Healthy Choco-Banoffee Ice Cream
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chocolate, banana, and coffee—quite a threesome, whether for breakfast or dessert, and this is healthy enough for breakfast while being decadent enough for dessert! With no dairy or added sugar, and lots of antioxidants, this is a healthy way to start or end your day.
You will need
- 3 bananas
- 2 tbsp cocoa powder, no additives
- 2 shots espresso, chilled
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
- On standby: milk of your choice—we recommend almond or hazelnut
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Peel, slice, and freeze the bananas (let them freeze for at least 2–3 hours)
2) Blend the ingredients, except the milk. Add milk as necessary if the mixture is too thick to blend. Be careful not to add too much at once though, or it will become less of an ice cream and more of a milkshake!
3) Scoop into a sundae glass to serve:
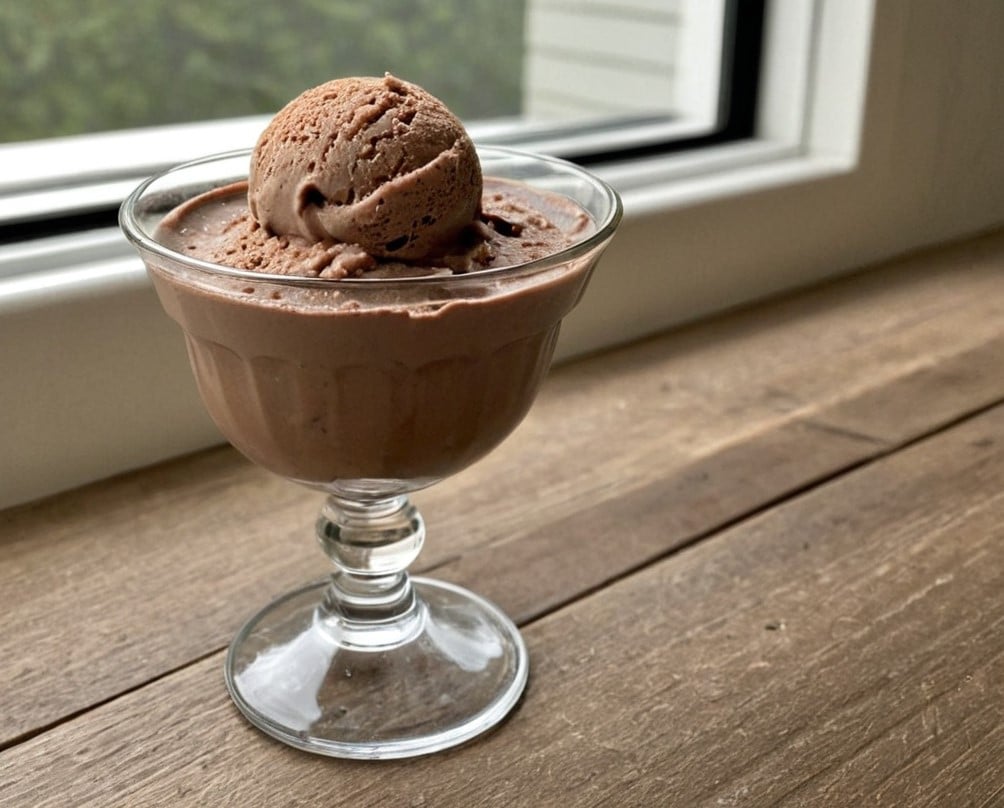

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Plant Milk?
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Apples vs Bananas – Which is Healthier?
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
“If the hardest thing you have to do in your day is eat a frog, eat that frog first!”, they say.
And, broadly speaking, it is indeed good to get anything stressful out of the way early, so that we can relax afterwards. But…
- Are we truly best at frog-eating when blurry-eyed and sleepy?
- Is there a spoonful of sugar that could make the medicine go down better?
- What do we need to turn eating the frog into an enjoyable activity?
Flow
“Flow” is a concept brought to public consciousness by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, and it refers to a state in which we feel good about what we’re doing, and just keep doing, at a peak performance level.
Writer’s note: as a writer, for example…
Sometimes I do not want to write, I pace to and fro near my computer, going on side-quests like getting a coffee or gazing out of the window into my garden. But once I get going, suddenly, something magical happens and before I know it, I have to trim my writing down because I’ve written too much. That magical window of effortless productivity was a state of flow.
Good morning!
What is a good morning, to you? Build that into your morning! Set parameters around it so you don’t get carried away timewise and find yourself in the afternoon (unless that would work for you!), but first thing in the morning is the time to light up each part of your brain with appropriate neurotransmitters.
Getting the brain juices flowing
Cortisol
When we wake up, we (unless we have some neurochemical imbalance, such as untreated depression) get a spike of cortisol. Cortisol is much-maligned and feared, and indeed it can be very much deleterious to the health in cases of chronic stress. But a little spike now and again is actually beneficial for us.
Quick Tip: if you want to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning cortisol spike, a cold shower is the way to go. Or even just a face-plunge into a bowl of ice-water (put ice in it, give it a couple of minutes to chill the water, then put your face in for a count of 30 seconds, or less if you can’t hold your breath that long).
Serotonin
Serotonin is generally thought of as “the happy chemical”, and it’s stimulated by blue/white light, and also by seeing greenery.
Quick tip: to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning serotonin boost, your best friend is sunlight. Even sun through a partly-clouded sky will tend to outperform artificial lighting, including artificial sunlight lighting. Try to get sun between 08:30 and 09:00, if you can. Best of all, do it in your garden or nearby park, as the greenery will be an extra boost!
Dopamine
Generally thought of as “the reward chemical”, but it’s also critical for a lot of kinds of brainwork, including language processing and problem-solving.
Quick Tip: to artificially stimulate* a dopamine surge to get you going, do something that you and/or your body finds rewarding. Examples include:
- Exercise, especially in a vigorous burst
- A good breakfast, a nice coffee, whatever feels right to you
- An app that has motivational bells and whistles, a streak for you to complete, etc
Note: another very enjoyable activity might come to mind that doesn’t even require you getting out of bed. Be aware, however, gentleman-readers specifically, that if you complete that activity, you’ll get a prolactin spike that will wipe out the dopamine you just worked up (because prolactin is antagonistic to dopamine). So that one’s probably better for a lazy morning when you can go back to sleep, than a day when you want to get up and go! Ladies, this is less of a worry for us as the physiology an orgasm driven by estrogen+progesterone rather than testosterone is different; there will not usually be a prolactin spike following the spike of dopamine; our orgasm-related dopamine spike is followed by a wave of oxytocin instead (“the cuddle chemical”), which is much more pleasant than prolactin.
*there’s no “(or enhance)” for this one; you won’t get dopamine from doing nothing, that’s just not how “the reward chemical” works
Flow-building in a stack
When you’ve just woken up and are in a blurry morning haze, that’s not the time to be figuring out “what should I be doing next?”, so instead:
- Work out the things you want to incorporate into your morning routine
- Put them in the order that will be easiest to perform—some things will go a lot better after others!
- Remember to also include things that are simply necessary—morning bathroom ablutions, for example
The goal here is to have a this-and-this-and-this-and-this list of items that you can go through without any deviations, and get in the habit of “after item 1 I automatically do item 2, after which I automatically do item 3, after which…”
Implement this, and your mornings will become practically automated, but in a joyous, life-enhancing way that sets you up in good order for whatever you want/need to do!
Share This Post
-
Could my glasses be making my eyesight worse?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, you got your eyesight tested and found out you need your first pair of glasses. Or you found out you need a stronger pair than the ones you have. You put them on and everything looks crystal clear. But after a few weeks things look blurrier without them than they did before your eye test. What’s going on?
Some people start to wear spectacles for the first time and perceive their vision is “bad” when they take their glasses off. They incorrectly interpret this as the glasses making their vision worse. Fear of this might make them less likely to wear their glasses.
But what they are noticing is how much better the world appears through the glasses. They become less tolerant of a blurry world when they remove them.
Here are some other things you might notice about eyesight and wearing glasses.
Lazy eyes?
Some people sense an increasing reliance on glasses and wonder if their eyes have become “lazy”.
Our eyes work in much the same way as an auto-focus camera. A flexible lens inside each eye is controlled by muscles that let us focus on objects in the distance (such as a footy scoreboard) by relaxing the muscle to flatten the lens. When the muscle contracts it makes the lens steeper and more powerful to see things that are much closer to us (such as a text message).
From the age of about 40, the lens in our eye progressively hardens and loses its ability to change shape. Gradually, we lose our capacity to focus on near objects. This is called “presbyopia” and at the moment there are no treatments for this lens hardening.
Optometrists correct this with prescription glasses that take the load of your natural lens. The lenses allow you to see those up-close images clearly by providing extra refractive power.
Once we are used to seeing clearly, our tolerance for blurry vision will be lower and we will reach for the glasses to see well again.
The wrong glasses?
Wearing old glasses, the wrong prescription (or even someone else’s glasses) won’t allow you to see as well as possible for day-to-day tasks. It could also cause eyestrain and headaches.
Incorrectly prescribed or dispensed prescription glasses can lead to vision impairment in children as their visual system is still in development.
But it is more common for kids to develop long-term vision problems as a result of not wearing glasses when they need them.
By the time children are about 10–12 years of age, wearing incorrect spectacles is less likely to cause their eyes to become lazy or damage vision in the long term, but it is likely to result in blurry or uncomfortable vision during daily wear.
Registered optometrists in Australia are trained to assess refractive error (whether the eye focuses light into the retina) as well as the different aspects of ocular function (including how the eyes work together, change focus, move around to see objects). All of these help us see clearly and comfortably.
Younger children with progressive vision impairments may need more frequent eye tests. Shutterstock What about dirty glasses?
Dirty or scratched glasses can give you the impression your vision is worse than it actually is. Just like a window, the dirtier your glasses are, the more difficult it is to see clearly through them. Cleaning glasses regularly with a microfibre lens cloth will help.
While dirty glasses are not commonly associated with eye infections, some research suggests dirty glasses can harbour bacteria with the remote but theoretical potential to cause eye infection.
To ensure best possible vision, people who wear prescription glasses every day should clean their lenses at least every morning and twice a day where required. Cleaning frames with alcohol wipes can reduce bacterial contamination by 96% – but care should be taken as alcohol can damage some frames, depending on what they are made of.
When should I get my eyes checked?
Regular eye exams, starting just before school age, are important for ocular health. Most prescriptions for corrective glasses expire within two years and contact lens prescriptions often expire after a year. So you’ll need an eye check for a new pair every year or so.
Kids with ocular conditions such as progressive myopia (short-sightedness), strabismus (poor eye alignment), or amblyopia (reduced vision in one eye) will need checks at least every year, but likely more often. Likewise, people over 65 or who have known eye conditions, such as glaucoma, will be recommended more frequent checks.
Eye checks can detect broader health issues. Shutterstock An online prescription estimator is no substitute for a full eye examination. If you have a valid prescription then you can order glasses online, but you miss out on the ability to check the fit of the frame or to have them adjusted properly. This is particularly important for multifocal lenses where even a millimetre or two of misalignment can cause uncomfortable or blurry vision.
Conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can affect the eyes so regular eye checks can also help flag broader health issues. The vast majority of eye conditions can be treated if caught early, highlighting the importance of regular preventative care.
James Andrew Armitage, Professor of Optometry and Course Director, Deakin University and Nick Hockley, Lecturer in Optometric Clinical Skills, Director Deakin Collaborative Eye Care Clinic, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Stop Sabotaging Your Weight Loss – by Jennifer Powter, MSc
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not a dieting book, and it’s not a motivational pep talk.
The book starts with the assumption that you do want to lose weight (it also assumes you’re a woman, and probably over 40… that’s just the book’s target market, but the same advice is good even if that’s not you), and that you’ve probably been trying, on and off, for a while. Her position is simple:
❝I don’t believe that you have a weight loss problem. I believe that you have a self-sabotage problem❞
As to how this sabotage may be occurring, Powter talks about fears that may be holding you back, including but not limited to:
- Fear of failure
- Fear of the unknown
- Fear of loss
- Fear of embarrassment
- Fear of your weight not being the reason your life sucks
Far from putting the reader down, though, Powter approaches everything with compassion. To this end, her prescription starts with encouraging self-love. Not when you’re down to a certain size, not when you’re conforming perfectly to a certain diet, but now. You don’t have to be perfect to be worthy of love.
On the topic of perfection: a recurring theme in the book is the danger of perfectionism. In her view, perfectionism is nothing more nor less than the most justifiable way to hold yourself back in life.
Lastly, she covers mental reframes, with useful questions to ask oneself on a daily basis, to ensure progressing step by step into your best life.
In short: if you’d like to lose weight and have been trying for a while, maybe on and off, this book could get you out of that cycle and into a much better state of being.
Get your copy of “Stop Sabotaging Your Weight Loss” from Amazon today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Qigong: A Breath Of Fresh Air?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Qigong: Breathing Is Good (Magic Remains Unverified)
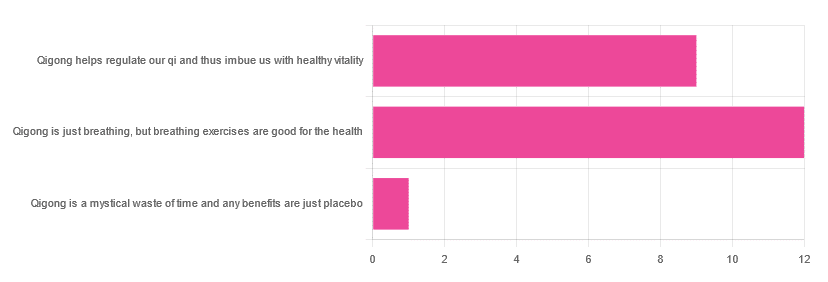
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinions of qigong, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 55% said “Qigong is just breathing, but breathing exercises are good for the health”
- About 41% said “Qigong helps regulate our qi and thus imbue us with healthy vitality”
- One (1) person said “Qigong is a mystical waste of time and any benefits are just placebo”
The sample size was a little low for this one, but the results were quite clearly favorable, one way or another.
So what does the science say?
Qigong is just breathing: True or False?
True or False, depending on how we want to define it—because qigong ranges in its presentation from indeed “just breathing exercises”, to “breathing exercises with visualization” to “special breathing exercises with visualization that have to be exactly this way, with these hand and sometimes body movements also, which also must be just right”, to far more complex definitions that involve qi by various mystical definitions, and/or an appeal to a scientific analog of qi; often some kind of bioelectrical field or such.
There is, it must be said, no good quality evidence for the existence of qi.
Writer’s note, lest 41% of you want my head now: I’ve been practicing qigong and related arts for about 30 years and find such to be of great merit. This personal experience and understanding does not, however, change the state of affairs when it comes to the availability (or rather, the lack) of high quality clinical evidence to point to.
Which is not to say there is no clinical evidence, for example:
Acute Physiological and Psychological Effects of Qigong Exercise in Older Practitioners
…found that qigong indeed increased meridian electrical conductance!
Except… Electrical conductance is measured with galvanic skin responses, which increase with sweat. But don’t worry, to control for that, they asked participants to dry themselves with a towel. Unfortunately, this overlooks the fact that a) more sweat can come where that came from, because the body will continue until it is satisfied of adequate homeostasis, and b) drying oneself with a towel will remove the moisture better than it’ll remove the salts from the skin—bearing in mind that it’s mostly the salts, rather than the moisture itself, that improve the conductivity (pure distilled water does conduct electricity, but not very well).
In other words, this was shoddy methodology. How did it pass peer review? Well, here’s an insight into that journal’s peer review process…
❝The peer-review system of EBCAM is farcical: potential authors who send their submissions to EBCAM are invited to suggest their preferred reviewers who subsequently are almost invariably appointed to do the job. It goes without saying that such a system is prone to all sorts of serious failures; in fact, this is not peer-review at all, in my opinion, it is an unethical sham.❞
~ Dr. Edzard Ernst, a founding editor of EBCAM (he since left, and decries what has happened to it since)
One of the other key problems is: how does one test qigong against placebo?
Scientists have looked into this question, and their answers have thus far been unsatisfying, and generally to the tune of the true-but-unhelpful statement that “future research needs to be better”:
Problems of scientific methodology related to placebo control in Qigong studies: A systematic review
Most studies into qigong are interventional studies, that is to say, they measure people’s metrics (for example, blood pressure, heart rate, maybe immune function biomarkers, sleep quality metrics of various kinds, subjective reports of stress levels, physical biomarkers of stress levels, things like that), then do a course of qigong (perhaps 6 weeks, for example), then measure them again, and see if the course of qigong improved things.
This almost always results in an improvement when looking at the before-and-after, but it says nothing for whether the benefits were purely placebo.
We did find one study that claimed to be placebo-controlled:
…but upon reading the paper itself carefully, it turned out that while the experimental group did qigong, the control group did a reading exercise. Which is… Saying how well qigong performs vs reading (qigong did outperform reading, for the record), but nothing for how well it performs vs placebo, because reading isn’t a remotely credible placebo.
See also: Placebo Effect: Making Things Work Since… Well, A Very Long Time Ago ← this one explains a lot about how placebo effect does work
Qigong is a mystical waste of time: True or False?
False! This one we can answer easily. Interventional studies invariably find it does help, and the fact remains that even if placebo is its primary mechanism of action, it is of benefit and therefore not a waste of time.
Which is not to say that placebo is its only, or even necessarily primary, mechanism of action.
Even from a purely empirical evidence-based medicine point of view, qigong is at the very least breathing exercises plus (usually) some low-impact body movement. Those are already two things that can be looked at, mechanistic processes pointed to, and declarations confidently made of “this is an activity that’s beneficial for health”.
See for example:
- Effects of Qigong practice in office workers with chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomized control trial
- Qigong for the Prevention, Treatment, and Rehabilitation of COVID-19 Infection in Older Adults
- Impact of Medical Qigong on quality of life, fatigue, mood and inflammation in cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial
…and those are all from respectable journals with meaningful peer review processes.
None of them are placebo-controlled, because there is no real option of “and group B will only be tricked into believing they are doing deep breathing exercises with low-impact movements”; that’s impossible.
But! They each show how doing qigong reliably outperforms not doing qigong for various measurable metrics of health.
And, we chose examples with physical symptoms and where possible empirically measurable outcomes (such as COVID-19 infection levels, or inflammatory responses); there are reams of studies showings qigong improves purely subjective wellbeing—but the latter could probably be claimed for any enjoyable activity, whereas changes in inflammatory biomarkers, not such much.
In short: for most people, it indeed reliably helps with many things. And importantly, it has no particular risks associated with it, and it’s almost universally framed as a complementary therapy rather than an alternative therapy.
This is critical, because it means that whereas someone may hold off on taking evidence-based medicines while trying out (for example) homeopathy, few people are likely to hold off on other treatments while trying out qigong—since it’s being viewed as a helper rather than a Hail-Mary.
Want to read more about qigong?
Here’s the NIH’s National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health has to say. It cites a lot of poor quality science, but it does mention when the science it’s citing is of poor quality, and over all gives quite a rounded view:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Eat to Change How You Drink – by Dr. Brooke Scheller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whether you want to stop drinking or just cut down, this book can help. But what makes it different from the other reduce/stop drinking books we’ve reviewed?
Mostly, it’s about nutrition. This book focuses on the way that alcohol changes our relationship to food, our gut, our blood sugars, and more. The author also explains how reducing/stopping drinking, without bearing these things in mind, can be unnecessarily extra hard.
The remedy? To bear them in mind, of course, but that requires knowing them. So what she does is explain the physiology of what’s going on in terms of each of the above things (and more), and how to adjust your diet to make up for what alcohol has been doing to you, so that you can reduce/quit without feeling constantly terrible.
The style is very pop-science, light in tone, readable. She makes reference to a lot of hard science, but doesn’t discuss it in more depth than is necessary to convey the useful information. So, this is a practical book, aimed at all people who want to reduce/quit drinking.
Bottom line: if you feel like it’s hard to drink less because it feels like something is missing, it’s probably because indeed something is missing, and this book can help you bridge that gap!
Click here to check out How To Eat To Change How You Drink, and do just that!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
This Naked Mind – by Annie Grace
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve all read about the many, many, dangers of drinking. We’ve also probably all read about how to make the change to not drinking. Put things out of sight, tell your friends, have this rule, have this excuse (for not drinking) ready to give to people who challenge you, consider a support group, and so on.
What Annie Grace offers in this #1 bestseller is different:
A blend of mostly psychology and sociology, to examine the “liminal thinking” stages that funnel us to drink in the first place… and where that leads, and how to clamber back out of the pitcher plant we weren’t necessarily aware we were sliding into.
While she kicks off citing Jung, from a psychological perspective more of this book is CBTish, as it pertains a lot to examining the process of:
- belief—held and defended, based on the…
- conclusion—drawn, often irrationally, from the…
- experience—that we had upon acting on an…
- observation—often mistaking an illusion for the underlying…
- reality
…and how we can and often do go wrong at each step, and how little of the previous steps we can perceive at any given time.
What does this mean for managing/treating alcoholism or a tendency towards alchoholism?
It means interrupting those processes in a careful, surgically precise fashion, so that suddenly… The thing has no more power over us.
Whether you or a loved one struggle with a tendency to addiction (any addiction, actually, the advice goes the same), or are just curious about the wider factors at hand in the epidemiology of addiction, this book is for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: