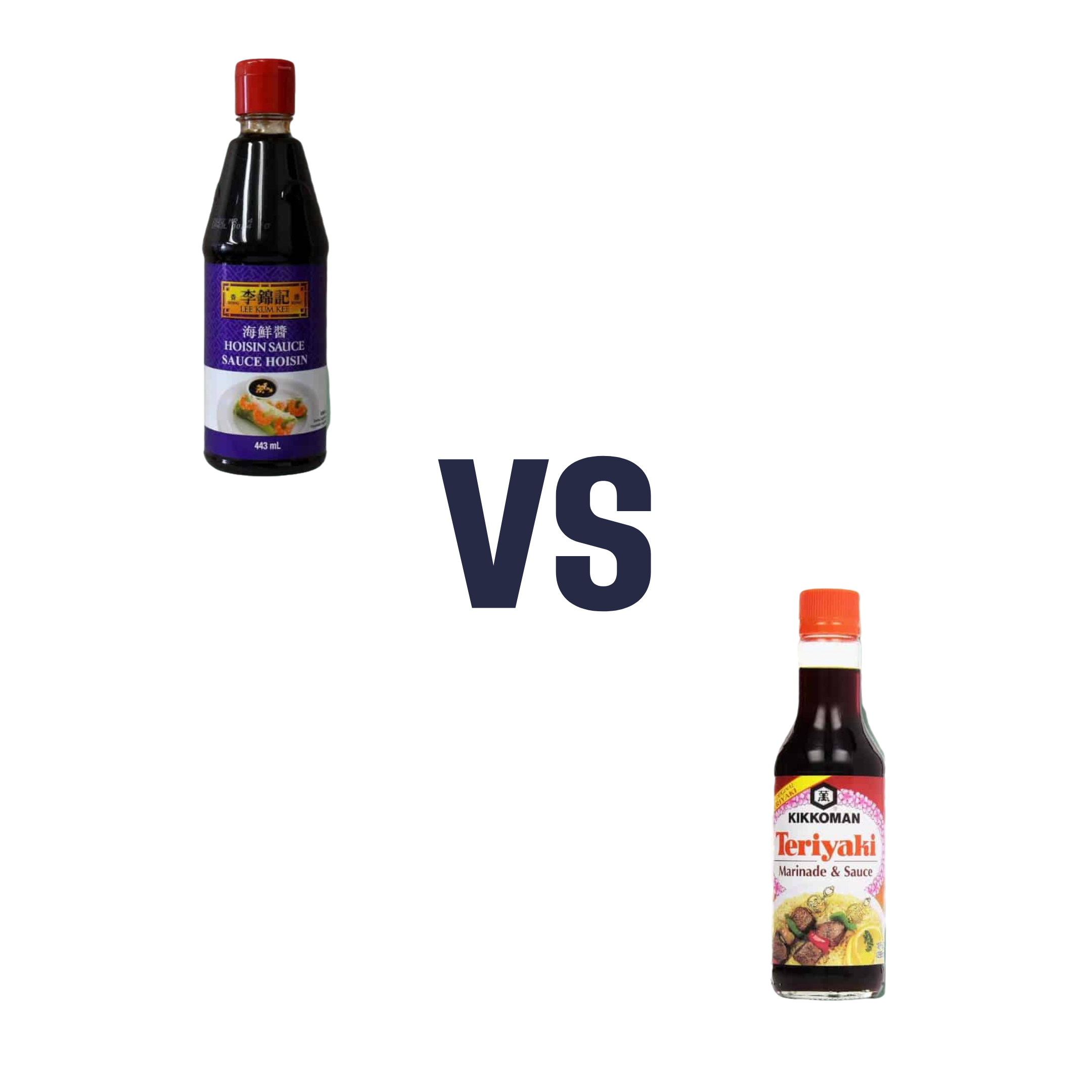
Hoisin Sauce vs Teriyaki Sauce – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hoisin sauce to teriyaki sauce, we picked the teriyaki sauce.
Why?
Neither are great! But spoonful for spoonful, the hoisin sauce has about 5x as much sugar.
Of course, exact amounts will vary by brand, but the hoisin will invariably be much more sugary than the teriyaki.
On the flipside, the teriyaki sauce may sometimes have slightly more salt, but they are usually in approximately the same ballpark of saltiness, so this is not a big deciding factor.
As a general rule of thumb, the first few ingredients will look like this for each, respectively:
Hoisin:
- Sugar
- Water
- Soybeans
Teriyaki:
- Soy sauce (water, soybeans, salt)
- Rice wine
- Sugar
In essence: hoisin is a soy-flavored syrup, while teriyaki is a sweetened soy sauce
Wondering about that rice wine? The alcohol content is negligible, sufficiently so that teriyaki sauce is not considered alcoholic. For health purposes, it is well under the 0.05% required to be considered alcohol-free.
For religious purposes, we are not your rabbi or imam, but to our best understanding, teriyaki sauce is generally considered kosher* (the rice wine being made from rice) and halal (the rice wine being de-alcoholized by the processing, making the sauce non-intoxicating).
Want to try some?
You can compare these examples side-by-side yourself:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What you need to know about xylazine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Xylazine is a non-opioid tranquilizer designed for veterinary use in animals. The sedative is not approved for use in people, yet it’s becoming more prevalent in the illicit drug supply.
Sometimes called “tranq,” it’s often mixed with other drugs, such as fentanyl, a potent opioid responsible for a growing number of overdose deaths. Last year, the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy declared fentanyl mixed with xylazine an “emerging threat.”
Read on to learn more about xylazine: what happens when people take it, what to do if an overdose is suspected, and how harm reduction tools can prevent overdose deaths.
How are people who use drugs exposed to xylazine?
Studies show people are exposed to xylazine—knowingly or unknowingly—when it’s mixed with other drugs like heroin, cocaine, meth, and, most frequently, fentanyl. When combined with opioids or other drugs, it increases the risk of a drug overdose.
What happens if someone takes xylazine?
Taking xylazine can cause drowsiness, amnesia, slow breathing, slow heart rate, dangerously low blood pressure, wounds that can become infected, and death, especially when taken in combination with other drugs.
Why does xylazine increase the risk of overdose?
Xylazine is a central nervous system depressant, which means that it slows down the body’s heart rate and breathing. It can also enhance the effects of other depressants, such as opioids, which may lead to suffocation.
What are the signs of a xylazine-related overdose?
Xylazine-related overdoses look like opioid overdoses. A person who has overdosed may exhibit a slow pulse, slow breathing, blurry vision, disorientation, drowsiness, confusion, blue skin, and loss of consciousness.
How many people die from xylazine-related overdoses in the U.S.?
Xylazine-related overdose deaths in the U.S. rose from 102 deaths in 2018 to 3,468 deaths in 2021. Most occurred in Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. Fentanyl was the most frequently co-occurring drug involved in those deaths.
What should I do if an overdose is suspected?
If you suspect that a person has overdosed on any drug, call 911 and give them naloxone—sometimes sold under the brand name Narcan—a medication that can reverse an opioid overdose. You should also stay with the person who has overdosed until first responders arrive. Most states have Good Samaritan laws, which protect people who have overdosed and those assisting them from certain criminal penalties.
While naloxone cannot reverse the effects of xylazine alone, experts recommend administering naloxone if an overdose is suspected because it’s often mixed with opioids.
You can get naloxone for free from some nonprofit organizations and government-run programs. You can also purchase over-the-counter naloxone at pharmacies, grocery and convenience stores, and other retailers.
Learn how to use naloxone in this short training video from the American Medical Association, or sign up for a free online training.
How can people prevent xylazine-related overdoses?
Harm reduction programs are community programs that prevent drug overdoses, reduce the spread of infectious diseases, and connect people to medical care. These programs provide lifesaving tools like naloxone, as well as fentanyl and xylazine test strips, which can detect the presence of these drugs in a substance and prevent overdoses. Drug test strips can also be ordered online.
However, test strips are considered “drug paraphernalia” in some states and are not legal everywhere. Learn more about state laws around drug checking equipment from the Network for Public Health Law.
Learn more about harm reduction from the CDC.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
What is a virtual emergency department? And when should you ‘visit’ one?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For many Australians the emergency department (ED) is the physical and emblematic front door to accessing urgent health-care services.
But health-care services are evolving rapidly to meet the population’s changing needs. In recent years, we’ve seen growing use of telephone, video, and online health services, including the national healthdirect helpline, 13YARN (a crisis support service for First Nations people), state-funded lines like 13 HEALTH, and bulk-billed telehealth services, which have helped millions of Australians to access health care on demand and from home.
The ED is similarly expanding into new telehealth models to improve access to emergency medical care. Virtual EDs allow people to access the expertise of a hospital ED through their phone, computer or tablet.
All Australian states and the Northern Territory have some form of virtual ED at least in development, although not all of these services are available to the general public at this stage.
So what is a virtual ED, and when is it appropriate to consider using one?
Shutterstock/Nils Versemann How does a virtual ED work?
A virtual ED is set up to mirror the way you would enter the physical ED front door. First you provide some basic information to administration staff, then you are triaged by a nurse (this means they categorise the level of urgency of your case), then you see the ED doctor. Generally, this all takes place in a single video call.
In some instances, virtual ED clinicians may consult with other specialists such as neurologists, cardiologists or trauma experts to make clinical decisions.
A virtual ED is not suitable for managing medical emergencies which would require immediate resuscitation, or potentially serious chest pains, difficulty breathing or severe injuries.
A virtual ED is best suited to conditions that require immediate attention but are not life-threatening. These could include wounds, sprains, respiratory illnesses, allergic reactions, rashes, bites, pain, infections, minor burns, children with fevers, gastroenteritis, vertigo, high blood pressure, and many more.
People with these sorts of conditions and concerns may not be able to get in to see a GP straight away and may feel they need emergency advice, care or treatment.
When attending the ED, they can be subject to long wait times and delayed specialist attention because more serious cases are naturally prioritised. Attending a virtual ED may mean they’re seen by a doctor more quickly, and can begin any relevant treatment sooner.
From the perspective of the health-care system, virtual EDs are about redirecting unnecessary presentations away from physical EDs, helping them be ready to respond to emergencies. The virtual ED will not hesitate in directing callers to come into the physical ED if staff believe it is an emergency.
The doctor in the virtual ED may also direct the patient to a GP or other health professional, for example if their condition can’t be assessed visually, or if they need physical treatment.
The results so far
Virtual EDs have developed significantly over the past three years, predominantly driven by the COVID pandemic. We are now starting to slowly see assessments of these services.
A recent evaluation my colleagues and I did of Queensland’s Metro North Virtual ED found roughly 30% of calls were directed to the physical ED. This suggests 70% of the time, cases could be managed effectively by the virtual ED.
Preliminary data from a Victorian virtual ED indicates it curbed a similar rate of avoidable ED presentations – 72% of patients were successfully managed by the virtual ED alone. A study on the cost-effectiveness of another Victorian virtual ED suggested it has the potential to generate savings in health-care costs if it prevents physical ED visits.
Only 1.2% of people assessed in Queensland’s Metro North Virtual ED required unexpected hospital admission within 48 hours of being “discharged” from the virtual ED. None of these cases were life-threatening. This indicates the virtual ED is very safe.
The service experienced an average growth rate of 65% each month over a two-year evaluation period, highlighting increasing demand and confidence in the service. Surveys suggested clinicians also view the virtual ED positively.
The right advice could tell you whether you need to visit hospital in person or not. 1st footage/Shutterstock What now?
We need further research into patient outcomes and satisfaction, as well as the demographics of those using virtual EDs, and how these measures compare to the physical ED across different triage categories.
There are also challenges associated with virtual EDs, including around technology (connection and skills among patients and health professionals), training (for health professionals) and the importance of maintaining security and privacy.
Nonetheless, these services have the potential to reduce congestion in physical EDs, and offer greater convenience for patients.
Eligibility differs between different programs, so if you want to use a virtual ED, you may need to check you are eligible in your jurisdiction. Most virtual EDs can be accessed online, and some have direct phone numbers.
Jaimon Kelly, Senior Research Fellow in Telehealth delivered health services, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Sweet Dreams Are Made Of Cheese (Or Are They?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝In order to lose a little weight I have cut out cheese from my diet – and am finding that I am sleeping better. Would be interested in your views on cheese and sleep, and whether some types of cheese are worse for sleep than others. I don’t want to give up cheese entirely!❞
In principle, there’s nothing in cheese that, biochemically, should impair sleep. If anything, its tryptophan content could aid good sleep.
Tryptophan is found in many foods, including cheese, which (of common foods, anyway), for example cheddar cheese ranks second only to pumpkin seeds in tryptophan content.
Tryptophan can be converted by the body into 5-HTP, which you’ve maybe seen sold as a supplement. Its full name is 5-hydroxytryptophan.
5-HTP can, in turn, be used to make melatonin and/or serotonin. Which of those you will get more of, depends on what your body is being cued to do by ambient light/darkness, and other environmental cues.
If you are having cheese and then checking your phone, for instance, or otherwise hanging out where there are white/blue lights, then your body may dutifully convert the tryptophan into serotonin (calm wakefulness) instead of melatonin (drowsiness and sleep).
In short: the cheese will (in terms of this biochemical pathway, anyway) augment some sleep-inducing or wakefulness-inducing cues, depending on which are available.
You may be wondering: what about casein?
Casein is oft-touted as producing deep sleep, or disturbed sleep, or vivid dreams, or bad dreams. There’s no science to back any of this up, though the following research review is fascinating:
Dreams of the Rarebit Fiend: food and diet as instigators of bizarre and disturbing dreams
(it largely supports the null hypothesis of “not a causal factor” but does look at the many more likely alternative explanations, ranging from associated actually casual factors (such as alcohol and caffeine) and placebo/nocebo effect)
Finally, simple digestive issues may be the real thing at hand:
Worth noting that around two thirds of all people, including those who regularly enjoy dairy products, have some degree of lactose intolerance:
Lactose Intolerance in Adults: Biological Mechanism and Dietary Management
So, in terms of what cheese may be better/worse for you in this context, you might try experimenting with lactose-free cheese, which will help you identify whether that was the issue!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Dates vs Banana – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to banana, we picked the dates.
Why?
It was close, and bananas do have some strengths too! We pitted these two against each other as they’re both sweet fruits often used as a sweetening and consistency-altering ingredient in desserts and sweet snacks, so if you’re making a choice between them, here are the things to consider:
In terms of macros, dates have more than 3x the fiber, more than 2x the protein, and a little over 3x the carbs. You may be wondering how this adds up in terms of glycemic index: dates have the lower GI. So, we pick dates, here, for that reason and overall nutritional density too.
When it comes to vitamins, bananas have their moment, albeit barely: dates have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, and K, while bananas have more of vitamins A, B6, C, E, and choline, making for a marginal victory for bananas in this category.
Looking at minerals next, however, it’s quite a different story: dates have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while bananas are not higher in any mineral. No, not even potassium, for which they are famous—dates have nearly 2x more potassium than bananas.
Adding up these sections makes for a clear win for dates in general!
Enjoy either/both, but dates are the more nutritious snack/ingredient.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10 Ways To Self-Soothe That Don’t Involve Food Or Drink
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If one is accustomed to comfort-eating or drowning one’s sorrows, what are the alternatives that can actually work? Holistic nutritionist Selin Bilgin has a list:
Self-Care That’s Not Self-Sabotage
You might want to make a note of these 10 things, so they can be a sort of “menu” for you when you need them:
- Give your introversion or extroversion what it needs (e.g. alone time to decompress, or social activities)
- Treat your senses: often we don’t actually need food/drink so much as culinary entertainment. So, we can sate this sensory mood in other ways, for example pleasant candles, flowers, and so forth.
- Bathe/shower nicely: it’s cliché but some personal pampering can go a long way
- Beautify yourself: it’s also cliché, but a makeover evening has its place
- Move! Go for a walk, do some yoga, whatever suits you, but move your body.
- Make movie nights luxurious: instead of making it about food/drink, focus on creating an enjoyable atmosphere
- Physically release tension: at 10almonds we recommend progressive relaxation for this!
- Create something: whether it’s art, craft, baking, or something else, creativity feels good
- Tackle things you’ve been procrastinating: this one doesn’t seem like self-soothing from the front end, but from the back end (i.e., having done it), it makes a big difference!
- Journal: expressing your thoughts and feelings can help a lot—really.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
- Rebalancing Dopamine (Without “Dopamine Fasting”)
- Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Herring vs Sardines – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing herring to sardine, we picked the sardines.
Why?
In terms of macros, they are about equal in protein and fat, but herring has about 2x the saturated fat and about 2x the cholesterol. So, sardines win this category easily.
When it comes to vitamins, herring has more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, and B12, while sardines have more of vitamins B3, E, and K. That’s a 5:3 win for herring, although it’s worth mentioning that the margins of difference are mostly not huge, except for that sardines have 26x the vitamin K content. Still, by the overall numbers, this one’s a win for herring.
In the category of minerals, herring is not richer in any minerals*, while sardines are richer in calcium, copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium, meaning a clear win for sardines.
*unless we want to consider mercury to be a mineral, in which case, let’s mention that on average, herring is 6x higher in mercury. However, we consider that also a win for sardines.
All in all, sardines are better for the heart (much lower in cholesterol), bones (much higher in calcium), and brain (much lower in mercury).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: Antibiotics, Mercury, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: