look after your gums first and last
Hollywood’s most “perfect” whites would be nothing without the gums holding them in place. So, set aside the cosmetic whitening products that often harm gums (anything containing bleach / hydrogen peroxide, is generally a bad idea), andinstead focus on your gums.
As for avoiding gum disease (periodontitis)?
❝In conclusion, periodontitis might enhance the association of biological aging with all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older adults.
Hence, maintaining and enhancing periodontal health is expected to become an intervention to slow aging and extend life span.❞
Source: Does Periodontitis Affect the Association of Biological Aging with Mortality?
Ways to look after gum health include the obvious “floss” and “brush often” and “use fluoride toothpaste”, along with other options we covered in our “Less Common Oral Hygiene Options” article above.
Also important: don’t smoke. It is bad for everything, and this is no exception.
We expect we probably don’t have many subscribers who smoke, but if you do, please consider making quitting a priority.
See also: Smoking, Gum Disease, and Tooth Loss
Consider supplementing with collagen
Everyone’s all about the calcium and vitamin D for bones (and teeth), but a large part of the mass of both is actually collagen. And unlike calcium, which most people not living in a food desert get plenty of, or vitamin D, which is one of the most popular supplements around, collagen is something that gets depleted as we get older. We’ve written about its importance for bones:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of—Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
And as for its role in combatting gum disease and tooth loss:
Nanoscale Dynamics of Streptococcal Adhesion to AGE-Modified Collagen
By the way, that “AGE” there isn’t about chronological age; it’s about advanced glycation end-products. Those are also something you can and should avoid:
A different kind of “spit and polish”
We imagine you have the “polishing” part in hand; that’s tooth-brushing, of course. But spit?
Saliva is hugely important for our oral health, but it’s not something most of us think about a lot. For example, you might not have known (or might have known but not thought much about) that many common medications affect our saliva, including many blood pressure medications and antidepressants:
Impact of ageing and drug consumption on oral health
Because there are so many possibilities, this is the kind of thing to check with your pharmacist or doctor about. But as a rule, if you take a medication whose side-effects include “dry mouth”, this might be you.
Here’s a really useful (academic) article that covers what drugs cause this, how to diagnose it, and what can be done about it:
Hyposalivation in Elderly Patients
If something’s difficult, find a way to make it easier
Sometimes, as we get older, some things that used to be easy, aren’t. We can lose strength, coordination, manual dexterity, memory, attention, and more. Obviously, we try not to, and do what we can to keep ourselves in good health.
But, if you do have some disability that makes for example brushing and/or flossing difficult to do consistently and/or well, consider talking to your doctor to see if there are assistive devices that can help, or some other kind of support that could allow you to do what you need to.
There’s never any shame in getting help if we need it.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
New California Laws Target Medical Debt, AI Care Decisions, Detention Centers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
SACRAMENTO, Calif. — As the nation braces for potential policy shifts under President-elect Donald Trump’s “Make America Healthy Again” mantra, the nation’s most populous state and largest health care market is preparing for a few changes of its own.
With supermajorities in both houses, Democrats in the California Legislature passed — and Democratic Gov. Gavin Newsom signed — laws taking effect this year that will erase medical debt from credit reports, allow public health officials to inspect immigrant detention centers, and require health insurance companies to cover fertility services such as in vitro fertilization.
Still, industry experts say it was a relatively quiet year for health policy in the Golden State, with more attention on a divisive presidential election and with several state legislators seeking to avoid controversial issues as they ran for Congress in competitive swing districts.
Newsom shot down some of legislators’ most ambitious health care policies, including proposals that would have regulated pharmaceutical industry middlemen and given the state more power to stop private equity deals in health care.
Health policy experts say advocates and legislators are now focused on how to defend progressive California policies such as sweeping abortion access in the state and health coverage for immigrants living in the U.S. without authorization.
“I think everyone’s just thinking about how we’re going to enter 2025,” said Rachel Linn Gish, a spokesperson with the consumer health advocacy group Health Access California. “We’re figuring out what is vulnerable, what we are exposed to on the federal side, and what do budget changes mean for our work. That’s kind of putting a cloud over everything.”
Here are some of the biggest new health care laws Californians should know about:
Medical debt
California becomes the eighth state in which medical debt will no longer affect patients’ credit reports or credit scores. SB 1061 bars health care providers and debt collectors from reporting unpaid medical bills to credit bureaus, a practice that supporters of the law say penalizes people for seeking critical care and can make it harder for patients to get a job, buy a car, or secure a mortgage.
Critics including the California Association of Collectors called the measure from Sen. Monique Limón (D-Santa Barbara) a “tremendous overreach” and successfully lobbied for amendments that limited the scope of the bill, including an exemption for any medical debt incurred on credit cards.
The Biden administration has finalized federal rules that would stop unpaid medical bills from affecting patients’ credit scores, but the fate of those changes remains unclear as Trump takes office.
Psychiatric hospital stays for violent offenders
Violent offenders with severe mental illness can now be held longer after a judge orders them released from a state mental hospital.
State officials and local law enforcement will now have 30 days to coordinate housing, medication, and behavioral health treatment for those parolees, giving them far more time than the five-day deadline previously in effect.
The bill drew overwhelming bipartisan support after a high-profile case in San Francisco in which a 61-year-old man was charged in the repeated stabbing of a bakery employee just days after his release from a state mental hospital. The bill’s author, Assembly member Matt Haney (D-San Francisco), called the previous five-day timeline “dangerously short.”
Cosmetics and ‘forever chemicals’
California was the first state to ban PFAS chemicals, also known as “forever chemicals,” in all cosmetics sold and manufactured within its borders. The synthetic compounds, found in everyday products including rain jackets, food packaging, lipstick, and shaving cream, have been linked to cancer, birth defects, and diminished immune function and have been increasingly detected in drinking water.
Industry representatives have argued that use of PFAS — perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances — is critical in some products and that some can be safely used at certain levels.
Immigration detention facilities
After covid-19 outbreaks, contaminated water, and moldy food became the subjects of detainee complaints and lawsuits, state legislators gave local county health officials the authority to enter and inspect privately run immigrant detention centers. SB 1132, from Sen. María Elena Durazo (D-Los Angeles), gives public health officials the ability to evaluate whether privately run facilities are complying with state and local public health regulations regarding proper ventilation, basic mental and physical health care, and food safety.
Although the federal government regulates immigration, six federal detention centers in California are operated by the GEO Group. One of the country’s largest private prison contractors, GEO has faced a litany of complaints related to health and safety. Unlike public prisons and jails, which are inspected annually, these facilities would be inspected only as deemed necessary.
The contractor filed suit in October to stop implementation of the law, saying it unconstitutionally oversteps the federal government’s authority to regulate immigration detention centers. A hearing in the case is set for March 3, said Bethany Lesser, a spokesperson for California Attorney General Rob Bonta. The law took effect Jan. 1.
Doctors vs. insurance companies using AI
As major insurance companies increasingly use artificial intelligence as a tool to analyze patient claims and authorize some treatment, trade groups representing doctors are concerned that AI algorithms are driving an increase in denials for necessary care. Legislators unanimously agreed.
SB 1120 states that decisions about whether a treatment is medically necessary can be made only by licensed, qualified physicians or other health care providers who review a patient’s medical history and other records.
Sick leave and protected time off
Two new laws expand the circumstances under which California workers may use sick days and other leave. SB 1105 entitles farmworkers who work outdoors to take paid sick leave to avoid heat, smoke, or flooding when local or state officials declare an emergency.
AB 2499 expands the list of reasons employees may take paid sick days or use protected unpaid leave to include assisting a family member who is experiencing domestic violence or other violent crimes.
Prescription labels for the visually impaired
Starting this year, pharmacies will be required to provide drug labels and use instructions in Braille, large print, or audio for blind patients.
Advocates of the move said state law, which already required translated instructions in five languages for non-English speakers, has overlooked blind patients, making it difficult for them to monitor prescriptions and take the correct dosage.
Maternal mental health screenings
Health insurers will be required to bolster maternal mental health programs by mandating additional screenings to better detect perinatal depression, which affects 1 in 5 people who give birth in California, according to state data. Pregnant people will now undergo screenings at least once during pregnancy and then six weeks postpartum, with further screenings as providers deem necessary.
Penalties for threatening health care workers (abortion clinics)
With abortion care at the center of national policy fights, California is cracking down on those who threaten, post personal information about, or otherwise target providers or patients at clinics that perform abortions. Penalties for such behavior will increase under AB 2099, and offenders can face felony charges, up to three years in jail, and $50,000 in fines for repeat or violent offenses. Previously, state law classified many of those offenses as misdemeanors.
Insurance coverage for IVF
Starting in July, state-regulated health plans covering 50 employees or more would be required to cover fertility services under SB 729, passed and signed last year. Advocates have long fought for this benefit, which they say is essential care for many families who have trouble getting pregnant and would ensure LGBTQ+ couples aren’t required to pay more out-of-pocket costs than straight couples when starting a family.
In a signing statement, Newsom asked legislators to delay implementation of the law until 2026 as state officials consider whether to add infertility treatments to the list of benefits that insurance plans are required to cover.
It’s unclear whether legislators intend to address that this session, but a spokesperson for the governor said that Newsom “clearly stated his position on the need for an extension” and that he “will continue to work with the legislature” on the matter.
Plans under CalPERS, the California Public Employees’ Retirement System, would have to comply by July 2027.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Plant Power Doctor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Prescription For GLOVES
This is Dr. Gemma Newman. She’s a GP (General Practitioner, British equivalent to what is called a family doctor in America), and she realized that she was treating a lot of patients while nobody was actually getting better.
So, she set out to help people actually get better… But how?
The biggest thing
The single biggest thing she recommends is a whole foods plant-based diet, as that’s a starting point for a lot of other things.
Click here for an assortment of short videos by her and other health professionals on this topic!
Specifically, she advocates to “love foods that love you back”, and make critical choices when deciding between ingredients.
Click here to see her recipes and tips (this writer is going to try out some of these!)
What’s this about GLOVES?
We recently reviewed her book “Get Well, Stay Well: The Six Healing Health Habits You Need To Know”, and now we’re going to talk about those six things in more words than we had room for previously.
They are six things that she says we should all try to get every day. It’s a lot simpler than a lot of checklists, and very worthwhile:
Gratitude
May seem like a wishy-washy one to start with, but there’s a lot of evidence for this making a big difference to health, largely on account of how it lowers stress and anxiety. See also:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Love
This is about social connections, mostly. We are evolved to be a social species, and while some of us want/need more or less social interaction than others, generally speaking we thrive best in a community, with all the social support that comes with that. See also:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Outside
This is about fresh air and it’s about moving and it’s about seeing some green plants (and if available, blue sky), marvelling at the wonder of nature and benefiting in many ways. See also:
Vegetables
We spoke earlier about the whole foods plant-based diet for which she advocates, so this is that. While reducing/skipping meat etc is absolutely a thing, the focus here is on diversity of vegetables; it is best to make a game of seeing how many different ones you can include in a week (not just the same three!). See also:
Three Critical Kitchen Prescriptions
Exercise
At least 150 minutes moderate exercise per week, and some kind of resistance work. It can be calisthenics or something; it doesn’t have to be lifting weights if that’s not your thing! See also:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Sleep
Quality and quantity. Yes, 7–9 hours, yes, regardless of age. Unless you’re a child or a bodybuilder, in which case make it nearer 12. But for most of us, 7–9. See also:
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
Want to know more?
As well as the book we mentioned earlier, you might also like:
The Plant Power Doctor – by Dr. Gemma Newman
While the other book we mentioned is available for pre-order for Americans (it’s already released for the rest of the world), this one is available to all right now, so that’s a bonus too.
If books aren’t your thing (or even if they are), you might like her award-winning podcast:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dogs Paired With Providers at Hospitals Help Ease Staff and Patient Stress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
DENVER — Outside HCA HealthONE Rose medical center, the snow is flying. Inside, on the third floor, there’s a flurry of activity within the labor and delivery unit.
“There’s a lot of action up here. It can be very stressful at times,” said Kristina Fraser, an OB-GYN in blue scrubs.
Nurses wheel a very pregnant mom past.
“We’re going to bring a baby into this world safely,” Fraser said, “and off we go.”
She said she feels ready in part due to a calming moment she had just a few minutes earlier with some canine colleagues.
A pair of dogs, tails wagging, had come by a nearby nursing station, causing about a dozen medical professionals to melt into a collective puddle of affection. A yellow Lab named Peppi showered Fraser in nuzzles and kisses. “I don’t know if a human baby smells as good as that puppy breath!” Fraser had said as her colleagues laughed.
The dogs aren’t visitors. They work here, too, specifically for the benefit of the staff. “I feel like that dog just walks on and everybody takes a big deep breath and gets down on the ground and has a few moments of just decompressing,” Fraser said. “It’s great. It’s amazing.”
Hospital staffers who work with the dogs say there is virtually no bite risk with the carefully trained Labradors, the preferred breed for this work.
The dogs are kept away from allergic patients and washed regularly to prevent germs from spreading, and people must wash their hands before and after petting them.
Doctors and nurses are facing a growing mental health crisis driven by their experiences at work. They and other health care colleagues face high rates of depression, anxiety, stress, suicidal ideation, and burnout. Nearly half of health workers reported often feeling burned out in 2022, an increase from 2018, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And the percentage of health care workers who reported harassment at work more than doubled over that four-year period. Advocates for the presence of dogs in hospitals see the animals as one thing that can help.
That includes Peppi’s handler, Susan Ryan, an emergency medicine physician at Rose.
Ryan said years working as an emergency room doctor left her with symptoms of PTSD. “I just was messed up and I knew it,” said Ryan, who isolated more at home and didn’t want to engage with friends. “I shoved it all in. I think we all do.”
She said doctors and other providers can be good at hiding their struggles, because they have to compartmentalize. “How else can I go from a patient who had a cardiac arrest, deal with the family members telling them that, and go to a room where another person is mad that they’ve had to wait 45 minutes for their ear pain? And I have to flip that switch.”
To cope with her symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, Ryan started doing therapy with horses. But she couldn’t have a horse in her backyard, so she got a Labrador.
Ryan received training from a national service dog group called Canine Companions, becoming the first doctor trained by the group to have a facility dog in an emergency room. Canine Companions has graduated more than 8,000 service dogs.
The Rose medical center gave Ryan approval to bring a dog to work during her ER shifts. Ryan’s colleagues said they are delighted that a dog is part of their work life.
“When I have a bad day at work and I come to Rose and Peppi is here, my day’s going to be made better,” EMT Jasmine Richardson said. “And if I have a patient who’s having a tough day, Peppi just knows how to light up the room.”
Nursing supervisor Eric Vaillancourt agreed, calling Peppi “joyful.”
Ryan had another dog, Wynn, working with her during the height of the pandemic. She said she thinks Wynn made a huge difference. “It saved people,” she said. “We had new nurses that had never seen death before, and now they’re seeing a covid death. And we were worried sick we were dying.”
She said her hospital system has lost a couple of physicians to suicide in the past two years, which HCA confirmed to KFF Health News and NPR. Ryan hopes the canine connection can help with trauma. “Anything that brings you back to the present time helps ground you again. A dog can be that calming influence,” she said. “You can get down on the ground, pet them, and you just get calm.”
Ryan said research has shown the advantages. For example, one review of dozens of original studies on human-animal interactions found benefits for a variety of conditions including behavioral and mood issues and physical symptoms of stress.
Rose’s president and CEO, Casey Guber, became such a believer in the canine connection he got his own trained dog to bring to the hospital, a black Lab-retriever mix named Ralphie.
She wears a badge: Chief Dog Officer.
Guber said she’s a big morale booster. “Phenomenal,” he said. “It is not uncommon to see a surgeon coming down to our administration office and rolling on the ground with Ralphie, or one of our nurses taking Ralphie out for a walk in the park.”
This article is from a partnership that includes CPR News, NPR, and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
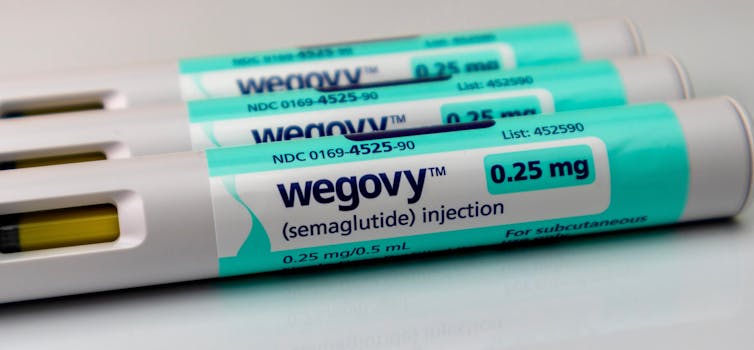
What happens when I stop taking a drug like Ozempic or Mounjaro?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Drugs like Ozempic are very effective at helping most people who take them lose weight. Semaglutide (sold as Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (sold as Zepbound and Mounjaro) are the most well known in the class of drugs that mimic hormones to reduce feelings of hunger.
But does weight come back when you stop using it?
The short answer is yes. Stopping tirzepatide and semaglutide will result in weight regain in most people.
So are these medications simply another (expensive) form of yo-yo dieting? Let’s look at what the evidence shows so far.
It’s a long-term treatment, not a short course
If you have a bacterial infection, antibiotics will help your body fight off the germs causing your illness. You take the full course of medication, and the infection is gone.
For obesity, taking tirzepatide or semaglutide can help your body get rid of fat. However it doesn’t fix the reasons you gained weight in the first place because obesity is a chronic, complex condition. When you stop the medications, the weight returns.
Perhaps a more useful comparison is with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Treatment for hypertension is lifelong. It’s the same with obesity. Medications work, but only while you are taking them. (Though obesity is more complicated than hypertension, as many different factors both cause and perpetuate it.)
Obesity drugs only work while you’re taking them. KK Stock/Shutterstock Therefore, several concurrent approaches are needed; taking medication can be an important part of effective management but on its own, it’s often insufficient. And in an unwanted knock-on effect, stopping medication can undermine other strategies to lose weight, like eating less.
Why do people stop?
Research trials show anywhere from 6% to 13.5% of participants stop taking these drugs, primarily because of side effects.
But these studies don’t account for those forced to stop because of cost or widespread supply issues. We don’t know how many people have needed to stop this medication over the past few years for these reasons.
Understanding what stopping does to the body is therefore important.
So what happens when you stop?
When you stop using tirzepatide or semaglutide, it takes several days (or even a couple of weeks) to move out of your system. As it does, a number of things happen:
- you start feeling hungry again, because both your brain and your gut no longer have the medication working to make you feel full
When you stop taking it, you feel hungry again. Stock-Asso/Shutterstock - blood sugars increase, because the medication is no longer acting on the pancreas to help control this. If you have diabetes as well as obesity you may need to take other medications to keep these in an acceptable range. Whether you have diabetes or not, you may need to eat foods with a low glycemic index to stabilise your blood sugars
- over the longer term, most people experience a return to their previous blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as the weight comes back
- weight regain will mostly be in the form of fat, because it will be gained faster than skeletal muscle.
While you were on the medication, you will have lost proportionally less skeletal muscle than fat, muscle loss is inevitable when you lose weight, no matter whether you use medications or not. The problem is, when you stop the medication, your body preferentially puts on fat.
Is stopping and starting the medications a problem?
People whose weight fluctuates with tirzepatide or semaglutide may experience some of the downsides of yo-yo dieting.
When you keep going on and off diets, it’s like a rollercoaster ride for your body. Each time you regain weight, your body has to deal with spikes in blood pressure, heart rate, and how your body handles sugars and fats. This can stress your heart and overall cardiovascular system, as it has to respond to greater fluctuations than usual.
Interestingly, the risk to the body from weight fluctuations is greater for people who are not obese. This should be a caution to those who are not obese but still using tirzepatide or semaglutide to try to lose unwanted weight.
How can you avoid gaining weight when you stop?
Fear of regaining weight when stopping these medications is valid, and needs to be addressed directly. As obesity has many causes and perpetuating factors, many evidence-based approaches are needed to reduce weight regain. This might include:
- getting quality sleep
- exercising in a way that builds and maintains muscle. While on the medication, you will likely have lost muscle as well as fat, although this is not inevitable, especially if you exercise regularly while taking it
Prioritise building and maintaining muscle. EvMedvedeva/Shutterstock - addressing emotional and cultural aspects of life that contribute to over-eating and/or eating unhealthy foods, and how you view your body. Stigma and shame around body shape and size is not cured by taking this medication. Even if you have a healthy relationship with food, we live in a culture that is fat-phobic and discriminates against people in larger bodies
- eating in a healthy way, hopefully continuing with habits that were formed while on the medication. Eating meals that have high nutrition and fibre, for example, and lower overall portion sizes.
Many people will stop taking tirzepatide or semaglutide at some point, given it is expensive and in short supply. When you do, it is important to understand what will happen and what you can do to help avoid the consequences. Regular reviews with your GP are also important.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Natasha Yates, General Practitioner, PhD Candidate, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: