General Tso’s Chickpeas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A fiber-rich, heart-healthy take on a classic:
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas, drained
- ¾ cup vegetable stock; ideally you made this yourself from vegetable cuttings that you kept in the freezer for this purpose, but failing that, you should be able to get low-sodium stock cubes at your local supermarket.
- ¼ cup arrowroot starch (cornstarch will do at a pinch, but arrowroot is better and has no flavor of its own)
- 3 tbsp coconut oil
- 2 tbsp grated fresh ginger
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tbsp honey (or maple syrup if you prefer, and if you don’t like sweetness, reduce this to 1 tbsp or even omit entirely, though it won’t be quite so “General Tso” if you do, but it’s your meal!)
- 2 tbsp tomato paste
- 2 tsp hot sauce
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 3 green onions, sliced
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Coat the chickpeas in the arrowroot starch by tossing them together in a bowl
2) Heat the coconut oil in a skillet on a medium-high heat, and when hot, add the chickpeas, stirring for 3 minutes
3) Add the remaining ingredients in the order we gave (except the vegetable stock, which goes in last), stirring for 5 more minutes, or until the sauce thickens
4) Serve with the carb of your choice; we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice Recipe
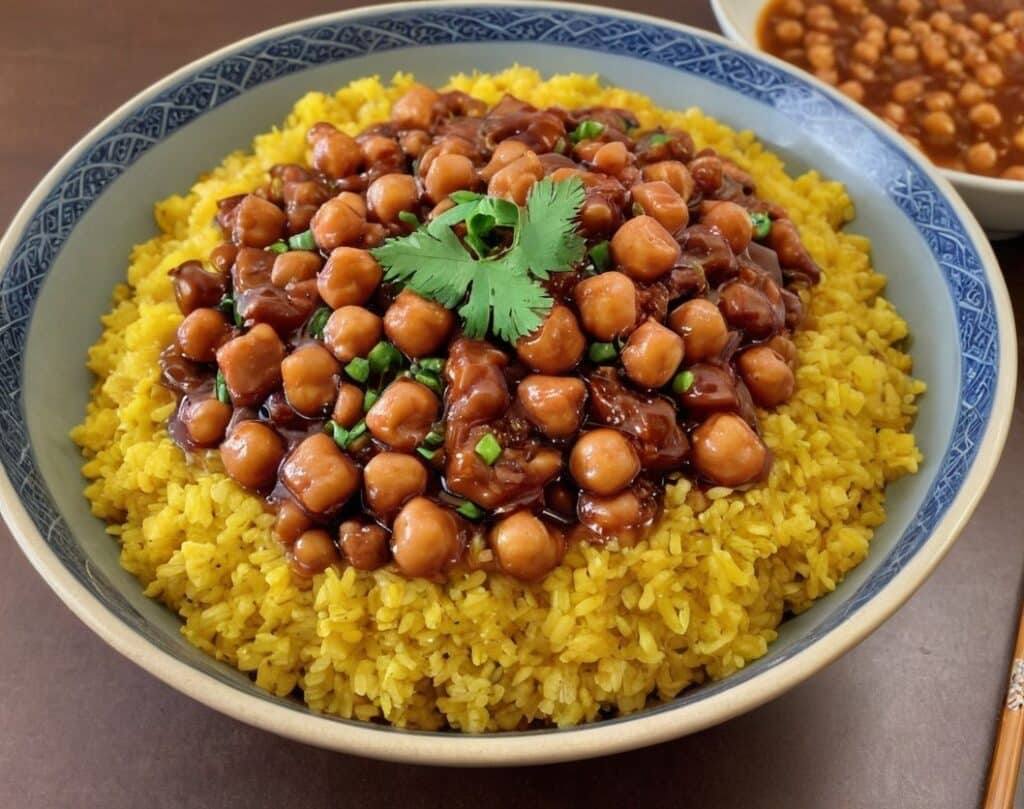

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Honey vs Maple Syrup – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Getting Things Done – by David Allen
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our “to-do” lists are usually hopelessly tangled:
“To do thing x needs thing y doing first but that can only be done with information that I must get by doing thing z”, and so on.
Suddenly that two-minute task is looking like half an hour, which is making our overall to-do list look gargantuan. Tackling tiny parts of tasks seems useless; tackling large tasks seems overwhelming. What a headache!
Getting Things Done (“GTD”, to its friends) shows us how to gather all our to-dos, and then use the quickest ways to break down a task (in reality, often a mini-project) into its constituent parts and which things can be done next, and what order to do them in (or defer, or delegate, or ditch).
In a nutshell: The GTD system aims to make all your tasks comprehensible and manageable, for stress-free productivity. No need to strategize everything every time; you have a system now, and always know where to begin.
And by popular accounts, it delivers—many put this book in the “life-changing” category.
Share This Post
-
100,000 People, 30 Years, One Clear Winner vs Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Generally speaking, the scientific community most highly lauds the Mediterranean diet as being best for general health:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for?!
However, even this can be tweaked with specific health considerations in mind, for example:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← these tweaks offer adjusted versions of the Mediterranean diet, optimized for anti-inflammation, gut health, heart health, or brain health
And today we present to you some very good research into…
The best diet for aging well
Let’s be clear on terms first: by “aging well”, this means reaching age 70 without chronic diseases and maintaining good cognitive, physical, and mental health.
105,015 participants (of whom, 66% women, average age 53 at the start of the study) were followed for up to 30 years. Not in the stalkery way, but in the longitudinal study way. We say “up to”, because as with any sizeable longitudinal study, some died before the end of the study.
9,771 of them were deemed, at the end of the study, to have achieved “healthy aging”.
So, how did those participants achieve that, in terms of diet?
The dietary patterns that had the strongest positive impact were:
- AHEI (Alternative Healthy Eating Index): best for mental and physical function, overall healthy aging.
- PHDI (Planetary Health Diet Index): best for cognitive health and survival to age 70.
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension): strongest general impact.
- MIND (Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay): best for brain health.
- rEDIH (Reversed Empirical Dietary Index for Hyperinsulinemia): most effective for chronic disease prevention.
In contrast:
- EIDP (Empirically Inflammatory Dietary Pattern): shocking nobody, performed least well in all areas
You are probably wondering what those dietary patterns actually consist of, so click here to see a chart of what’s included or excluded in each dietary pattern.
As you can see, the AHEI diet that was “best for mental and physical function, overall healthy aging” is essentially the Mediterranean diet with three small tweaks:
- no seafood, but long-chain omega-3 fatty acids include to compensate
- no sugar-sweetened beverages or fruit juices
- “no” sodium (in other words, minimal sodium, since almost everything contains trace amounts)
The PHDI diet, which was “best for cognitive health and survival to age 70” is essentially a whole-foods plant-based diet. Which in turn is very consistent with the Mediterranean, except that it excludes animal products, of which the Mediterranean diet uses small amounts.
You can read the paper in its entirety here:
Optimal dietary patterns for healthy aging
Want to know more?
A panel of 69 doctors and nutritionists examined the evidence for 38 diets (including Mediterranean, MIND, DASH, Vegan, Keto, Slimfast, WeightWatchers, Nutrisystem, and more) and scored them in 21 categories (e.g. best for general health, best for weight loss, best for heart, best against diabetes, etc):
Which Diet? Top Diets Ranked By Experts
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Minerals That Neutralize Viruses (While Being Harmless To Humans)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Researchers in Estonia and Sweden (it was a joint project, with five researchers from each country) have found a way to use titanium dioxide nanoparticles to neutralize viruses, including COVID & flu.
Titanium dioxide, yes, the common additive to foods, cosmetics, and more (in most cases, added as a non-bleaching whitening agent—simply, titanium dioxide is body-safe, white in color, and very reflective, making it a brilliant, shiny white). Also used in sunscreens, for its excellent safety profile and again, its full-spectrum reflectiveness.
See also: Who Screens The Sunscreens?
How it works
Some viruses, including coronaviruses and influenza viruses, have an outer layer that’s a lipid membrane. The researchers found (by testing against multiple viruses, and by using a control of silicotungstate polyoxymethalate nanoparticles), that the ability of titanium dioxide to bind to phospholipids (and ability that the silicotungstate polyoxymethalate doesn’t have) means that the nanoparticles bind to the virus’s outer case, thus preventing it from effectively entering human cells (which it needs to do in order to infect the host, as this is how viruses replicate themselves).
What this means, in practical terms
While more research will be needed to know whether this can be used in the medicinal sense, it already means that a nanoparticle spray can be used to create virus-neutralizing layers on surfaces and in air filters. This alone could greatly reduce transmission in enclosed spaces such as public transport (ranging from taxis to airplanes), as well as other places where people get packed into a small space.
If you have an air purifier at home, keep an eye out for when improved filters arrive on the market!
See also: What’s Lurking In Your Household Air?
Wait, you said “minerals”; are there more?
It seems so, but we can’t truly say for sure until they’ve been tested. However, the researchers see no reason why other small metal oxides that bind strongly to phospholipids shouldn’t work exactly the same way—which would include iron oxide (yes, as in rust) and aluminum oxide (the coating that automatically forms immediately when aluminum is exposed to oxygen (aluminum is so reactive to oxygen, that it’s almost impossible to get aluminum without an oxidized surface, unless you use something else to coat it, or cut it in an oxygen-free atmosphere and keep it there).
You can read the paper itself here:
Molecular mechanisms behind the anti corona virus activity of small metal oxide nanoparticles
And on a related note (different scientists, different science, similar principle, though, using mineral nanotechnology to kill microbes):
❝Researchers report that laboratory tests of their nanoflower-coated dressings demonstrate antibiotic, anti-inflammatory and biocompatible properties. They say these results show these tannic acid and copper(II) phosphate sprouted nanoflower bandages are promising candidates for treating infections and inflammatory conditions.❞
Read in full: This delicate nanoflower is downright deadly to bacteria
Want to learn more?
Check out:
Move over, COVID and Flu! We Have “Hybrid Viruses” To Contend With Now
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & Neuroprotectant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Think Pink For Brain Health!
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid that’s found in:
- certain marine microalgae
- tiny crustaceans that eat the algae
- fish (and flamingos!) that eat the crustaceans
Yes, it’s the one that makes things pink.
But it does a lot more than that…
Super-antioxidant
Move over, green tea! Astaxanthin has higher antioxidant activity than most carotenoids. For example, it is 2–5 times more effective than alpha-carotene, lutein, beta-carotene, and lycopene:
Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids
We can’t claim credit for naming it a super-antioxidant though, because:
Astaxanthin: A super antioxidant from microalgae and its therapeutic potential
Grow new brain cells
Axtaxanthin is a neuroprotectant, but that’s to be expected from something with such a powerful antioxidant ability.
What’s more special to astaxanthin is that it assists continued adult neurogenesis (creation of new brain cells):
❝The unique chemical structure of astaxanthin enables it to cross the blood-brain barrier and easily reach the brain, where it may positively influence adult neurogenesis.
Furthermore, astaxanthin appears to modulate neuroinflammation by suppressing the NF-κB pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and limiting neuroinflammation associated with aging and chronic microglial activation.
By modulating these pathways, along with its potent antioxidant properties, astaxanthin may contribute to the restoration of a healthy neurogenic microenvironment, thereby preserving the activity of neurogenic niches during both normal and pathological aging. ❞
That first part is very important, by the way! There are so many things that our brain needs, and we can eat, but the molecules are unable to pass the blood-brain barrier, meaning they either get wasted, or used elsewhere, or dismantled for their constituent parts. In this case, it zips straight into the brain instead.
See also:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
(Probably) good for the joints, too
First, astaxanthin got a glowing report in a study we knew not to trust blindly:
…and breathe. What a title that was! But, did you catch why it’s not to be trusted blindly? It was down at the bottom…
❝Conflict of interest statement
NOVAREX Co., Ltd. funded the study. Valensa International provided the FlexPro MD® ingredients, and NOVAREX Co., Ltd. encapsulated the test products (e.g., both FlexPro MD® and placebo)❞
Studies where a supplement company funded the study are not necessarily corrupt, but they can certainly sway publication bias, i.e. the company funds a bunch of studies and then pulls funding from the ones that aren’t going the way it wants.
So instead let’s look at:
Astaxanthin attenuates joint inflammation induced by monosodium urate crystals
and
Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis
…which had no such conflicts of interest.
They agree that astaxanthin indeed does the things (attenuates joint inflammation & ameliorates cartilage damage).
However, they are animal studies (rats), so we’d like to see studies with humans to be able to say for sure how much it helps these things.
Summary of benefits
Based on the available research, astaxanthin…
- is indeed a super-antioxidant
- is a neuroprotective agent
- also assists adult neurogenesis
- is probablygood for joints too
How much do I take, and is it safe?
A 2019 safety review concluded:
❝Recommended or approved doses varied in different countries and ranged between 2 and 24 mg.
We reviewed 87 human studies, none of which found safety concerns with natural astaxanthin supplementation, 35 with doses ≥12 mg/day.❞
Source: Astaxanthin: How much is too much? A safety review
In short: for most people, it’s very safe and well-tolerated. If you consume it to an extreme, you will likely turn pink, much as you would turn orange if you did the same thing with carrots. But aside from that, the risks appear to be minimal.
However! If you have a seafood allergy, please take care to get a supplement that’s made from microalgae, not one that’s made from krill or other crustaceans, or from other creatures that eat those.
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why We Sleep – by Dr Matthew Walker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
- We all know sleep is important.
- We all know that without it, we’ll suffer rapid cognitive decline.
- We all know approximately what we’re supposed to do to get good sleep.
So what does this book bring to the table? Mostly, deep understanding (written from the perspective of a career in sleep science) presented in such a way as to be applicable, by you, in your life. Stop sabotaging yourself before you even get out of your bed in the morning!
Hustle culture champions early mornings and late nights, and either or both of those might be difficult to avoid. But to make what you’re doing sustainable, you’re going to have to make some informed decisions about looking after your #1 asset—you!
Dr. Walker writes in a clear and accessible fashion, without skimping on the hard science, and always with practical application in mind. All in all, we can’t recommend this one enough.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Fiber Of Good Health
We’ve written before about how most people in industrialized nations in general, and N. America in particular, do not get nearly enough fiber:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Fiber’s important for many aspects of health, not least of all the heart:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
As well, of course, as being critical for gut health:
Gut Health 101: Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
But is all fiber “prebiotic fiber”, and/or are some better than others?
Beta-glucan
A recent study (it’s a mouse study, but promising in its applicability for humans) examined the health impacts of 5 different fiber types:
- pectin
- β-glucan
- wheat dextrin
- resistant starch
- cellulose (control)
As for health metrics, they measured:
- body weight
- adiposity
- indirect calorimetry
- glucose tolerance
- gut microbiota
- metabolites thereof
What they found was…
❝Only β-glucan supplementation during HFD-feeding decreased adiposity and body weight gain and improved glucose tolerance compared with HFD-cellulose, whereas all other fibers had no effect. This was associated with increased energy expenditure and locomotor activity in mice compared with HFD-cellulose.
All fibers supplemented into an HFD uniquely shifted the intestinal microbiota and cecal short-chain fatty acids; however, only β-glucan supplementation increased cecal butyrate concentrations. Lastly, all fibers altered the small-intestinal microbiota and portal bile acid composition. ❞
If you’d like to read more, the study itself is here:
If you’d like to read less, the short version is that they are all good but β-glucan scored best in several metrics.
It also acts indirectly as a GLP-1 agonist, by the way:
The right fiber may help you lose weight
You may be wondering: what is β-glucan found in?
It’s found in many (non-animal product) foods, but oats, barley, mushrooms, and yeasts are all good sources.
Is it available as a supplement?
More or less; there are supplements that contain it generously, here’s an example product on Amazon, a cordyceps extract, of which >30% is β-glucan.
As an aside, cordyceps itself has many other healthful properties too:
Cordyceps: Friend Or Foe? ← the answer is, it depends! If you’re human, it’s a friend.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: