Body on Fire – by Dr. Monica Aggarwal and Dr. Jyothi Rao
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are times when you do really need a doctor, not a dietician. But there are also times when a doctor will prescribe something for the symptom, leaving the underlying issue untouched. If only there were a way to have the best of both worlds!
That’s where Drs. Rao and Aggarwal come in. They’re both medical doctors… with a keen interest in nutrition and healthy lifestyle changes to make us less sick such that we have less need to go to the doctor at all.
Best of all, they understand—while some things are true for everyone—there’s not a one-size-fits all diet or exercise regime or even sleep setup.
So instead, they take us hand-in-hand (chapter by chapter!) through the various parts of our life (including our diet) that might need tweaking. Each of these changes, if taken up, promise a net improvement that becomes synergistic with the other changes. There’s a degree of biofeedback involved, and listening to your body, to be sure of what’s really best for you, not what merely should be best for you on paper.
The writing style is accessible while science-heavy. They don’t assume prior knowledge, and/but they sure deliver a lot. The book is more text than images, but there are plenty of medical diagrams, explanations, charts, and the like. You will feed like a medical student! And it’s very much worth studying.
Bottom line: highly recommendable even if you don’t have inflammation issues, and worth its weight in gold if you do.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
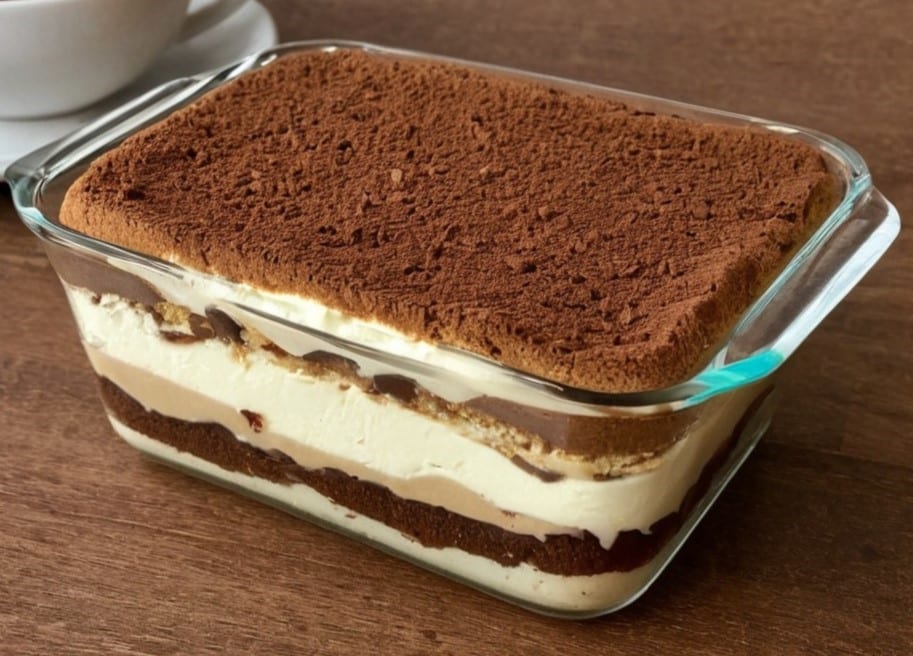
Healthy Tiramisu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tiramisu (literally “pick-me-up”, “tira-mi-su”) is a delightful dish that, in its traditional form, is also a trainwreck for the health, being loaded with inflammatory cream and sugar, not to mention the cholesterol content. Here we recreate the dish in healthy fashion, being loaded with protein, fiber, and healthy fats, not to mention that the optional sweetener is an essential amino acid. The coffee and cocoa, of course, are full of antioxidants too. All in all, what’s not celebrate?
You will need
- 2 cups silken tofu (no need to press it) (do not substitute with any firmer tofu or it will not work)
- 1 cup oat cream (you can buy this ready-made, or make it yourself by blending oats in water until you get the desired consistency) (you can also just use dairy cream, but that will be less healthy)
- 1 cup almond flour (also simply called “ground almonds”)
- 1 cup espresso ristretto, or otherwise the strongest black coffee you have facility to make
- ¼ cup unsweetened cocoa powder, plus more for dusting
- 1 pack savoiardi biscuits, also called “ladyfinger” biscuits (this was the only part we couldn’t make healthy—if you figure out a way to make it healthy, let us know!) (if vegan, obviously use a vegan substitute biscuit; this writer uses Lotus/Biscoff biscuits, which work well)
- 1 tsp vanilla essence
- ½ tsp almond essence
- Optional: glycine, per taste
- Garnish: roasted coffee beans
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add glycine to the coffee first if you want the overall dish to be sweeter. Glycine has approximately the same sweetness as sugar, and can be used as a 1:1 substitution. Use that information as you see fit.
2) Blend the tofu and the oat cream together in a high-speed blender until smooth. It should have a consistency like cake-batter; if it is too liquidy, add small amounts of almond flour until it is thicker. If it’s too thick, add oat cream until it isn’t. If you want it to be sweeter than it is, add glycine to taste. When happy with its taste and consistency, divide it evenly into two bowls.
3) Add the vanilla essence and almond essence to one bowl, and the cocoa powder to the other, mixing well (in a food processor, or just by using a whisk)
4) Coat the base of a glass dish (such as a Pyrex oven dish, but any dish is fine, and any glass dish will allow for viewing the pretty layers we’ll be making) with a very thin layer of almond flour (if you want sweetness there, you can mix some glycine in with the almond flour first).
4) One by one, soak the biscuits briefly in the coffee, and use them to line to base of the dish.
5) Add a thin layer of chocolate cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
6) Add a thin layer of vanilla-and-almond cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
7) Stop and assess: do you have enough ingredients left to repeat these layers? It will depend on the size and shape dish you used. If you do, repeat them, finishing with a vanilla-and-almond cream layer.
8) Dust the final layer with cocoa powder if you haven’t already, and add the coffee bean garnish, if using.
9) Refrigerate for at least 8 hours, and if you have time to prepare it the day before you will eat it, that is best of all.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- Tiramisu Crunch Bites ← craving tiramisu but not keen on all that effort? Enjoy these!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What’s the difference between a food allergy and an intolerance?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
At one time or another, you’ve probably come across someone who is lactose intolerant and might experience some unpleasant gut symptoms if they have dairy. Maybe it’s you – food intolerances are estimated to affect up to 25% of Australians.
Meanwhile, cow’s milk allergy is one of the most common food allergies in infants and young children, affecting around one in 100 infants.
But what’s the difference between food allergies and food intolerances? While they might seem alike, there are some fundamental differences between the two.
Feel good studio/Shutterstock What is an allergy?
Australia has one of the highest rates of food allergies in the world. Food allergies can develop at any age but are more common in children, affecting more than 10% of one-year-olds and 6% of children at age ten.
A food allergy happens when the body’s immune system mistakenly reacts to certain foods as if they were dangerous. The most common foods that trigger allergies include eggs, peanuts and other nuts, milk, shellfish, fish, soy and wheat.
Mild to moderate signs of food allergy include a swollen face, lips or eyes; hives or welts on your skin; or vomiting. A severe allergic reaction (called anaphylaxis) can cause trouble breathing, persistent dizziness or collapse.
What is an intolerance?
Food intolerances (sometimes called non-allergic reactions) are also reactions to food, but they don’t involve your immune system.
For example, lactose intolerance is a metabolic condition that happens when the body doesn’t produce enough lactase. This enzyme is needed to break down the lactose (a type of sugar) in dairy products.
Food intolerances can also include reactions to natural chemicals in foods (such as salicylates, found in some fruits, vegetables, herbs and spices) and problems with artificial preservatives or flavour enhancers.
Lactose intolerance is caused by a problem with breaking down lactose in milk. Pormezz/Shutterstock Symptoms of food intolerances can include an upset stomach, headaches and fatigue, among others.
Food intolerances don’t cause life-threatening reactions (anaphylaxis) so are less dangerous than allergies in the short term, although they can cause problems in the longer term such as malnutrition.
We don’t know a lot about how common food intolerances are, but they appear to be more commonly reported than allergies. They can develop at any age.
It can be confusing
Some foods, such as peanuts and tree nuts, are more often associated with allergy. Other foods or ingredients, such as caffeine, are more often associated with intolerance.
Meanwhile, certain foods, such as cow’s milk and wheat or gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye and barley), can cause both allergic and non-allergic reactions in different people. But these reactions, even when they’re caused by the same foods, are quite different.
For example, children with a cow’s milk allergy can react to very small amounts of milk, and serious reactions (such as throat swelling or difficulty breathing) can happen within minutes. Conversely, many people with lactose intolerance can tolerate small amounts of lactose without symptoms.
There are other differences too. Cow’s milk allergy is more common in children, though many infants will grow out of this allergy during childhood.
Lactose intolerance is more common in adults, but can also sometimes be temporary. One type of lactose intolerance, secondary lactase deficiency, can be caused by damage to the gut after infection or with medication use (such as antibiotics or cancer treatment). This can go away by itself when the underlying condition resolves or the person stops using the relevant medication.
Whether an allergy or intolerance is likely to be lifelong depends on the food and the reason that the child or adult is reacting to it.
Allergies to some foods, such as milk, egg, wheat and soy, often resolve during childhood, whereas allergies to nuts, fish or shellfish, often (but not always) persist into adulthood. We don’t know much about how likely children are to grow out of different types of food intolerances.
How do you find out what’s wrong?
If you think you may have a food allergy or intolerance, see a doctor.
Allergy tests help doctors find out which foods might be causing your allergic reactions (but can’t diagnose food intolerances). There are two common types: skin prick tests and blood tests.
In a skin prick test, doctors put tiny amounts of allergens (the things that can cause allergies) on your skin and make small pricks to see if your body reacts.
A blood test checks for allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in your blood that show if you might be allergic to a particular food.
Blood tests can help diagnose allergies. RossHelen/Shutterstock Food intolerances can be tricky to figure out because the symptoms depend on what foods you eat and how much. To diagnose them, doctors look at your health history, and may do some tests (such as a breath test). They may ask you to keep a record of foods you eat and timing of symptoms.
A temporary elimination diet, where you stop eating certain foods, can also help to work out which foods you might be intolerant to. But this should only be done with the help of a doctor or dietitian, because eliminating particular foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies, especially in children.
Is there a cure?
There’s currently no cure for food allergies or intolerances. For allergies in particular, it’s important to strictly avoid allergens. This means reading food labels carefully and being vigilant when eating out.
However, researchers are studying a treatment called oral immunotherapy, which may help some people with food allergies become less sensitive to certain foods.
Whether you have a food allergy or intolerance, your doctor or dietitian can help you to make sure you’re eating the right foods.
Victoria Gibson, a Higher Degree by Research student and Research Officer at the School of Nursing, Midwifery and Social Work at the University of Queensland, and Rani Scott-Farmer, a Senior Research Assistant at the University of Queensland, contributed to this article.
Jennifer Koplin, Group Leader, Childhood Allergy & Epidemiology, The University of Queensland and Desalegn Markos Shifti, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Child Health Research Centre, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Radical Longevity – by Dr. Ann Gittleman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Gittleman takes a comprehensive approach, advising us about avoiding AGEs, freeing up fascia, stimulating cellular rejuvenation, the mind-gut connection, keeping the immune system healthy, and more.
The “plan” promised by the subtitle involves identifying the key factors of nutrition and lifestyle most impactful to you, and adjusting them accordingly, in a multistep, author-walks-the-reader-by-the-hand process.
There’s also, for those who prefer it, a large section (seven chapters) on a body part/system by body part/system approach, e.g. brain health, heart health, revitalizing skin, reversing hair loss, repairing bones, muscles, joints, etc.
The writing style is quite casual,butalso with a mind to education, with its call-out boxes, bullet-point summaries, and so forth. There is a “select references” section, but if one wants to find studies, it’s often necessary to go looking, as there aren’t inline citations.
Bottom line: we’d love to see better referencing, but otherwise this is a top-tier anti-aging book, and a lot more accessible than most, without skimping on depth and breadth.
Click here to check out Radical Longevity, and get rejuvenating radically!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hope: A research-based explainer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This year, more than 60 countries, representing more than 4 billion people, will hold major elections. News headlines already are reporting that voters are hanging on to hope. When things get tough or don’t go our way, we’re told to hang on to hope. HOPE was the only word printed on President Barack Obama’s iconic campaign poster in 2008.
Research on hope has flourished only in recent decades. There’s now a growing recognition that hope has a role in physical, social, and mental health outcomes, including promoting resilience. As we embark on a challenging year of news, it’s important for journalists to learn about hope.
So what is hope? And what does the research say about it?
Merriam-Webster defines hope as a “desire accompanied by expectation of or belief in fulfillment.” This definition highlights the two basic dimensions of hope: a desire and a belief in the possibility of attaining that desire.
Hope is not Pollyannaish optimism, writes psychologist Everett Worthington in a 2020 article for The Conversation. “Instead, hope is a motivation to persevere toward a goal or end state, even if we’re skeptical that a positive outcome is likely.”
There are several scientific theories about hope.
One of the first, and most well-known, theories on hope was introduced in 1991 by American psychologist Charles R. Snyder.
In a paper published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, Snyder defined hope as a cognitive trait centered on the pursuit of goals and built on two components: a sense of agency in achieving a goal, and a perceived ability to create pathways to achieve that goal. He defined hope as something individualistic.
Snyder also introduced the Hope Scale, which continues to be used today, as a way to measure hope. He suggested that some people have higher levels of hope than others and there seem to be benefits to being more hopeful.
“For example, we would expect that higher as compared with lower hope people are more likely to have a healthy lifestyle, to avoid life crises, and to cope better with stressors when they are encountered,” they write.
Others have suggested broader definitions.
In 1992, Kaye Herth, a professor of nursing and a scholar on hope, defined hope as “a multidimensional dynamic life force characterized by a confident yet uncertain expectation of achieving good, which to the hoping person, is realistically possible and personally significant.” Herth also developed the Herth Hope Index, which is used in various settings, including clinical practice and research.
More recently, others have offered an even broader definition of hope.
Anthony Scioli, a clinical psychologist and author of several books on hope, defines hope “as an emotion with spiritual dimensions,” in a 2023 review published in Current Opinion in Psychology. “Hope is best viewed as an ameliorating emotion, designed to fill the liminal space between need and reality.”
Hope is also nuanced.
“Our hopes may be active or passive, patient or critical, private or collective, grounded in the evidence or resolute in spite of it, socially conservative or socially transformative,” writes Darren Webb in a 2007 study published in History of the Human Sciences. “We all hope, but we experience this most human of all mental feelings in a variety of modes.”
To be sure, a few studies have shown that hope can have negative outcomes in certain populations and situations. For example, one study highlighted in the research roundup below finds that Black college students who had higher levels of hope experienced more stress due to racial discrimination compared with Black students who had lower levels of hope.
Today, hope is one of the most well-studied constructs within the field of positive psychology, according to the journal Current Opinion in Psychology, which dedicated its August 2023 issue to the subject. (Positive psychology is a branch of psychology focused on characters and behaviors that allow people to flourish.)
We’ve gathered several studies below to help you think more deeply about hope and recognize its role in your everyday lives.
Research roundup
The Role of Hope in Subsequent Health and Well-Being For Older Adults: An Outcome-Wide Longitudinal Approach
Katelyn N.G. Long, et al. Global Epidemiology, November 2020.The study: To explore the potential public health implications of hope, researchers examine the relationship between hope and physical, behavioral and psychosocial outcomes in 12,998 older adults in the U.S. with a mean age of 66.
Researchers note that most investigations on hope have focused on psychological and social well-being outcomes and less attention has been paid to its impact on physical and behavioral health, particularly among older adults.
The findings: Results show a positive association between an increased sense of hope and a variety of behavioral and psychosocial outcomes, such as fewer sleep problems, more physical activity, optimism and satisfaction with life. However, there wasn’t a clear association between hope and all physical health outcomes. For instance, hope was associated with a reduced number of chronic conditions, but not with stroke, diabetes and hypertension.
The takeaway: “The later stages of life are often defined by loss: the loss of health, loved ones, social support networks, independence, and (eventually) loss of life itself,” the authors write. “Our results suggest that standard public health promotion activities, which often focus solely on physical health, might be expanded to include a wider range of factors that may lead to gains in hope. For example, alongside community-based health and nutrition programs aimed at reducing chronic conditions like hypertension, programs that help strengthen marital relations (e.g., closeness with a spouse), provide opportunities to volunteer, help lower anxiety, or increase connection with friends may potentially increase levels of hope, which in turn, may improve levels of health and well-being in a variety of domains.”
Associated Factors of Hope in Cancer Patients During Treatment: A Systematic Literature Review
Corine Nierop-van Baalen, Maria Grypdonck, Ann van Hecke and Sofie Verhaeghe. Journal of Advanced Nursing, March 2020.The study: The authors review 33 studies, written in English or Dutch and published in the past decade, on the relationship between hope and the quality of life and well-being of patients with cancer. Studies have shown that many cancer patients respond to their diagnosis by nurturing hope, while many health professionals feel uneasy when patients’ hopes go far beyond their prognosis, the authors write.
The findings: Quality of life, social support and spiritual well-being were positively associated with hope, as measured with various scales. Whereas symptoms, psychological distress and depression had a negative association with hope. Hope didn’t seem to be affected by the type or stage of cancer or the patient’s demographics.
The takeaway: “Hope seems to be a process that is determined by a person’s inner being rather than influenced from the outside,” the authors write. “These factors are typically given meaning by the patients themselves. Social support, for example, is not about how many patients experience support, but that this support has real meaning for them.”
Characterizing Hope: An Interdisciplinary Overview of the Characteristics of Hope
Emma Pleeging, Job van Exel and Martijn Burger. Applied Research in Quality of Life, September 2021.The study: This systematic review provides an overview of the concept of hope based on 66 academic papers in ten academic fields, including economics and business studies, environmental studies, health studies, history, humanities, philosophy, political science, psychology, social science, theology and youth studies, resulting in seven themes and 41 sub-themes.
The findings: The authors boil down their findings to seven components: internal and external sources, the individual and social experience of hope, internal and external effects, and the object of hope, which can be “just about anything we can imagine,” the authors write.
The takeaway: “An important implication of these results lies in the way hope is measured in applied and scientific research,” researchers write. “When measuring hope or developing instruments to measure it, researchers could be well-advised to take note of the broader understanding of the topic, to prevent that important characteristics might be overlooked.”
Revisiting the Paradox of Hope: The Role of Discrimination Among First-Year Black College Students
Ryon C. McDermott, et al. Journal of Counseling Psychology, March 2020.The study: Researchers examine the moderating effects of hope on the association between experiencing racial discrimination, stress and academic well-being among 203 first-year U.S. Black college students. They build on a small body of evidence that suggests high levels of hope might have a negative effect on Black college students who experience racial discrimination.
The authors use data gathered as part of an annual paper-and-pencil survey of first-year college students at a university on the Gulf Coast, which the study doesn’t identify.
The findings: Researchers find that Black students who had higher levels of hope experienced more stress due to racial discrimination compared with students who had lower levels of hope. On the other hand, Black students with low levels of hope may be less likely to experience stress when they encounter discrimination.
Meanwhile, Black students who had high levels of hope were more successful in academic integration — which researchers define as satisfaction with and integration into the academic aspects of college life — despite facing discrimination. But low levels of hope had a negative impact on students’ academic well-being.
“The present study found evidence that a core construct in positive psychology, hope, may not always protect Black students from experiencing the psychological sting of discrimination, but it was still beneficial to their academic well-being,” the authors write.
The takeaway: “Our findings also highlight an urgent need to reduce discrimination on college campuses,” the researchers write. “Reducing discrimination could help Black students (and other racial minorities) avoid additional stress, as well as help them realize the full psychological and academic benefits of having high levels of hope.”
Additional reading
Hope Across Cultural Groups Lisa M. Edwards and Kat McConnell. Current Opinion in Psychology, February 2023.
The Psychology of Hope: A Diagnostic and Prescriptive Account Anthony Scioli. “Historical and Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Hope,” July 2020.
Hope Theory: Rainbows in the Mind C.R. Snyder. Psychological Inquiry, 2002
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fitness Walking and Bodyweight Exercises – by Frank S. Ring
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of exercise manuals assume that the reader has a “basic” body (nothing Olympian, but nothing damaged either). As we get older, increasingly few of us fall into the “but nothing damaged either” category!
Here’s where Ring brings to bear his decades of experience as a coach and educator, and also his personal recovery from a serious back injury.
The book covers direct, actionable exercise advice (with all manner of detail), and also offers mental health tips he’s learned along the way.
Ring, like us, is a big fan of keeping things simple, so he focusses on “the core four” of bodyweight exercises:
- Pushups
- Squats
- Lunges
- Planks
These four exercises get a whole chapter devoted to them, though! Because there are ways to make each exercise easier or harder, or have different benefits. For example, adjustments include:
- Body angle
- Points of contact
- Speed
- Pausing
- Range of motion
This, in effect, makes a few square meters of floor (and perhaps a chair or bench) your fully-equipped gym.
As for walking? Ring enjoys and extols the health benefits, and/but also uses his walks a lot for assorted mental exercises, and recommends we try them too.
A fine book for anyone who wants to gain and/or maintain good health, but doesn’t pressingly want to join a gym or start pumping iron!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
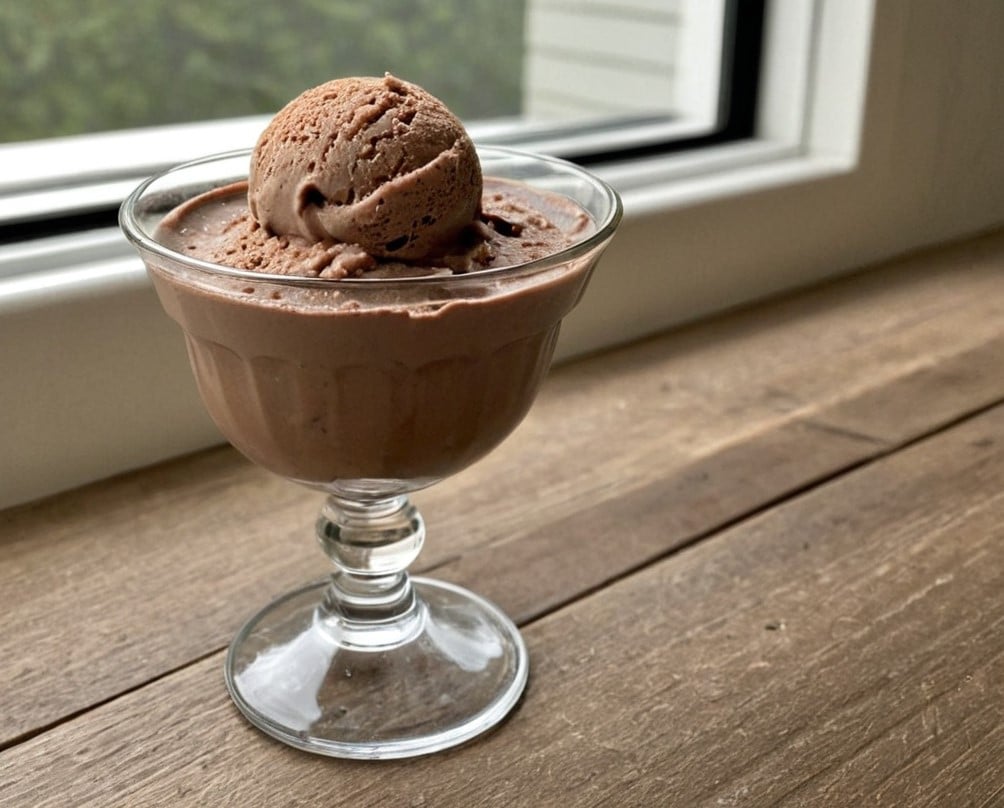
Healthy Choco-Banoffee Ice Cream
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chocolate, banana, and coffee—quite a threesome, whether for breakfast or dessert, and this is healthy enough for breakfast while being decadent enough for dessert! With no dairy or added sugar, and lots of antioxidants, this is a healthy way to start or end your day.
You will need
- 3 bananas
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder, no additives
- 2 shots espresso, chilled
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- On standby: milk of your choice—we recommend almond or hazelnut
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Peel, slice, and freeze the bananas (let them freeze for at least 2–3 hours)
2) Blend the ingredients, except the milk. Add milk as necessary if the mixture is too thick to blend. Be careful not to add too much at once though, or it will become less of an ice cream and more of a milkshake!
3) Scoop into a sundae glass to serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Plant Milk?
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Apples vs Bananas – Which is Healthier?
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: