Hot And Sour Shiitake Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a popular, easy, and delicious soup that nonetheless is not found in many western kitchens, despite being enjoyed in restaurants/take-out. Best of all, making it at home means that you know all the ingredients, can account for quality, and also can customize it per your preferences (i.e. how much heat/sourness you like).
You will need
- 3 cups shiitake mushrooms, sliced
- 3 cups bok choy, chopped
- 2 cups cherry tomatoes, quartered
- 1 cup carrot, grated
- 3 spring onions, chopped
- 2 shallots, sliced lengthways
- 2 serrano chilis (or similar), sliced thinly
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tbsp fresh ginger, sliced into 1″ strips
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 6 cups low-sodium vegetable stock. Ideally you will have made it yourself from vegetable cuttings that you saved in the freezer until you had enough to make stock from, but if that’s not an option, then low-sodium vegetable stock cubes can be purchased and used.
- Garnish: ¼ cup (or 4 tbsp) cilantro, chopped, or if you have the soap gene, then this time we recommend chopped basil as the subsitution
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the ginger in a big pot with the stock; cover and simmer for about 20 minutes (otherwise the ginger flavor will remain mostly concentrated in the ginger strips).
2) Bring it to a boil and add the bok choy, mushrooms, shallots, chili peppers, and the carrot; simmer for another 5 minutes
3) Add the remaining ingredients except for the garnish, and simmer for another 5 minutes
4) Serve, adding the garnish
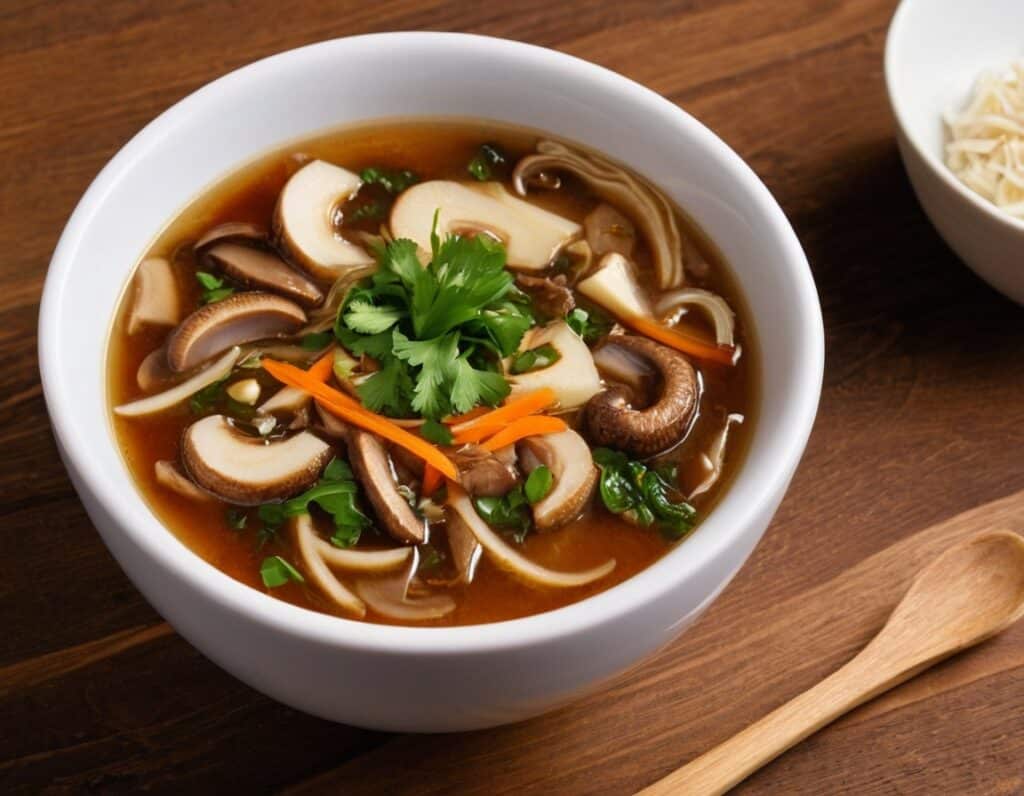

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The (Longevity) Magic of Mushrooms
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Enjoy Bitter/Hot/Sour/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Body on Fire – by Dr. Monica Aggarwal and Dr. Jyothi Rao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are times when you do really need a doctor, not a dietician. But there are also times when a doctor will prescribe something for the symptom, leaving the underlying issue untouched. If only there were a way to have the best of both worlds!
That’s where Drs. Rao and Aggarwal come in. They’re both medical doctors… with a keen interest in nutrition and healthy lifestyle changes to make us less sick such that we have less need to go to the doctor at all.
Best of all, they understand—while some things are true for everyone—there’s not a one-size-fits all diet or exercise regime or even sleep setup.
So instead, they take us hand-in-hand (chapter by chapter!) through the various parts of our life (including our diet) that might need tweaking. Each of these changes, if taken up, promise a net improvement that becomes synergistic with the other changes. There’s a degree of biofeedback involved, and listening to your body, to be sure of what’s really best for you, not what merely should be best for you on paper.
The writing style is accessible while science-heavy. They don’t assume prior knowledge, and/but they sure deliver a lot. The book is more text than images, but there are plenty of medical diagrams, explanations, charts, and the like. You will feed like a medical student! And it’s very much worth studying.
Bottom line: highly recommendable even if you don’t have inflammation issues, and worth its weight in gold if you do.
Share This Post
-
Bold Beans – by Amelia Christie-Miller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know beans are one of the most healthful foods around, but how to include more of them, without getting boring?
This book has the answer, giving 80 exciting recipes, divided into the following sections:
- Speedy beans
- Bean snacks & sharing plates
- Brothy beans
- Bean bowls
- Hearty salads
- Bean feasts
The recipes are obviously all bean-centric, though if you have a particular dietary restriction, watch out for the warning labels on some (e.g. meat, fish, dairy, gluten, etc), and make a substitution if appropriate.
The recipes themselves have a happily short introductory paragraph, followed by all you’d expect from a recipe book (ingredients, measurements, method, picture)
There’s also a reference section, to learn about different kinds of beans and bean-related culinary methods that can be applied per your preferences.
Bottom line: if you’d like to include more beans in your daily diet but are stuck for making them varied and interesting, this is the book for you!
Click here to check out Bold Beans, and get your pulse racing (in a good way!)
Share This Post
-
Ageless Aging – by Maddy Dychtwald
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Maddy Dychtwald, herself 73, has spent her career working in the field of aging. She’s not a gerontologist or even a doctor, but she’s nevertheless been up-to-the-ears in the industry for decades, mostly as an organizer, strategist, facilitator, and so forth. As such, she’s had her finger on the pulse of the healthy longevity movement for a long time.
This book was written to address a problem, and the problem is: lifespan is increasing (especially for women), but healthspan has not been keeping up the pace.
In other words: people (especially women) are living longer, but often with more health problems along the way than before.
And mostly, it’s for lack of information (or sometimes: too much competing incorrect information).
Fortunately, information is something that a woman in Dychtwald’s position has an abundance of, because she has researchers and academics in many fields on speed-dial and happy to answer her questions (we get a lot of input from such experts throughout the book—which is why this book is so science-based, despite the author not being a scientist).
The book answers a lot of important questions beyond the obvious “what diet/exercise/sleep/supplements/etc are best for healthy aging” (spoiler: it’s quite consistent with the things we recommend here, because guess what, science is science), questions like how best to prepare for this that or the other, how to get a head start on preventative healthcare for some things, how to avoid being a burden to our families (one can argue that families are supposed to look after each other, but still, it’s a legitimate worry for many, and understandably so), and even how to balance the sometimes conflicting worlds of health and finances.
Unlike many authors, she also talks about the different kinds of aging, and tackles each of them separately and together. We love to see it!
Bottom line: this book is a very good one-stop-shop for all things healthy aging. It’s aimed squarely at women, but most advice goes for men the same too, aside from the section on hormones and such.
Click here to check out Ageless Aging, and plan your future!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Younger For Life – by Dr. Anthony Youn
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed anti-aging books before, so what makes this one different? Mostly, it’s the very practical focus.
Which is not to say there’s not also good science in here; there is. But the focus is on what everything means for the reader, not what happened with a certain cohort of lab mice. Instead, he looks at the causes of aging, the process of aging, and what interventions to implement to address those, and reverse many of them.
Some parts are more general lifestyle interventions that 10almonds readers will know well already, but other parts are very specific advices, protocols, and regimes; in particular his skincare section is well worth reading. As for nutrition, there’s even a respectable recipes section, so this book does have it all!
The final section of the book is dedicated to plastic surgeries (the author is a plastic surgeon who believes that most people should not need those, and would do well to stick to the advices in the rest of the book). We suspect this last part of the book will be of least interest to 10almonds readers.
Bottom line: if you’re of the view that getting older should come with as little as possible physical deterioration along the way, then this book can help a lot with that.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What you need to know about menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menopause describes the time when a person with ovaries has gone one full year without a menstrual period. Reaching this phase is a natural aging process that marks the end of reproductive years.
Read on to learn more about the causes, stages, signs, and management of menopause.
What causes menopause?
As you age, your ovaries begin making less estrogen and progesterone—two of the hormones involved in menstruation—and your fertility declines, causing menopause.
Most people begin perimenopause, the transitional time that ends in menopause, in their late 40s, but it can start earlier. On average, people in the U.S. experience menopause in their early 50s.
Your body may reach early menopause for a variety of reasons, including having an oophorectomy, a surgery that removes the ovaries. In this case, the hormonal changes happen abruptly rather than gradually.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer patients may also induce menopause, as these treatments may impact ovary function.
What are the stages of menopause?
There are three stages:
- Perimenopause typically occurs eight to 10 years before menopause happens. During this stage, estrogen production begins to decline and ovaries release eggs less frequently.
- Menopause marks the point when you have gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. This means the ovaries have stopped releasing eggs and producing estrogen.
- Postmenopause describes the time after menopause. Once your body reaches this phase, it remains there for the rest of your life.
How do the stages of menopause affect fertility?
Your ovaries still produce eggs during perimenopause, so it is still possible to get pregnant during that stage. If you do not wish to become pregnant, continue using your preferred form of birth control throughout perimenopause.
Once you’ve reached menopause, you can no longer get pregnant naturally. People who would like to become pregnant after that may pursue in vitro fertilization (IVF) using eggs that were frozen earlier in life or donor eggs.
What are the signs of menopause?
Hormonal shifts result in a number of bodily changes. Signs you are approaching menopause may include:
- Hot flashes (a sudden feeling of warmth).
- Irregular menstrual periods, or unusually heavy or light menstrual periods.
- Night sweats and/or cold flashes.
- Insomnia.
- Slowed metabolism.
- Irritability, mood swings, and depression.
- Vaginal dryness.
- Changes in libido.
- Dry skin, eyes, and/or mouth.
- Worsening of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
- Urinary urgency (a sudden need to urinate).
- Brain fog.
How can I manage the effects of menopause?
You may not need any treatment to manage the effects of menopause. However, if the effects are disrupting your life, your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy.
If you have had a hysterectomy, your doctor may prescribe estrogen therapy (ET), which may be administered via a pill, patch, cream, spray, or vaginal ring. If you still have a uterus, your doctor may prescribe estrogen progesterone/progestin hormone therapy (EPT), which is sometimes called “combination therapy.”
Both of these therapies work by replacing the hormones your body has stopped making, which can reduce the physical and mental effects of menopause.
Other treatment options may include antidepressants, which can help manage mood swings and hot flashes; prescription creams to alleviate vaginal dryness; or gabapentin, an anti-seizure medication that has been shown to reduce hot flashes.
Lifestyle changes may help alleviate the effects on their own or in combination with prescription medication. Those changes include:
- Incorporating movement into your daily life.
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol.
- Quitting smoking.
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule.
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation.
- Consuming foods rich in plant estrogens, such as grains, beans, fruits, vegetables, and seeds.
- Seeking support from a therapist and from loved ones.
What health risks are associated with menopause?
Having lower levels of estrogen may put you at greater risk of certain health complications, including osteoporosis and coronary artery disease.
Osteoporosis occurs when bones lose their density, increasing the risk of fractures. A 2022 study found that the prevalence of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women was 82.2 percent.
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that send blood to your heart become narrow or blocked with fatty plaque.
Estrogen therapy can reduce your risk of osteoporosis and coronary artery disease by preserving bone mass and maintaining cardiovascular function.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pistachios vs Almonds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to almonds, we picked the almonds.
Why?
It was very close! And those who’ve been following our “This or That” comparisons might be aware that pistachios and almonds have both been winning their respective comparisons with other nuts so far, so today we put them head-to-head.
In terms of macros, almonds have a little more protein and a little more fiber—as well as slightly more fat, though the fats are healthy. Pistachios, meanwhile, are higher in carbs. A moderate win for almonds on the macro front.
When it comes to vitamins, pistachios have more of vitamins A, B1, and B6, while almonds have more of vitamins B2, B3, and E. We could claim a slight victory for pistachios, based on the larger margins, or else a slight victory for almonds, based on vitamin E being a more common nutritional deficiency than vitamin A, and therefore the more useful vitamin to have more of. We’re going to call this category a tie.
In the category of minerals, almonds lead with more calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while pistachios boast more copper, potassium, and selenium, though the margins are more modest for pistachios. A moderate win for almonds on minerals, therefore.
Adding up the sections gives a win for almonds, but of course, do enjoy both, because both are excellent in their own right.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Pistachios vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
- Almonds vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: