HIIT, But Make It HIRT
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This May HIRT A Bit

This is Ingrid Clay. She’s a professional athlete, personal trainer, chef*, and science writer.
*A vegan bodybuilding chef, no less:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
For those who prefer reading…
This writer does too 😉
We’ve previously reviewed her book, “Science of HIIT”, and we’re going to be talking a bit about High Intensity Interval Training today.
If you’d like to know a little more about the woman herself first, then…
Centr | Meet Ingrid: Your HIIT HIRT trainer
Yes, that is Centr, as in Chris Hemsworth’s personal training app, where Clay is the resident HIIT & HIRT expert & trainer.
What’s this HIIT & HIRT?
“HIIT” is High Intensity Interval Training, which we’ve written about before:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Basically, it’s a super-efficient way of working out, that gets better results than working out for longer with other methods, especially because of how it raises the metabolism for a couple of hours after training (this effect is called EPOC, by the way—Excessive Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption), and is a good thing.
You can read more about the science of it, in the above-linked main feature.
And HIRT?
“HIRT” is High Intensity Resistance Training, and is resistance training performed with HIIT principles.
See also: Chris Hemsworth’s Trainer Ingrid Clay Explains HIRT
An example is doing 10 reps of a resistance exercise (e.g., a dumbbell press) every minute on odd-numbered minutes, and 10 reps of a different resistance exercise (e.g. dumbbell squats) on even-numbered minutes.
If dumbbells aren’t your thing, it could be resistance bands, or even the floor (press-ups are a resistance exercise!)
For HIRT that’s not also a cardio exercise, gaps between different exercises can be quite minimal, as we only need to confuse the muscles, not the heart. So, effectively, it becomes a specially focused kind of circuit training!
If doing planks though, you might want to check out Clay’s troubleshooting guide:
Want more from Clay?
Here she gives a full 20-minute full-body HIIT HIRT workout:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Proteinaholic – by Dr. Garth Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Protein is important, yes. However, you can have too much of a good thing, and you can also get it from bad sources that do more harm than good.
That’s what this book is about, and how to go about understanding the science in a world where marketing has outstripped the conclusions of research scientists.
Firstly, let’s mention that Dr. Davis’ main issue here is (as the subtitle suggests) about animal proteins, not plant-based proteins. The former are associated with very many health risks that the latter are not. And yes, even just the lean protein, not considering the animal fat.
He does not argue that the reader must, or even necessarily needs to, adopt a vegan diet. However, he does argue for minimizing animal proteins, and getting more plants in.
A lot of the book is about the research to back this approach, and specifically, it’s largely a polemic against animal protein. He also shares anecdotes throughout, about his own health journey—from an overweight cheeseburger-fueled heart attack machine with exciting cholesterol levels, to a healthy, muscular, plant-fueled advocate for healthier eating.
He talks us through the science at hand, including chapters for each of the main health risks associated with meat consumption, as well as how the science got misrepresented by popular marketing for [not necessarily, but usually] meat-heavy diets such as Atkins and Paleo. That yes, they will give short term weight loss, but bring extra health risks in the longer term, and how.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut down your meat consumption but worry “will I get enough protein?”, this book will set your mind at ease with an abundance of science.
Click here to check out Proteinaholic, and give your body better!
Share This Post
-
Radiant Rebellion – by Karen Walrond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In health terms, we are often about fighting aging here. But to be more specific, what we’re fighting in those cases is not truly aging itself, so much as age-related decline.
Karen Walrond makes a case that we’ve made from the very start of 10almonds (but she wrote a whole book about it), that there’s merit in looking at what we can and can’t control about aging, doing what we reasonably can, and embracing what we can’t.
And yes, embracing, not merely accepting. This is not a downer of a book; it’s a call to revolution. It asks us to be proud of our grey hairs, to see our smile-lines around our eyes as the sign of a lived-in body, and even to embrace some of the unavoidable “actual decline” things as part of the journey of life. Maybe we’re not as strong as we used to be and now need a grippety-doodah to open jars; not everyone gets to live long enough to experience that! How lucky we are.
Perhaps most importantly, she bids us be the change we want to see in the world, and inspire others with our choices and actions, and shake off ageist biases for good.
Bottom line: if you want to foster a better attitude to aging not only for yourself, but also those around you, then this is a top-tier book for that.
Click here to check out Radiant Rebellion, and reclaim aging!
Share This Post
-
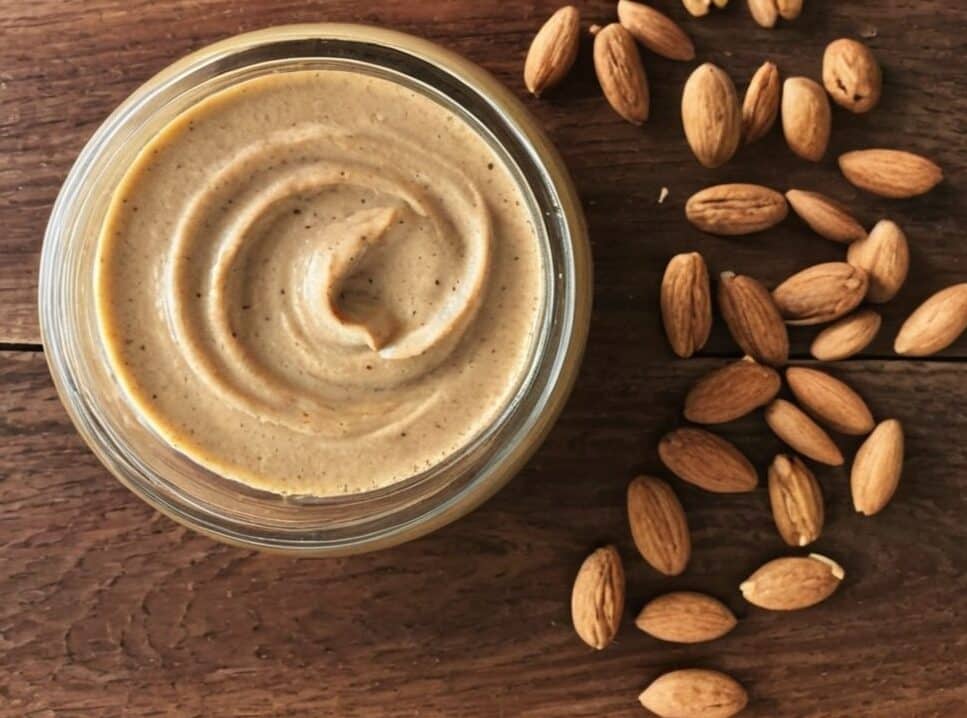
Healthiest-Three-Nut Butter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re often telling you to “diversify your nuts”, so here’s a great way to get in three at once with no added sugar, palm oil, or preservatives, and only the salt you choose to put in. We’ve picked three of the healthiest nuts around, but if you happen to be allergic, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered too.
You will need
- 1 cup almonds (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. chia, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup walnuts (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. pumpkin, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup pistachios (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. poppy, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 tbsp almond oil (if allergic, substitute extra virgin olive oil) (if you prefer sweet nut butter, substitute 1 tbsp maple syrup; the role here is to emulsify the nuts, and this will do the same job)
- Optional: ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1a) If using nuts, heat your oven to 350℉ / 180℃. Place the nuts on a baking tray lined with baking paper, and bake/roast for about 10 minutes, but keep an eye on it to ensure the nuts don’t burn, and jiggle them if necessary to ensure they toast evenly. Once done, allow to cool.
1b) If using seeds, you can either omit that step, or do the same for 5 minutes if you want to, but really it’s not necessary.
2) Blend all ingredients (nuts/seeds, oil, MSG/salt) in a high-speed blender. Note: this will take about 10 minutes in total, and we recommend you do it in 30-second bursts so as to not overheat the motor. You also may need to periodically scrape the mixture down the side of the blender, to ensure a smooth consistency.
3) Transfer to a clean jar, and enjoy at your leisure:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Sesame Seeds vs Poppy Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why Diets Make Us Fat – by Dr. Sandra Aamodt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known that crash-dieting doesn’t work. Restrictive diets will achieve short-term weight loss, but it’ll come back later. In the long term, weight creeps slowly upwards. Why?
Dr. Sandra Aamodt explores the science and sociology behind this phenomenon, and offers an evidence-based alternative.
A lot of the book is given over to explanations of what is typically going wrong—that is the title of the book, after all. From metabolic starvation responses to genetics to the negative feedback loop of poor body image, there’s a lot to address.
However, what alternative does she propose?
The book takes us on a shift away from focusing on the numbers on the scale, and more on building consistent healthy habits. It might not feel like it if you desperately want to lose weight, but it’s better to have healthy habits at any weight, than to have a wreck of physical and mental health for the sake of a lower body mass.
Dr. Aamodt lays out a plan for shifting perspectives, building health, and letting weight loss come by itself—as a side effect, not a goal.
In fact, as she argues (in agreement with the best current science, science that we’ve covered before at 10almonds, for that matter), that over a certain age, people in the “overweight” category of BMI have a reduced mortality risk compared to those in the “healthy weight” category. It really underlines how there’s no point in making oneself miserably unhealthy with the end goal of having a lighter coffin—and getting it sooner.
Bottom line: will this book make you hit those glossy-magazine weight goals by your next vacation? Quite possibly not, but it will set you up for actually healthier living, for life, at any weight.
Click here to check out Why Diets Make Us Fat, and live healthier and better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Your Brain Chooses What To Remember
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
During the day, your brain is simply too busy to encode memories without interfering with normal processing. At night, however…
The filing system
The brain decides which memories to keep based on significance, using sharp brain wave ripples as an internal bookmarking system. Everyday memories fade, while important events are tagged in this manner for consolidation during sleep.
How does it do this? It starts in the hippocampus, which records experiences during wakefulness and replays them repeatedly at high speed during sleep, preparing them for transfer to the neocortex.
How do we know? Uniform Manifold Approximation & Projection (UMAP) for dimension reduction is a tool that condenses 400-dimensional neural activity data into 3D for visualization. Mice navigating a maze showed hippocampal activity encoding location and learning progression; it also showed neural patterns reflecting maze layout and task mastery.
What this means in practical terms: you need to get good sleep if you don’t want to lose your memories!
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Boost Your Memory Immediately (Without Supplements)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What is PNF stretching, and will it improve my flexibility?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether improving your flexibility was one of your new year’s resolutions, or you’ve been inspired watching certain tennis stars warming up at the Australian Open, maybe 2025 has you keen to focus on regular stretching.
However, a quick Google search might leave you overwhelmed by all the different stretching techniques. There’s static stretching and dynamic stretching, which can be regarded as the main types of stretching.
But there are also some other potentially lesser known types of stretching, such as PNF stretching. So if you’ve come across PNF stretching and it piques your interest, what do you need to know?
Undrey/Shutterstock What is PNF stretching?
PNF stretching stands for proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation. It was developed in the 1940s in the United States by neurologist Herman Kabat and physical therapists Margaret Knott and Dorothy Voss.
PNF stretching was initially designed to help patients with neurological conditions that affect the movement of muscles, such as polio and multiple sclerosis.
By the 1970s, its popularity had seen PNF stretching expand beyond the clinic and into the sporting arena where it was used by athletes and fitness enthusiasts during their warm-up and to improve their flexibility.
Although the specifics have evolved over time, PNF essentially combines static stretching (where a muscle is held in a lengthened position for a short period of time) with isometric muscle contractions (where the muscle produces force without changing length).
PNF stretching is typically performed with the help of a partner.
There are 2 main types
The two most common types of PNF stretching are the “contract-relax” and “contract-relax-agonist-contract” methods.
The contract-relax method involves putting a muscle into a stretched position, followed immediately by an isometric contraction of the same muscle. When the person stops contracting, the muscle is then moved into a deeper stretch before the process is repeated.
For example, to improve your hamstring flexibility, you could lie down and get a partner to lift your leg up just to the point where you begin to feel a stretch in the back of your thigh.
Once this sensation eases, attempt to push your leg back towards the ground as your partner resists the movement. After this, your partner should now be able to lift your leg up slightly higher than before until you feel the same stretching sensation.
This technique was based on the premise that the contracted muscle would fall “electrically silent” following the isometric contraction and therefore not offer its usual level of resistance to further stretching (called “autogenic inhibition”). The contract-relax method attempts to exploit this brief window to create a deeper stretch than would otherwise be possible without the prior muscle contraction.
The contract-relax-agonist-contract method is similar. But after the isometric contraction of the stretched muscle, you perform an additional contraction of the muscle group opposing the muscle being stretched (referred to as the “agonist” muscle), before the muscle is moved into a static stretch once more.
Again, if you’re trying to improve hamstring flexibility, immediately after trying to push your leg towards the ground you would attempt to lift it back towards the ceiling (this bit without partner resistance). You would do this by contracting the muscles on the front of the thigh (the quadriceps, the agonist muscle in this case).
Likewise, after this, your partner should be able to lift your leg up slightly higher than before.
The contract-relax-agonist-contract method is said to take advantage of a phenomenon known as “reciprocal inhibition.” This is where contracting the muscle group opposite that of the muscle being stretched leads to a short period of reduced activation of the stretched muscle, allowing the muscle to stretch further than normal.
What does the evidence say?
Research has shown PNF stretching is associated with improved flexibility.
While it has been suggested that both PNF methods improve flexibility via changes in nervous system function, research suggests they may simply improve our ability to tolerate stretching.
It’s worth noting most of the research on PNF stretching and flexibility has focused on healthy populations. This makes it difficult to provide evidence-based recommendations for people with clinical conditions.
And it may not be the most effective method if you’re looking to improve your flexibility in the long term. A 2018 review found static stretching was better for improving flexibility compared to PNF stretching. But other research has found it could offer greater immediate benefits for flexibility than static stretching.
At present, similar to other types of stretching, research linking PNF stretching to injury prevention and improved athletic performance is relatively inconclusive.
PNF stretching may actually lead to small temporary deficits in performance of strength, power, and speed-based activities if performed immediately beforehand. So it’s probably best done after exercise or as a part of a standalone flexibility session.
Static stretching may be a more effective way to improve flexibility over the long-term. GaudiLab/Shutterstock How much should you do?
It appears that a single contract-relax or contract-relax-agonist-contract repetition per muscle, performed twice per week, is enough to improve flexibility.
The contraction itself doesn’t need to be hard and forceful – only about 20% of your maximal effort should suffice. The contraction should be held for at least three seconds, while the static stretching component should be maintained until the stretching sensation eases.
So PNF stretching is potentially a more time-efficient way to improve flexibility, compared to, for example, static stretching. In a recent study we found four minutes of static stretching per muscle during a single session is optimal for an immediate improvement in flexibility.
Is PNF stretching the right choice for me?
Providing you have a partner who can help you, PNF stretching could be a good option. It might also provide a faster way to become more flexible for those who are time poor.
However, if you’re about to perform any activities that require strength, power, or speed, it may be wise to limit PNF stretching to afterwards to avoid any potential deficits in performance.
Lewis Ingram, Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia and Hunter Bennett, Lecturer in Exercise Science, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: